Portal:Heraldry
Welcome to the Heraldry and Vexillology Portal!


Heraldry encompasses all of the duties of a herald, including the science and art of designing, displaying, describing and recording coats of arms and badges, as well as the formal ceremonies and laws that regulate the use and inheritance of arms. The origins of heraldry lie in the medieval need to distinguish participants in battles or jousts, whose faces were hidden by steel helmets.
Vexillology (from the Latin vexillum, a flag or banner) is the scholarly study of flags, including the creation and development of a body of knowledge about flags of all types, their forms and functions, and of scientific theories and principles based on that knowledge. Flags were originally used to assist military coordination on the battlefield, and have evolved into a general tool for signalling and identification, particularly identification of countries.
Selected article
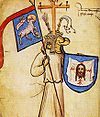
Attributed arms are coats of arms given to legendary figures, or to notable persons from times before the rise of heraldry. Beginning in the 12th century, imaginary arms were assigned to the knights of the Round Table, and soon arms were given to biblical figures, to Roman and Greek heroes, and to kings and popes who had not historically borne arms. The specific arms could vary, but the arms for major figures soon became fixed.
Notable arms attributed to biblical figures include the arms of Jesus based on the instruments of the Passion, and the shield of the Trinity. Medieval literature attributed coats of arms to the Nine Worthies, including Alexander the Great, Julius Caesar, and King Arthur. Arms were given to many kings predating heraldry, including Edward the Confessor and William I of England. These attributed arms were sometimes used in practice as quarterings in the arms of their descendants. (more...)
Selected biography

Elias Ashmole was an antiquarian, collector, politician and officer of arms. He supported the royalist side during the English Civil War, and at the restoration of Charles II he was rewarded with several lucrative offices, including Windsor Herald of Arms in Ordinary. Throughout his life he was an avid collector of curiosities and other artifacts. Many of these he acquired from the traveller, botanist, and collector John Tradescant the elder and his son of the same name, and most he donated to Oxford University to create the Ashmolean Museum. He also donated his library and priceless manuscript collection to Oxford. Apart from his collecting activities, Ashmole illustrates the passing of the pre-scientific world view in the seventeenth century: while he immersed himself in alchemical, magical and astrological studies and was consulted on astrological questions by Charles II and his court, these studies were essentially backward-looking. Although he was one of the founding members of the Royal Society, a key institution in the development of experimental science, he never participated actively. (more...)
Selected flag

The colors of the national flag of Romania (Romanian: Drapelul României) have a long history. Red, yellow and blue were found on late 16th-century royal grants of Michael the Brave, as well as shields and banners. During the Wallachian uprising of 1821, they were present on the canvas of the revolutionaries' flag and its fringes; for the first time a meaning was attributed to them: "Liberty (sky-blue), Justice (field yellow), Fraternity (blood red)". Article 124 of the 1866 Constitution of Romania provided that “the colors of the United Principalities will be Blue, Yellow and Red”. The order and placement of the colors were decided by the Assembly of Deputies in its session of 26 March 1867. Thus, following a proposal by Nicolae Golescu, they were placed just as in 1848.
On 30 December 1947, Romania was proclaimed a people’s republic and all the kingdom’s symbols were outlawed, including the coats of arms and the tricolor flags that showed them. According to article 101 of the 1948 Constitution, “The flag of the Romanian People’s Republic is composed of the colors: blue, yellow and red, arranged vertically. In the middle is placed the national coat of arms”. (more...)
Selected picture

The town hall of Dendermonde, a city in Flanders, displaying heraldic banners.
Did you know...
- ...that the Norwegian heraldic authority forbade any other municipality to use the dog rose which appears on the Flag of Trondheim (pictured), because of the symbol's long association with that city?
- ...that Raymond Jacobs maintained that he was the last surviving member of the original party of Marines who raised the first flag on Mount Suribachi during the Battle of Iwo Jima?
- ...that the tiger in the Coat of arms of Singapore represents Malaysia?
- ...that the American Palestine Line claimed that its ship the SS President Arthur was the first ocean liner to fly the Zionist flag when it began service in 1925?
- ...that for United States heraldry, federal and state governments do not employ coats of arms, but have chosen to use seals as their official emblems?
Related portals
Major topics and navigation
|
|
|
Heraldry Web resources
Authorities
- Belgium - The Council of Nobility, Flemish Heraldic Council and Council of Heraldry and Vexillology of the French Community
- Canada - Canadian Heraldic Authority and see also Public Register of Arms, Flags and Badges
- England, Wales, and Northern Ireland - The College of Arms
- Ireland - The Office of the Chief Herald of Ireland
- Netherlands - High Council of Nobility
- Portugal - Instituto da Nobreza Portuguesa
- Scotland - The Court of the Lord Lyon
- South Africa - South African Bureau of Heraldry
- Sweden - National Board of Heraldry, The National Archive
- United States Army - The United States Army Institute of Heraldry
Societies
- Greek Heraldry Society
- The Academy of Heraldic Science Czech republic
- The American College of Heraldry
- The American Heraldry Society
- The Augustan Society
- The Australian Heraldry Society Inc.
- Bulgarian Heraldry and Vexillology Society
- The Center for Research of Orthodox Monarchism
- Cambridge University Heraldic and Genealogical Society
- Chiltern Heraldry Group
- The College of Dracology
- Croatian Heraldic and Vexillologic Association
- The Finnish Heraldic Society
- Fryske Rie foar Heraldyk
- Hellenic Armigers Society
- Guild of Heraldic Artists
- Genealogical Society of Ireland
- Heraldry Research Institute (Japan)
- The Heraldry Society
- The Heraldry Society of Africa
- The Heraldry Society of New Zealand Inc.
- The Heraldry Society of Scotland
- The Heraldry Society of Southern Africa
- The Institute of Heraldic and Genealogical Studies
- The International Association of Amateur Heralds
- Italian Center of Vexillological Studies
- Lancashire Heraldry Group
- Macedonian Heraldry Society
- New England Historic Genealogical Society Committee on Heraldry
- Norwegian Heraldry Society
- Oxford University Heraldry Society
- Polish Heraldry Society
- Polish Nobility Confederation
- Real Academia Matritense de Heráldica y Genealogía - Royal Academy of Heraldry and Genealogy of Madrid
- Romanian Institute for Genealogy and Heraldry
- The Royal Heraldry Society of Canada
- The Russian College of HeraldryThe Russian College of Heraldry
- Serbian Heraldic Society
- Societas Heraldica Scandinavica
- Societas Heraldica Slovenica
- Swedish Heraldic Society
- Ukrainian Heraldry Society
- Royal Association Genealogical and Heraldic Office of Belgium
Vexillology
Software
- Coat of Arms Visual Designer web-based program
- Puncher Heraldry Program
- Blazonry Server - pyBlazon
- DrawShield - creates SVG shield or arms image from blazon
- CoaMaker - web-based tool
- Blazon95 and BLAZONS! 2000, older Windows applications
- Heraldicon
Texts
- Heraldry, historical and popular : with seven hundred illustrations (1863)
- A Complete Guide to Heraldry (1909)
Other
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus












