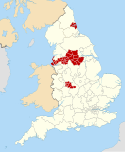
Metropolitan borough
| Metropolitan district | |
|---|---|
| |
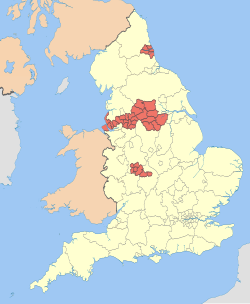 | |
| Category | Districts |
| Location | England |
| Found in | Metropolitan county |
| Created by | Local Government Act 1972 |
| Created |
|
| Number | 36 (as of 2008) |
| Possible status |
|
| Populations | 0.1 - 1.1 million |
A metropolitan borough is a type of local government district in England, and is a subdivision of a metropolitan county. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972, metropolitan boroughs are defined in English law as metropolitan districts. However, all of them have been granted or regranted royal charters to give them borough status (as well as, in some cases, city status).[1] Metropolitan boroughs have been effectively unitary authority areas since the abolition of the metropolitan county councils by the Local Government Act 1985.[2] However, metropolitan boroughs pool much of their authority in joint boards and other arrangements that cover whole metropolitan counties, such as combined authorities.
History
The term "metropolitan borough" was first used for administrative subdivisions of the County of London between 1900 and 1965. However, the present boroughs of Greater London, which have different boundaries and functions, and are much larger in area, are known as London Boroughs rather than metropolitan boroughs.
The current metropolitan boroughs were created in 1974 as subdivisions of the new metropolitan counties, created to cover the six largest urban areas in England outside Greater London. The new districts replaced the previous system of county boroughs, municipal boroughs, urban and rural districts. The districts typically have populations of 174,000 to 1.1 million.
Metropolitan districts were originally parts of a two-tier structure of local government, and shared power with the metropolitan county councils (MCCs). They differed from non-metropolitan districts in the division of powers between district and county councils. Metropolitan districts were local education authorities, and were also responsible for social services and libraries, but in non-metropolitan counties these services were the responsibility of county councils.[3]
In 1986, the metropolitan county councils were abolished under the Local Government Act 1985 and most of their functions were devolved to the metropolitan boroughs, making them, to a large extent, unitary authorities in all but name. At the same time, however, some of the functions of the abolished metropolitan county councils were taken over by joint bodies such as passenger transport authorities, and joint fire, police and waste disposal authorities.[2]
Metropolitan district councils
The metropolitan districts are administered by metropolitan district councils. They are the principal local authorities in the six metropolitan counties and are responsible for running most local services, such as schools, social services, waste collection and roads. [citation needed]
List of metropolitan boroughs
The 36 metropolitan boroughs are:
| Metropolitan county | Metropolitan districts | Number | County population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Manchester | Manchester, Bolton, Bury, Oldham, Rochdale, Salford, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford, Wigan | 10 | 2,573,200 |
| Merseyside | Liverpool, Knowsley, St Helens, Sefton, Wirral | 5 | 1,365,000 |
| South Yorkshire | Sheffield, Barnsley, Doncaster, Rotherham | 4 | 1,290,000 |
| Tyne and Wear | Newcastle upon Tyne, Gateshead, South Tyneside, North Tyneside, Sunderland | 5 | 1,089,400 |
| West Midlands | Birmingham, Coventry, Dudley, Sandwell, Solihull, Walsall, Wolverhampton | 7 | 2,591,300 |
| West Yorkshire | Leeds, Bradford, Calderdale, Kirklees, Wakefield | 5 | 2,161,200 |
See also
- Metropolitan boroughs of the County of London
- Borough
- Non-metropolitan district
- County borough
- Subdivisions of England
- ISO 3166-2:GB, subdivision codes for the United Kingdom
- Political make-up of Metropolitan borough councils