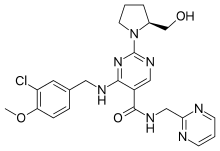
Avanafil
 | |
 Avanafil is a PDE5 inhibitor | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Stendra |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a614010 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H26ClN7O3 |
| Molar mass | 483.96 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Avanafil is a PDE5 inhibitor approved for erectile dysfunction by the FDA on April 27, 2012[1] and by EMA on June 21, 2013.[2] Avanafil is sold under the brand names Stendra and Spedra. It was invented at Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, formerly known as Tanabe Seiyaku Co.,<[3] and licensed to Vivus Inc., which partnered with Menarini Group to commercialise Spedra in over forty European countries, Australia, and New Zealand.[4] Metuchen Pharmaceuticals obtained exclusive rights within the United States.[5]
Avanafil acts by inhibiting a specific phosphodiesterase type 5 enzyme found in various body tissues, primarily in the corpus cavernosum penis.[6] Other similar drugs are sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil. The advantage of avanafil is that it has very fast onset of action compared with other PDE5 inhibitors. It is absorbed quickly, reaching a maximum serum concentration in about thirty to forty-five minutes.[7] About two-thirds of the participants were able to engage in sexual activity within fifteen minutes.[7]
Synthesis
Avanafil can be synthesized from a benzylamine derivative and a pyrimidine derivative:[3]
References
- ^ "FDA approves Stendra for erectile dysfunction" (Press release). Food and Drug Administration (FDA). April 27, 2012.[dead link]
- ^ "Spedra (avanafil)". European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ a b US 6797709, Yamada K, Matsuki K, Omori K Kikkawa K, "Aromatic nitrogen-containig 6-membered cyclic compounds", issued 11 December 2003, assigned to Tanabe Seiyaku Co
- ^ "VIVUS Announces Avanafil Partnership With Menarini". Vivus Inc. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08.
- ^ "VIVUS and Metuchen Pharmaceuticals Announce License Agreement for Commercial Rights to Stendra". Vivus Inc. 3 October 2016.
- ^ "avanafil, Spedra". Medicine Net. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ a b Kyle JA, Brown DA, Hill JK (October 2013). "Avanafil for erectile dysfunction". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 47 (10). Sage Publishing: 1312–20. doi:10.1177/1060028013501989. PMID 24259695. S2CID 6562049.
External links
- "Avanafil". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.

