Italian campaign (World War II)
| Italian Campaign | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II | |||||||
 American soldiers of the U.S. 92nd Infantry Division fire a bazooka at a German machine gun nest, Lucca 1944. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
(until 8 September 1943) (from 18 September 1943) | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
C-in-C Allied Forces Headquarters: (from December 1944) |
C-in-C Army Group C: | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 1,333,856 (1945)[1] |
1,621 aircraft (average)[3] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Sicily: 22,000 casualties[5] Total: 327,000–335,495 |
Sicily: 165,000 casualties (of whom 30,000 were Germans)[11] Italian mainland: 336,650 casualties[nb 4]–580,630 [nb 5][13][14] 4,500+ aircraft lost[15] Surrender of Caserta: 1,000,000 captured[16] Total: 1,501,650–1,745,630+ | ||||||
| ~152,940 civilians dead | |||||||
The Italian Campaign of World War II was the name of Allied operations in and around Italy, from 1943 to the end of the war in Europe. Joint Allied Forces Headquarters (AFHQ) was operationally responsible for all Allied land forces in the Mediterranean theatre, and it planned and commanded the invasion of Sicily in July 1943, followed shortly thereafter in September by the invasion of the Italian mainland and the campaign on Italian soil until the surrender of the German Armed Forces in Italy in May 1945.
It is estimated that between September 1943 and April 1945, some 60,000–70,000 Allied and 60,000–150,000 German soldiers died in Italy.[6][17][nb 6] Overall Allied casualties during the campaign totaled about 320,000[nb 7] and the corresponding German figure (excluding those involved in the final surrender) was well over 600,000.[6] Fascist Italy, prior to its collapse, suffered about 200,000 casualties, mostly POWs taken in the Allied invasion of Sicily, including more than 40,000 killed or missing.[19] Besides them, over 150,000 Italian civilians died, as did 15,197 anti-Fascist partisans and 13,021 troops of the Italian Social Republic.[20]
In the West, no other campaign cost more than Italy in terms of lives lost and wounds suffered by infantry forces of both sides, during bitter small-scale fighting around strongpoints at the Winter Line, the Anzio beachhead and the Gothic Line.[21] The campaign ended when Army Group C surrendered unconditionally to the Allies on May 2, 1945, one week before the formal German Instrument of Surrender. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican, both surrounded by Italian territory, also suffered damage during the campaign.
Strategic background
Even prior to victory in the North African Campaign in May 1943, there was disagreement between the Allies on the best strategy to defeat the Axis.[citation needed] The British, especially the Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, advocated their traditional naval-based peripheral strategy. Even with a large army, but greater naval power, the traditional British answer against a continental enemy was to fight as part of a coalition and mount small peripheral operations designed to gradually weaken the enemy. The United States, with an even larger army, favoured a more direct method of fighting the main force of the German Army in Northern Europe. The ability to launch such a campaign depended on first winning the Battle of the Atlantic.
The strategic disagreement was fierce, with the U.S. service chiefs arguing for an invasion of France as early as possible, while their British counterparts advocated a policy centred on operations in the Mediterranean. There was even pressure from some Latin American countries to stage an invasion of Spain, which under Francisco Franco was friendly to the Axis nations, although not a participant in the war.[22] The American staff believed that a full-scale invasion of France at the earliest possible time was required to end the war in Europe, and that no operations should be undertaken that might delay that effort. The British argued that the presence of large numbers of troops trained for amphibious landings in the Mediterranean made a limited-scale invasion possible and useful.[citation needed]
Eventually the U.S. and British political leadership reached a compromise in which both would commit most of their forces to an invasion of France in early 1944, but also launch a relatively small scale Italian campaign. A contributing factor was Franklin D. Roosevelt's desire to keep US troops active in the European theatre during 1943 and his attraction to the idea of eliminating Italy from the war.[23] It was hoped that an invasion might knock Italy out of the conflict,[24] or at least increase the pressure on it and weaken it.[25][26] The elimination of Italy would enable Allied naval forces, principally the Royal Navy, to dominate the Mediterranean Sea, securing the lines of communications with Egypt, the Far East, the Middle East and India.[26][27] Italian divisions on occupation and coastal defence duties in the Balkans and France would be withdrawn to defend Italy, while the Germans would have to transfer troops from the Eastern Front to defend Italy and the entire southern coast of France, thus aiding the Soviets.[28][29]
Campaign
Invasion of Sicily

A combined Allied invasion of Sicily began on 10 July 1943 with both amphibious and airborne landings at the Gulf of Gela. The land forces involved were the U.S. Seventh Army, under Lieutenant General George S. Patton, and the British Eighth Army, under General Bernard Montgomery. The original plan contemplated a strong advance by the British northwards along the east coast to Messina, with the Americans in a supporting role along their left flank. When the Eighth Army were held up by stubborn defences in the rugged hills south of Mount Etna, Patton amplified the American role by a wide advance northwest toward Palermo and then directly north to cut the northern coastal road. This was followed by an eastward advance north of Etna towards Messina, supported by a series of amphibious landings on the north coast, that propelled Patton's troops into Messina shortly before the first elements of the Eighth Army. The defending German and Italian forces were unable to prevent the Allied capture of the island, but succeeded in evacuating most of their troops to the mainland, the last leaving on 17 August 1943. The Allied forces gained experience in opposed amphibious operations, coalition warfare and mass airborne drops.
Invasion of Continental Italy

Forces of the British Eighth Army, still under Montgomery, landed in the 'toe' of Italy on 3 September 1943 in Operation Baytown, the day the Italian government agreed to an armistice with the Allies. The armistice was publicly announced on 8 September by two broadcasts, first by General Eisenhower and then by a proclamation by Marshal Badoglio. Although the German forces prepared to defend without Italian assistance, only two of their divisions opposite the Eighth Army and one at Salerno were not tied up disarming the Royal Italian Army.
On 9 September, forces of the U.S. Fifth Army, under Lieutenant General Mark W. Clark, expecting little resistance, landed against heavy German resistance at Salerno in Operation Avalanche; in addition, British forces landed at Taranto in Operation Slapstick, which was almost unopposed. There had been a hope that, with the surrender of the Italian government, the Germans would withdraw to the north, since at the time Adolf Hitler had been persuaded that Southern Italy was strategically unimportant. However, this was not to be; although, for a while, the Eighth Army was able to make relatively easy progress up the eastern coast, capturing the port of Bari and the important airfields around Foggia. Although none of the northern reserves were made available to the German 10th Army, it nevertheless came close to repelling the Salerno landing, due mainly to the cautious command of Clark. The main Allied effort in the west initially centred on the port of Naples: that city was selected because it was the northernmost port that could receive Allied air support by fighter aircraft operating from Sicily.
As the Allies advanced, they encountered increasingly difficult terrain: the Apennine Mountains form a spine along the Italian peninsula offset somewhat to the east. In the most mountainous areas of Abruzzo, more than half the width of the peninsula comprises crests and peaks over 3,000 feet (910 m) that are relatively easy to defend; and the spurs and re-entrants to the spine confronted the Allies with a succession of ridges and rivers across their line of advance. The rivers were subject to sudden and unexpected flooding, which constantly thwarted the Allied commanders' plans.[30]
Allied advance to Rome
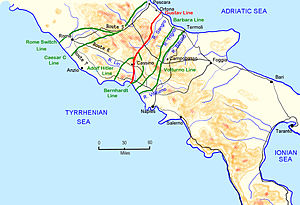
In early October 1943, Hitler was persuaded by his Army Group Commander in Southern Italy, Field Marshal Albert Kesselring, that the defence of Italy should be conducted as far away from Germany as possible. This would make the most of the natural defensive geography of Central Italy, whilst denying the Allies the easy capture of a succession of airfields; each one being ever closer to Germany. Hitler was also convinced that yielding southern Italy would provide the Allies with a springboard for an invasion of the Balkans with its vital resources of oil, bauxite and copper.[31]

Kesselring was given command of the whole of Italy and immediately ordered the preparation of a series of defensive lines across Italy, south of Rome. Two lines, the Volturno and the Barbara, were used to delay the Allied advance so as to buy time to prepare the most formidable defensive positions, which formed the Winter Line – the collective name for the Gustav Line and two associated defensive lines on the west of the Apennine Mountains, the Bernhardt and Hitler lines (the latter had been renamed the Senger Line by 23 May 1944).[32]

The Winter Line proved a major obstacle to the Allies at the end of 1943, halting the Fifth Army's advance on the western side of Italy. Although the Gustav Line was penetrated on the Eighth Army's Adriatic front, and Ortona captured, blizzards, drifting snow and zero visibility at the end of December caused the advance to grind to a halt. The Allies' focus then turned to the western front, where an attack through the Liri valley was considered to have the best chance of a breakthrough towards the Italian capital. Landings at Anzio during Operation Shingle, advocated by the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, behind the line were intended to destabilise the German Gustav line defences, but the early thrust inland to cut off the German defences did not occur, thanks to the indecisiveness of the American commander (Major General John P. Lucas), and the Anzio forces became bottled up in their beachhead. Lucas was replaced by Major General Lucian Truscott.

It took four major offensives between January and May 1944 before the line was eventually broken by a combined assault of the Fifth and Eighth Armies (including British, American, French, Polish and Canadian Corps) concentrated along a twenty-mile front between Monte Cassino and the western seaboard. In a concurrent action, American General Mark Clark was ordered to break out of the stagnant position at Anzio and cash-in on the opportunity to cut off and destroy a large part of the German 10th Army retreating from the Gustav Line between them and the Canadians. But this opportunity was lost on the brink of success, when Clark disobeyed his orders and sent his U.S. forces to enter the vacant Rome instead.[33] Rome had been declared an open city by the German Army so no resistance was encountered.

The American forces took possession of Rome on 4 June 1944.[34] The German Tenth Army were allowed to get away and, in the next few weeks, were responsible for doubling the Allied casualties in the next few months. Clark was hailed as a hero in the United States. The Canadians were sent through the city without stopping at 3:00am the next morning.
Allied advance into Northern Italy

After the capture of Rome, and the Allied invasion of Normandy in June, the U.S. VI Corps and the French Expeditionary Corps (CEF), which together amounted to seven divisions, were pulled out of Italy during the summer of 1944 to participate in Operation Dragoon, codename for the Allied invasion of Southern France. The sudden removal of these experienced units from the Italian front was only partially compensated for by the gradual arrival of three divisions, the Brazilian 1st Infantry Division, the U.S. 92nd Infantry Division, both in the second half of 1944, and the U.S. 10th Mountain Division in January 1945.[34]
In the period from June to August 1944, the Allies advanced beyond Rome, taking Florence and closing up on the Gothic Line.[35] This last major defensive line ran from the coast some 30 miles (48 km) north of Pisa, along the jagged Apennine Mountains chain between Florence and Bologna to the Adriatic coast, just south of Rimini. In order to shorten the Allied lines of communication for the advance into Northern Italy, the Polish II Corps advanced towards the port of Ancona and, after a month-long battle, succeeded in capturing it on 18 July.

During Operation Olive, the major Allied offensive in the autumn of 1944, which commenced on 25 August, the Gothic Line defences were penetrated on both the Fifth and Eighth Army fronts; but, there was no decisive breakthrough. Churchill, the British Prime Minister, had hoped that a major advance in the autumn of 1944 would open the way for the Allied armies to advance north eastwards through the 'Ljubljana Gap' (the area between Venice and Vienna, modern Slovenia) to Vienna and Hungary to forestall the Russians advancing into Eastern Europe. Churchill's proposal had been strongly opposed by the U.S. Chiefs of Staff who, understanding its importance to British post-war interests in the region, did not feel it aligned with prevailing overall Allied war priorities.[34]
In October Lieutenant General Sir Richard McCreery succeeded Lieutenant General Sir Oliver Leese as commander of the Eighth Army. In December, Lieutenant General Mark Clark, the Fifth Army commander, was appointed to command the 15th Army Group, thereby succeeding British General Sir Harold Alexander as commander of all Allied ground troops in Italy, after Alexander succeeded Field Marshal Sir Henry Wilson as the Supreme Allied Commander in the Mediterranean theatre. Clark was succeeded in command of the Fifth Army by Lieutenant General Lucian K. Truscott, Jr.. In the winter and spring of 1944–45, extensive partisan activity in Northern Italy took place. As there were two Italian governments during this period, (one on each side of the war), the struggle took on some characteristics of a civil war.

The poor winter weather, which made armoured manoeuvre and the exploitation of overwhelming air superiority impossible, coupled with the massive losses suffered to its ranks during the autumn fighting,[36][37] the need to transfer some British troops to Greece (as well as the need to withdraw the British 5th Infantry Division and I Canadian Corps to northwest Europe) made it impractical for the Allies to continue their offensive in early 1945. Instead, the Allies adopted a strategy of "offensive defence" while preparing for a final attack when better weather and ground conditions arrived in the spring.

In late February-early March 1945, Operation Encore saw elements of the U.S. IV Corps (1st Brazilian Division and the newly arrived U.S. 10th Mountain Division) battling forward across minefields in the Apennines to align their front with that of the U.S. II Corps on their right.[38] They pushed the German defenders from the commanding high point of Monte Castello and the adjacent Monte Belvedere and Castelnuovo, depriving them of artillery positions that had been commanding the approaches to Bologna since the narrowly failed Allied attempt to take the city in the autumn.[39][40][41] Meanwhile, damage to other transport infrastructure forced Axis forces to use sea, canal and river routes for re-supply, leading to Operation Bowler against shipping in Venice harbour on 21 March 1945.
The Allies' final offensive commenced with massive aerial and artillery bombardments on 9 April 1945.[42] By 18 April, Eighth Army forces in the east had broken through the Argenta Gap and sent armour racing forward in an encircling move to meet the U.S. IV Corps advancing from the Apennines in Central Italy and to trap the remaining defenders of Bologna.[34] On 21 April, Bologna was entered by the 3rd Carpathian Division, the Italian Friuli Group (both from the Eighth Army) and the U.S. 34th Infantry Division (from the Fifth Army).[43] The U.S. 10th Mountain Division, which had bypassed Bologna, reached the River Po on 22 April; the 8th Indian Infantry Division, on the Eighth Army front, reached the river on 23 April.[44]
By 25 April, the Italian Partisans' Committee of Liberation declared a general uprising,[45] and on the same day, having crossed the Po on the right flank, forces of Eighth Army advanced north northeast towards Venice and Trieste. On the U.S. Fifth Army front, elements drove north toward Austria and north west to Milan. On the Fifth Army's left flank, the U.S. 92nd Infantry Division (the "Buffalo Soldiers Division") went along the coast to Genoa; and a rapid advance towards Turin, by the Brazilian division on their right, took the German–Italian Army of Liguria by surprise, causing its collapse.[40]


As April came to an end, Army Group C, the Axis forces in Italy, retreating on all fronts and having lost most of its fighting strength, was left with little option but surrender.[40] General Heinrich von Vietinghoff, who had taken command of Army Group C after Kesselring had been transferred to become Commander-in-Chief of the Western Front (OB West) in March 1945, signed the instrument of surrender on behalf of the German armies in Italy on 29 April, formally bringing hostilities to an end on 2 May 1945.[46]
Casualties
| Battle | Dates | Allies | Axis | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allied invasion of Sicily | 9 July – 17 August 1943 | 25,121 (2,267 POWs) |
173,939 (124,430 POWs) |
Allied victory |
| Allied invasion of Italy | 3 – 16 September 1943 | 12,560 | 3,500 | Allied victory |
| Battle of Monte Cassino | 17 January – 18 May 1944 | 55,000 | 20,000 | Allied victory |
| Battle of Anzio | 22 January – 5 June 1944 | 43,000 | 40,000 | Allied victory |
| Gothic Line | Late August 1944 – Early March 1945 | 34,500 | 42,000 | Inconclusive |
| Spring 1945 offensive in Italy | 6 April 1945 – 2 May 1945 | 16,258 | 32,000 | German surrender in Italy |
| Total casualties | 1943 – 1945 | 186,000 | 311,000 |
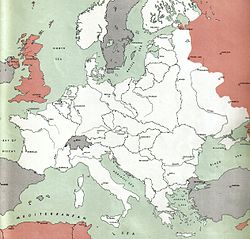 1 July 1943 |
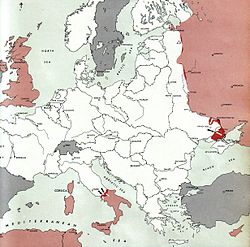 ] ]1 November 1943 |
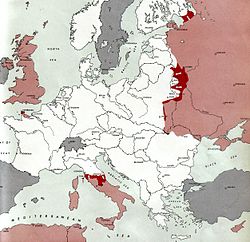 ] ]1 July 1944 |
 ] ]1 September 1944 |
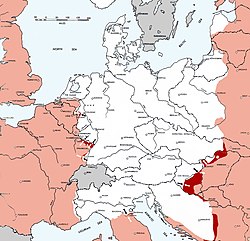 1 December 1944 |
 1 May 1945 |
See also
- Military history of Italy during World War II
- Italian Co-Belligerent Army
- Italian Co-Belligerent Navy
- Italian Co-Belligerent Air Force
- Italian Social Republic
- Italian resistance movement
- Italian Civil War
Notes
- Footnotes
- ^ Ellis provides the following information on Allied losses for the campaign, but includes no dates. American: 29,560 killed and missing, 82,180 wounded, 7,410 captured; British: 89,440 killed, wounded, or missing, no information is provided on those captured; Indian: 4,720 killed or missing, 17,310 wounded, and 46 captured; Canadian: 5,400 killed or missing, 19,490 wounded, and 1,000 captured; Pole: 2,460 killed or missing, 8,460 wounded, no information is provided for those captured; South African: 710 killed or missing, 2,670 wounded, and 160 captured; French: 8,600 killed or missing, 23,510 wounded, no information is provided on those captured; Brazilian: 510 killed or missing, 1,900 wounded, no information is provided on those captured; New Zealand: no information is provided for the campaign.[6]
- ^ United States: 114,000 casualties;[7] British Commonwealth: 198,000 casualties;[8] Total Allied casualties: 59,151 killed,[9] 30,849 missing and 230,000 wounded.
- ^ American: 119,279 casualties; Brazilian: 2,211 casualties; British: 89,436 casualties; British Colonial troops: 448 casualties; Canadian: 25,889 casualties; French: 27,625 casualties; Greeks: 452 casualties; Indian, 19,373 casualties; Italian: 4,729 casualties; New Zealand; 8,668 casualties; Polish: 11,217 casualties; South African: 4,168 casualties.[10]
- ^ Between 1 September 1943 – 10 May 1944: 87,579 casualties. Between 11 May 1944 – 31 January 1945: 194,330 casualties. Between February and March 1945: 13,741 casualties. British estimates for 1–22 April 1945: 41,000 casualties. This total excludes Axis forces that surrendered at the end of the campaign[12]
- ^ Ellis states that from various sources, between September 1939 and 31 December 1944, the German Armed Forces (including the Waffen SS and foreign volunteers) lost 59,940 killed, 163,600 wounded, and 357,090 captured within Italy. He notes that other sources, for only the army, losses between June 1941 and 10 April 1945 amount to 46,800 killed, 208,240 captured, and 168,570 wounded.[6]
- ^ In Alexander's Generals Blaxland quotes 59,151 Allied deaths between 3 September 1943 and 2 May 1945 as recorded at AFHQ and gives the breakdown between 20 nationalities: United States 20,442; United Kingdom, 18,737; France, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Senegal and Belgium 5,241; Canada, 4,798; India, Pakistan, Nepal 4,078; Poland 2,028; New Zealand 1,688; Italy (excluding irregulars) 917; South Africa 800; Brazil 275; Greece 115; Jewish volunteers from the British Mandate in Palestine 32. In addition 35 soldiers were killed by enemy action while serving with pioneer units from Botswana, Lesotho, Swaziland, Seychelles, Mauritius, Sri Lanka, Lebanon, Cyprus and the West Indies[9]
- ^ Field Marshal Sir Harold Alexander after the war used a figure of 312,000[18] but later historians generally arrive at a slightly higher figure.
- Citations
- ^ Jackson, p. 230
- ^ Horst Boog, Gerhard Krebs, Detlef Vogel: "Germany and the Second World War: Volume VII", Clarendon Press, May 4, 2006, page 522. Quoting Alfred Jodl's "Strategic situation in spring 1944" presentation. The total given for German forces in Italy in May 1944 is 961,000 personnel. 1,000,000 German soldiers were present for the Surrender of Caserta in May 1945.
- ^ Don Caldwell. "Luftwaffe Aircraft Losses By Theater, September 1943-October 1944". The Air Force Historical Foundation. Retrieved March 1, 2016. Average strength from September 1943 to October 1944 alone.
- ^ Blaxland, p. 243.
- ^ Shaw, p. 120.
- ^ a b c d Ellis, p. 255
- ^ "European Theater". Worldwar2history.info. Retrieved 2011-07-28.
- ^ "The Italian Campaign". Webcitation.org. Archived from the original on October 26, 2009. Retrieved 2011-07-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Blaxland (1979), p. 11
- ^ a b Jackson, p. 335
- ^ Hosch 2009, page 122.
- ^ Jackson, p. 400
- ^ Rüdiger Overmans, Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1, P. 336 and P.174. Overmans lists the total death toll of German troops in Italy (including Sicily) as 150,660.
- ^ George C Marshall, Biennial reports of the Chief of Staff of the United States Army to the Secretary of War : 1 July 1939-30 June 1945. Washington, DC : Center of Military History, 1996. Page 202. The US military estimated 91,000 German dead in the Italian campaign, thereof 5,000 in Sicily and 86,000 on the Italian mainland, and 364,189 captured prior to the surrender of Army Group C, thereof 7,100 in Sicily and 357,086 on the Italian mainland. This is a total of 455,189 losses. The document does not provide an estimate for wounded; using Ellis's 168,570 figure, German casualties would total 623,759.
- ^ Don Caldwell. "Luftwaffe Aircraft Losses By Theater, September 1943-October 1944". The Air Force Historical Foundation. Retrieved March 1, 2016. 4,468 operational losses are given from the brief period of September 1943 to October 1944 alone.
- ^ Daily Telegraph Story of the War fifth volume page 153
- ^ Rüdiger Overmans, Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1, P. 336 and P.174. Overmans lists the total death toll of German troops in Italy (including Sicily) as 150,660. However, Overmans' figures, which are extrapolations from a statistical sample (see German casualties in World War II#Statistical study by Rüdiger Overmans) may be much too high (see Western Allied invasion of Germany#cite note-13). The US military estimated 91,000 German and Italian military dead in the Italian campaign, thereof 5,000 in Sicily and 86,000 on the Italian mainland (see German casualties in World War II#United States Army Figures for German and Italian Losses).
- ^ Blaxland, p. 284.
- ^ Le Operazioni in Sicilia e in Calabria (Luglio-Settembre 1943), Alberto Santoni, p.401, Stato maggiore dell'Esercito, Ufficio storico, 1989
- ^ Updated studies (2010) by the Ufficio dell'Albo d'Oro of the Italian Ministry of Defence, p. 4
- ^ Keegan, John "The Second World War" Penguin Books 2005 ISBN 0143035738 p.368
- ^ "Batista's Boost", TIME, January 18, 1943, Retrieved March 2, 2010
- ^ Carver, pp4 & 59
- ^ Blumenson 1969, p. 7.
- ^ Weinberg 1994, pp. 588 & 591.
- ^ a b Liddell Hart 1970, p. 457.
- ^ Keegan 2005, p. 287.
- ^ Weinberg 1994, p. 591.
- ^ Churchill 1959, p. 669.
- ^ Phillips (1957), p. 20
- ^ Orgill, The Gothic Line, p5
- ^ Carver, p. 195
- ^ Katz, The Battle for Rome
- ^ a b c d Clark, Calculated Risk
- ^ Video: Allies Liberate Florence etc. Universal Newsreel. 1944. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- ^ Keegan, p367
- ^ R.Brooks, The War North of Rome, Chps XIX-XX spec.p254
- ^ Brooks 2003, Chapters XX to XXII
- ^ Moraes, "The Brazilian Expeditionary Force By Its Commander" Chapter V (The IV Corps Offensive); Sections Monte Castello & Castelnuovo
- ^ a b c Bohmler, Rudolf, Monte Cassino, Chapter XI
- ^ Clark, (2007) [1950], p.608 View on Google Books
- ^ Blaxland, pp.254–255
- ^ Blaxland, p.271
- ^ Blaxland, pp. 272–273
- ^ Blaxland, p.275
- ^ Blaxland, p. 277
References
- Blaxland, Gregory (1979). Alexander's Generals (the Italian Campaign 1944–1945). London: William Kimber. ISBN 0-7183-0386-5.
- Blumenson, Martin (1969). Salerno to Cassino. United States Army in World War II, Mediterranean Theater of Operations. Vol. Volume 3. Washington, D.C.: Office of the Chief of Military History, U.S. Army. OCLC 22107.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - Bohmler, Rudolf (1964). Monte Cassino: a German View. Cassell. ASIN B000MMKAYM.
- Brooks, Thomas R. (2003). The War North of Rome (June 1944 – May 1945). Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81256-9.
- Carver, Field Marshal Lord (2001). The Imperial War Museum Book of the War in Italy 1943–1945. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. ISBN 0-330-48230-0.
- Churchill, Winston (2002) [1959]. The Second World War. London: Pimlico. ISBN 0712667024.
- Clark, Mark (2007) [1950]. Calculated Risk. New York: Enigma Books. ISBN 978-1-929631-59-9.
- D'Este, Carlo (1990). World War II in the Mediterranean (1942–1945 Major Battles and Campaigns). Algonquin Books. ISBN 978-0-945575-04-7.
- Ellis, John (1993). The World War II Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for all the combatants. BCA. ISBN 978-1-85410-254-6.
- Harpur, Brian (1981). The Impossible Victory. Hippocrene Books. ISBN 0-88254-518-3.
- Hosch, William L. (2009). World War II: People, Politics, and Power. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing/The Rosen Publishing Group. ISBN 1-61530-046-5.
- Jackson, General W.G.F.; with Gleave, Group Captain T.P. (2004) [1st. pub. HMSO 1988]. Butler, J.R.M. (ed.). The Mediterranean and Middle East, Volume VI: Part III – November 1944 to May 1945. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series. Uckfield, UK: Naval & Military Press. ISBN 1-84574-072-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Katz, Robert (2003). The Battle for Rome. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-1642-5.
- Keegan, John (2005) [1989]. The Second World War. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-303573-2.
- Liddell Hart, Basil (1992) [1970]. History of the Second World War. London: Papermac. ISBN 0333582624.
- Moraes, Mascarenhas (1966). The Brazilian Expeditionary Force By Its Commander. US Government Printing Office. ASIN: B000PIBXCG.
- Montemaggi, Amedeo (2002). LINEA GOTICA 1944. La battaglia di Rimini e lo sbarco in Grecia decisivi per l'Europa sud-orientale e il Mediterraneo. Rimini: Museo dell'Aviazione.
- Montemaggi, Amedeo (2006). LINEA GOTICA 1944: scontro di civiltà. Rimini: Museo dell'Aviazione.
- Montemaggi, Amedeo (2008). CLAUSEWITZ SULLA LINEA GOTICA. Imola: Angelini Editore.
- Montemaggi, Amedeo (2010). ITINERARI DELLA LINEA GOTICA 1944. Guida storico iconografica ai campi di battaglia. Rimini: Museo dell'Aviazione.
- Orgill, Douglas (1967). The Gothic Line (The Autumn Campaign in Italy 1944). London: Heinemann.
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. (1994). A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521443173.
Further reading
- Mavrogordato, Ralph S. (2000) [1960]. "Chapter 12: Hitler's Decision on the Defense of Italy". In Kent Roberts Greenfield (ed.). Command Decisions. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 70-7.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - Matthews, Sidney T. (2000) [1960]. "Chapter 14: General Clark's Decision to Drive to Rome". In Kent Roberts Greenfield (ed.). Command Decisions. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 70-7.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - Brown, Shaun R. G. (1986). The Loyal Edmonton Regiment at War, 1943–1945 (MA, Wilfrid Laurier University, 1984). Ottawa: National Library of Canada. ISBN 978-0-31519-038-2. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
External links
- "Gothic Line". Retrieved 2011-07-03.
- Winter Line Stories Original stories from the front lines of the Italian Campaign by US Army Liaison Officer Major Ralph R. Hotchkiss
- World War II
- Ortona and the Italian Campaign – 65th Anniversary
- Canadians in Italy, 1943–1945 Lots of media and photos and info on Canadians in the Italian theatre.
- Brazilian WWII Veterans website Template:Pt icon
- Brazilian Expeditionary Force Website Template:Pt icon with histories, biographies, photos, videos on Italian Campaign.
- New Zealand Official War History Italy volume I: From The Sangro to Cassino, Italy Volume II: From Cassino to Trieste
- Memoirs of Lt-Col Donald, NZEF (Italy, Chapters 8–15)
- Dal Volturno a Cassino, website (in Italian) covering the autumn /winter of 1943 – 44
- World War II propaganda leaflets – use in Italy: A website about airdropped, artillery-delivered or rocket-fired propaganda leaflets. Italian campaign.
- BBC's flash video of the Italian Campaign
- Canadian Newspapers and the Second World War – The Sicilian and Italian Campaigns, 1943–1945
- Liberatori: A website on the Po river breakout and the liberation of the small town of Cornuda.
- Royal Engineers Museum Royal Engineers and Second World War (Italian Campaign)
- CBC Digital Archives – The Italian Campaign
- Template:It icon La Città Invisibile Collection of signs, stories and memories during the Gothic Line age.
- Template:It icon Italian Partisan Collection of stories and memories from Italian partisan.
- Italy Volume I, The Sangro to Cassino the New Zealand Official War History
- Italy Volume II, From Cassino to Trieste the New Zealand Official War History
- Italian Campaign (World War II)
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Brazil
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Canada
- Military history of Canada during World War II
- Battles and operations of World War II involving France
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Greece
- Battles and operations of World War II involving India
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Italy
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Poland
- Battles and operations of World War II involving New Zealand
- Battles and operations of World War II involving South Africa
- Battles and operations of World War II involving the United States
- Battles and operations of World War II involving Australia
- Modern history of Italy
- World War II campaigns of the Mediterranean Theatre
- Campaigns, operations and battles of World War II involving the United Kingdom
