Cologne Stadtbahn
| Cologne Stadtbahn | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 Light rail trainset in front of the river Rhine and Cologne Cathedral | |||
| Overview | |||
| Locale | Cologne (Köln) Germany | ||
| Transit type | Light rail (Stadtbahn)/Tram | ||
| Number of lines | 12 | ||
| Number of stations | 233 | ||
| Daily ridership | 760,821 (2016)[1] | ||
| Annual ridership | 210,800,000 (2016)[1] | ||
| Website | www.kvb-koeln.de | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1876[2] | ||
| Operator(s) | Kölner Verkehrs-Betriebe (KVB) | ||
| Number of vehicles | 382 (2013)[1] | ||
| Train length | 60 meters (200 ft) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 245.7 kilometers (152.7 mi) (2016)[1] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | (?) V DC overhead line | ||
| Average speed | 16.2 mph (26.1 km/h) (2013)[1] | ||
| |||
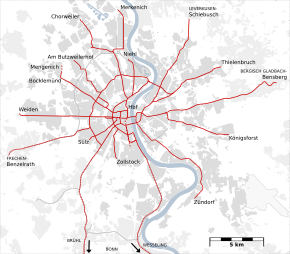
The Cologne Stadtbahn is a light rail system in the German city of Cologne, including several surrounding cities of the Cologne Bonn Region (Bergisch Gladbach, Bonn, Bornheim, Brühl, Frechen, Hürth, Leverkusen-Schlebusch, Wesseling). The term Stadtbahn denotes a system that encompasses elements of trams as well as an underground railway network (U-Bahn) and interurban rail, even including three lines that are licensed as heavy rail and used by freight trains as well as Stadtbahn vehicles. Two of these lines connect the Cologne Stadtbahn to the Bonn Stadtbahn. These lines (16 and 18) are jointly operated by both cities' transport authorities, resulting in both systems and the lines connecting them sometimes collectively referred to as Stadtbahn Rhein-Sieg. The Cologne Stadtbahn is operated by the Kölner Verkehrsbetriebe (KVB) and the Bonn Stadtbahn is operated by the Stadtwerke Bonn (SWB - City of Bonn Utilities Division). The KVB and SWB are members of the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Sieg (VRS - Rhein-Sieg Transit Authority), formed in 1987 to consolidate the transit authorities in the metropolitan Cologne area and operate a joint fare structure. There are 38 underground stations, 4 more are currently[when?] under construction.
History
The Cologne Stadtbahn traces its history to the first horsecar lines that started operating in 1877. Within a few years, several companies had built an extensive network. Because none of these companies showed interest in electrifying their lines, the city of Cologne bought them on 1 January 1900. Electric streetcars were introduced and additional lines built until 1912, including Vorortbahnen to surrounding villages outside the city limits. Outside the city center, these lines had separated right-of-way and were more similar to "real" railroads than to trams.[citation needed]
During World War II, Cologne suffered heavy damage. The city center was almost completely destroyed and the tram lines with it. After the war, only a few of the existing lines were rebuilt in the downtown area, while at the same time automobile traffic increased heavily. To improve the situation, construction of the first tunnel began in 1963. When the tunnel was opened in November 1968, it was integrated into the tram network, instead of a separate subway operation. Since then, street-running tram lines have gradually been replaced with tunnels, some elevated track and surface lines with separated right of way. From 1973 until 2006 light rail vehicles have operated together with classic trams on the same lines.[citation needed]
Underground construction in downtown Cologne, one of Germany's oldest cities, is often obstructed by archeologists' legal rights to dig in all future building sites within the medieval city limits before all heavy construction machinery.[citation needed]
Current routes


Because the light rail network evolved from the tram network instead of replacing it, there were numerous stations served by both light rail and tram vehicles for almost three decades. While high platforms for stepless entry into light rail vehicles could be built on the outer branches, stations in the city center had to have low platforms to support trams as well. The introduction of low-floor technology in the early 1990s promised wheelchair-accessible entry throughout the network without having to build several hundred high platforms. To allow the introduction of low-floor trains without having to demolish existing high platforms, the network was divided into two sub-networks of different floor heights.
On weekdays, all lines are served in 5- to 10-minute intervals from 6 am to 8 pm, with little or no service between around 1 am and about 4.30 am, and usually 15-minute intervals in the early night and early morning. On weekends, there is an hourly service throughout the night. Because several lines overlap on the routes through the city center, some stations are served by up to 30 trains per hour in each direction.
| route | length | avg. speed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weiden West – Junkersdorf – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz - Kalk Post - Kalk Kapelle – Brück – Refrath - Bensberg during peak hours 5-minute intervals Junkersdorf–Brück |
24.9 km (15.5 mi) | 27.2 km/h (16.9 mph) |
| 3 | Mengenich – Bocklemünd – Bickendorf - Bf Ehrenfeld – Bf West – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz – Buchheim – Holweide – Thielenbruch off-peak service ends at Holweide |
20.1 km (12.5 mi) | 26.2 km/h (16.3 mph) |
| 4 | Bocklemünd – Bickendorf – Bf Ehrenfeld – Bf West – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz – Mülheim, Wiener Platz – Dünnwald - Schlebusch evening service starts at Bickendorf |
21.5 km (13.4 mi) | 28.0 km/h (17.4 mph) |
| 5 | Sparkasse Am Butzweilerhof - Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld - Bf West – Dom/Hbf – Rathaus - Heumarkt | 10.3 km (6.4 mi) | 20.4 km/h (12.7 mph) |
| 7 | Frechen – Marsdorf – Braunsfeld – Neumarkt – Poll - Porz – Zündorf Frechen–Braunsfeld served in 20-minute intervals except for peak hours |
25.5 km (15.8 mi) | 25.5 km/h (15.8 mph) |
| 9 | Sülz – Universität – Bf Süd – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz – Kalk Post - Kalk Kapelle – Ostheim - Königsforst 5-minute intervals Universität–Bf Deutz except for school holidays |
15.4 km (9.6 mi) | 25.0 km/h (15.5 mph) |
| 12 | Merkenich – Niehl – Ebertplatz – Hansaring – Ringe – Zollstock Merkenich–Niehl served in 20-minute intervals from 9am to 1pm |
16.5 km (10.3 mi) | 22.0 km/h (13.7 mph) |
| 13 | Sülzgürtel – Aachener Str. – Bf Ehrenfeld – Gürtel – Bf Mülheim – Buchheim - Holweide | 15.4 km (9.6 mi) | 28.9 km/h (18.0 mph) |
| 15 | Chorweiler – Longerich – Ebertplatz – Hansaring – Ringe – Ubierring during peak hours 5-minute intervals Longerich–Ubierring |
15.2 km (9.4 mi) | 24.0 km/h (14.9 mph) |
| 16 | Niehl, Sebastianstraße – Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Ubierring – Sürth – Wesseling – Bonn Hbf – Bonn-Bad-Godesberg 20-minute intervals from Sürth (during peak hours from Wesseling) |
44.4 km (27.6 mi) | 33.3 km/h (20.7 mph) |
| 17 |
Severinstr. – Chlodwigplatz – Rodenkirchen (– Sürth) | ||
| 18 | Thielenbruch – Buchheim – Bf Mülheim – Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Klettenberg – Brühl – Bonn Hbf 5-minute intervals Buchheim–Klettenberg, 20-minute intervals from Brühl |
46.2 km (28.7 mi) | 33.4 km/h (20.8 mph) |

Former Lines
| Line | Route | from | to |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weiden Schulstr.- Junkersdorf – Müngersdorf – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Höhenberg – Merheim – Brück – Refrath – Bensberg | 16. June 2002 | 27. May 2006 |
| Junkersdorf – Müngersdorf – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Höhenberg – Merheim – Brück – Refrath – Bensberg | 2. August 1980 | 15. June 2002 | |
| Sülz, Hermeskeiler Platz – Universität – Zülpicher Platz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Höhenberg – Merheim – Brück – Refrath – Bensberg | 19. October 1970 | 1. August 1980 | |
| Bocklemünd – Bickendorf – Venloer Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Brabanter Str. – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Höhenberg – Merheim – Brück – Refrath – Bensberg | 12. June 1967 | 18. October 1970 | |
| 2 | stopped service | 30. May 1999 | |
| Benzelrath – Frechen – Marsdorf – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt (– Heumarkt – Deutz – Poll – Porz – Zündorf) | 25. September 1994 | 30. May 1999 | |
| Benzelrath – Frechen – Marsdorf – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt (– Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim) | 2. August 1980 | 24. September 1994 | |
| Sülz, Hermeskeiler Platz – Universität – Zülpicher Platz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz – Vingst – Ostheim | 19. October 1970 | 2. August 1980 | |
| Zollstock, Südfriedhof – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf. | 6. October 1969 | 18. October 1970 | |
| Zollstock, Südfriedhof – Barbarossaplatz – Zülpicher Platz – Mauritiuskirche – Neumarkt – Poststraße – Barbarossaplatz – Zollstock, Südfriedhof | 12. June 1967 | 5. October 1969 | |
| 3 | Bocklemünd – Venloer Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Appellhofplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Buchheim – Holweide – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch | 19. October 1970 | 15. June 2002 |
| während des U-Bahn-Baus in Ehrenfeld nur ab Venloer Str./Gürtel | 16. September 1989 | 30. May 1992 | |
| Bickendorf, Schleife am Erlenweg – Akazienweg – Venloer Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Brabanter Str. – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Kleiner Griechenmarkt – Severinsbrücke – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Buchheim – Holweide – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch | 12. June 1967 | 18. October 1970 | |
| 4 | Bickendorf, Äußere Kanalstraße – Subbelrather Straße/Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Appellhofplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Mülheim – Höhenhaus – Dünnwald – Schlebusch; | 24. June 1989 | 30. May 1992 |
| Bocklemünd – Subbelrather Straße/Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Appellhofplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Mülheim – Höhenhaus – Dünnwald – Schlebusch; | 24. April 1985 | 23. June 1989 | |
| Bocklemünd – Venloer Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Appellhofplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Mülheim – Höhenhaus – Dünnwald – Schlebusch; | 7. January 1975 | 23. April 1985 | |
| Bickendorf, Akazienweg – Venloer Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Appellhofplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Mülheim – Höhenhaus – Dünnwald – Schlebusch; | 19. October 1970 | 6. January 1975 | |
| Rudolfplatz (Moltkestr.) – Neumarkt – Severinstr. – Bf. Deutz/Messe – Mülheim – Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg; | 8. April 1968 | 18. October 1970 | |
| 5 | Am Butzweilerhof – Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf. – Rathaus | 12/2012 | 12/2013 |
| Am Butzweilerhof – Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf. – Ebertplatz – Reichenspergerplatz | 12/2010 | 12/2012 | |
| Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf. – Ebertplatz – Reichenspergerplatz | 23. May 1993 | 12/2010 | |
| Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf. – Ebertplatz – Reichenspergerplatz – Zoo/Flora – Mülheim – Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg | 9. November 1986 | 22. May 1993 | |
| Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf. – Ebertplatz – Reichenspergerplatz | 25. August 1974 | 8. November 1986 | |
| 6 | stopped service | 06/2007 | |
| Longerich – Weidenpesch – Nippes – Ebertplatz („6 Nord“) | 10/2006 | 06/2007 | |
| Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Ubierring („6 Süd“) | 10/2006 | 06/2007 | |
| Longerich – Weidenpesch – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Ubierring | 09/2002 | 10/2006 | |
| Longerich – Weidenpesch – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Bayenthal – Marienburg, Südpark | 27.07.1974 | 7. September 2002 | |
| (HVZ: Fordwerke, Ölhafen -) Niehl – Weidenpesch – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Bayenthal – Marienburg, Südpark | 19. October 1970 | 26. July 1974 | |
| 7 | Sülz, Hermeskeiler Platz – Universität – Zülpicher Platz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz – Poll – Porz – Zündorf | 2. August 1980 | 29. May 1999 |
| Junkersdorf – Müngersdorf – Melaten – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz – Poll – Porz – Zündorf | 12. June 1967 | 2. August 1980 | |
| 8 | stopped service | 06/2007 | |
| Universität – Zülpicher Platz – Neumarkt (– Poll – Porz) / (– Bf. Deutz/Messe) | 1999 | 06/2007 | |
| stopped service | 2. August 1980 | 1999 | |
| Müngersdorf (Stadion) – Melaten – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Heumarkt – Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Höhenberg – Merheim – Brück (– Refrath) | 8. April 1968 | 2. August 1980 | |
| 9 | Chorweiler – Heimersdorf – Longerich – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Deutz – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim – Rath-Heumar – Königsforst | 17. November 1973 | 24. September 1994 |
| Heimersdorf – Longerich – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Deutz – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim – Rath-Heumar – Königsforst | 18. May 1971 | 16. November 1973 | |
| Longerich – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Dom/Hbf – Neumarkt – Deutz – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim – Rath-Heumar – Königsforst | 19. October 1970 | 17. May 1971 | |
| Longerich – Niehl – Fordwerke, Ölhafen | 12. June 1967 | 18. October 1970 | |
| 10 | stopped service | 26. September 1994 | |
| Zollstock, Südfriedhof – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Niehl – Merkenich | 31. October 1987 | 26. September 1994 | |
| Klettenberg – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Niehl – Fordwerke, Ölhafen; | 25. August 1974 | 9. November 1986 | |
| Klettenberg – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Weidenpesch – Longerich; | 6. October 1969 | 27. July 1974 | |
| 11 | stopped service | 9. November 1986 | |
| Klettenberg – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg | 27. July 1974 | 9. November 1986 | |
| 12 | Zollstock, Südfriedhof – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf. – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Niehl – Merkenich | 18. October 1970 | 12/2003 |
| 13 | Sülzgürtel – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Ehrenfeld – Nippes – Riehl – Mülheim – Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg | 23. May 1993 | 31. May 1997 |
| Sülzgürtel – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Ehrenfeld – Nippes – Riehl – Mülheim, Wiener Platz | 25. August 1974 | 22. May 1993 | |
| Sülzgürtel – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Ehrenfeld – Neuehrenfeld, Takuplatz | 23. October 1972 | 25. August 1974 | |
| Sülzgürtel – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Ehrenfeld – Bilderstöckchen, Longericher Str. | 30. September 1963 | 22. October 1972 | |
| 14 | stopped service | 2003 | |
| KölnMesse – Deutz/Messe – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf. (Einsatz nur an Messetagen) |
17. January 1984 | 27. May 2003 | |
| 15 | Thielenbruch – Dellbrück – Buchheim – Mülheim – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Ubierring | 25. September 1994 | 13. December 2003 |
| Thielenbruch – Dellbrück – Buchheim – Mülheim – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Chlodwigplatz – Ubierring – Rodenkirchen – Sürth | 12. August 1978 | 24. September 1994 | |
| Ossendorf – Neuehrenfeld – Friesenplatz – Neumarkt – Severinsbrücke – Deutz – Mülheim – Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg (nur in der HVZ) |
19. October 1970 | 23. October 1972 | |
| 16 | Bonn-Bad Godesberg – Bonn Hbf – Wesseling – Sürth – Rodenkirchen – Ubierring – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Niehl, Sebastianstr. | 10/2006 | 06/2007 |
| Bonn-Bad Godesberg – Bonn Hbf – Wesseling – Sürth – Rodenkirchen – Ubierring – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Buchheim, Herler Straße | 1997 | 2003 | |
| Bonn-Bad Godesberg – Bonn Hbf – Wesseling – Sürth – Rodenkirchen – Ubierring – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim, Wiener Platz | 12. August 1978 | 31. May 1997 | |
| Rodenkirchen, Siegfriedstraße – Rheinufer – Ubierring – Chlodwigplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Holweide – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch | 11. August 1978 | ||
| 17 | stopped service | 10/2006 | 12/2015 |
| Ubierring – Chlodwigplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Buchheim, Herler Straße (nur abends und am Wochenende) |
12/2003 | 10/2006 | |
| Ubierring – Chlodwigplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Niehl, Sebastianstraße (nur abends und am Wochenende) |
31. May 1997 | 12/2003 | |
| Klettenbergpark – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Reichenspergerplatz | 9. November 1986 | 1992 | |
| 18 | Bonn Hbf – Brühl – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Buchheim – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch | 10/2006 | 06/2007 |
| Bonn Hbf – Brühl – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Longerich – Heimersdorf – Chorweiler | 9/1994 | 10/2003 | |
| Bonn Hbf – Brühl – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim | 9. November 1986 | 09/1994 | |
| Bonn, Rheinuferbahnhof – Brühl – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz Betrieb durch die Köln-Bonner Eisenbahnen |
12. August 1978 | 9. November 1986 | |
| 19 | stopped service | 5. August 2007' | |
| Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf („19 Süd“) | 9. October 2006 | 5. August 2007 | |
| Breslauer Platz – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Buchheim, Herler Str. („19 Nord“) | 9. October 2006 | 5. August 2007 | |
| Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf – Ebertplatz – Mülheim – Buchheim, Herler Str. | 15. December 2003 | 8. October 2006 | |
| Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Niehl, Sebastianstr. | 31. May 1992 | 14. December 2003 | |
| Hürth-Hermülheim – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Niehl, Sebastianstr. | 27. September 1991 | 30. May 1992 | |
| Hürth-Hermülheim – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Weidenpesch – Niehl | 9. November 1986 | 26. September 1991 | |
| Brühl Mitte – Brühl Ost – Berzdorf – Wesseling Querbahn, Betrieb durch die Köln-Bonner Eisenbahnen |
12. August 1978 | 31. May 1981 | |
| Longerich – Nippes – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Deutz – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim – Rath-Heumar – Königsforst | 5. October 1964 | 19. October 1970 | |
| 20 | stopped service | 2. August 1980 | |
| Benzelrath – Frechen – Marsdorf – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt | 10. October 1969 | 2. August 1980 | |
| Benzelrath – Frechen – Marsdorf – Lindenthal – Braunsfeld – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt (– Heumarkt – Deutz – Poll not so frequent) | 6. October 1969 | 9. October 1969 | |
| Klettenberg – Barbarossaplatz – Rudolfplatz – Friesenplatz – Ebertplatz – Nippes – Niehl – Fordwerke, Ölhafen; | 10. June 1967 | 8. April 1968 | |
Low-floor lines
East-West lines

The first step towards the introduction of a low-floor light rail network was concentrating four lines on similar routes on a common east-west-corridor in 1994. Within short time, these lines were equipped with low platforms 35 cm above street level on every single station. While there are some stretches that can be described as classic tramway lines, the majority of the east-west-network has been upgraded to a high standard with long sections having separated right-of-way, justifying the term "low-floor light rail" (Niederflurstadtbahn).
In 2006, during the 2006 FIFA World Cup, route 1 was extended to Weiden-West, via Schulstraße, which connects to the RheinEnergieStadion.
In 2007, the 8 line, which previously operated during peak hours, stopped service. All its runs were integrated into the schedules of the lines 7 and 9.
| 1 | Weiden West (S-Bahn) – Junkersdorf – Rheinenergiestadion – Aachener Straße/Gürtel – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Brück – Refrath – Bensberg | |
| 7 | Frechen – Marsdorf – Aachener Straße/Gürtel – Rudolfplatz – Neumarkt – Poll – Porz – Zündorf | |
| 9 | Sülz – Zülpicher Straße/Gürtel – University – Zülpicher Platz – Neumarkt – Bf Deutz/Messe – Kalk – Vingst – Ostheim – Rath/Heumar – Königsforst | |
Ring lines

When it became clear to city authorities that the construction of a large number of additional high platforms was not financially feasible, other options were investigated. It was deemed most economical to create a second low-floor network and equip the remaining lines with high platforms. Between the stations "Ebertplatz" and "Barbarossaplatz", there are two possible routes. It was decided that the future low-floor lines would be concentrated in the tunnel underneath the Cologne Ring road, while high-floor lines would use the tunnel under the Central station.
This change was implemented in December 2003, after the high platforms at the Hansaring station were removed. In 2006, the tracks of the Chorweiler station were raised with additional gravel. Since then, all "Ringe" lines are operated with low-floor vehicles. In 2007, the line 6, which had only operated during peak hours, was replaced by additional trains of line 15.
| 12 | Merkenich – Fordwerke – | Wilh.-Sollmann-Straße – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Eifelstraße | – Zollstock | |
| 15 | Chorweiler – | Longerich – | Wilh.-Sollmann-Straße – Ebertplatz – Friesenplatz – Barbarossaplatz – Eifelstraße | – Chlodwigplatz – Ubierring |
High-floor lines

The high-floor network consists of all lines operated by "classic" light rail vehicles with a floor height of roughly one meter above street level. Since the separation from the low-Floor network, high platforms are being built in stations in the city center at a rate of one or two per year. As of 2009, the most frequented stations have been upgraded with the exception of the Barbarossaplatz station.
Lines 3 and 4, since the construction of temporary platforms at the Severinstraße station while the actual station gets modernized and connected to the North-Southern tunnel, are Cologne's first HF lines completely equipped with level entrance. The western branch of line 5 still has a two stops (Subbelrather Straße/Gürtel and Nußbaumerstraße) with low platforms, the rest of its stations were made high-floor when the line was extended into the Butzweilerhof industrial area.
Line 13 is also referred to as the "beltway" (Gürtel) line, because it is the only line that does not touch the city center. Line 13 is also referred somitimes as the Outer Ring line, while lines 12 and 15 can be referred as the inner ring line. Most of the line runs along a series of roads of the same name. The northern part of the 13 is built as an elevated railway. High-floor platforms are still very rare on this line.
Since the timetable change on 12.13.2015 a section of the north-south rail was put into operation. Since then drives the new line 17 of the Severinstr. on the Chlodwigplatz. From Chlodwigplatz it comes to stop Bonner Wall. After leaving the line 17 the NSS-Tunnel and embarks on the route of the line 16 and the next stop loud Schönhauser Str. The left 17 then moves to the terminus Rodenkirchen Bf. In the morning between 7:00 to 8:00 and 16:30 to 18:00, the line serves 17 rail stations Siegstr. and Michaelshoven up to Sürth to.
Lines 16 and 18 are the longest lines in the network, connecting Cologne to Bonn via railway lines.
| 3 | Mengenich – Bocklemünd – Venloer Straße/Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstraße – Bf Deutz/LANxess Arena – Buchheim – Holweide – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch |
| 4 | Bocklemünd – Venloer Straße/Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Neumarkt – Severinstraße – Bf Deutz/LANxess Arena – Mülheim – Höhenhaus – Dünnwald – Schlebusch |
| 5 | Sparkasse Am Butzweilerhof - IKEA Am Butzweilerhof - Alter Flughafen Butzweilerhof – Subbelrather Str./Gürtel – Hans-Böckler-Platz – Friesenplatz – Dom/Hbf (Central Station) – Rathaus – Heumarkt |
| 13 | Sülzgürtel – Zülpicher Straße/Gürtel – Dürener Straße/Gürtel – Aachener Straße/Gürtel – Venloer Straße/Gürtel – Subbelrather Straße/Gürtel – Nußbaumer Straße – Escher Straße –Neusser Straße/Gürtel – Amsterdamer Straße/Gürtel – Slabystraße – Mülheim – Buchheim – Holweide |
| 16 | Bonn-Bad Godesberg – Bonn Hbf (Main Station) – Wesseling – Sürth – Rodenkirchen – Ubierring – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf (Central Station) – Ebertplatz – Reichensperger Platz – Niehl |
| 17 |
Severinstr. – Chlodwigplatz – Rodenkirchen (– Sürth) |
| 18 | Bonn Hbf (Main Station) – Brühl – Klettenberg – Sülzgürtel – Barbarossaplatz – Neumarkt – Dom/Hbf (Central Station) – Ebertplatz – Reichensperger Platz – Slabystraße – Mülheim – Buchheim – Holweide – Dellbrück – Thielenbruch |
Butzweilerhof extension (Line 5)

The Kölner Verkehrsbetriebe (KVB) has recently constructed a new 1.85 km (1.15 mi)-long extension from the former Ossendorf terminus into the Butzweilerhof/Gewerbegebiet Ossendorf area, which opened in December 2010.[3] Three new stations (Alter Flughafen Butzweilerhof, IKEA am Butzweilerhof and the new terminus, Sparkasse Am Butzweilerhof) were added to the existing Line 5. Construction of the extension cost about €18,000,000, with €5 million being financed through a charge on the companies which will benefit from the extension. The remaining €13 million was financed by the KVB Köln (Cologne Transit Authority).
The extension begins near the former Ossendorf terminus (which has been closed), crosses the tracks of the HGK,[4] follows the southern edge of the Hugo-Eckener-Strasse with the 1st station (Alter Flughafen Butzweilerhof) being sited at the corner of Hugo-Eckener-Strasse and Köhlstrasse. It then follows a new street which continues east from Köhlstraße. The line passes the new IKEA am Butzweilerhof store (2nd station), crosses the new extension of Richard-Byrd-Straße, and ends at the intersection of Richard-Byrd-Straße and Von-Hünefeld-Straße.
Future expansion
History

The oldest tunnel of the Cologne Stadtbahn is currently served by 30 trains per hour in each direction. Many consider this beyond the tunnel's capacity. Because the tunnel was built using a cut-and-cover technique, it follows major roads distant from the old city center with its narrow alleys. To solve both problems, an additional pair of tunnels was bored directly underneath the historic downtown areas. As a bonus, the travel time for line 16 will be decreased by about 10 minutes, because the NSS enables it to avoid the detour from Ubierring to Barbarossaplatz, only to return to the Rhine at the Central Station. It is also the final step in the separation of the high-floor and low-floor networks.
The current expansion project under construction is a new North-South tunnel (Nord-Süd-Stadtbahn, NSS). The new 3 km long tunnel will be the first newly built line since the opening of the original downtown tunnel in 1968. Every line opened in between had been just a replacement for current or previous surface lines.
Tunnel Collapse and Delays
On March 3, 2009 the building of the City's archive collapsed into a Stadtbahn's tunnel under construction on the Severinstraße, killing two people.[5] Poor construction, the theft of necessary iron reinforcements and several ground water break-ins into the tunnel, which were not reported or controlled properly by the construction company, are among the alleged causes for this catastrophe.[5][6]
In order to make use of the already completed tunnels and stations, a shorter service running from Dom/Central Station to Rathaus (city hall) started operation in December 2012,[7] re-routing line 5 from its previous terminus at Reichenspergerplatz to serve the new NSS. A further expansion to Heumarkt opened in December 2013.[7] Starting December 13, 2015, four underground stations from Bonner Wall to Severinstraße were opened.[8]
The next step of the expansion will be an above ground extension from the Marktstr. station down Bonner Straße, through Bayenthal. Construction will start Spring 2016 and should be completed sometime in 2018.[9] Full operation of the North-South Rail Tunnel will not be achieved until 2023 due to the issues of stabilizing the section of tunnel that collapsed in 2009.[10]
Cost
The extra cost of approximately 4 million euro is planned to mitigate the negative perception of the NSS project due to the collapse as well as budget increases, late completion (originally planned for 2011) and disruption. In order to avoid the possible destruction of archaeological artefacts underneath one of the oldest cities in Germany, the NSS was bored down to nearly 30 meters below ground level. At the location of the future stations however, archaeological digs were still required and are cited as one of the reasons for the already significant cost overruns. While initially estimated to cost around 600 million euro, the current price tag is calculated at around 960 million euro. Because the second stage, connecting the tunnel to the line along the Rhine river has not yet been tendered, but is expected to cost another 100 million, total cost is likely to exceed 1 billion euro.
Other Plans
- Extension of line 3 to Görlinger-Zentrum (stop, Schumacherring). Beginning of the preparatory work should begin early 2016 [citation needed] and took place in early February 2016. A later connection from Cologne-Pesch or Cologne-Esch / Auweiler was no longer taken into account in the planning. [11]
- (Line 5 and 13) Nußbaumerstraße and Subbelrather Straße as well as an additional stop Ehrenfeld railway station
- Extension of the Nord-Süd-Stadtbahn from Arnoldshöhe south to Cologne-Meschenich.
- Extension of line 1 from Bergisch Gladbach-Bensberg from further east Bergisch Gladbach-Moitzfeld to Gladbach-Herkenrath Kürten-Spitze [12]
- Extension of line 5 via the Gewerbegebiet Am Butzweilerhof to Longerich and there follow the S-Bahn Rhein-Ruhr And / or the urban railway line 15
- Connection of the district Widdersdorf either from Mengenich (line 4) or from Weiden-West, The city being preferred when registering to the public transport requirement plan 2017, the variant over the line 1 because of lower costs and higher development effect preferential [13]
- Extension of the Kölner Gürtel#Gürtelbahn (line 13) in the south to the DB line (planned S-Bahn Rhein-Sieg) and on the right from the Rhine from Mülheim to Ostheim and later to the S-Bahnhof Frankfurter Straße
- Extension of the tunnel on the Neusser Straße from Mollwitzstraße to Wilhelm-Sollmann-Straße
- Extension of line 7 to the new development area Ranzeler Straße in Cologne-Zündorf [14] to end 2019,[15] possibly later on via Niederkassel to Bonn
- Extension of line 7 to the new development area Grube Carl in Frechen and possibly further to Frechen-Habbelrath
- Stichstrecke from Hürth-Hermülheim to Hürth-Center
- Construction of a new railway line from Deutz to Flittard and the headquarters and route over the planned district of Mülheim-Süd;[16] A further connection to Leverkusen (- Wiesdorf) or even to (- Opladen) is discussed.
Closures
- The route from the Mannsfeld to Arnoldshöhe (decommissioned on 10 September 1951) is to be rebuilt as the 3rd construction phase of the north-south railway
- The route from Bonntor via the Brühler Straße to Raderthal, Annastraße (closed on October 24, 1955)
- The route from Cologne-Junkersdorf to Lövenich (decommissioned on 22 October 1956), rebuilt since 2002 and further led to pastures
- The branch from Buchheim to the Bf. Mülheim (decommissioned on November 22, 1956)
- The route from Thielenbruch to Bergisch Gladbach (closed on May 6, 1957 and November 16, 1958), since 1975 S-Bahn S 11 (Cologne - Bergisch Gladbach)
- The route from Nittumer Weg (city boundary) to Leverkusen-Schlebusch (cemetery, at the former southern edge of the village) (closed on May 1, 1958)
- The route over Niehler Straße to Niehl (closed on October 26, 1958). As alternatives were later the branch of the Neußer road over Niehl after Merkenich as well as the underground of the Reichensperger place over the Amsterdamer road to Niehl / Sebastianstraße built.
- The route from Cologne-Mülheim via Stammheim, Flittard, Bayerwerk and Wiesdorf to Opladen (closed on 26 October 1958), since 1991 partly replaced by the S-Bahn S 6 (Cologne - Leverkusen - Dusseldorf). Opladen can be reached by the DB regional train.
- The route from Deutz / Messe via Deutz-Mülheimer Straße. This route was replaced by the new line over the Pfälzischen ring, remained on the southern remainder as Werksberufsverkehr to KHD on the southern piece first received, was then shortened on two siding under the Zoobrücke. This remained until the last reconstruction of the Deutz / Messe station. (Decommissioned between December 16, 1962 and August 27, 1976)
- The small train Siegburg-Zündorf belonging route from Porz-Zündorf via Niederkassel to Troisdorf and Siegburg (closed on 6 September 1964). A reconstruction of the section from Zündorf to Langel and possibly later on via Niederkassel to Bonn has been under discussion for a long time.
- The street-level route from Höhenberg, Bennoplatz via Olpener Straße to crossing Höhenberg, Frankfurter Straße. Neutrassierung on own tracks parallel to the Olpener road; later lowered into tunnel (closed on 17 November 1964)
- The distance from the cathedral / Hbf. via the Christophstraße (later replaced by the underground line Dom / Hbf. - Appellhofplatz - Friesenplatz) and further on the Gladbacher Straße with a branch to Escherstraße (closed on October 11, 1968)
- The route Friesenplatz over Brabanter road to Rudolfplatz (closed on 18 October 1970). Until 1981 still use as operating distance.
- On the cross-track (then line 19) there is no more passenger traffic since 1981. The trains drove from Brühl Mitte via Brühl Nord, Brühl Bridge, Brühl East, Berzdorf North, Berzdorf, Wesseling North to Wesseling. Since there is an extensive freight traffic of the HGK, the route was not reduced. For entrances and disembarkations of the depot Wesseling the route is also used by light rail vehicles.
- The Weidenpescher Park loop from Neusser Straße via Rennbahnstraße, Weidenpescher Park and Scheibenstraße in the course of tunnel construction in Neusser Straße (closed on 25 August 1974)
- The route to Loop Bickendorf, Acacia Trail from Venloer Straße to Grüner Brunnenweg (closed on January 7, 1975)
- The branch from the Rheinuferbahnstrecke to the Siegfriedstraße in the center of Rodenkirchen was given up on the occasion of the conversion of the Rheinuferbahn to Stadtbahn on 12 August 1978. Before, the tram line 16 drove him.
- The route from the Friesenplatz via Venloer Straße to Hans-Böckler-Platz (closed on May 31, 1981) was replaced because of the tunnel construction (construction section West I) by the detour route over Gladbacher Straße and later replaced by the tunnel route.
- The route Mülheim, Wiener Platz via Bergisch Gladbacher road to Holweide, Vischeringstraße. Decommissioning with the opening of the subway Mülheim on May 31, 1997.
- The route to the loop Merkenich, Ölhafen (closed on 30 December 2000)
- The route from Chlodwigplatz via Bonner Straße, Koblenzer Straße and Goltsteinstrasse to Cologne-Marienburg (line 6) was completed on 30 August 2002 in the course of preparation for the construction of the north-south light rail, replaced by the bus 106.
Tram Stop Closures
- Äußere Kanalstraße (Neuehrenfeld) (now: Iltisstraße)
- Bahnhof Deutz, Justinianstraße and Constantinstraße (unterirdisch now: Bahnhof Deutz/Messe; oberirdisch then: Bahnhof Deutz/KölnArena; heute: Bahnhof Deutz/LANXESS arena)
- Bayenthalgürtel (Marienburg) (then: Goltsteinstraße/Gürtel)
- Bensberg (alt) (then: Im Hoppenkamp)
- Betzdorfer Straße (Deutz)
- Bickendorf, stillgelegt
- Bonntor (Bayenthal)
- Deutz-Kalker Bad (now: Deutz Technische Hochschule)
- Fixheider Weg (Höhenhaus), replaced by Im Weidenbruch
- Fordwerke, Ölhafen (Niehl)
- Frankstraße (Rodenkirchen)
- Gotenring (Deutz) (then: Deutz-Kalker Straße)
- Gumprechtstraße (Ehrenfeld)
- Herler Ring (Buchheim)
- Homarstraße (Vingst)
- Innere Kanalstraße (Ehrenfeld)
- Kalk, Markt (zusätzliche Haltestelle während des U-Bahn-Baus)
- Keupstraße (auf der Bergisch Gladbacher Straße), then: Montanusstraße (Mülheim)
- Kitschburger Straße (Lindenthal)
- Klettenberg (Klettenberg), now Klettenbergpark
- Krückelstraße (Poll)
- Marienburg (now: Heinrich-Lübke-Ufer)
- Marienburg, Südpark (Marienburg)
- Marienburger Straße (Marienburg)
- Maternusstraße (Rodenkirchen)
- Messe/Sporthalle (then: KölnMesse/Osthallen; now: KölnMesse)
- Militärringstraße (Bayenthal)
- Mülheimer Ring (Buchheim)
- Müngersdorf (now: Alter Militärring)
- Neuenhöfer Allee (Sülz)
- Neurather Ring (Höhenhaus) (später: Höhenhaus, Neurather Weg)
- Ossendorf, im Zuge der Verlängerung der Linie 5 stillgelegt
- Poll, Autobahn (Poll), ersetzt durch Baumschulenweg
- Rixdorfer Straße (now: Mülheim, Berliner Straße)
- Rochusstraße (Bickendorf), umbenannt in Äußere Kanalstr.
- Rolandstraße (Neustadt-Süd)
- Schönhauser Straße (Bayenthal) (then: Koblenzer Straße)
- Stadion (now: Rheinenergie-Stadion)
- Südbrücke (Poll)
- Tacitusstraße (Bayenthal)
- Takuplatz (Neuehrenfeld)
- Tulpenweg (Zündorf)
- Venloer Wall (Neustadt-Nord)
- Vingst Ost (Vingst)
- Ziehglaswerke (Zündorf) (then: Porz Glaswerke)
Rolling stock




Since the last traditional tramcars were retired in 2006, the Stadtbahn's active rolling stock consists exclusively of modern articulated light rail vehicles. All of them are about 30 m (98 ft 5 in) long, 2.65 m (8 ft 8 in) wide, seat approximately 70 passengers and are approved for speeds of up to 80 km/h (50 mph). With rare exceptions, all services are operated by two units coupled together.
Stadtbahnwagen B
In 1973, Cologne received two prototypes of the DUEWAG Stadtbahnwagen B LRV. Since then, 172 units in four batches were delivered to Cologne until 1996. The first generation (series 2000) is currently being retired, while the second generation (series 2100) is due to receive a major overhaul for at least another 15 years of service.
Low-floor LRVs (K4000 and K4500)
After tests with a low-floor tram from Vienna, a similar vehicle was developed for Cologne by Bombardier Transportation, later becoming part of Bombardier's standardized Flexity Swift family. A total of 124 low-floor trams were delivered between 1995 and 1998, referred to as "K4000". These vehicles received numbers starting with 4001.
When it was decided to create a second low-floor network, an option for high-floor vehicles was changed to additional low-floor vehicles. Bombardier developed a new low-floor tram based more on the K5000 (see below) than on the K4000. These new trams were named "K4500". Delivery of 69 units started in 2005 and was completed in late 2007.
The CR4000 trams operating on Tramlink in Croydon, England are largely based on the original K4000 stock used in Cologne.
CitySprinter
By the time a new series of high-floor vehicles was needed, DUEWAG had been sold to Siemens Transportation Systems and later dissolved, meaning that additional Type B cars were no longer being made. Siemens subsequently proposed the "CitySprinter", a high-floor derivative of its Combino series of low-floor city trams.
In August 1999, after two months of testing, the first CitySprinter prototype crashed into another tram at 50 km/h (30 mph) at the "Christophstraße/MediaPark" U-Bahn station. The accident was caused by a simultaneous electronics shutdown resulting in the train's inability to apply its brakes. Eight people sustained serious injuries. A second prototype was produced but as a result of the crash was never delivered.
High-floor LRVs (K5000 and K5200)
Following the failure of the CitySprinter, Bombardier derived a high-floor tram from the K4000. 59 units, named "K5000", were delivered in 2002 and 2003. The numbering was changed to 5101 at short notice to avoid re-using the number 5001, which had been the number of the ill-fated CitySprinter. Another 15 vehicles of the same design, named "K5200", were delivered before 2011.
The M5000 trams used by Metrolink in Manchester, England are almost identical to the K5000/K5200 series used in Cologne.
Tram interiors
-
B100S 2000
-
B100S 2100
-
B80D 2200
-
B80D 2300
-
K4000
-
K5000
See also
References
Inline citations
- ^ a b c d e "Kölner Verkehrs-Betriebe AG". Kvb-koeln.de. Retrieved 2017-07-14.
- ^ "DAS UNTERNEHMEN". Kvb-koeln.de. Archived from the original on 2017-03-22. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Kölner Verkehrs-Betriebe AG". Kvb-koeln.de. 2008-11-24. Retrieved 2013-08-25.
- ^ "Häfen und Güterverkehr Köln AG". S253428520.online.de. Retrieved 2013-08-25.
- ^ a b "U-Bahn: Das Protokoll eines Versagens | Köln Übersicht - Kölner Stadt-Anzeiger" (in German). Ksta.de. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
- ^ "Archiveinsturz: Beschädigtes Fugenblech als Indiz | Köln Übersicht - Kölner Stadt-Anzeiger" (in German). Ksta.de. Archived from the original on 2013-02-06. Retrieved 2013-04-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b http://stadtbahn.relaunch.net/german/news/press.html?NID=737[permanent dead link]
- ^ Reimann, Anna. "Nord-Süd-Stadtbahn in Köln: Das sind die neuen Haltestellen der KVB-Linie 17". ksta.de. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "3. Baustufe Nord-Süd Stadtbahn". www.stadt-koeln.de. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ Damm, Andreas. "Kölner Stadtarchiv: Wer soll die U-Bahn weiterbauen?". ksta.de. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "Verkehr in Köln Neue Endstation für die KVB-Linie 3" [Traffic in Cologne: New terminus for the KVB line 3]. Cologne town hall (in German).
- ^ Claus Boelen-Partile. "Der Zug ist noch nicht abgefahren" [The train has not yet been moved].
- ^ "Tagesordnungspunkt". ratsinformation.stadt-koeln.de. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "KVB-Verlängerung: Linie 7 kommt nur langsam voran" [KVB extension: line 7 is progressing slowly] (in German).
- ^ Nadine Carstens (2014-09-29). "Die Bürger bleiben skeptisch" [The citizens remain skeptical]. Cologne city-advertisement. Retrieved 2015-02-19.
- ^ "Kölner Initiative fordert Straßenbahn-Trasse bis Flittard" [Cologne initiative calls for tramway route to Flittard] (in German).
Books
- Groneck, Christoph (2005). Köln/Bonn Stadtbahn Album. Robert Schwandl Verlag. ISBN 3-936573-07-7.
- Höltge, Dieter; Reuther, Axel (2001). Straßen- und Stadtbahnen in Deutschland Band 7: Köln, Düren, Aachen (in German). EK-Verlag. ISBN 3-88255-338-3.
- Lindemann, Doris; Verkehrs-Betriebe, Kölner, eds. (2002). Kölner Mobilität - 125 Jahre Bahnen und Busse (in German). Du Mont Verlag. ISBN 3-8321-7177-0.