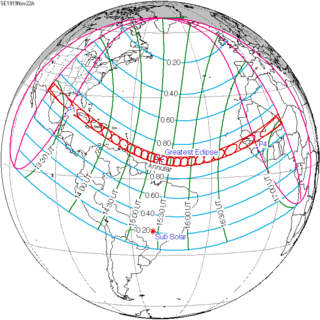
Solar eclipse of November 22, 1919
| Solar eclipse of November 22, 1919 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.4549 |
| Magnitude | 0.9198 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 697 s (11 min 37 s) |
| Coordinates | 6°54′N 48°54′W / 6.9°N 48.9°W |
| Max. width of band | 341 km (212 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 15:14:12 |
| References | |
| Saros | 141 (18 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9327 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Saturday, November 22, 1919. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. It occurred in over half of North America, much of South America, a part of Western Europe and about a third of Africa.
Places inside the annular eclipse included North America and the Caribbean, including Austin, San Antonio, Houston and Galveston, Texas in the United States and was close to Mexico at around 7:30 CT (13:30 UTC), more than a quarter of the Gulf of Mexico and close to the Florida Keys in the United States which occurred before 8:45 ET (13:45 UTC), it also included Cuba, most of Haiti and the southwesternmost Dominican Republic , it was almost near Venezuela and it included Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Barbados which happened in the mid morning hours. The greatest eclipse occurred at 15:14:12 UTC. In Africa, it included the Gambia, southern Senegal including Casamance, Portuguese Guinea (now Guinea-Bissau), the northern part of French Guinea (now Guinea) which occurred before 15:45 (16:45 UTC) and southeasternmost Mauritania and the middle portion of the French Sudan (now Mali) which included Bamako and Timbuktu, it occurred in the late afternoon before sunset at 17:00 UTC.
The duration of annularity at maximum eclipse (closest to but slightly shorter than the longest duration) was 11 minutes, 36.56 seconds in the Atlantic Ocean north of Brazil. It was the longest annular solar eclipse since January 5, 1647, but the Solar eclipse of December 2, 1937 lasted longer.[1]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1916–1920
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
The solar eclipses on February 3, 1916 (total), July 30, 1916 (annular), January 23, 1917 (partial), and July 19, 1917 (partial) occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1916 to 1920 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 111 | December 24, 1916 Partial |
−1.5321 | 116 | June 19, 1917 Partial |
1.2857 | |
| 121 | December 14, 1917 Annular |
−0.9157 | 126 | June 8, 1918 Total |
0.4658 | |
| 131 | December 3, 1918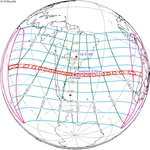 Annular |
−0.2387 | 136 Totality in Príncipe |
May 29, 1919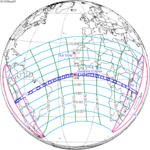 Total |
−0.2955 | |
| 141 | November 22, 1919 Annular |
0.4549 | 146 | May 18, 1920 Partial |
−1.0239 | |
| 151 | November 10, 1920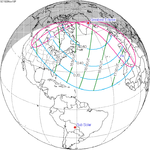 Partial |
1.1287 | ||||
Saros 141
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 141, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 70 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on May 19, 1613. It contains annular eclipses from August 4, 1739 through October 14, 2640. There are no hybrid or total eclipses in this set. The series ends at member 70 as a partial eclipse on June 13, 2857. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 20 at 12 minutes, 9 seconds on December 14, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[3]
| Series members 12–33 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 13 | 14 |
 September 17, 1811 |
 September 28, 1829 |
 October 9, 1847 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 October 19, 1865 |
 October 30, 1883 |
 November 11, 1901 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 November 22, 1919 |
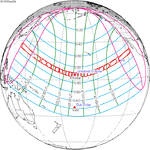 December 2, 1937 |
 December 14, 1955 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 December 24, 1973 |
 January 4, 1992 |
 January 15, 2010 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
 January 26, 2028 |
 February 5, 2046 |
 February 17, 2064 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 February 27, 2082 |
 March 10, 2100 |
 March 22, 2118 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
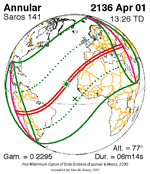 April 1, 2136 |
 April 12, 2154 |
 April 23, 2172 |
| 33 | ||
 May 4, 2190 | ||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 November 22, 1919 (Saros 141) |
 November 1, 1948 (Saros 142) |
 October 12, 1977 (Saros 143) |
 September 22, 2006 (Saros 144) |
 September 2, 2035 (Saros 145) |
 August 12, 2064 (Saros 146) |
 July 23, 2093 (Saros 147) |
||
Notes
- ^ "Annular Solar Eclipses with Durations Exceeding 11m 00s: -3999 to 6000". NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 141". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC