Cobalt(II) nitrate

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Caviar, Cobaltous nitrate
Nitric acid, cobalt(2+) salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.353 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Co(NO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 182.943 g/mol (anhydrous) 291.03 g/mol (hexahydrate) |
| Appearance | pale red powder (anhydrous) red crystalline (hexahydrate) |
| Odor | odorless (hexahydrate) |
| Density | 2.49 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.87 g/cm3 (hexahydrate) |
| Melting point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) decomposes (anhydrous) 55 °C (hexahydrate) |
| Boiling point | 100 to 105 °C (212 to 221 °F; 373 to 378 K) decomposes (hexahydrate) 74 °C, decomposes (hexahydrate) |
| anhydrous:[1] 84.03 g/100 mL (0 °C) 334.9 g/100 mL (90 °C) soluble (anhydrous) | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, acetone, ethanol, ammonia (hexahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hexahydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
434 mg/kg; rat, oral (anhydrous) 691 mg/kg; rat, oral (hexahydrate) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Cobalt (II) Nitrate MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Cobalt(II) sulfate Cobalt(II) chloride Cobalt oxalate |
Other cations
|
Iron(III) nitrate Nickel(II) nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cobalt Nitrate is the inorganic cobalt(II) salt of nitric acid, often with various amounts of water. It is more commonly found as a hexahydrate, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a red-brown deliquescent salt that is soluble in water and other polar solvents.[2]
Composition and structures
As well as the anhydrous compound Co(NO3)2, several hydrates of cobalt(II) nitrate exist. These hydrates have the chemical formula Co(NO3)2·nH2O, where n = 0, 2, 4, 6.
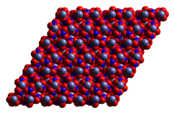
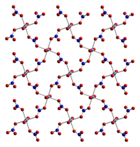
Anhydrous cobalt(II) nitrate adopts a three-dimensional polymeric network structure, with each cobalt(II) atom approximately octahedrally coordinated by six oxygen atoms, each from a different nitrate ion. Each nitrate ion coordinates to three cobalts.[3] The dihydrate is a two-dimensional polymer, with nitrate bridges between Co(II) centres and hydrogen bonding holding the layers together. The tetrahydrate consists of discrete, octahedral [(H2O)4Co(NO3)2] molecules. The hexahydrate is better described as hexaaquacobalt(II) nitrate, [Co(OH2)6][NO3]2, as it consists of discrete [Co(OH2)6]2+ and [NO3]− ions.[4] Above 55 °C, the hexahydrate converts to the trihydrate and at higher temperatures to the monohydrate.[2]
Uses
It is commonly reduced to metallic high purity cobalt.[2] It can be absorbed on to various catalyst supports for use in Fischer-Tropsch catalysis.[5] It is used in the preparation of dyes and inks.[6]
Production
The hexahydrate is prepared treating metallic cobalt or one of its oxides, hydroxides, or carbonate with nitric acid:
- Co + 4 HNO3 + 4 H2O → Co(H2O)6(NO3)2 + 2 NO2
- CoO + 2 HNO3 + 5 H2O → Co(H2O)6(NO3)2
- CoCO3 + 2 HNO3 + 5 H2O → Co(H2O)6(NO3)2 + CO2
 |
 |
 |

|
References
- ^ Perrys' Chem Eng Handbook, 7th Ed
- ^ a b c John Dallas Donaldson, Detmar Beyersmann, "Cobalt and Cobalt Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a07_281.pub2
- ^ Tikhomirov, G. A.; Znamenkov, K. O.; Morozov, I. V.; Kemnitz, E.; Troyanov, S. I. (2002). "Anhydrous Nitrates and Nitrosonium Nitratometallates of Manganese and Cobalt, M(NO3)2, NO[Mn(NO3)3], and (NO)2[Co(NO3)4]: Synthesis and Crystal Structure". Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 628 (1): 269–273. doi:10.1002/1521-3749(200201)628:1<269::AID-ZAAC269>3.0.CO;2-P.
- ^ Prelesnik, P. V.; Gabela, F.; Ribar, B.; Krstanovic, I. (1973). "Hexaaquacobalt(II) nitrate". Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2 (4): 581–583.
- ^ Ernst B, Libs S, Chaumette P, Kiennemann A. Appl. Catal. A 186 (1-2): 145-168 1999
- ^ Lewis, Richard J., Sr. (2002). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary (14th Edition). John Wiley & Sons. http://www.knovel.com/knovel2/Toc.jsp?BookID=704&VerticalID=0

