Sewage treatment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
BethNaught (talk | contribs) Reverted 1 edit by 182.237.167.140 (talk): Blanking. (TW) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Sewer Plant.jpg|250px|thumb|The objective of sewage treatment is to produce a disposable effluent without causing harm to the surrounding environment, and prevent [[pollution]].<ref>{{cite book |title= Environmental Pollution Monitoring And Control |last= Khopkar |first= S. M.|year= 2004|publisher= New Age International |location=New Delhi |isbn= 81-224-1507-5 |page= 299|url= http://books.google.com/?id=TAk21grzDZgC}}</ref>]] |
|||
'''Sewage treatment''' is the process of removing [[contaminants]] from [[wastewater]] and household [[sewage]], both [[Surface runoff|runoff]] ([[effluents]]), domestic, commercial and institutional. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants. Its objective is to produce an environmentally safe fluid waste stream (or treated [[effluent]]) and a solid waste (or treated [[sludge]]) suitable for disposal or reuse (usually as farm [[fertilizer]]). Using advanced technology it is now possible to re-use sewage effluent for drinking water, although [[Singapore]] is the only country to implement such technology on a production scale in its production of [[NEWater]].<ref>PUB (Singapore National Water Agency)(2011). [http://www.pub.gov.sg/about/historyfuture/Pages/NEWater.aspx "NEWater: History."]</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
'''Sewage treatment''' is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and household sewage,both Surface runoff ,effluents]]), domestic, commercial and institutional. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants. Its objective is to produce an environmentally safe fluid waste stream or solid waste or treated sludge suitable for disposal or reuse usually as farm fertilizer. Using advanced technology it is now possible to re-use sewage effluent for drinking water |
|||
[[Image:FaradayFatherThames.jpg|thumb|right|The [[Great Stink]] of 1858 stimulated research into the problem of sewage treatment. In this caricature in ''[[The Times]]'', [[Michael Faraday]] reports to ''Father [[River Thames|Thames]]'' on the state of the river.]] |
|||
Basic sewer systems were used for waste removal in ancient [[Mesopotamia]], where vertical shafts carried the waste away into cesspools. Similar systems existed in the [[Indus Valley]] civilization in modern day [[India]] and in Ancient [[Crete]] and [[Greece]]. In the [[Middle Ages]] the sewer systems built by the [[Roman Empire|Romans]] fell into disuse and waste was collected into cesspools that were periodically emptied by workers known as 'rakers' who would often sell it as [[fertilizer]] to farmers outside the city. |
|||
Modern sewage systems were first built in the mid-nineteenth century as a reaction to the exacerbation of sanitary conditions brought on by heavy [[industrialization]] and [[urbanization]]. Due to the contaminated water supply, [[cholera]] outbreaks occurred in [[Cholera outbreaks and pandemics|1832, 1849 and 1855]] in [[London]], killing tens of thousands of people. This, combined with the [[Great Stink]] of 1858, when the smell of untreated human waste in the [[River Thames]] became overpowering, and the report into sanitation reform of the [[Royal Commission]]er [[Edwin Chadwick]],<ref name=Ashton-Ubido>{{cite journal|last=Ashton|first=John|coauthors=Ubido, Janet|title=The Healthy City and the Ecological Idea|journal=Journal of the Society for the Social History of Medicine|year=1991|volume=4|issue=1|pages=173–181|url=http://www.johnrashton.securemachines.co.uk/documentbank/the%20healthy%20city%20and%20the%20ecological%20idea.pdf|accessdate=8 July 2013}}</ref> led to the [[Metropolitan Commission of Sewers]] appointing Sir [[Joseph Bazalgette]] to construct a vast underground sewage system for the safe removal of waste. Contrary to Chadwick's recommendations, Bazalgette's system, and others later built in [[Continental Europe]], did not pump the sewage onto farm land for use as fertilizer; it was simply piped to a natural waterway away from population centres, and pumped back into the environment. |
|||
===Early attempts=== |
|||
One of the first attempts at diverting sewage for use as a fertilizer in the farm was made by the [[cotton mill]] owner [[James Smith (inventor)|James Smith]] in the 1840s. He experimented with a piped distribution system initially proposed by James Vetch<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books/about/A_short_description_of_the_plans_of_Capt.html?id=GV1YAAAAYAAJ|title=A short description of the plans of Captain James Vetch for the sewerage of the metropolis|author=Lewis Dunbar B. Gordon|year=1851|publisher=}}</ref> that collected sewage from his factory and pumped it into the outlying farms, and his success was enthusiastically followed by Edwin Chadwick and supported by organic chemist [[Justus von Liebig]]. |
|||
The idea was officially adopted by the [[Health of Towns Association|Health of Towns Commission]], and various schemes (known as sewage farms) were trialled by different municipalities over the next 50 years. At first, the heavier solids were channeled into ditches on the side of the farm and were covered over when full, but soon flat-bottomed tanks were employed as reservoirs for the sewage; the earliest patent was taken out by William Higgs in 1846 for "tanks or reservoirs in which the contents of sewers and drains from cities, towns and villages are to be collected and the solid animal or vegetable matters therein contained, solidified and dried..."<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=w6tvSwAACAAJ|title=History of Sewage Treatment in Britain|author=H. H. Stanbridge|year=1976|publisher=Institute of Water Pollution Control}}</ref> Improvements to the design of the tanks included the introduction of the horizontal-flow tank in the 1850s and the radial-flow tank in 1905. These tanks had to be manually de-sludged periodically, until the introduction of automatic mechanical de-sludgers in the early 1900s.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.bvsde.paho.org/bvsacd/leeds/cooper.pdf|title=Historical aspects of wastewater treatment|author=P. F. Cooper|accessdate=2013-12-21}}</ref> |
|||
The precursor to the modern [[septic tank]] was the [[cesspool]] in which the water was sealed off to prevent contamination and the solid waste was slowly liquified due to anaerobic action; it was invented by L.H Mouras in France in the 1860s. Donald Cameron, as [[Surveying|City Surveyor]] for [[Exeter]] patented an improved version in 1895, which he called a 'septic tank'; septic having the meaning of 'bacterial'. These are still in worldwide use, especially in rural areas unconnected to large scale sewage systems.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=NXnX4KkV00YC|title=The Sanitary City: Environmental Services in Urban America from Colonial Times to the Present|author=Martin V. Melosi|year=2010|publisher=University of Pittsburgh Press|page=110}}</ref> |
|||
===Chemical treatment=== |
|||
[[File:Frankland Edward 1894.jpg|thumb|200px|Sir [[Edward Frankland]], a distinguished chemist, who demonstrated the possibility of chemically treating sewage in the 1870s.]] |
|||
It was not until the late 19th century that it became possible to treat the sewage by chemically breaking it down through the use of [[microorganism]]s and removing the pollutants. Land treatment was also steadily becoming less feasible, as cities grew and the volume of sewage produced could no longer be absorbed by the farmland on the outskirts. |
|||
Sir [[Edward Frankland]] conducted experiments at the Sewage Farm in [[Croydon]], England, during the 1870s and was able to demonstrate that filtration of sewage through porous gravel produced a nitrified effluent (the ammonia was converted into nitrate) and that the filter remained unclogged over long periods of time.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=o-2rWpwJevEC|title=Edward Frankland: Chemistry, Controversy and Conspiracy in Victorian England|author=Colin A. Russell|year=2003|publisher=Cambridge University Press|pages=372–380}}</ref> This established the then revolutionary possibility of biological treatment of sewage using a contact bed to oxidize the waste. This concept was taken up by the chief chemist for the London [[Metropolitan Board of Works]], William Libdin, in 1887: |
|||
:...in all probability the true way of purifying sewage...will be first to separate the sludge, and then turn into neutral effluent... retain it for a sufficient period, during which time it should be fully aerated, and finally discharge it into the stream in a purified condition. This is indeed what is aimed at and imperfectly accomplished on a sewage farm.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=thEigV6yl64C&source=gbs_navlinks_s|title=Advances in Water Treatment and Pollution Prevention |
|||
|author=Sharma, Sanjay Kumar; Sanghi, Rashmi|year=2012|publisher=Springer|accessdate=2013-02-07}}</ref> |
|||
From 1885 to 1891 filters working on this principle were constructed throughout the UK and the idea was also taken up in the US at the [[Lawrence Experiment Station]] in [[Massachusetts]], where Frankland's work was confirmed. In 1890 the LES developed a '[[trickling filter]]' that gave a much more reliable performance.<ref>[http://ironwood.cpe.uchicago.edu/CPE_Workshop/paper/Cain-Rotella-Sept2005.pdf EPIDEMICS, DEMONSTRATION EFFECTS, AND MUNICIPAL INVESTMENT IN SANITATION CAPITAL]</ref> |
|||
Contact beds were developed in [[City of Salford|Salford]], [[Manchester]] and by scientists working for the [[London City Council]] in the early 1890s. According to Christopher Hamlin, this was part of a conceptual revolution that replaced the philosophy that saw "sewage purification as the prevention of decomposition with one that tried to facilitate the biological process that destroy sewage naturally."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.homepages.ucl.ac.uk/~ucessjb/Hamlin%201992.pdf|title=Edwin Chadwick and the Engineers, 1842-1854: Systems and Antisystems in the Pipe-and-Brick Sewers War Technology and Culture|year=1992}}</ref> |
|||
Contact beds were tanks containing the inert substance, such as stones or slate, that maximized the surface area available for the microbial growth to break down the sewage. The sewage was held in the tank until it was fully decomposed and it was then filtered out into the ground. This method quickly became widespread, especially in the UK, where it was used in [[Leicester]], [[Sheffield]], [[Manchester]] and [[Leeds]]. The bacterial bed was simultaneously developed by Joseph Corbett as Borough Engineer in [[City of Salford|Salford]] and experiments in 1905 showed that his method was superior in that greater volumes of sewage could be purified better for longer periods of time than could be achieved by the contact bed.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=ZRY6rrpKFGgC&source=gbs_navlinks_s|title=Aerobic Wastewater Treatment Processes: History and Development|author=Tilley, David F.|year=2011|publisher=IWA Publishing|accessdate=2013-02-07}}</ref> |
|||
The Royal Commission on Sewage Disposal published it's eighth report in 1912 that set what became the international standard for sewage discharge into rivers; the '20:30 standard', which allowed 20 mg [[Biochemical oxygen demand]] and 30 mg suspended solid per litre.<ref>[http://ia700404.us.archive.org/35/items/cu31924003641929/cu31924003641929.pdf FINAL REPORT OF THE COMMISSIONERS APPOINTED TO INQUIRE AND REPORT WHAT METHODS OF Treating and Disposing of Sewage. 1912 ]</ref> |
|||
===Activated sludge=== |
|||
The development of secondary treatments to sewage in the early twentieth century led to arguably the single most significant improvement in [[public health]] and the [[Ecology#Physical environments|environment]] during the course of the century, the invention of the '[[activated sludge]]' process for the treatment of sewage. |
|||
[[File:Davyhulme Laboratory - early 20th century.jpg|thumb|left|The [[Davyhulme#Davyhulme Sewage Works|Davyhulme Sewage Works Laboratory]], where the [[activated sludge]] process was developed in the early 20th century.]] |
|||
In 1912, Dr. Gilbert Fowler, a scientist at the [[University of Manchester]], observed experiments being conducted at the Lawrence Experiment Station at [[Massachusetts]] involving the aeration of sewage in a bottle that had been coated with algae. Fowler's engineering colleagues, Edward Ardern and William Lockett,<ref name=Beychok>{{cite book | author=Beychok, Milton R. | title=[[Aqueous Wastes from Petroleum and Petrochemical Plants]]| edition=1st | publisher=John Wiley & Sons Ltd | year=1967 | id=[[Library of Congress Control Number|LCCN 67019834]]}}</ref> who were conducting research for the Manchester Corporation Rivers Department at [[Davyhulme#Davyhulme Sewage Works|Davyhulme Sewage Works]],<ref>[http://www.waterengineering.co.uk/fbda-history.asp Condensed History of Fine Bubble Diffused Air (FBDA)]</ref> experimented on treating sewage in a [[sequencing batch reactor|draw-and-fill reactor]], which produced a highly treated effluent. They aerated the waste-water continuously for about a month and were able to achieve a complete nitrification of the sample material. Believing that the sludge had been activated (in a similar manner to [[activated carbon]]) the process was named ''activated sludge''. |
|||
Their results were published in their seminal 1914 paper, and the first full-scale continuous-flow system was installed at [[Worcester]] two years later. In the aftermath of the [[First World War]] the new treatment method spread rapidly, especially to the USA, [[Denmark]], [[Germany]] and [[Canada]]. By the late 1930s, the activated sludge treatment was the predominant process used around the world.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=_v0WjdM6sLoC&source=gbs_navlinks_s|title=The Culture of Flushing: A Social and Legal History of Sewage|author=Benidickson, Jamie|year=2011|publisher=UBC Press|accessdate=2013-02-07}}</ref> |
|||
==Origins of sewage== |
==Origins of sewage== |
||
Sewage is generated by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial establishments. It includes household waste liquid from |
Sewage is generated by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial establishments. It includes [[household waste]] liquid from [[toilet]]s, [[bathing|baths]], [[shower]]s, [[kitchen]]s, [[sink]]s and so forth that is disposed of via [[sanitary sewer|sewer]]s. In many areas, sewage also includes liquid waste from industry and commerce. The separation and draining of household waste into [[greywater]] and [[blackwater (waste)|blackwater]] is becoming more common in the developed world, with greywater being permitted to be used for watering plants or recycled for flushing toilets. |
||
Sewage may include stormwater runoff. Sewerage systems capable of handling storm water are known as combined sewer systems. Combined sewers require much larger and more expensive treatment facilities than [[sanitary sewer]]s. Heavy volumes of storm runoff may overwhelm the sewage treatment system, causing a spill or overflow. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller than combined sewers, and they are not designed to transport stormwater. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive Infiltration/Inflow|infiltration/inflow]dilution by stormwater and/or groundwater is allowed into a sanitary sewer system. |
Sewage may include [[stormwater]] runoff. [[Sewerage]] systems capable of handling storm water are known as [[combined sewer]] systems. This design was common when urban sewerage systems were first developed, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.<ref name="Metcalf & Eddy">{{cite book | author=Metcalf & Eddy, Inc. | title=Wastewater Engineering | year=1972 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Book Company |location=New York | isbn=0-07-041675-3}}</ref>{{rp|119}} Combined sewers require much larger and more expensive treatment facilities than [[sanitary sewer]]s. Heavy volumes of storm runoff may overwhelm the sewage treatment system, causing a spill or overflow. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller than combined sewers, and they are not designed to transport stormwater. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive [[Infiltration/Inflow|infiltration/inflow]] (dilution by stormwater and/or groundwater) is allowed into a sanitary sewer system. Communities that have [[Urbanization|urbanized]] in the mid-20th century or later generally have built separate systems for sewage (sanitary sewers) and stormwater, because precipitation causes widely varying flows, reducing sewage treatment plant efficiency.<ref name="Burrian">Burrian, Steven J., et al. (1999).[http://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=2000E6J7.txt "The Historical Development of Wet-Weather Flow Management."] US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Cincinnati, OH. Document No. EPA/600/JA-99/275.</ref> |
||
As rainfall travels over roofs and the ground, it may pick up various contaminants including soil particles and other sediment,heavy metals]], organic |
As rainfall travels over roofs and the ground, it may pick up various contaminants including [[soil]] particles and other [[sediment]], [[heavy metals]], [[organic compound]]s, animal waste, and [[oil]] and [[Grease (lubricant)|grease]]. (''See [[urban runoff]]''.)<ref>{{cite book|title=Stormwater Effects Handbook: A Toolbox for Watershed Managers, Scientists, and Engineers|publisher=CRC/Lewis Publishers|location=New York |year=2001 |isbn=0-87371-924-7 |url=http://unix.eng.ua.edu/~rpitt/Publications/BooksandReports/Stormwater%20Effects%20Handbook%20by%20%20Burton%20and%20Pitt%20book/MainEDFS_Book.html |author8=G. Allen Burton, Jr., Robert Pitt}} Chapter 2.</ref> Some [[jurisdiction]]s require stormwater to receive some level of treatment before being discharged directly into waterways. Examples of treatment processes used for stormwater include [[retention basin]]s, [[constructed wetland|wetlands]], buried [[Stormwater detention vault|vaults]] with various kinds of [[media filter]]s, and [[Hydrodynamic separator|vortex separators]] (to remove coarse solids). |
||
==Process overview== |
==Process overview== |
||
| Line 17: | Line 52: | ||
*''Primary treatment'' consists of temporarily holding the sewage in a quiescent basin where heavy solids can settle to the bottom while oil, grease and lighter solids float to the surface. The settled and floating materials are removed and the remaining liquid may be discharged or subjected to secondary treatment. |
*''Primary treatment'' consists of temporarily holding the sewage in a quiescent basin where heavy solids can settle to the bottom while oil, grease and lighter solids float to the surface. The settled and floating materials are removed and the remaining liquid may be discharged or subjected to secondary treatment. |
||
*''Secondary treatment'' removes dissolved and suspended biological matter. Secondary treatment is typically performed by [[Indigenous (ecology)|indigenous]], water-borne micro-organisms in a managed habitat. Secondary treatment may require a separation process to remove the micro-organisms from the treated water prior to discharge or tertiary treatment. |
*''Secondary treatment'' removes dissolved and suspended biological matter. Secondary treatment is typically performed by [[Indigenous (ecology)|indigenous]], water-borne micro-organisms in a managed habitat. Secondary treatment may require a separation process to remove the micro-organisms from the treated water prior to discharge or tertiary treatment. |
||
*''Tertiary treatment'' is sometimes defined as anything more than primary and secondary treatment in order to allow rejection into a highly sensitive or fragile ecosystem (estuaries, low-flow rivers, coral reefs,...). Treated water is sometimes disinfected chemically or physically (for example, by lagoons and microfiltration prior to discharge into a stream,river, bay, lagoon or wetland, or it can be used for the irrigation of a golf course, green way or park. If it is sufficiently clean, it can also be used for groundwater recharge or agricultural purposes. |
*''Tertiary treatment'' is sometimes defined as anything more than primary and secondary treatment in order to allow rejection into a highly sensitive or fragile ecosystem (estuaries, low-flow rivers, coral reefs,...). Treated water is sometimes disinfected chemically or physically (for example, by lagoons and [[microfiltration]]) prior to discharge into a [[stream]], [[river]], [[bay]], [[lagoon]] or [[wetland]], or it can be used for the [[irrigation]] of a golf course, green way or park. If it is sufficiently clean, it can also be used for [[groundwater recharge]] or agricultural purposes. |
||
[[File:ESQUEMPEQUE-EN.jpg|675px|thumb|center|<center>Simplified [[process flow diagram]] for a typical large-scale treatment plant</center>]] |
|||
[[File:SchemConstructedWetlandSewage.jpg|675px|thumb|center|[[Process flow diagram]] for a typical treatment plant via subsurface flow constructed wetlands (SFCW)]] |
|||
===Pretreatment=== |
===Pretreatment=== |
||
Pretreatment removes all materials that can be easily collected from the raw sewage before they damage or clog the pumps and sewage lines of primary treatment |
Pretreatment removes all materials that can be easily collected from the raw sewage before they damage or clog the pumps and sewage lines of primary treatment [[clarifier]]s. Objects that are commonly removed during pretreatment include trash, tree limbs, leaves, branches, and other large objects. |
||
The influent in sewage water passes through a [[bar screen]] to remove all large objects like cans, rags, sticks, plastic packets etc. carried in the sewage stream.most commonly done with an automated mechanically raked bar screen in modern plants serving large populations, while in smaller or less modern plants, a manually cleaned screen may be used. The raking action of a mechanical bar screen is typically paced according to the accumulation on the bar screens and/or flow rate. The solids are collected and later disposed in a landfill, or incinerated. Bar screens or mesh screens of varying sizes may be used to optimize solids removal. If gross solids are not removed, they become entrained in pipes and moving parts of the treatment plant, and can cause substantial damage and inefficiency in the process. |
The influent in sewage water passes through a [[bar screen]] to remove all large objects like cans, rags, sticks, plastic packets etc. carried in the sewage stream.<ref>Water and Environmental Health at London and Loughborough (1999). [http://www.lut.ac.uk/well/resources/technical-briefs/64-wastewater-treatment-options.pdf "Waste water Treatment Options."] Technical brief no. 64. London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and Loughborough University.</ref> This is most commonly done with an automated mechanically raked bar screen in modern plants serving large populations, while in smaller or less modern plants, a manually cleaned screen may be used. The raking action of a mechanical bar screen is typically paced according to the accumulation on the bar screens and/or flow rate. The solids are collected and later disposed in a landfill, or incinerated. Bar screens or mesh screens of varying sizes may be used to optimize solids removal. If gross solids are not removed, they become entrained in pipes and moving parts of the treatment plant, and can cause substantial damage and inefficiency in the process.<ref name="EPA Primer">EPA. Washington, DC (2004). [http://www.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/primer.pdf "Primer for Municipal Waste water Treatment Systems."] Document no. EPA 832-R-04-001.</ref>{{rp|9}} |
||
====Grit removal==== |
====Grit removal==== |
||
Pretreatment may include a sand or grit channel or chamber, where the velocity of the incoming sewage is adjusted to allow the settlement of sand, grit, stones, and broken glass. These particles are removed because they may damage pumps and other equipment. For small sanitary sewer systems, the grit chambers may not be necessary, but grit removal is desirable at larger plants. |
Pretreatment may include a sand or grit channel or chamber, where the velocity of the incoming sewage is adjusted to allow the settlement of sand, grit, stones, and broken glass. These particles are removed because they may damage pumps and other equipment. For small sanitary sewer systems, the grit chambers may not be necessary, but grit removal is desirable at larger plants.<ref name="EPA Primer" /> Grit chambers come in 3 types: horizontal grit chambers, aerated grit chambers and vortex grit chambers. |
||
====Flow equalization==== |
====Flow equalization==== |
||
[[Clarifier]]s and mechanized secondary treatment are more efficient under uniform flow conditions. [[Equalizing basin|Equalization basins]] may be used for temporary storage of diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks. Basins provide a place to temporarily hold incoming sewage during plant maintenance and a means of diluting and distributing batch discharges of toxic or high-strength waste which might otherwise inhibit biological secondary treatment (including portable toilet waste, vehicle holding tanks, and septic tank pumpers). Flow equalization basins require variable discharge control, typically include provisions for bypass and cleaning, and may also include aerators. Cleaning may be easier if the basin is downstream of screening and grit removal.<ref>Roy F. Weston, Inc. (1971). ''Process Design Manual for Upgrading Existing Wastewater Treatment Plants.'' Washington, D.C.: EPA. Chapter 3.</ref> |
|||
====Fat and grease removal==== |
====Fat and grease removal==== |
||
In some larger plants, fat and Grease lubricant are removed by passing the sewage through a small tank where skimmers collect the fat floating on the surface. Air blowers in the base of the tank may also be used to help recover the fat as a froth. Many plants, however, use primary clarifiers with mechanical surface skimmers for fat and grease removal. |
In some larger plants, [[fat]] and [[Grease (lubricant)|grease]] are removed by passing the sewage through a small tank where skimmers collect the fat floating on the surface. Air blowers in the base of the tank may also be used to help recover the fat as a froth. Many plants, however, use primary clarifiers with mechanical surface skimmers for fat and grease removal. |
||
===Primary treatment=== |
===Primary treatment=== |
||
In the primary stage, sewage flows through large tanks, commonly called "pre-settling basins", "primary sedimentation tanks" or "primary |
In the primary [[sedimentation (water treatment)|sedimentation]] stage, sewage flows through large tanks, commonly called "pre-settling basins", "primary sedimentation tanks" or "primary [[clarifier]]s".<ref>Huber Company, Berching, Germany (2012). [http://www.huber.de/products/sedimentation-tanks.html "Sedimentation Tanks."]</ref> The tanks are used to settle sludge while grease and oils rise to the surface and are skimmed off. Primary settling tanks are usually equipped with mechanically driven scrapers that continually drive the collected sludge towards a hopper in the base of the tank where it is pumped to sludge treatment facilities.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|9–11}} Grease and oil from the floating material can sometimes be recovered for [[saponification]]. |
||
===Secondary treatment=== |
|||
'''Secondary treatment''' is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage which are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent. The majority of municipal plants treat the settled sewage liquor using aerobic biological processes. To be effective, the require both oxygen and food to live. The bacteria and protozoa consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants e.g. sugar, fats, organic short-chain carbon molecules, and bind much of the less soluble fractions into flocculation. Secondary treatment systems are classified as ''fixed-film'' or ''suspended-growth'' systems. |
|||
*'''Fixed-film''' or '''attached growth''' systems include trickling filters, biotowers, and where the biomass grows on media and the sewage passes over its surface. |
|||
*'''Suspended-growth''' systems include activated sludge,where the biomass is mixed with the sewage and can be operated in a smaller space than trickling filters that treat the same amount of water. However, fixed-film systems are more able to cope with drastic changes in the amount of biological material and can provide higher removal rates for organic material and suspended solids than suspended growth systems. |
|||
===Secondary treatment=== |
|||
Roughing filters are intended to treat particularly strong or variable organic loads, typically industrial, to allow them to then be treated by conventional secondary treatment processes. Characteristics include filters filled with media to which wastewater is applied. They are designed to allow high hydraulic loading and a high level of aeration. On larger installations, air is forced through the media using blowers. The resultant wastewater is usually within the normal range for conventional treatment processes. |
|||
'''Secondary treatment''' is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage which are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent. The majority of municipal plants treat the settled sewage liquor using aerobic biological processes. To be effective, the [[biota (ecology)|biota]] require both [[oxygen]] and food to live. The [[bacteria]] and [[protozoa]] consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants (e.g. [[sugar]]s, fats, organic short-chain [[carbon]] molecules, etc.) and bind much of the less soluble fractions into [[flocculation|floc]]. Secondary treatment systems are classified as ''fixed-film'' or ''suspended-growth'' systems. |
|||
*'''Fixed-film''' or '''attached growth''' systems include [[trickling filter]]s, biotowers, and [[rotating biological contactor]]s, where the biomass grows on media and the sewage passes over its surface.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|11–13}} The fixed-film principle has further developed into Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors ([http://www.waterworld.com/_search?q=mbbr&x=0&y=0 MBBR]), and Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge ([http://www.waterworld.com/_search?q=mbbr&x=0&y=0 IFAS]) processes. An MBBR system typically requires smaller footprint than suspended-growth systems.<ref>{{Wayback |date=20101026171954 |url=http://bv.com/Downloads/Resources/Brochures/rsrc_WTR_IFASMBBR.pdf |title=Black & Veatch, Inc. leaflet }}.</ref> |
|||
*'''Suspended-growth''' systems include [[activated sludge]], where the biomass is mixed with the sewage and can be operated in a smaller space than trickling filters that treat the same amount of water. However, fixed-film systems are more able to cope with drastic changes in the amount of biological material and can provide higher removal rates for organic material and suspended solids than suspended growth systems.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|11–13}} |
|||
[[Roughing filter]]s are intended to treat particularly strong or variable organic loads, typically industrial, to allow them to then be treated by conventional secondary treatment processes. Characteristics include filters filled with media to which wastewater is applied. They are designed to allow high hydraulic loading and a high level of aeration. On larger installations, air is forced through the media using blowers. The resultant wastewater is usually within the normal range for conventional treatment processes. |
|||
[[File:Activated Sludge 1.svg|thumb|right|318px|A generalized schematic of an activated sludge process.]] |
|||
A filter removes a small percentage of the suspended organic matter, while the majority of the organic matter undergoes a change of character, only due to the biological oxidation and nitrification taking place in the filter. With this aerobic oxidation and nitrification, the organic solids are converted into coagulated suspended mass, which is heavier and bulkier, and can settle to the bottom of a tank. The effluent of the filter is therefore passed through a sedimentation tank, called a secondary clarifier, secondary settling tank or humus tank. |
A filter removes a small percentage of the suspended organic matter, while the majority of the organic matter undergoes a change of character, only due to the biological oxidation and nitrification taking place in the filter. With this aerobic oxidation and nitrification, the organic solids are converted into coagulated suspended mass, which is heavier and bulkier, and can settle to the bottom of a tank. The effluent of the filter is therefore passed through a sedimentation tank, called a secondary clarifier, secondary settling tank or humus tank. |
||
====Activated sludge==== |
====Activated sludge==== |
||
{{main|Activated sludge}} |
|||
In general, activated sludge plants encompass a variety of mechanisms and processes that use dissolved oxygen to promote the growth of biological floc that substantially removes organic material. |
In general, activated sludge plants encompass a variety of mechanisms and processes that use dissolved [[oxygen]] to promote the growth of biological floc that substantially removes organic material.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|12–13}} |
||
Biological floc, as mentioned above, is an ecosystem of living biota that subsists on nutrients from the inflowing primary settling tank or clarifier effluent. These mostly carbonaceous dissolved solids undergo aeration to be broken down and biologically oxidized or converted to carbon dioxide. Likewise, nitrogenous dissolved solids amino acids, ammonia, etc. are also oxidized by the floc to |
Biological floc, as mentioned above, is an ecosystem of living biota that subsists on nutrients from the inflowing primary settling tank (or clarifier) effluent. These mostly carbonaceous dissolved solids undergo aeration to be broken down and biologically oxidized or converted to carbon dioxide. Likewise, nitrogenous dissolved solids (amino acids, [[ammonia]], etc.) are also oxidized (=eaten) by the floc to [[nitrite]]s, [[nitrate]]s, and, in some processes, to [[nitrogen]] gas through [[denitrification]]. |
||
While denitrification is encouraged in some treatment processes, in many suspended aeration plants denitrification will impair the settling of the floc and lead to poor quality effluent. |
While denitrification is encouraged in some treatment processes, in many suspended aeration plants denitrification will impair the settling of the floc and lead to poor quality effluent. |
||
In either case, the settled floc is both recycled to the inflowing primary effluent to regrow, or is partially 'wasted' to solids dewatering, or digesting, and then dewatering. |
In either case, the settled floc is both recycled to the inflowing primary effluent to regrow, or is partially 'wasted' (or diverted) to solids dewatering, or digesting, and then dewatering. |
||
Interestingly, like most living creatures, activated sludge biota can get sick. This many times takes the form of the floating brown foam, Nocardia. While this so-called 'sewage fungus' is the best known, there are many different fungi and protists that can overpopulate a the floc and cause process upsets. Additionally, certain incoming chemical species, such as a heavy pesticide, a heavy metal load, or extreme pH, can kill the biota of an activated sludge reactor ecosystem. Such problems are tested for, and if caught in time, can be neutralized. |
|||
Interestingly, like most living creatures, activated sludge biota can get sick. This many times takes the form of the floating brown foam, Nocardia. While this so-called 'sewage fungus' (it isn't really a fungus) is the best known, there are many different fungi and protists that can overpopulate a the floc and cause process upsets. Additionally, certain incoming chemical species, such as a heavy pesticide, a heavy metal (e.g.: plating company effluent) load, or extreme pH, can kill the biota of an activated sludge reactor ecosystem. Such problems are tested for, and if caught in time, can be neutralized. |
|||
[[File:Surface-Aerated Basin.png|thumb|right|318px|A typical surface-aerated basin (using motor-driven floating aerators)]] |
|||
====Aerobic granular sludge==== |
====Aerobic granular sludge==== |
||
{{Main|Aerobic granulation}} |
|||
Activated sludge systems can be transformed into aerobic granular sludge systems ([[aerobic granulation]]) which enhance the benefits of activated sludge, like increased biomass retention due to high sludge settlability. |
|||
====Surface-aerated basins (lagoons)==== |
|||
Activated sludge systems can be transformed into aerobic granular sludge systems which enhance the benefits of activated sludge, like increased biomass retention due to high sludge settlability. |
|||
Many small municipal sewage systems in the United States (1 million gal./day or less) use aerated lagoons.<ref>Maine Department of Environmental Protection. Augusta, ME. [http://www.lagoonsonline.com "Aerated Lagoons – Wastewater Treatment."] Maine Lagoon Systems Task Force. Accessed 2010-07-11.</ref> |
|||
Most biological oxidation processes for treating industrial wastewaters have in common the use of oxygen (or air) and microbial action. Surface-aerated basins achieve 80 to 90 percent removal of BOD with retention times of 1 to 10 days.<ref name=Basin>{{cite journal|author=Beychok, M.R.|year=1971|month=|title=Performance of surface-aerated basins|journal=Chemical Engineering Progress Symposium Series|volume=67|issue=107|pages=322–339}} [http://md1.csa.com/partners/viewrecord.php?requester=gs&collection=ENV&recid=7112203&q=&uid=788301038&setcookie=yes Available at CSA Illumina website]</ref> The basins may range in depth from 1.5 to 5.0 metres and use motor-driven aerators floating on the surface of the wastewater.<ref name=Basin/> |
|||
In an aerated basin system, the aerators provide two functions: they transfer air into the basins required by the biological oxidation reactions, and they provide the mixing required for dispersing the air and for contacting the reactants (that is, oxygen, wastewater and microbes). Typically, the floating surface aerators are rated to deliver the amount of air equivalent to 1.8 to 2.7 kg [[Oxygen|O<sub>2</sub>]]/[[watt-hour|kW·h]]. However, they do not provide as good mixing as is normally achieved in activated sludge systems and therefore aerated basins do not achieve the same performance level as activated sludge units.<ref name=Basin/> |
|||
Biological oxidation processes are sensitive to temperature and, between 0 °C and 40 °C, the rate of biological reactions increase with temperature. Most surface aerated vessels operate at between 4 °C and 32 °C.<ref name="Basin"/> |
|||
. |
|||
====Filter beds (oxidizing beds)==== |
|||
{{main|Trickling filter}} |
|||
In older plants and those receiving variable loadings, [[trickling filter]] beds are used where the settled sewage liquor is spread onto the surface of a bed made up of [[coke (fuel)|coke]] (carbonized coal), [[limestone]] chips or specially fabricated plastic media. Such media must have large surface areas to support the biofilms that form. The liquor is typically distributed through perforated spray arms. The distributed liquor trickles through the bed and is collected in drains at the base. These drains also provide a source of air which percolates up through the bed, keeping it aerobic. Biological films of bacteria, protozoa and fungi form on the media’s surfaces and eat or otherwise reduce the organic content.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|12}} This [[biofilm]] is often grazed by insect larvae, snails, and worms which help maintain an optimal thickness. Overloading of beds increases the thickness of the film leading to clogging of the filter media and ponding on the surface. Recent advances in media and process micro-biology design overcome many issues with trickling filter designs. |
|||
====Constructed wetlands==== |
|||
[[Constructed wetland]]s (can either be surface flow or subsurface flow, horizontal or vertical flow), include engineered [[reedbed]]s and belong to the family of phytorestoration and ecotechnologies; they provide a high degree of biological improvement and depending on design, act as a primary, secondary and sometimes tertiary treatment, also see [[phytoremediation]]. One example is a small reedbed used to clean the drainage from the [[elephant]]s' enclosure at [[Chester Zoo]] in [[England]]; numerous CWs are used to recycle the water of the city of Honfleur in France and numerous other towns in Europe, the US, Asia and Australia. They are known to be highly productive systems as they copy natural wetlands, called the "kidneys of the earth" for their fundamental recycling capacity of the hydrological cycle in the biosphere. Robust and reliable, their treatment capacities improve as time go by, at the opposite of conventional treatment plants whose machinery age with time. They are being increasingly used, although adequate and experienced design are more fundamental than for other systems and space limitation may impede their use. |
|||
====Soil bio-technology==== |
====Soil bio-technology==== |
||
A new process called soil bio-technology (SBT) developed at |
A new process called soil bio-technology (SBT) developed at [[Indian Institute of Technology Bombay|IIT Bombay]] has shown tremendous improvements in process efficiency enabling total water reuse, due to extremely low operating power requirements of less than 50 joules per kg of treated water.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kadam |first1=A. |last2=Ozaa |first2=G. |last3=Nemadea |first3=P. |last4=Duttaa |first4=S. |last5=Shankar |first5=H. |year=2008 |title=Municipal wastewater treatment using novel constructed soil filter system |journal=Chemosphere |publisher=Elsevier |pmid=18207216 |volume=71 |issue=5 |pages=975–981 |url= |doi=10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.048}}</ref> Typically SBT systems can achieve [[chemical oxygen demand]] (COD) levels less than 10 mg/L from sewage input of COD 400 mg/L.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Nemade |first1=P.D. |last2=Kadam |first2=A.M. |last3=Shankar |first3=H.S. |year=2009 |title=Wastewater renovation using constructed soil filter (CSF): A novel approach |journal=Journal of Hazardous Materials |publisher=Elsevier |pmid=19501460 |volume=170 |issue=2–3 |pages=657–665 |url=http://www.che.iitb.ac.in/online/bibliography/wastewater-renovation-using-constructed-soil-filter-csf-a-novel-approach |doi=10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.015}}</ref> SBT plants exhibit high reductions in COD values and bacterial counts as a result of the very high microbial densities available in the media. Unlike conventional treatment plants, SBT plants produce insignificant amounts of sludge, precluding the need for sludge disposal areas that are required by other technologies.<ref>A documentary video detailing a 3 MLD SBT plant deployed at the [[Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai|Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation]] for [[Mumbai]] city can be seen at {{YouTube|dKWVtZ81mY0|"SBT at BMC Mumbai"}}</ref> |
||
In the Indian context, conventional sewage treatment plants fall into systemic disrepair due to 1) high operating costs, 2) equipment corrosion due to methanogenesis and hydrogen sulphide, 3) non-reusability of treated water due to high COD (>30 mg/L) and high [[fecal coliform]] (>3000 NFU) counts, 4) lack of skilled operating personnel and 5) equipment replacement issues. Examples of such systemic failures has been documented by [[Sankat Mochan Foundation]] at the [[Ganges]] basin after a massive cleanup effort by the Indian government in 1986 by setting up sewage treatment plants under the [[Ganga Action Plan]] failed to improve river water quality. |
|||
====Biological aerated filters==== |
====Biological aerated filters==== |
||
Biological Aerated Filter (BAF) or Biofilters combine filtration with biological carbon reduction, nitrification or denitrification. BAF usually includes a reactor filled with a |
Biological Aerated (or Anoxic) Filter (BAF) or Biofilters combine filtration with biological carbon reduction, [[nitrification]] or denitrification. BAF usually includes a reactor filled with a [[filter (water)|filter]] media. The media is either in suspension or supported by a gravel layer at the foot of the filter. The dual purpose of this media is to support highly active biomass that is attached to it and to filter suspended solids. Carbon reduction and ammonia conversion occurs in aerobic mode and sometime achieved in a single reactor while nitrate conversion occurs in [[hypoxia (environmental)|anoxic]] mode. BAF is operated either in upflow or downflow configuration depending on design specified by manufacturer. |
||
[[File:Rotating Biological Contactor.png|thumb|right|373 px|Schematic of a typical rotating biological contactor (RBC). The treated effluent clarifier/settler is not included in the diagram.]] |
|||
====Rotating biological contactors==== |
====Rotating biological contactors==== |
||
{{main|Rotating biological contactor}} |
|||
Rotating biological contactors (RBCs) are mechanical secondary treatment systems, which are robust and capable of withstanding surges in organic load. RBCs were first installed in [[Germany]] in 1960 and have since been developed and refined into a reliable operating unit. The rotating disks support the growth of bacteria and micro-organisms present in the sewage, which break down and stabilize organic pollutants. To be successful, micro-organisms need both oxygen to live and food to grow. Oxygen is obtained from the atmosphere as the disks rotate. As the micro-organisms grow, they build up on the media until they are sloughed off due to shear forces provided by the rotating discs in the sewage. Effluent from the RBC is then passed through final clarifiers where the micro-organisms in suspension settle as a sludge. The sludge is withdrawn from the clarifier for further treatment. |
|||
A functionally similar biological filtering system has become popular as part of home [[aquarium]] filtration and purification. The aquarium water is drawn up out of the tank and then cascaded over a freely spinning corrugated fiber-mesh wheel before passing through a media filter and back into the aquarium. The spinning mesh wheel develops a [[biofilm]] coating of microorganisms that feed on the suspended wastes in the aquarium water and are also exposed to the atmosphere as the wheel rotates. This is especially good at removing waste [[urea]] and [[ammonia]] urinated into the aquarium water by the fish and other animals. |
|||
Rotating biological contactors (RBCs) are mechanical secondary treatment systems, which are robust and capable of withstanding surges in organic load. RBCs were first installed in Germany.in 1960 and have since been developed and refined into a reliable operating unit. The rotating disks support the growth of bacteria and micro-organisms present in the sewage, which break down and stabilize organic pollutants. To be successful, micro-organisms need both oxygen to live and food to grow. Oxygen is obtained from the atmosphere as the disks rotate. As the micro-organisms grow, they build up on the media until they are sloughed off due to shear forces provided by the rotating discs in the sewage. Effluent from the RBC is then passed through final clarifiers where the micro-organisms in suspension settle as a sludge. The sludge is withdrawn from the clarifier for further treatment. |
|||
A functionally similar biological filtering system has become popular as part of home aquarium filtration and purification. The aquarium water is drawn up out of the tank and then cascaded over a freely spinning corrugated fiber-mesh wheel before passing through a media filter and back into the aquarium. The spinning mesh wheel develops a biofilm coating of microorganisms that feed on the suspended wastes in the aquarium water and are also exposed to the atmosphere as the wheel rotates. This is especially good at removing waste urea and ammonia urinated into the aquarium water by the fish and other animals. |
|||
====Membrane bioreactors==== |
====Membrane bioreactors==== |
||
Membrane |
[[Membrane bioreactor]]s (MBR) combine activated sludge treatment with a [[Membrane technology|membrane]] liquid-solid separation process. The membrane component uses low pressure [[microfiltration]] or [[ultrafiltration]] membranes and eliminates the need for clarification and tertiary filtration. The membranes are typically immersed in the aeration tank; however, some applications utilize a separate membrane tank. One of the key benefits of an MBR system is that it effectively overcomes the limitations associated with poor settling of sludge in conventional [[activated sludge]] (CAS) processes. The technology permits bioreactor operation with considerably higher mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration than CAS systems, which are limited by sludge settling. The process is typically operated at MLSS in the range of 8,000–12,000 mg/L, while CAS are operated in the range of 2,000–3,000 mg/L. The elevated biomass concentration in the MBR process allows for very effective removal of both soluble and particulate biodegradable materials at higher loading rates. Thus increased sludge retention times, usually exceeding 15 days, ensure complete nitrification even in extremely cold weather. |
||
The cost of building and operating an MBR is often higher than conventional methods of sewage treatment. Membrane filters can be blinded with grease or abraded by suspended grit and lack a clarifier's flexibility to pass peak flows. The technology has become increasingly popular for reliably pretreated waste streams and has gained wider acceptance where infiltration and inflow have been controlled, however, and the life-cycle costs have been steadily decreasing. The small footprint of MBR systems, and the high quality effluent produced, make them particularly useful for water reuse applications. |
The cost of building and operating an MBR is often higher than conventional methods of sewage treatment. Membrane filters can be blinded with grease or abraded by suspended grit and lack a clarifier's flexibility to pass peak flows. The technology has become increasingly popular for reliably pretreated waste streams and has gained wider acceptance where infiltration and inflow have been controlled, however, and the life-cycle costs have been steadily decreasing. The small footprint of MBR systems, and the high quality effluent produced, make them particularly useful for water reuse applications.<ref>EPA. Washington, DC (2007). [http://water.epa.gov/scitech/wastetech/upload/2008_01_23_mtb_etfs_membrane-bioreactors.pdf "Membrane Bioreactors."] Wastewater Management Fact Sheet.</ref> |
||
====Secondary sedimentation==== |
====Secondary sedimentation==== |
||
[[File:Secondary sedimentation tank 1 w.JPG|thumb|Secondary [[Sedimentation (water treatment)|sedimentation tank]] at a rural treatment plant.]] |
|||
The final step in the secondary treatment stage is to settle out the biological floc or filter material through a secondary clarifier and to produce sewage water containing low levels of organic material and suspended matter. |
The final step in the secondary treatment stage is to settle out the biological floc or filter material through a secondary clarifier and to produce sewage water containing low levels of organic material and suspended matter. |
||
| Line 94: | Line 149: | ||
====Filtration==== |
====Filtration==== |
||
Sand filtration removes much of the residual suspended matter. |
[[Sand filter|Sand filtration]] removes much of the residual suspended matter.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|22–23}} Filtration over [[activated carbon]], also called ''carbon adsorption,'' removes residual [[toxin]]s.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|19}} |
||
====Lagooning==== |
====Lagooning==== |
||
[[File:Everett sewage.jpg|thumb|right|A sewage treatment plant and lagoon in [[Everett, Washington]], [[United States]].]] |
|||
Lagooning provides settlement and further biological improvement through storage in large man-made ponds or lagoons. These lagoons are highly aerobic and colonization by native [[macrophyte]]s, especially reeds, is often encouraged. Small filter feeding [[invertebrate]]s such as ''[[Daphnia]]'' and species of ''[[Rotifera]]'' greatly assist in treatment by removing fine particulates. |
|||
Lagooning provides settlement and further biological improvement through storage in large man-made ponds or lagoons. These lagoons are highly aerobic and colonization by native macrophytes, especially reeds, is often encouraged. |
|||
====Nutrient removal==== |
====Nutrient removal==== |
||
Wastewater may contain high levels of the nutrients nitrogen and phosphorus. Excessive release to the environment can lead to a build up of nutrients, called eutrophication,which can in turn encourage the overgrowth of weeds, algae,and cyanobacteria. This may cause an algal |
Wastewater may contain high levels of the nutrients [[nitrogen]] and [[phosphorus]]. Excessive release to the environment can lead to a build up of nutrients, called [[eutrophication]], which can in turn encourage the overgrowth of weeds, [[algae]], and [[cyanobacteria]] (blue-green algae). This may cause an [[algal bloom]], a rapid growth in the population of algae. The algae numbers are unsustainable and eventually most of them die. The decomposition of the algae by bacteria uses up so much of the oxygen in the water that most or all of the animals die, which creates more organic matter for the bacteria to decompose. In addition to causing deoxygenation, some algal species produce toxins that contaminate [[drinking water]] supplies. Different treatment processes are required to remove nitrogen and phosphorus. |
||
=====Nitrogen removal===== |
=====Nitrogen removal===== |
||
The removal of nitrogen is effected through the biological |
The removal of nitrogen is effected through the biological [[redox|oxidation]] of nitrogen from [[ammonia]] to [[nitrate]] ([[nitrification]]), followed by [[denitrification]], the reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas. Nitrogen gas is released to the atmosphere and thus removed from the water. |
||
Nitrification itself is a two-step aerobic process, each step facilitated by a different type of bacteria. The oxidation of ammonia to nitrite is most often facilitated by ''Nitrosomonas'' spp. group). Nitrite oxidation to nitrate though traditionally believed to be facilitated by ''Nitrobacter'' is known to be facilitated in the environment almost exclusively by ''Nitrospira'' spp. |
Nitrification itself is a two-step aerobic process, each step facilitated by a different type of bacteria. The oxidation of ammonia (NH<sub>3</sub>) to nitrite (NO<sub>2</sub><sup>−</sup>) is most often facilitated by ''Nitrosomonas'' spp. ("nitroso" referring to the formation of a [[nitroso]] functional group). Nitrite oxidation to nitrate (NO<sub>3</sub><sup>−</sup>), though traditionally believed to be facilitated by ''Nitrobacter'' spp. (nitro referring the formation of a [[nitro functional group]]), is now known to be facilitated in the environment almost exclusively by ''Nitrospira'' spp. |
||
Denitrification requires anoxic conditions to encourage the appropriate biological communities to form. It is facilitated by a wide diversity of bacteria. Sand filters, lagooning and reed beds can all be used to reduce nitrogen, but the activated sludge process (if designed well) can do the job the most easily. Since denitrification is the reduction of nitrate to dinitrogen gas, an electron donor is needed. This can be, depending on the wastewater, organic matter from faeces, sulfide, or an added donor like methanol. The sludge in the anoxic tanks must be mixed well mixture of recirculated mixed liquor, return activated sludge RAS, and raw influent e.g. by using submersible |
Denitrification requires anoxic conditions to encourage the appropriate biological communities to form. It is facilitated by a wide diversity of bacteria. Sand filters, lagooning and reed beds can all be used to reduce nitrogen, but the activated sludge process (if designed well) can do the job the most easily.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|17–18}} Since denitrification is the reduction of nitrate to dinitrogen gas, an [[electron donor]] is needed. This can be, depending on the wastewater, organic matter (from faeces), [[sulfide]], or an added donor like [[methanol]]. The sludge in the anoxic tanks (denitrification tanks) must be mixed well (mixture of recirculated mixed liquor, return activated sludge [RAS], and raw influent) e.g. by using [[submersible mixer]]s in order to achieve the desired denitrification. |
||
Sometimes the conversion of toxic ammonia to nitrate alone is referred to as tertiary treatment. |
Sometimes the conversion of toxic ammonia to nitrate alone is referred to as tertiary treatment. |
||
Many sewage treatment plants use centrifugal |
Many sewage treatment plants use [[centrifugal pump]]s to transfer the nitrified mixed liquor from the aeration zone to the anoxic zone for denitrification. These pumps are often referred to as ''Internal Mixed Liquor Recycle'' (IMLR) pumps. |
||
The bacteria Brocadia anammoxidans, is being researched for it's potential in sewage treatment. It can remove nitrogen from waste water. |
The bacteria [[Brocadia anammoxidans]], is being researched for it's potential in sewage treatment. It can remove nitrogen from waste water.<ref>B. Kartal, G.J. Kuenen and M.C.M van Loosdrecht Sewage Treatment with Anammox, Science, 2010, vol 328 p 702-3</ref> In addition the bacteria can perform the [[anaerobic oxidation of ammonium]] and can produce the rocket fuel [[hydrazine]] from waste water.<ref>http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2005/11/1109_051109_rocketfuel.html</ref><ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3264106/</ref> |
||
=====Phosphorus removal===== |
=====Phosphorus removal===== |
||
Each person excretes between 200 and 1000 grams of phosphorus annually. Studies of United States sewage in the late 1960s estimated mean per capita contributions of 500 grams in urine and feces, 1000 grams in synthetic detergents, and lesser variable amounts used as corrosion and scale control chemicals in water supplies. Source control via alternative detergent formulations has subsequently reduced the largest contribution, but the content of urine and feces will remain unchanged. Phosphorus removal is important as it is a limiting nutrient for algae growth in many fresh water systems. (For a description of the negative effects of algae, ''see'' Sewage treatment Nutrient removal. It is also particularly important for water reuse systems where high phosphorus concentrations may lead to fouling of downstream equipment such as reverse osmosis. |
Each person excretes between 200 and 1000 grams of phosphorus annually. Studies of United States sewage in the late 1960s estimated mean per capita contributions of 500 grams in urine and feces, 1000 grams in synthetic detergents, and lesser variable amounts used as corrosion and scale control chemicals in water supplies.<ref>Black & Veatch, Inc. (1971). [http://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=20007TYZ.txt ''Process Design Manual for Phosphorus Removal.''] Washington, D.C.: EPA. p. 2-1.</ref> Source control via alternative detergent formulations has subsequently reduced the largest contribution, but the content of urine and feces will remain unchanged. Phosphorus removal is important as it is a limiting nutrient for algae growth in many fresh water systems. (For a description of the negative effects of algae, ''see'' [[Sewage treatment#Nutrient removal|Nutrient removal]]). It is also particularly important for water reuse systems where high phosphorus concentrations may lead to fouling of downstream equipment such as [[reverse osmosis]]. |
||
Phosphorus can be removed biologically in a process called enhanced biological phosphorus removal.In this process, specific bacteria, called polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs), are selectively enriched and accumulate large quantities of phosphorus within their cells (up to 20 percent of their mass). When the biomass enriched in these bacteria is separated from the treated water, these biosolids have a high [[fertilizer]] value. |
|||
Phosphorus can be removed biologically in a process called [[enhanced biological phosphorus removal]]. In this process, specific bacteria, called [[polyphosphate-accumulating organisms]] (PAOs), are selectively enriched and accumulate large quantities of phosphorus within their cells (up to 20 percent of their mass). When the biomass enriched in these bacteria is separated from the treated water, these biosolids have a high [[fertilizer]] value. |
|||
Phosphorus removal can also be achieved by chemical [[Precipitation (chemistry)|precipitation]], usually with [[salt]]s of [[iron]] (e.g. [[ferric chloride]]), [[aluminum]] (e.g. [[alum]]), or lime.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|18}} This may lead to excessive sludge production as hydroxides precipitates and the added chemicals can be expensive. Chemical phosphorus removal requires significantly smaller equipment footprint than biological removal, is easier to operate and is often more reliable than biological phosphorus removal.{{citation needed|date=May 2013}} Another method for phosphorus removal is to use granular [[Laterite#Waste water treatment|laterite]]. |
|||
Once removed, phosphorus, in the form of a phosphate-rich sludge, may be stored in a land fill or resold for use in fertilizer. |
Once removed, phosphorus, in the form of a phosphate-rich sludge, may be stored in a land fill or resold for use in fertilizer. |
||
===Disinfection=== |
===Disinfection=== |
||
The purpose of disinfection in the treatment of waste water is to substantially reduce the number of |
The purpose of [[disinfection]] in the treatment of waste water is to substantially reduce the number of [[microorganism]]s in the water to be discharged back into the environment for the later use of drinking, bathing, irrigation, etc. The effectiveness of disinfection depends on the quality of the water being treated (e.g., cloudiness, pH, etc.), the type of disinfection being used, the disinfectant dosage (concentration and time), and other environmental variables. Cloudy water will be treated less successfully, since solid matter can shield organisms, especially from [[ultraviolet light]] or if contact times are low. Generally, short contact times, low doses and high flows all militate against effective disinfection. Common methods of disinfection include [[ozone]], [[chlorine]], ultraviolet light, or sodium hypochlorite.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|16}} [[Chloramine]], which is used for drinking water, is not used in the treatment of waste water because of its persistence. After multiple steps of disinfection, the treated water is ready to be released back into the water cycle by means of the nearest body of water or agriculture. Afterwards, the water can be transferred to reserves for everyday human uses. |
||
Water chlorination|Chlorination remains the most common form of waste water disinfection in North America due to its low cost and long-term history of effectiveness. One disadvantage is that chlorination of residual organic material can generate chlorinated-organic compounds that may be[carcinogenic or harmful to the environment. Residual chlorine or chloramines may also be capable of chlorinating organic material in the natural aquatic environment. Further, because residual chlorine is toxic to aquatic species, the treated effluent must also be chemically dechlorinated, adding to the complexity and cost of treatment. |
[[Water chlorination|Chlorination]] remains the most common form of waste water disinfection in [[North America]] due to its low cost and long-term history of effectiveness. One disadvantage is that chlorination of residual organic material can generate chlorinated-organic compounds that may be [[carcinogenic]] or harmful to the environment. Residual chlorine or chloramines may also be capable of chlorinating organic material in the natural aquatic environment. Further, because residual chlorine is toxic to aquatic species, the treated effluent must also be chemically dechlorinated, adding to the complexity and cost of treatment. |
||
Ultraviolet (UV) light can be used instead of chlorine, iodine, or other chemicals. Because no chemicals are used, the treated water has no adverse effect on organisms that later consume it, as may be the case with other methods. UV radiation causes damage to the structure of bacteria, virus]]es, and making them incapable of reproduction. The key disadvantages of UV disinfection are the need for frequent lamp maintenance and replacement and the need for a highly treated effluent to ensure that the target microorganisms are not shielded from the UV radiation (i.e., any solids present in the treated effluent may protect microorganisms from the UV light). In the United Kingdom, UV light is becoming the most common means of disinfection because of the concerns about the impacts of chlorine in chlorinating residual organics in the wastewater and in chlorinating organics in the receiving water. Some sewage treatment systems in Canada and the US also use UV light for their effluent water disinfection. |
[[Ultraviolet]] (UV) light can be used instead of chlorine, iodine, or other chemicals. Because no chemicals are used, the treated water has no adverse effect on organisms that later consume it, as may be the case with other methods. UV radiation causes damage to the [[gene]]tic structure of bacteria, [[virus]]es, and other [[pathogen]]s, making them incapable of reproduction. The key disadvantages of UV disinfection are the need for frequent lamp maintenance and replacement and the need for a highly treated effluent to ensure that the target microorganisms are not shielded from the UV radiation (i.e., any solids present in the treated effluent may protect microorganisms from the UV light). In the United Kingdom, UV light is becoming the most common means of disinfection because of the concerns about the impacts of chlorine in chlorinating residual organics in the wastewater and in chlorinating organics in the receiving water. Some sewage treatment systems in Canada and the US also use UV light for their effluent water disinfection.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Das |first1=Tapas K. |date=August 2001 |title=Ultraviolet disinfection application to a wastewater treatment plant |journal=Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy |publisher=Springer Berlin/Heidelberg |volume=3 |issue=2 |pages=69–80 |url= |doi=10.1007/S100980100108}}</ref><ref>Florida Department of Environmental Protection. Talahassee, FL. [http://www.dep.state.fl.us/water/wastewater/dom/domuv.htm "Ultraviolet Disinfection for Domestic Waste water."] 2010-03-17.</ref> |
||
Ozone oxygen is generated by passing oxygen potential resulting in a third oxygen atom becoming attached and forming oxygen. Ozone is very unstable and reactive and oxidizes most organic material it comes in contact with, thereby destroying many pathogenic microorganisms. Ozone is considered to be safer than chlorine because, unlike chlorine which has to be stored on site (highly poisonous in the event of an accidental release), ozone is generated onsite as needed. Ozonation also produces fewer disinfection by-products than chlorination. A disadvantage of ozone disinfection is the high cost of the ozone generation equipment and the requirements for special operators. |
[[Ozone]] ({{oxygen}}<sub>3</sub>) is generated by passing oxygen ({{oxygen}}<sub>2</sub>) through a high [[voltage]] potential resulting in a third oxygen [[atom]] becoming attached and forming {{oxygen}}<sub>3</sub>. Ozone is very unstable and reactive and oxidizes most organic material it comes in contact with, thereby destroying many pathogenic microorganisms. Ozone is considered to be safer than chlorine because, unlike chlorine which has to be stored on site (highly poisonous in the event of an accidental release), ozone is generated onsite as needed. Ozonation also produces fewer disinfection by-products than chlorination. A disadvantage of ozone disinfection is the high cost of the ozone generation equipment and the requirements for special operators. |
||
===Odor control=== |
===Odor control=== |
||
Odors emitted by sewage treatment are typically an indication of an anaerobic or "septic" condition. Early stages of processing will tend to produce foul smelling gases, with [[hydrogen sulfide]] being most common in generating complaints. Large process plants in urban areas will often treat the odors with carbon reactors, a contact media with bio-slimes, small doses of chlorine or circulating fluids to biologically capture and metabolize the noxious gases. Other methods of odor control exist, including addition of iron salts, hydrogen peroxide, calcium nitrate etc. to manage sulfide levels. |
Odors emitted by sewage treatment are typically an indication of an anaerobic or "septic" condition.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Harshman |first1=Vaughan |last2=Barnette |first2=Tony |date=2000-12-28|title=Wastewater Odor Control: An Evaluation of Technologies |journal=Water Engineering & Management |volume= |issue= |pages= |url=http://www.wwdmag.com/Wastewater-Odor-Control-An-Evaluation-of-Technologies-article1698 |issn=0273-2238}}</ref> Early stages of processing will tend to produce foul smelling gases, with [[hydrogen sulfide]] being most common in generating complaints. Large process plants in urban areas will often treat the odors with carbon reactors, a contact media with bio-slimes, small doses of [[chlorine]], or circulating fluids to biologically capture and metabolize the noxious gases.<ref>Walker, James D. and Welles Products Corporation (1976).[http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4421534.html "Tower for removing odors from gases."] U.S. Patent No. 4421534.</ref> Other methods of odor control exist, including addition of iron salts, [[hydrogen peroxide]], [[calcium nitrate]], etc. to manage [[hydrogen sulfide]] levels. |
||
High-density solids |
[[High-density solids pump]]s are suitable for reducing odors by conveying sludge through hermetic closed pipework. |
||
==Package plants and batch reactors== |
|||
To use less space, treat difficult waste and intermittent flows, a number of designs of hybrid treatment plants have been produced. Such plants often combine at least two stages of the three main treatment stages into one combined stage. In the UK, where a large number of wastewater treatment plants serve small populations, package plants are a viable alternative to building a large structure for each process stage. In the US, package plants are typically used in rural areas, highway rest stops and trailer parks.<ref name="EPA Package">EPA. Washington, DC (2000). [http://www.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/package_plant.pdf "Package Plants."] Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet. Document no. EPA 832-F-00-016.</ref> |
|||
One type of system that combines secondary treatment and settlement is the [[cyclic activated sludge]] (CASSBR). Typically, [[activated sludge]] is mixed with raw incoming sewage, and then mixed and aerated. The settled sludge is run off and re-aerated before a proportion is returned to the headworks.<ref>EPA. Washington, DC (1999). [http://www.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/sbr_new.pdf "Sequencing Batch Reactors."] Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet. Document no. EPA 832-F-99-073.</ref> SBR plants are now being deployed in many parts of the world. |
|||
The disadvantage of the CASSBR process is that it requires a precise control of timing, mixing and aeration. This precision is typically achieved with computer controls linked to sensors. Such a complex, fragile system is unsuited to places where controls may be unreliable, poorly maintained, or where the power supply may be intermittent. [[Extended aeration]] package plants use separate basins for aeration and settling, and are somewhat larger than SBR plants with reduced timing sensitivity.<ref>{{cite book | author=Hammer, Mark J. | title=Water and Waste-Water Technology | year=1975 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons | pages=390–391 | isbn=0-471-34726-4}}</ref> |
|||
==Sludge tr{eatment and disposal== |
|||
Package plants may be referred to as ''high charged'' or ''low charged''. This refers to the way the biological load is processed. In high charged systems, the biological stage is presented with a high organic load and the combined floc and organic material is then oxygenated for a few hours before being charged again with a new load. In the low charged system the biological stage contains a low organic load and is combined with [[Flocculation|flocculate]] for longer times. |
|||
==Sludge treatment and disposal== |
|||
{{main|Sewage sludge treatment}} |
|||
The sludges accumulated in a wastewater treatment process must be treated and disposed of in a safe and effective manner. The purpose of digestion is to reduce the amount of [[organic matter]] and the number of disease-causing [[microorganism]]s present in the solids. The most common treatment options include [[anaerobic digestion]], [[aerobic digestion]], and [[composting]]. [[Incineration]] is also used, albeit to a much lesser degree.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|19–21}} |
|||
The sludges accumulated in a wastewater treatment process must be treated and disposed of in a safe and effective manner. The purpose of digestion is to reduce the amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting. Incineration is also used, albeit to a much lesser degree. |
|||
Sludge treatment depends on the amount of solids generated and other site-specific conditions. Composting is most often applied to small-scale plants with aerobic digestion for mid sized operations, and anaerobic digestion for the larger-scale operations. |
Sludge treatment depends on the amount of solids generated and other site-specific conditions. Composting is most often applied to small-scale plants with aerobic digestion for mid sized operations, and anaerobic digestion for the larger-scale operations. |
||
The sludge is sometimes passed through a so-called pre-thickener which de-waters the sludge. Types of pre-thickeners include centrifugal sludge thickeners |
The sludge is sometimes passed through a so-called pre-thickener which de-waters the sludge. Types of pre-thickeners include centrifugal sludge thickeners<ref>IPEC Consultants, Ltd., Burnaby, BC, Canada. [http://www.ipec.ca/products3.html?id=15# "IFT – Internally-fed – rotary thickener."] Accessed 2012-06-16.</ref> rotary drum sludge thickeners and belt filter presses.<ref>Mine-engineer.com, Long Beach, CA. [http://www.mine-engineer.com/mining/belt_fp.html "Belt Filter Press, How Does It Work?"] Accessed 2012-06-16.</ref><ref>GlobalSpec, Inc., East Greenbush, NY. [http://www.globalspec.com/learnmore/manufacturing_process_equipment/filtration_separation_products/dewatering_equipment "How to Select Dewatering Equipment."] Accessed 2012-06-12.</ref> |
||
===Anaerobic digestion=== |
===Anaerobic digestion=== |
||
{{main|Anaerobic digestion}} |
|||
Anaerobic digestion is a bacterial process that is carried out in the absence of oxygen. The process can either be ''[[thermophile|thermophilic]]'' digestion, in which sludge is fermentation (biochemistry)|fermented]] in tanks at a temperature of 55 °C, or ''|mesophilic'', at a temperature of around 36 °C. Though allowing shorter retention time (and thus smaller tanks), thermophilic digestion is more expensive in terms of energy consumption for heating the sludge. |
Anaerobic digestion is a bacterial process that is carried out in the absence of oxygen. The process can either be ''[[thermophile|thermophilic]]'' digestion, in which sludge is [[fermentation (biochemistry)|fermented]] in tanks at a temperature of 55 °C, or ''[[mesophile|mesophilic]]'', at a temperature of around 36 °C. Though allowing shorter retention time (and thus smaller tanks), thermophilic digestion is more expensive in terms of energy consumption for heating the sludge. |
||
Anaerobic digestion is the most common (mesophilic) treatment of domestic sewage in septic tanks, which normally retain the sewage from one day to two days, reducing the [[biochemical oxygen demand]] (BOD) by about 35 to 40 percent. This reduction can be increased with a combination of anaerobic and aerobic treatment by installing ''Aerobic Treatment Units'' (ATUs) in the septic tank. |
Anaerobic digestion is the most common (mesophilic) treatment of domestic sewage in septic tanks, which normally retain the sewage from one day to two days, reducing the [[biochemical oxygen demand]] (BOD) by about 35 to 40 percent. This reduction can be increased with a combination of anaerobic and aerobic treatment by installing ''Aerobic Treatment Units'' (ATUs) in the septic tank. |
||
Mesophilic anaerobic digestion (MAD) is also a common method for treating sludge produced at sewage treatment plants. The sludge is fed into large tanks and held for a minimum of 12 days to allow the digestion process to perform the four stages necessary to digest the sludge. These are hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. In this process the complex proteins and sugars are broken down to form more simple compounds such as water, carbon dioxide and methane. |
Mesophilic anaerobic digestion (MAD) is also a common method for treating sludge produced at sewage treatment plants. The sludge is fed into large tanks and held for a minimum of 12 days to allow the digestion process to perform the four stages necessary to digest the sludge. These are hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. In this process the complex proteins and sugars are broken down to form more simple compounds such as water, carbon dioxide and methane.<ref>[http://www.esru.strath.ac.uk/EandE/Web_sites/03-04/biomass/background%20info8.html Biomass – Using Anaerobic Digestion]. esru.strath.ac.uk</ref> |
||
One major feature of anaerobic digestion is the production of biogas with the most useful component being methane,which can be used in generators for electricity production and/or in boilers for heating purposes. Many larger sites utilize the biogas for combined heat and power, using the cooling water from the generators to maintain the temperature of the digestion plant at the required 35 ± 3 °C. |
|||
One major feature of anaerobic digestion is the production of [[biogas]] (with the most useful component being [[methane]]), which can be used in generators for electricity production and/or in boilers for heating purposes. Many larger sites utilize the biogas for combined heat and power, using the cooling water from the generators to maintain the temperature of the digestion plant at the required 35 ± 3 °C. |
|||
===Aerobic digestion=== |
===Aerobic digestion=== |
||
Aerobic organism|Aerobic digestion (a subset of the activated sludge process) is a bacterial process occurring in the presence of oxygen. Under aerobic conditions, bacteria rapidly consume organic matter and convert it into carbon dioxide The operating costs used to be characteristically much greater for aerobic digestion because of the energy used by the blowers, pumps and motors needed to add oxygen to the process. However, recent technological advances include non-electric aerated filter systems that use natural air currents for the aeration instead of electrically operated machinery. |
[[Aerobic organism|Aerobic]] digestion (a subset of the activated sludge process) is a bacterial process occurring in the presence of oxygen. Under aerobic conditions, bacteria rapidly consume organic matter and convert it into [[carbon dioxide]]. The operating costs used to be characteristically much greater for aerobic digestion because of the energy used by the blowers, pumps and motors needed to add oxygen to the process. However, recent technological advances include non-electric aerated filter systems that use natural air currents for the aeration instead of electrically operated machinery. |
||
Aerobic digestion can also be achieved by using [[Diffuser (sewage)|diffuser systems]] or [[jet aerators]] to oxidize the sludge. Fine bubble diffusers are typically the more cost-efficient diffusion method, however, plugging is typically a problem due to sediment settling into the smaller air holes. Coarse bubble diffusers are more commonly used in activated sludge tanks (generally a side process in waste water management) or in the flocculation stages. A key component for selecting diffuser type is to ensure it will produce the required oxygen transfer rate. |
|||
===Composting=== |
|||
[[Composting]] is also an aerobic process that involves mixing the sludge with sources of carbon such as sawdust, straw or wood chips. In the presence of oxygen, bacteria digest both the wastewater solids and the added carbon source and, in doing so, produce a large amount of heat.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|20}} |
|||
===Incineration=== |
|||
[[Incineration]] of sludge is less common because of air emissions concerns and the supplemental fuel (typically natural gases or fuel oil) required to burn the low calorific value sludge and vaporize residual water. Stepped multiple hearth incinerators |
|||
with high [[residence time]] and [[Fluidized bed combustion|fluidized bed]] incinerators are the most common systems used to combust wastewater sludge. Co-firing in municipal [[waste-to-energy]] plants is occasionally done, this option being less expensive |
|||
assuming the facilities already exist for solid waste and there is no need for auxiliary fuel.<ref name="EPA Primer" />{{rp|20–21}} |
|||
===Sludge disposal=== |
|||
When a liquid sludge is produced, further treatment may be required to make it suitable for final disposal. |
|||
Typically, sludges are thickened (dewatered) to reduce the volumes transported off-site for disposal. There is no process which completely eliminates the need to dispose of biosolids. There is, however, an additional step some cities are taking to superheat sludge and convert it into small pelletized granules that are high in nitrogen and other organic materials. In [[New York City]], for example, several sewage treatment plants have dewatering facilities that use large centrifuges along with the addition of chemicals such as polymer to further remove liquid from the sludge. The removed fluid, called "centrate," is typically reintroduced into the wastewater process. The product which is left is called "cake," and that is picked up by companies which turn it into fertilizer pellets. This product is then sold to local farmers and turf farms as a soil amendment or fertilizer, reducing the amount of space required to dispose of sludge in landfills. Much sludge originating from commercial or industrial areas is contaminated with toxic materials that are released into the sewers from the industrial processes.<ref>Langenkamp, H., Part, P. (2001). [http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/sludge/pdf/organics_in_sludge.pdf "Organic Contaminants in Sewage Sludge for Agricultural Use."] European Commission Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Soil and Waste Unit. Brussels, Belgium.</ref> Elevated concentrations of such materials may make the sludge unsuitable for agricultural use and it may then have to be incinerated or disposed of to landfill. |
|||
==Treatment in the receiving environment== |
|||
[[File:MiRO3.jpg|thumb|The outlet of the [[:en:Karlsruhe|Karlsruhe]] sewage treatment plant flows into the [[:en:Alb (Northern Black Forest)|Alb]].]] |
|||
Many processes in a wastewater treatment plant are designed to mimic the natural treatment processes that occur in the environment, whether that environment is a natural water body or the ground. If not overloaded, bacteria in the environment will consume organic contaminants, although this will reduce the levels of oxygen in the water and may significantly change the overall [[ecology]] of the receiving water. Native bacterial populations feed on the organic contaminants, and the numbers of disease-causing microorganisms are reduced by natural environmental conditions such as predation or exposure to [[ultraviolet]] radiation. Consequently, in cases where the receiving environment provides a high level of dilution, a high degree of wastewater treatment may not be required. However, recent evidence has demonstrated that very low levels of specific contaminants in wastewater, including [[hormone]]s (from [[animal husbandry]] and residue from human [[hormonal contraception]] methods) and synthetic materials such as [[phthalate]]s that mimic hormones in their action, can have an unpredictable adverse impact on the natural biota and potentially on humans if the water is re-used for drinking water.<ref>{{Wayback |date=20060804195610 |url=http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/business/444304/1290036/1290100/1290353/1294402/1311542/?version=1&lang=_e |title=Environment Agency (archive) – Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic PBT substances }}. environment-agency.gov.uk. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.</ref><ref>[http://planetearth.nerc.ac.uk/news/story.aspx?id=297 Natural Environmental Research Council – River sewage pollution found to be disrupting fish hormones]. Planetearth.nerc.ac.uk. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.</ref><ref>{{Wayback |date=20111015161223 |url=http://toxics.usgs.gov/highlights/wastewater_fish.html |title=Endocrine Disruption Found in Fish Exposed to Municipal Wastewater }}. USGS</ref> In the US and [[European Union|EU]], uncontrolled discharges of wastewater to the environment are not permitted under law, and strict water quality requirements are to be met, as clean drinking water is essential. (For requirements in the US, ''see [[Clean Water Act#Point sources|Clean Water Act]].'') A significant threat in the coming decades will be the increasing uncontrolled discharges of wastewater within rapidly developing countries. |
|||
===Effects on biology=== |
|||
Sewage treatment plants can have multiple effects on nutrient levels in the water that the treated sewage flows into. These effects on nutrients can have large effects on the biological life in the water in contact with the effluent. |
|||
[[Stabilization pond]]s (or treatment ponds) can include any of the following: |
|||
* Oxidation ponds, which are aerobic bodies of water usually 1–2 meters in depth that receive effluent from sedimentation tanks or other forms of primary treatment. |
|||
:* Dominated by [[algae]] |
|||
* Polishing ponds are similar to oxidation ponds but receive effluent from an oxidation pond or from a plant with an extended mechanical treatment. |
|||
:* Dominated by [[zooplankton]] |
|||
* [[Facultative lagoon]]s, raw sewage lagoons, or sewage lagoons are ponds where sewage is added with no primary treatment other than coarse screening. These ponds provide effective treatment when the surface remains aerobic; although anaerobic conditions may develop near the layer of settled sludge on the bottom of the pond.<ref name="Metcalf & Eddy" />{{rp|552–554}} |
|||
* Anaerobic lagoons are heavily loaded ponds. |
|||
:* Dominated by [[bacteria]] |
|||
* Sludge lagoons are aerobic ponds, usually 2 to 5 meters in depth, that receive anaerobically digested primary sludge, or activated secondary sludge under water. |
|||
:* Upper layers are dominated by algae <ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1080/00288330.1968.9515271|author=Haughey, A. |year=1968|title=The Planktonic Algae of Auckland Sewage Treatment Ponds|journal=New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research|volume=2|issue=4|pages=721}}</ref> |
|||
Phosphorus limitation is a possible result from sewage treatment and results in flagellate-dominated [[plankton]], particularly in summer and fall.<ref>Edmondson, W.T. (1972). "Nutrients and Phytoplankton in Lake Washington." in ''Nutrients and Eutrophication: The Limiting Nutrient Controversy.'' American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Special Symposia. Vol. 1.</ref> |
|||
At the same time a different study found high nutrient concentrations linked to sewage effluents. High nutrient concentration leads to high [[chlorophyll a]] concentrations, which is a proxy for primary production in marine environments. High primary production means high [[phytoplankton]] populations and most likely high zooplankton populations because zooplankton feed on phytoplankton. However, effluent released into marine systems also leads to greater population instability.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Caperon, J.; Cattell, S. A. and Krasnick, G.|url=http://www.nospam.aslo.org/lo/toc/vol_16/issue_4/0599.pdf |title=Phytoplankton Kinetics in a Subtropical Estuary: Eutrophication|journal= Limnology and Oceanography|volume=16|issue=4|pages=599|year=1971|doi=10.4319/lo.1971.16.4.0599}}</ref> |
|||
A study carried out in Britain found that the quality of effluent affected the planktonic life in the water in direct contact with the wastewater effluent. Turbid, low-quality effluents either did not contain [[ciliated]] [[protozoa]] or contained only a few species in small numbers. On the other hand, high-quality effluents contained a wide variety of ciliated protozoa in large numbers. Because of these findings, it seems unlikely that any particular component of the industrial effluent has, by itself, any harmful effects on the protozoan populations of activated sludge plants.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1016/0043-1354(70)90069-2 |title=Protozoa in biological sewage-treatment processes—I. A survey of the protozoan fauna of British percolating filters and activated-sludge plants|year=1970|last1=Curds|first1=C.R|last2=Cockburn|first2=A|journal=Water Research|volume=4|issue=3|pages=225}}</ref> |
|||
The planktonic trends of high populations close to input of treated sewage is contrasted by the [[bacterial]] trend. In a study of ''[[Aeromonas]]'' spp. in increasing distance from a wastewater source, greater change in seasonal cycles was found the furthest from the effluent. This trend is so strong that the furthest location studied actually had an inversion of the ''Aeromonas'' spp. cycle in comparison to that of [[fecal coliforms]]. Since there is a main pattern in the cycles that occurred simultaneously at all stations it indicates seasonal factors (temperature, solar radiation, phytoplankton) control of the bacterial population. The effluent dominant species changes from ''Aeromonas caviae'' in winter to ''Aeromonas sobria'' in the spring and fall while the inflow dominant species is ''Aeromonas caviae'', which is constant throughout the seasons.<ref>{{cite journal |pmc=184551 |pmid=2389929 |year=1990 |last1=Monfort |first1=P |last2=Baleux |first2=B |title=Dynamics of Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas sobria, and Aeromonas caviae in a sewage treatment pond |volume=56 |issue=7 |pages=1999–2006 |journal=Applied and environmental microbiology}}</ref> |
|||
==Sewage treatment in developing countries== |
|||
Few reliable figures exist on the share of the wastewater collected in sewers that is being treated in the world. In many developing countries the bulk of domestic and industrial wastewater is discharged without any treatment or after primary treatment only. In Latin America about 15 percent of collected wastewater passes through treatment plants (with varying levels of actual treatment). In [[Venezuela]], a below average country in [[South America]] with respect to wastewater treatment, 97 percent of the country’s [[sewage]] is discharged raw into the environment.<ref>{{cite book |title = Appropriate Technology for Sewage Pollution Control in the Wider Caribbean Region |last = Caribbean Environment Programme |year=1998 |publisher= United Nations Environment Programme |location=Kingston, Jamaica |isbn= |pages= |url=http://www.cep.unep.org/publications-and-resources/technical-reports/tr40en.pdf |accessdate=2009-10-12}} Technical Report No. 40.</ref> In a relatively developed [[Middle East]]ern country such as [[Iran]], the majority of [[Tehran]]'s population has totally untreated sewage injected to the city’s groundwater.<ref>Massoud Tajrishy and Ahmad Abrishamchi (2005). "Integrated Approach to Water and Wastewater Management for Tehran, Iran." ''Water Conservation, Reuse, and Recycling: Proceedings of the Iranian-American Workshop.'' Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press.</ref> However, the construction of major parts of the sewage system, collection and treatment, in Tehran is almost complete, and under development, due to be fully completed by the end of 2012. In Isfahan, Iran's third largest city, sewage treatment was started more than 100 years ago. |
|||
In Israel, about 50 percent of agricultural water usage (total use was 1 billion cubic metres in 2008) is provided through reclaimed sewer water. Future plans call for increased use of treated sewer water as well as more [[desalination plant]]s.<ref> |
|||
{{cite news |title=Farming in Israel, without a drop to spare |first=Andrew |last=Martin |newspaper=New York Times |date=2008-08-10 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2008/08/10/business/worldbusiness/10iht-10feed.15134930.html}}</ref> |
|||
Most of [[sub-Saharan Africa]] is without wastewater treatment.{{citation needed|date=June 2012}} |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{columns-list|2| |
|||
*[[Aerobic granulation]] |
|||
*[[Composting toilet]] |
|||
*[[Waste disposal]] |
|||
*[[Water pollution]] |
|||
*[[Water reclamation]] |
|||
*[[Advanced oxidation process]]es |
|||
*[[Environmental Persistent Pharmaceutical Pollutant]] EPPP}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{commons category|Wastewater treatment plants}} |
|||
*[http://www.wef.org/Publications/page.aspx?id=981 Interactive Diagram of Wastewater Treatment – "Go with the Flow"] – Water Environment Federation, (available in English and Spanish and French). |
|||
*[ Improved Modelling of Wastewater Treatment Primary Clarifier Using Hybrid Anns]https://pureapps2.hw.ac.uk/portal/files/2687114/IJCSAI10061_20121228_164131_8693_9362.pdf |
|||
{{Environmental technology}} |
|||
{{waste}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sewage Treatment}} |
|||
[[Category:Aquatic ecology]] |
|||
[[Category:Environmental engineering]] |
|||
[[Category:Environmental soil science]] |
|||
[[Category:Pollution control technologies]] |
|||
[[Category:Sewerage]] |
|||
[[Category:Water pollution]] |
|||
[[Category:Sanitation]] |
|||
[[Category:Sewerage infrastructure]] |
|||
{{Link FA|nl}} |
|||
Aerobic digestion can also be achieved by using [[Diffuser (sewage)|diffuser systems]] or jet aerators to oxidize the sludge. Fine bubble diffusers are typically the more cost-efficient diffusion method, however, plugging is typically a problem due to sediment settling into the smaller air holes. Coarse bubble diffusers are more commonly used in activated sludge tanks (generally a side process in waste water management) or in the flocculation stages. A key component for selecting diffuser type is to ensure it will produce the required oxygen transfer rate. |
|||
Revision as of 09:46, 6 March 2014

Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and household sewage, both runoff (effluents), domestic, commercial and institutional. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants. Its objective is to produce an environmentally safe fluid waste stream (or treated effluent) and a solid waste (or treated sludge) suitable for disposal or reuse (usually as farm fertilizer). Using advanced technology it is now possible to re-use sewage effluent for drinking water, although Singapore is the only country to implement such technology on a production scale in its production of NEWater.[2]
History

Basic sewer systems were used for waste removal in ancient Mesopotamia, where vertical shafts carried the waste away into cesspools. Similar systems existed in the Indus Valley civilization in modern day India and in Ancient Crete and Greece. In the Middle Ages the sewer systems built by the Romans fell into disuse and waste was collected into cesspools that were periodically emptied by workers known as 'rakers' who would often sell it as fertilizer to farmers outside the city.
Modern sewage systems were first built in the mid-nineteenth century as a reaction to the exacerbation of sanitary conditions brought on by heavy industrialization and urbanization. Due to the contaminated water supply, cholera outbreaks occurred in 1832, 1849 and 1855 in London, killing tens of thousands of people. This, combined with the Great Stink of 1858, when the smell of untreated human waste in the River Thames became overpowering, and the report into sanitation reform of the Royal Commissioner Edwin Chadwick,[3] led to the Metropolitan Commission of Sewers appointing Sir Joseph Bazalgette to construct a vast underground sewage system for the safe removal of waste. Contrary to Chadwick's recommendations, Bazalgette's system, and others later built in Continental Europe, did not pump the sewage onto farm land for use as fertilizer; it was simply piped to a natural waterway away from population centres, and pumped back into the environment.
Early attempts
One of the first attempts at diverting sewage for use as a fertilizer in the farm was made by the cotton mill owner James Smith in the 1840s. He experimented with a piped distribution system initially proposed by James Vetch[4] that collected sewage from his factory and pumped it into the outlying farms, and his success was enthusiastically followed by Edwin Chadwick and supported by organic chemist Justus von Liebig.
The idea was officially adopted by the Health of Towns Commission, and various schemes (known as sewage farms) were trialled by different municipalities over the next 50 years. At first, the heavier solids were channeled into ditches on the side of the farm and were covered over when full, but soon flat-bottomed tanks were employed as reservoirs for the sewage; the earliest patent was taken out by William Higgs in 1846 for "tanks or reservoirs in which the contents of sewers and drains from cities, towns and villages are to be collected and the solid animal or vegetable matters therein contained, solidified and dried..."[5] Improvements to the design of the tanks included the introduction of the horizontal-flow tank in the 1850s and the radial-flow tank in 1905. These tanks had to be manually de-sludged periodically, until the introduction of automatic mechanical de-sludgers in the early 1900s.[6]
The precursor to the modern septic tank was the cesspool in which the water was sealed off to prevent contamination and the solid waste was slowly liquified due to anaerobic action; it was invented by L.H Mouras in France in the 1860s. Donald Cameron, as City Surveyor for Exeter patented an improved version in 1895, which he called a 'septic tank'; septic having the meaning of 'bacterial'. These are still in worldwide use, especially in rural areas unconnected to large scale sewage systems.[7]
Chemical treatment

It was not until the late 19th century that it became possible to treat the sewage by chemically breaking it down through the use of microorganisms and removing the pollutants. Land treatment was also steadily becoming less feasible, as cities grew and the volume of sewage produced could no longer be absorbed by the farmland on the outskirts.
Sir Edward Frankland conducted experiments at the Sewage Farm in Croydon, England, during the 1870s and was able to demonstrate that filtration of sewage through porous gravel produced a nitrified effluent (the ammonia was converted into nitrate) and that the filter remained unclogged over long periods of time.[8] This established the then revolutionary possibility of biological treatment of sewage using a contact bed to oxidize the waste. This concept was taken up by the chief chemist for the London Metropolitan Board of Works, William Libdin, in 1887:
- ...in all probability the true way of purifying sewage...will be first to separate the sludge, and then turn into neutral effluent... retain it for a sufficient period, during which time it should be fully aerated, and finally discharge it into the stream in a purified condition. This is indeed what is aimed at and imperfectly accomplished on a sewage farm.[9]
From 1885 to 1891 filters working on this principle were constructed throughout the UK and the idea was also taken up in the US at the Lawrence Experiment Station in Massachusetts, where Frankland's work was confirmed. In 1890 the LES developed a 'trickling filter' that gave a much more reliable performance.[10]
Contact beds were developed in Salford, Manchester and by scientists working for the London City Council in the early 1890s. According to Christopher Hamlin, this was part of a conceptual revolution that replaced the philosophy that saw "sewage purification as the prevention of decomposition with one that tried to facilitate the biological process that destroy sewage naturally."[11]
Contact beds were tanks containing the inert substance, such as stones or slate, that maximized the surface area available for the microbial growth to break down the sewage. The sewage was held in the tank until it was fully decomposed and it was then filtered out into the ground. This method quickly became widespread, especially in the UK, where it was used in Leicester, Sheffield, Manchester and Leeds. The bacterial bed was simultaneously developed by Joseph Corbett as Borough Engineer in Salford and experiments in 1905 showed that his method was superior in that greater volumes of sewage could be purified better for longer periods of time than could be achieved by the contact bed.[12]
The Royal Commission on Sewage Disposal published it's eighth report in 1912 that set what became the international standard for sewage discharge into rivers; the '20:30 standard', which allowed 20 mg Biochemical oxygen demand and 30 mg suspended solid per litre.[13]
Activated sludge
The development of secondary treatments to sewage in the early twentieth century led to arguably the single most significant improvement in public health and the environment during the course of the century, the invention of the 'activated sludge' process for the treatment of sewage.

In 1912, Dr. Gilbert Fowler, a scientist at the University of Manchester, observed experiments being conducted at the Lawrence Experiment Station at Massachusetts involving the aeration of sewage in a bottle that had been coated with algae. Fowler's engineering colleagues, Edward Ardern and William Lockett,[14] who were conducting research for the Manchester Corporation Rivers Department at Davyhulme Sewage Works,[15] experimented on treating sewage in a draw-and-fill reactor, which produced a highly treated effluent. They aerated the waste-water continuously for about a month and were able to achieve a complete nitrification of the sample material. Believing that the sludge had been activated (in a similar manner to activated carbon) the process was named activated sludge.
Their results were published in their seminal 1914 paper, and the first full-scale continuous-flow system was installed at Worcester two years later. In the aftermath of the First World War the new treatment method spread rapidly, especially to the USA, Denmark, Germany and Canada. By the late 1930s, the activated sludge treatment was the predominant process used around the world.[16]
Origins of sewage
Sewage is generated by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial establishments. It includes household waste liquid from toilets, baths, showers, kitchens, sinks and so forth that is disposed of via sewers. In many areas, sewage also includes liquid waste from industry and commerce. The separation and draining of household waste into greywater and blackwater is becoming more common in the developed world, with greywater being permitted to be used for watering plants or recycled for flushing toilets.
Sewage may include stormwater runoff. Sewerage systems capable of handling storm water are known as combined sewer systems. This design was common when urban sewerage systems were first developed, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.[17]: 119 Combined sewers require much larger and more expensive treatment facilities than sanitary sewers. Heavy volumes of storm runoff may overwhelm the sewage treatment system, causing a spill or overflow. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller than combined sewers, and they are not designed to transport stormwater. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive infiltration/inflow (dilution by stormwater and/or groundwater) is allowed into a sanitary sewer system. Communities that have urbanized in the mid-20th century or later generally have built separate systems for sewage (sanitary sewers) and stormwater, because precipitation causes widely varying flows, reducing sewage treatment plant efficiency.[18]
As rainfall travels over roofs and the ground, it may pick up various contaminants including soil particles and other sediment, heavy metals, organic compounds, animal waste, and oil and grease. (See urban runoff.)[19] Some jurisdictions require stormwater to receive some level of treatment before being discharged directly into waterways. Examples of treatment processes used for stormwater include retention basins, wetlands, buried vaults with various kinds of media filters, and vortex separators (to remove coarse solids).
Process overview
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created, a decentralized system (in septic tanks, biofilters or aerobic treatment systems), or be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant, a centralized system (see sewerage and pipes and infrastructure). Sewage collection and treatment is typically subject to local, state and federal regulations and standards. Industrial sources of sewage often require specialized treatment processes (see Industrial wastewater treatment).
Sewage treatment generally involves three stages, called primary, secondary and tertiary treatment.
- Primary treatment consists of temporarily holding the sewage in a quiescent basin where heavy solids can settle to the bottom while oil, grease and lighter solids float to the surface. The settled and floating materials are removed and the remaining liquid may be discharged or subjected to secondary treatment.
- Secondary treatment removes dissolved and suspended biological matter. Secondary treatment is typically performed by indigenous, water-borne micro-organisms in a managed habitat. Secondary treatment may require a separation process to remove the micro-organisms from the treated water prior to discharge or tertiary treatment.
- Tertiary treatment is sometimes defined as anything more than primary and secondary treatment in order to allow rejection into a highly sensitive or fragile ecosystem (estuaries, low-flow rivers, coral reefs,...). Treated water is sometimes disinfected chemically or physically (for example, by lagoons and microfiltration) prior to discharge into a stream, river, bay, lagoon or wetland, or it can be used for the irrigation of a golf course, green way or park. If it is sufficiently clean, it can also be used for groundwater recharge or agricultural purposes.
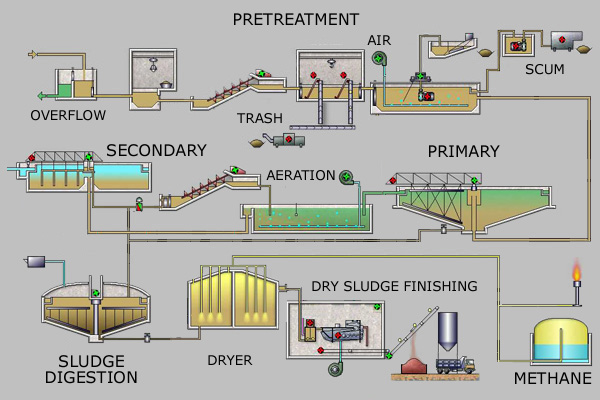

Pretreatment
Pretreatment removes all materials that can be easily collected from the raw sewage before they damage or clog the pumps and sewage lines of primary treatment clarifiers. Objects that are commonly removed during pretreatment include trash, tree limbs, leaves, branches, and other large objects.
The influent in sewage water passes through a bar screen to remove all large objects like cans, rags, sticks, plastic packets etc. carried in the sewage stream.[20] This is most commonly done with an automated mechanically raked bar screen in modern plants serving large populations, while in smaller or less modern plants, a manually cleaned screen may be used. The raking action of a mechanical bar screen is typically paced according to the accumulation on the bar screens and/or flow rate. The solids are collected and later disposed in a landfill, or incinerated. Bar screens or mesh screens of varying sizes may be used to optimize solids removal. If gross solids are not removed, they become entrained in pipes and moving parts of the treatment plant, and can cause substantial damage and inefficiency in the process.[21]: 9
Grit removal
Pretreatment may include a sand or grit channel or chamber, where the velocity of the incoming sewage is adjusted to allow the settlement of sand, grit, stones, and broken glass. These particles are removed because they may damage pumps and other equipment. For small sanitary sewer systems, the grit chambers may not be necessary, but grit removal is desirable at larger plants.[21] Grit chambers come in 3 types: horizontal grit chambers, aerated grit chambers and vortex grit chambers.
Flow equalization
Clarifiers and mechanized secondary treatment are more efficient under uniform flow conditions. Equalization basins may be used for temporary storage of diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks. Basins provide a place to temporarily hold incoming sewage during plant maintenance and a means of diluting and distributing batch discharges of toxic or high-strength waste which might otherwise inhibit biological secondary treatment (including portable toilet waste, vehicle holding tanks, and septic tank pumpers). Flow equalization basins require variable discharge control, typically include provisions for bypass and cleaning, and may also include aerators. Cleaning may be easier if the basin is downstream of screening and grit removal.[22]
Fat and grease removal
In some larger plants, fat and grease are removed by passing the sewage through a small tank where skimmers collect the fat floating on the surface. Air blowers in the base of the tank may also be used to help recover the fat as a froth. Many plants, however, use primary clarifiers with mechanical surface skimmers for fat and grease removal.
Primary treatment
In the primary sedimentation stage, sewage flows through large tanks, commonly called "pre-settling basins", "primary sedimentation tanks" or "primary clarifiers".[23] The tanks are used to settle sludge while grease and oils rise to the surface and are skimmed off. Primary settling tanks are usually equipped with mechanically driven scrapers that continually drive the collected sludge towards a hopper in the base of the tank where it is pumped to sludge treatment facilities.[21]: 9–11 Grease and oil from the floating material can sometimes be recovered for saponification.
Secondary treatment
Secondary treatment is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage which are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent. The majority of municipal plants treat the settled sewage liquor using aerobic biological processes. To be effective, the biota require both oxygen and food to live. The bacteria and protozoa consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants (e.g. sugars, fats, organic short-chain carbon molecules, etc.) and bind much of the less soluble fractions into floc. Secondary treatment systems are classified as fixed-film or suspended-growth systems.
- Fixed-film or attached growth systems include trickling filters, biotowers, and rotating biological contactors, where the biomass grows on media and the sewage passes over its surface.[21]: 11–13 The fixed-film principle has further developed into Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR), and Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge (IFAS) processes. An MBBR system typically requires smaller footprint than suspended-growth systems.[24]
- Suspended-growth systems include activated sludge, where the biomass is mixed with the sewage and can be operated in a smaller space than trickling filters that treat the same amount of water. However, fixed-film systems are more able to cope with drastic changes in the amount of biological material and can provide higher removal rates for organic material and suspended solids than suspended growth systems.[21]: 11–13
Roughing filters are intended to treat particularly strong or variable organic loads, typically industrial, to allow them to then be treated by conventional secondary treatment processes. Characteristics include filters filled with media to which wastewater is applied. They are designed to allow high hydraulic loading and a high level of aeration. On larger installations, air is forced through the media using blowers. The resultant wastewater is usually within the normal range for conventional treatment processes.

A filter removes a small percentage of the suspended organic matter, while the majority of the organic matter undergoes a change of character, only due to the biological oxidation and nitrification taking place in the filter. With this aerobic oxidation and nitrification, the organic solids are converted into coagulated suspended mass, which is heavier and bulkier, and can settle to the bottom of a tank. The effluent of the filter is therefore passed through a sedimentation tank, called a secondary clarifier, secondary settling tank or humus tank.
Activated sludge
In general, activated sludge plants encompass a variety of mechanisms and processes that use dissolved oxygen to promote the growth of biological floc that substantially removes organic material.[21]: 12–13
Biological floc, as mentioned above, is an ecosystem of living biota that subsists on nutrients from the inflowing primary settling tank (or clarifier) effluent. These mostly carbonaceous dissolved solids undergo aeration to be broken down and biologically oxidized or converted to carbon dioxide. Likewise, nitrogenous dissolved solids (amino acids, ammonia, etc.) are also oxidized (=eaten) by the floc to nitrites, nitrates, and, in some processes, to nitrogen gas through denitrification.
While denitrification is encouraged in some treatment processes, in many suspended aeration plants denitrification will impair the settling of the floc and lead to poor quality effluent.
In either case, the settled floc is both recycled to the inflowing primary effluent to regrow, or is partially 'wasted' (or diverted) to solids dewatering, or digesting, and then dewatering.
Interestingly, like most living creatures, activated sludge biota can get sick. This many times takes the form of the floating brown foam, Nocardia. While this so-called 'sewage fungus' (it isn't really a fungus) is the best known, there are many different fungi and protists that can overpopulate a the floc and cause process upsets. Additionally, certain incoming chemical species, such as a heavy pesticide, a heavy metal (e.g.: plating company effluent) load, or extreme pH, can kill the biota of an activated sludge reactor ecosystem. Such problems are tested for, and if caught in time, can be neutralized.

Aerobic granular sludge
Activated sludge systems can be transformed into aerobic granular sludge systems (aerobic granulation) which enhance the benefits of activated sludge, like increased biomass retention due to high sludge settlability.
Surface-aerated basins (lagoons)
Many small municipal sewage systems in the United States (1 million gal./day or less) use aerated lagoons.[25]
Most biological oxidation processes for treating industrial wastewaters have in common the use of oxygen (or air) and microbial action. Surface-aerated basins achieve 80 to 90 percent removal of BOD with retention times of 1 to 10 days.[26] The basins may range in depth from 1.5 to 5.0 metres and use motor-driven aerators floating on the surface of the wastewater.[26]
In an aerated basin system, the aerators provide two functions: they transfer air into the basins required by the biological oxidation reactions, and they provide the mixing required for dispersing the air and for contacting the reactants (that is, oxygen, wastewater and microbes). Typically, the floating surface aerators are rated to deliver the amount of air equivalent to 1.8 to 2.7 kg O2/kW·h. However, they do not provide as good mixing as is normally achieved in activated sludge systems and therefore aerated basins do not achieve the same performance level as activated sludge units.[26]
Biological oxidation processes are sensitive to temperature and, between 0 °C and 40 °C, the rate of biological reactions increase with temperature. Most surface aerated vessels operate at between 4 °C and 32 °C.[26]
Filter beds (oxidizing beds)
In older plants and those receiving variable loadings, trickling filter beds are used where the settled sewage liquor is spread onto the surface of a bed made up of coke (carbonized coal), limestone chips or specially fabricated plastic media. Such media must have large surface areas to support the biofilms that form. The liquor is typically distributed through perforated spray arms. The distributed liquor trickles through the bed and is collected in drains at the base. These drains also provide a source of air which percolates up through the bed, keeping it aerobic. Biological films of bacteria, protozoa and fungi form on the media’s surfaces and eat or otherwise reduce the organic content.[21]: 12 This biofilm is often grazed by insect larvae, snails, and worms which help maintain an optimal thickness. Overloading of beds increases the thickness of the film leading to clogging of the filter media and ponding on the surface. Recent advances in media and process micro-biology design overcome many issues with trickling filter designs.
Constructed wetlands
Constructed wetlands (can either be surface flow or subsurface flow, horizontal or vertical flow), include engineered reedbeds and belong to the family of phytorestoration and ecotechnologies; they provide a high degree of biological improvement and depending on design, act as a primary, secondary and sometimes tertiary treatment, also see phytoremediation. One example is a small reedbed used to clean the drainage from the elephants' enclosure at Chester Zoo in England; numerous CWs are used to recycle the water of the city of Honfleur in France and numerous other towns in Europe, the US, Asia and Australia. They are known to be highly productive systems as they copy natural wetlands, called the "kidneys of the earth" for their fundamental recycling capacity of the hydrological cycle in the biosphere. Robust and reliable, their treatment capacities improve as time go by, at the opposite of conventional treatment plants whose machinery age with time. They are being increasingly used, although adequate and experienced design are more fundamental than for other systems and space limitation may impede their use.
Soil bio-technology
A new process called soil bio-technology (SBT) developed at IIT Bombay has shown tremendous improvements in process efficiency enabling total water reuse, due to extremely low operating power requirements of less than 50 joules per kg of treated water.[27] Typically SBT systems can achieve chemical oxygen demand (COD) levels less than 10 mg/L from sewage input of COD 400 mg/L.[28] SBT plants exhibit high reductions in COD values and bacterial counts as a result of the very high microbial densities available in the media. Unlike conventional treatment plants, SBT plants produce insignificant amounts of sludge, precluding the need for sludge disposal areas that are required by other technologies.[29]
In the Indian context, conventional sewage treatment plants fall into systemic disrepair due to 1) high operating costs, 2) equipment corrosion due to methanogenesis and hydrogen sulphide, 3) non-reusability of treated water due to high COD (>30 mg/L) and high fecal coliform (>3000 NFU) counts, 4) lack of skilled operating personnel and 5) equipment replacement issues. Examples of such systemic failures has been documented by Sankat Mochan Foundation at the Ganges basin after a massive cleanup effort by the Indian government in 1986 by setting up sewage treatment plants under the Ganga Action Plan failed to improve river water quality.
Biological aerated filters
Biological Aerated (or Anoxic) Filter (BAF) or Biofilters combine filtration with biological carbon reduction, nitrification or denitrification. BAF usually includes a reactor filled with a filter media. The media is either in suspension or supported by a gravel layer at the foot of the filter. The dual purpose of this media is to support highly active biomass that is attached to it and to filter suspended solids. Carbon reduction and ammonia conversion occurs in aerobic mode and sometime achieved in a single reactor while nitrate conversion occurs in anoxic mode. BAF is operated either in upflow or downflow configuration depending on design specified by manufacturer.

Rotating biological contactors
Rotating biological contactors (RBCs) are mechanical secondary treatment systems, which are robust and capable of withstanding surges in organic load. RBCs were first installed in Germany in 1960 and have since been developed and refined into a reliable operating unit. The rotating disks support the growth of bacteria and micro-organisms present in the sewage, which break down and stabilize organic pollutants. To be successful, micro-organisms need both oxygen to live and food to grow. Oxygen is obtained from the atmosphere as the disks rotate. As the micro-organisms grow, they build up on the media until they are sloughed off due to shear forces provided by the rotating discs in the sewage. Effluent from the RBC is then passed through final clarifiers where the micro-organisms in suspension settle as a sludge. The sludge is withdrawn from the clarifier for further treatment.
A functionally similar biological filtering system has become popular as part of home aquarium filtration and purification. The aquarium water is drawn up out of the tank and then cascaded over a freely spinning corrugated fiber-mesh wheel before passing through a media filter and back into the aquarium. The spinning mesh wheel develops a biofilm coating of microorganisms that feed on the suspended wastes in the aquarium water and are also exposed to the atmosphere as the wheel rotates. This is especially good at removing waste urea and ammonia urinated into the aquarium water by the fish and other animals.
Membrane bioreactors
Membrane bioreactors (MBR) combine activated sludge treatment with a membrane liquid-solid separation process. The membrane component uses low pressure microfiltration or ultrafiltration membranes and eliminates the need for clarification and tertiary filtration. The membranes are typically immersed in the aeration tank; however, some applications utilize a separate membrane tank. One of the key benefits of an MBR system is that it effectively overcomes the limitations associated with poor settling of sludge in conventional activated sludge (CAS) processes. The technology permits bioreactor operation with considerably higher mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration than CAS systems, which are limited by sludge settling. The process is typically operated at MLSS in the range of 8,000–12,000 mg/L, while CAS are operated in the range of 2,000–3,000 mg/L. The elevated biomass concentration in the MBR process allows for very effective removal of both soluble and particulate biodegradable materials at higher loading rates. Thus increased sludge retention times, usually exceeding 15 days, ensure complete nitrification even in extremely cold weather.
The cost of building and operating an MBR is often higher than conventional methods of sewage treatment. Membrane filters can be blinded with grease or abraded by suspended grit and lack a clarifier's flexibility to pass peak flows. The technology has become increasingly popular for reliably pretreated waste streams and has gained wider acceptance where infiltration and inflow have been controlled, however, and the life-cycle costs have been steadily decreasing. The small footprint of MBR systems, and the high quality effluent produced, make them particularly useful for water reuse applications.[30]
Secondary sedimentation

The final step in the secondary treatment stage is to settle out the biological floc or filter material through a secondary clarifier and to produce sewage water containing low levels of organic material and suspended matter.
Tertiary treatment
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final treatment stage to further improve the effluent quality before it is discharged to the receiving environment (sea, river, lake, wet lands,ground, etc.). More than one tertiary treatment process may be used at any treatment plant. If disinfection is practiced, it is always the final process. It is also called "effluent polishing."
Filtration
Sand filtration removes much of the residual suspended matter.[21]: 22–23 Filtration over activated carbon, also called carbon adsorption, removes residual toxins.[21]: 19
Lagooning

Lagooning provides settlement and further biological improvement through storage in large man-made ponds or lagoons. These lagoons are highly aerobic and colonization by native macrophytes, especially reeds, is often encouraged. Small filter feeding invertebrates such as Daphnia and species of Rotifera greatly assist in treatment by removing fine particulates.
Nutrient removal
Wastewater may contain high levels of the nutrients nitrogen and phosphorus. Excessive release to the environment can lead to a build up of nutrients, called eutrophication, which can in turn encourage the overgrowth of weeds, algae, and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). This may cause an algal bloom, a rapid growth in the population of algae. The algae numbers are unsustainable and eventually most of them die. The decomposition of the algae by bacteria uses up so much of the oxygen in the water that most or all of the animals die, which creates more organic matter for the bacteria to decompose. In addition to causing deoxygenation, some algal species produce toxins that contaminate drinking water supplies. Different treatment processes are required to remove nitrogen and phosphorus.
Nitrogen removal
The removal of nitrogen is effected through the biological oxidation of nitrogen from ammonia to nitrate (nitrification), followed by denitrification, the reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas. Nitrogen gas is released to the atmosphere and thus removed from the water.
Nitrification itself is a two-step aerobic process, each step facilitated by a different type of bacteria. The oxidation of ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (NO2−) is most often facilitated by Nitrosomonas spp. ("nitroso" referring to the formation of a nitroso functional group). Nitrite oxidation to nitrate (NO3−), though traditionally believed to be facilitated by Nitrobacter spp. (nitro referring the formation of a nitro functional group), is now known to be facilitated in the environment almost exclusively by Nitrospira spp.
Denitrification requires anoxic conditions to encourage the appropriate biological communities to form. It is facilitated by a wide diversity of bacteria. Sand filters, lagooning and reed beds can all be used to reduce nitrogen, but the activated sludge process (if designed well) can do the job the most easily.[21]: 17–18 Since denitrification is the reduction of nitrate to dinitrogen gas, an electron donor is needed. This can be, depending on the wastewater, organic matter (from faeces), sulfide, or an added donor like methanol. The sludge in the anoxic tanks (denitrification tanks) must be mixed well (mixture of recirculated mixed liquor, return activated sludge [RAS], and raw influent) e.g. by using submersible mixers in order to achieve the desired denitrification.
Sometimes the conversion of toxic ammonia to nitrate alone is referred to as tertiary treatment.
Many sewage treatment plants use centrifugal pumps to transfer the nitrified mixed liquor from the aeration zone to the anoxic zone for denitrification. These pumps are often referred to as Internal Mixed Liquor Recycle (IMLR) pumps.
The bacteria Brocadia anammoxidans, is being researched for it's potential in sewage treatment. It can remove nitrogen from waste water.[31] In addition the bacteria can perform the anaerobic oxidation of ammonium and can produce the rocket fuel hydrazine from waste water.[32][33]
Phosphorus removal
Each person excretes between 200 and 1000 grams of phosphorus annually. Studies of United States sewage in the late 1960s estimated mean per capita contributions of 500 grams in urine and feces, 1000 grams in synthetic detergents, and lesser variable amounts used as corrosion and scale control chemicals in water supplies.[34] Source control via alternative detergent formulations has subsequently reduced the largest contribution, but the content of urine and feces will remain unchanged. Phosphorus removal is important as it is a limiting nutrient for algae growth in many fresh water systems. (For a description of the negative effects of algae, see Nutrient removal). It is also particularly important for water reuse systems where high phosphorus concentrations may lead to fouling of downstream equipment such as reverse osmosis.
Phosphorus can be removed biologically in a process called enhanced biological phosphorus removal. In this process, specific bacteria, called polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs), are selectively enriched and accumulate large quantities of phosphorus within their cells (up to 20 percent of their mass). When the biomass enriched in these bacteria is separated from the treated water, these biosolids have a high fertilizer value.
Phosphorus removal can also be achieved by chemical precipitation, usually with salts of iron (e.g. ferric chloride), aluminum (e.g. alum), or lime.[21]: 18 This may lead to excessive sludge production as hydroxides precipitates and the added chemicals can be expensive. Chemical phosphorus removal requires significantly smaller equipment footprint than biological removal, is easier to operate and is often more reliable than biological phosphorus removal.[citation needed] Another method for phosphorus removal is to use granular laterite.
Once removed, phosphorus, in the form of a phosphate-rich sludge, may be stored in a land fill or resold for use in fertilizer.
Disinfection
The purpose of disinfection in the treatment of waste water is to substantially reduce the number of microorganisms in the water to be discharged back into the environment for the later use of drinking, bathing, irrigation, etc. The effectiveness of disinfection depends on the quality of the water being treated (e.g., cloudiness, pH, etc.), the type of disinfection being used, the disinfectant dosage (concentration and time), and other environmental variables. Cloudy water will be treated less successfully, since solid matter can shield organisms, especially from ultraviolet light or if contact times are low. Generally, short contact times, low doses and high flows all militate against effective disinfection. Common methods of disinfection include ozone, chlorine, ultraviolet light, or sodium hypochlorite.[21]: 16 Chloramine, which is used for drinking water, is not used in the treatment of waste water because of its persistence. After multiple steps of disinfection, the treated water is ready to be released back into the water cycle by means of the nearest body of water or agriculture. Afterwards, the water can be transferred to reserves for everyday human uses.
Chlorination remains the most common form of waste water disinfection in North America due to its low cost and long-term history of effectiveness. One disadvantage is that chlorination of residual organic material can generate chlorinated-organic compounds that may be carcinogenic or harmful to the environment. Residual chlorine or chloramines may also be capable of chlorinating organic material in the natural aquatic environment. Further, because residual chlorine is toxic to aquatic species, the treated effluent must also be chemically dechlorinated, adding to the complexity and cost of treatment.
Ultraviolet (UV) light can be used instead of chlorine, iodine, or other chemicals. Because no chemicals are used, the treated water has no adverse effect on organisms that later consume it, as may be the case with other methods. UV radiation causes damage to the genetic structure of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, making them incapable of reproduction. The key disadvantages of UV disinfection are the need for frequent lamp maintenance and replacement and the need for a highly treated effluent to ensure that the target microorganisms are not shielded from the UV radiation (i.e., any solids present in the treated effluent may protect microorganisms from the UV light). In the United Kingdom, UV light is becoming the most common means of disinfection because of the concerns about the impacts of chlorine in chlorinating residual organics in the wastewater and in chlorinating organics in the receiving water. Some sewage treatment systems in Canada and the US also use UV light for their effluent water disinfection.[35][36]
Ozone (Template:Oxygen3) is generated by passing oxygen (Template:Oxygen2) through a high voltage potential resulting in a third oxygen atom becoming attached and forming Template:Oxygen3. Ozone is very unstable and reactive and oxidizes most organic material it comes in contact with, thereby destroying many pathogenic microorganisms. Ozone is considered to be safer than chlorine because, unlike chlorine which has to be stored on site (highly poisonous in the event of an accidental release), ozone is generated onsite as needed. Ozonation also produces fewer disinfection by-products than chlorination. A disadvantage of ozone disinfection is the high cost of the ozone generation equipment and the requirements for special operators.
Odor control
Odors emitted by sewage treatment are typically an indication of an anaerobic or "septic" condition.[37] Early stages of processing will tend to produce foul smelling gases, with hydrogen sulfide being most common in generating complaints. Large process plants in urban areas will often treat the odors with carbon reactors, a contact media with bio-slimes, small doses of chlorine, or circulating fluids to biologically capture and metabolize the noxious gases.[38] Other methods of odor control exist, including addition of iron salts, hydrogen peroxide, calcium nitrate, etc. to manage hydrogen sulfide levels.
High-density solids pumps are suitable for reducing odors by conveying sludge through hermetic closed pipework.
Package plants and batch reactors
To use less space, treat difficult waste and intermittent flows, a number of designs of hybrid treatment plants have been produced. Such plants often combine at least two stages of the three main treatment stages into one combined stage. In the UK, where a large number of wastewater treatment plants serve small populations, package plants are a viable alternative to building a large structure for each process stage. In the US, package plants are typically used in rural areas, highway rest stops and trailer parks.[39]
One type of system that combines secondary treatment and settlement is the cyclic activated sludge (CASSBR). Typically, activated sludge is mixed with raw incoming sewage, and then mixed and aerated. The settled sludge is run off and re-aerated before a proportion is returned to the headworks.[40] SBR plants are now being deployed in many parts of the world.
The disadvantage of the CASSBR process is that it requires a precise control of timing, mixing and aeration. This precision is typically achieved with computer controls linked to sensors. Such a complex, fragile system is unsuited to places where controls may be unreliable, poorly maintained, or where the power supply may be intermittent. Extended aeration package plants use separate basins for aeration and settling, and are somewhat larger than SBR plants with reduced timing sensitivity.[41]
Package plants may be referred to as high charged or low charged. This refers to the way the biological load is processed. In high charged systems, the biological stage is presented with a high organic load and the combined floc and organic material is then oxygenated for a few hours before being charged again with a new load. In the low charged system the biological stage contains a low organic load and is combined with flocculate for longer times.
Sludge treatment and disposal
The sludges accumulated in a wastewater treatment process must be treated and disposed of in a safe and effective manner. The purpose of digestion is to reduce the amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting. Incineration is also used, albeit to a much lesser degree.[21]: 19–21
Sludge treatment depends on the amount of solids generated and other site-specific conditions. Composting is most often applied to small-scale plants with aerobic digestion for mid sized operations, and anaerobic digestion for the larger-scale operations.
The sludge is sometimes passed through a so-called pre-thickener which de-waters the sludge. Types of pre-thickeners include centrifugal sludge thickeners[42] rotary drum sludge thickeners and belt filter presses.[43][44]
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a bacterial process that is carried out in the absence of oxygen. The process can either be thermophilic digestion, in which sludge is fermented in tanks at a temperature of 55 °C, or mesophilic, at a temperature of around 36 °C. Though allowing shorter retention time (and thus smaller tanks), thermophilic digestion is more expensive in terms of energy consumption for heating the sludge.
Anaerobic digestion is the most common (mesophilic) treatment of domestic sewage in septic tanks, which normally retain the sewage from one day to two days, reducing the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) by about 35 to 40 percent. This reduction can be increased with a combination of anaerobic and aerobic treatment by installing Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs) in the septic tank.
Mesophilic anaerobic digestion (MAD) is also a common method for treating sludge produced at sewage treatment plants. The sludge is fed into large tanks and held for a minimum of 12 days to allow the digestion process to perform the four stages necessary to digest the sludge. These are hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. In this process the complex proteins and sugars are broken down to form more simple compounds such as water, carbon dioxide and methane.[45]
One major feature of anaerobic digestion is the production of biogas (with the most useful component being methane), which can be used in generators for electricity production and/or in boilers for heating purposes. Many larger sites utilize the biogas for combined heat and power, using the cooling water from the generators to maintain the temperature of the digestion plant at the required 35 ± 3 °C.
Aerobic digestion
Aerobic digestion (a subset of the activated sludge process) is a bacterial process occurring in the presence of oxygen. Under aerobic conditions, bacteria rapidly consume organic matter and convert it into carbon dioxide. The operating costs used to be characteristically much greater for aerobic digestion because of the energy used by the blowers, pumps and motors needed to add oxygen to the process. However, recent technological advances include non-electric aerated filter systems that use natural air currents for the aeration instead of electrically operated machinery.
Aerobic digestion can also be achieved by using diffuser systems or jet aerators to oxidize the sludge. Fine bubble diffusers are typically the more cost-efficient diffusion method, however, plugging is typically a problem due to sediment settling into the smaller air holes. Coarse bubble diffusers are more commonly used in activated sludge tanks (generally a side process in waste water management) or in the flocculation stages. A key component for selecting diffuser type is to ensure it will produce the required oxygen transfer rate.
Composting
Composting is also an aerobic process that involves mixing the sludge with sources of carbon such as sawdust, straw or wood chips. In the presence of oxygen, bacteria digest both the wastewater solids and the added carbon source and, in doing so, produce a large amount of heat.[21]: 20
Incineration
Incineration of sludge is less common because of air emissions concerns and the supplemental fuel (typically natural gases or fuel oil) required to burn the low calorific value sludge and vaporize residual water. Stepped multiple hearth incinerators with high residence time and fluidized bed incinerators are the most common systems used to combust wastewater sludge. Co-firing in municipal waste-to-energy plants is occasionally done, this option being less expensive assuming the facilities already exist for solid waste and there is no need for auxiliary fuel.[21]: 20–21
Sludge disposal
When a liquid sludge is produced, further treatment may be required to make it suitable for final disposal.
Typically, sludges are thickened (dewatered) to reduce the volumes transported off-site for disposal. There is no process which completely eliminates the need to dispose of biosolids. There is, however, an additional step some cities are taking to superheat sludge and convert it into small pelletized granules that are high in nitrogen and other organic materials. In New York City, for example, several sewage treatment plants have dewatering facilities that use large centrifuges along with the addition of chemicals such as polymer to further remove liquid from the sludge. The removed fluid, called "centrate," is typically reintroduced into the wastewater process. The product which is left is called "cake," and that is picked up by companies which turn it into fertilizer pellets. This product is then sold to local farmers and turf farms as a soil amendment or fertilizer, reducing the amount of space required to dispose of sludge in landfills. Much sludge originating from commercial or industrial areas is contaminated with toxic materials that are released into the sewers from the industrial processes.[46] Elevated concentrations of such materials may make the sludge unsuitable for agricultural use and it may then have to be incinerated or disposed of to landfill.
Treatment in the receiving environment

Many processes in a wastewater treatment plant are designed to mimic the natural treatment processes that occur in the environment, whether that environment is a natural water body or the ground. If not overloaded, bacteria in the environment will consume organic contaminants, although this will reduce the levels of oxygen in the water and may significantly change the overall ecology of the receiving water. Native bacterial populations feed on the organic contaminants, and the numbers of disease-causing microorganisms are reduced by natural environmental conditions such as predation or exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Consequently, in cases where the receiving environment provides a high level of dilution, a high degree of wastewater treatment may not be required. However, recent evidence has demonstrated that very low levels of specific contaminants in wastewater, including hormones (from animal husbandry and residue from human hormonal contraception methods) and synthetic materials such as phthalates that mimic hormones in their action, can have an unpredictable adverse impact on the natural biota and potentially on humans if the water is re-used for drinking water.[47][48][49] In the US and EU, uncontrolled discharges of wastewater to the environment are not permitted under law, and strict water quality requirements are to be met, as clean drinking water is essential. (For requirements in the US, see Clean Water Act.) A significant threat in the coming decades will be the increasing uncontrolled discharges of wastewater within rapidly developing countries.
Effects on biology
Sewage treatment plants can have multiple effects on nutrient levels in the water that the treated sewage flows into. These effects on nutrients can have large effects on the biological life in the water in contact with the effluent. Stabilization ponds (or treatment ponds) can include any of the following:
- Oxidation ponds, which are aerobic bodies of water usually 1–2 meters in depth that receive effluent from sedimentation tanks or other forms of primary treatment.
- Dominated by algae
- Polishing ponds are similar to oxidation ponds but receive effluent from an oxidation pond or from a plant with an extended mechanical treatment.
- Dominated by zooplankton
- Facultative lagoons, raw sewage lagoons, or sewage lagoons are ponds where sewage is added with no primary treatment other than coarse screening. These ponds provide effective treatment when the surface remains aerobic; although anaerobic conditions may develop near the layer of settled sludge on the bottom of the pond.[17]: 552–554
- Anaerobic lagoons are heavily loaded ponds.
- Dominated by bacteria
- Sludge lagoons are aerobic ponds, usually 2 to 5 meters in depth, that receive anaerobically digested primary sludge, or activated secondary sludge under water.
- Upper layers are dominated by algae [50]
Phosphorus limitation is a possible result from sewage treatment and results in flagellate-dominated plankton, particularly in summer and fall.[51]
At the same time a different study found high nutrient concentrations linked to sewage effluents. High nutrient concentration leads to high chlorophyll a concentrations, which is a proxy for primary production in marine environments. High primary production means high phytoplankton populations and most likely high zooplankton populations because zooplankton feed on phytoplankton. However, effluent released into marine systems also leads to greater population instability.[52]
A study carried out in Britain found that the quality of effluent affected the planktonic life in the water in direct contact with the wastewater effluent. Turbid, low-quality effluents either did not contain ciliated protozoa or contained only a few species in small numbers. On the other hand, high-quality effluents contained a wide variety of ciliated protozoa in large numbers. Because of these findings, it seems unlikely that any particular component of the industrial effluent has, by itself, any harmful effects on the protozoan populations of activated sludge plants.[53]
The planktonic trends of high populations close to input of treated sewage is contrasted by the bacterial trend. In a study of Aeromonas spp. in increasing distance from a wastewater source, greater change in seasonal cycles was found the furthest from the effluent. This trend is so strong that the furthest location studied actually had an inversion of the Aeromonas spp. cycle in comparison to that of fecal coliforms. Since there is a main pattern in the cycles that occurred simultaneously at all stations it indicates seasonal factors (temperature, solar radiation, phytoplankton) control of the bacterial population. The effluent dominant species changes from Aeromonas caviae in winter to Aeromonas sobria in the spring and fall while the inflow dominant species is Aeromonas caviae, which is constant throughout the seasons.[54]
Sewage treatment in developing countries
Few reliable figures exist on the share of the wastewater collected in sewers that is being treated in the world. In many developing countries the bulk of domestic and industrial wastewater is discharged without any treatment or after primary treatment only. In Latin America about 15 percent of collected wastewater passes through treatment plants (with varying levels of actual treatment). In Venezuela, a below average country in South America with respect to wastewater treatment, 97 percent of the country’s sewage is discharged raw into the environment.[55] In a relatively developed Middle Eastern country such as Iran, the majority of Tehran's population has totally untreated sewage injected to the city’s groundwater.[56] However, the construction of major parts of the sewage system, collection and treatment, in Tehran is almost complete, and under development, due to be fully completed by the end of 2012. In Isfahan, Iran's third largest city, sewage treatment was started more than 100 years ago.
In Israel, about 50 percent of agricultural water usage (total use was 1 billion cubic metres in 2008) is provided through reclaimed sewer water. Future plans call for increased use of treated sewer water as well as more desalination plants.[57]
Most of sub-Saharan Africa is without wastewater treatment.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Khopkar, S. M. (2004). Environmental Pollution Monitoring And Control. New Delhi: New Age International. p. 299. ISBN 81-224-1507-5.
- ^ PUB (Singapore National Water Agency)(2011). "NEWater: History."
- ^ Ashton, John (1991). "The Healthy City and the Ecological Idea" (PDF). Journal of the Society for the Social History of Medicine. 4 (1): 173–181. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Lewis Dunbar B. Gordon (1851). A short description of the plans of Captain James Vetch for the sewerage of the metropolis.
- ^ H. H. Stanbridge (1976). History of Sewage Treatment in Britain. Institute of Water Pollution Control.
- ^ P. F. Cooper. "Historical aspects of wastewater treatment" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- ^ Martin V. Melosi (2010). The Sanitary City: Environmental Services in Urban America from Colonial Times to the Present. University of Pittsburgh Press. p. 110.
- ^ Colin A. Russell (2003). Edward Frankland: Chemistry, Controversy and Conspiracy in Victorian England. Cambridge University Press. pp. 372–380.
- ^ Sharma, Sanjay Kumar; Sanghi, Rashmi (2012). Advances in Water Treatment and Pollution Prevention. Springer. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ EPIDEMICS, DEMONSTRATION EFFECTS, AND MUNICIPAL INVESTMENT IN SANITATION CAPITAL
- ^ "Edwin Chadwick and the Engineers, 1842-1854: Systems and Antisystems in the Pipe-and-Brick Sewers War Technology and Culture" (PDF). 1992.
- ^ Tilley, David F. (2011). Aerobic Wastewater Treatment Processes: History and Development. IWA Publishing. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ FINAL REPORT OF THE COMMISSIONERS APPOINTED TO INQUIRE AND REPORT WHAT METHODS OF Treating and Disposing of Sewage. 1912
- ^ Beychok, Milton R. (1967). Aqueous Wastes from Petroleum and Petrochemical Plants (1st ed.). John Wiley & Sons Ltd. LCCN 67019834.
- ^ Condensed History of Fine Bubble Diffused Air (FBDA)
- ^ Benidickson, Jamie (2011). The Culture of Flushing: A Social and Legal History of Sewage. UBC Press. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ a b Metcalf & Eddy, Inc. (1972). Wastewater Engineering. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company. ISBN 0-07-041675-3.
- ^ Burrian, Steven J., et al. (1999)."The Historical Development of Wet-Weather Flow Management." US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Cincinnati, OH. Document No. EPA/600/JA-99/275.
- ^ Stormwater Effects Handbook: A Toolbox for Watershed Managers, Scientists, and Engineers. New York: CRC/Lewis Publishers. 2001. ISBN 0-87371-924-7. Chapter 2.
- ^ Water and Environmental Health at London and Loughborough (1999). "Waste water Treatment Options." Technical brief no. 64. London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and Loughborough University.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o EPA. Washington, DC (2004). "Primer for Municipal Waste water Treatment Systems." Document no. EPA 832-R-04-001.
- ^ Roy F. Weston, Inc. (1971). Process Design Manual for Upgrading Existing Wastewater Treatment Plants. Washington, D.C.: EPA. Chapter 3.
- ^ Huber Company, Berching, Germany (2012). "Sedimentation Tanks."
- ^ Archived 2010-10-26 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Maine Department of Environmental Protection. Augusta, ME. "Aerated Lagoons – Wastewater Treatment." Maine Lagoon Systems Task Force. Accessed 2010-07-11.
- ^ a b c d Beychok, M.R. (1971). "Performance of surface-aerated basins". Chemical Engineering Progress Symposium Series. 67 (107): 322–339.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) Available at CSA Illumina website - ^ Kadam, A.; Ozaa, G.; Nemadea, P.; Duttaa, S.; Shankar, H. (2008). "Municipal wastewater treatment using novel constructed soil filter system". Chemosphere. 71 (5). Elsevier: 975–981. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.048. PMID 18207216.
- ^ Nemade, P.D.; Kadam, A.M.; Shankar, H.S. (2009). "Wastewater renovation using constructed soil filter (CSF): A novel approach". Journal of Hazardous Materials. 170 (2–3). Elsevier: 657–665. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.015. PMID 19501460.
- ^ A documentary video detailing a 3 MLD SBT plant deployed at the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation for Mumbai city can be seen at "SBT at BMC Mumbai" on YouTube
- ^ EPA. Washington, DC (2007). "Membrane Bioreactors." Wastewater Management Fact Sheet.
- ^ B. Kartal, G.J. Kuenen and M.C.M van Loosdrecht Sewage Treatment with Anammox, Science, 2010, vol 328 p 702-3
- ^ http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2005/11/1109_051109_rocketfuel.html
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3264106/
- ^ Black & Veatch, Inc. (1971). Process Design Manual for Phosphorus Removal. Washington, D.C.: EPA. p. 2-1.
- ^ Das, Tapas K. (August 2001). "Ultraviolet disinfection application to a wastewater treatment plant". Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy. 3 (2). Springer Berlin/Heidelberg: 69–80. doi:10.1007/S100980100108.
- ^ Florida Department of Environmental Protection. Talahassee, FL. "Ultraviolet Disinfection for Domestic Waste water." 2010-03-17.
- ^ Harshman, Vaughan; Barnette, Tony (2000-12-28). "Wastewater Odor Control: An Evaluation of Technologies". Water Engineering & Management. ISSN 0273-2238.
- ^ Walker, James D. and Welles Products Corporation (1976)."Tower for removing odors from gases." U.S. Patent No. 4421534.
- ^ EPA. Washington, DC (2000). "Package Plants." Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet. Document no. EPA 832-F-00-016.
- ^ EPA. Washington, DC (1999). "Sequencing Batch Reactors." Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet. Document no. EPA 832-F-99-073.
- ^ Hammer, Mark J. (1975). Water and Waste-Water Technology. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 390–391. ISBN 0-471-34726-4.
- ^ IPEC Consultants, Ltd., Burnaby, BC, Canada. "IFT – Internally-fed – rotary thickener." Accessed 2012-06-16.
- ^ Mine-engineer.com, Long Beach, CA. "Belt Filter Press, How Does It Work?" Accessed 2012-06-16.
- ^ GlobalSpec, Inc., East Greenbush, NY. "How to Select Dewatering Equipment." Accessed 2012-06-12.
- ^ Biomass – Using Anaerobic Digestion. esru.strath.ac.uk
- ^ Langenkamp, H., Part, P. (2001). "Organic Contaminants in Sewage Sludge for Agricultural Use." European Commission Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Soil and Waste Unit. Brussels, Belgium.
- ^ Archived 2006-08-04 at the Wayback Machine. environment-agency.gov.uk. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.
- ^ Natural Environmental Research Council – River sewage pollution found to be disrupting fish hormones. Planetearth.nerc.ac.uk. Retrieved on 2012-12-19.
- ^ Archived 2011-10-15 at the Wayback Machine. USGS
- ^ Haughey, A. (1968). "The Planktonic Algae of Auckland Sewage Treatment Ponds". New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 2 (4): 721. doi:10.1080/00288330.1968.9515271.
- ^ Edmondson, W.T. (1972). "Nutrients and Phytoplankton in Lake Washington." in Nutrients and Eutrophication: The Limiting Nutrient Controversy. American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Special Symposia. Vol. 1.
- ^ Caperon, J.; Cattell, S. A. and Krasnick, G. (1971). "Phytoplankton Kinetics in a Subtropical Estuary: Eutrophication" (PDF). Limnology and Oceanography. 16 (4): 599. doi:10.4319/lo.1971.16.4.0599.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Curds, C.R; Cockburn, A (1970). "Protozoa in biological sewage-treatment processes—I. A survey of the protozoan fauna of British percolating filters and activated-sludge plants". Water Research. 4 (3): 225. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(70)90069-2.
- ^ Monfort, P; Baleux, B (1990). "Dynamics of Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas sobria, and Aeromonas caviae in a sewage treatment pond". Applied and environmental microbiology. 56 (7): 1999–2006. PMC 184551. PMID 2389929.
- ^ Caribbean Environment Programme (1998). Appropriate Technology for Sewage Pollution Control in the Wider Caribbean Region (PDF). Kingston, Jamaica: United Nations Environment Programme. Retrieved 2009-10-12. Technical Report No. 40.
- ^ Massoud Tajrishy and Ahmad Abrishamchi (2005). "Integrated Approach to Water and Wastewater Management for Tehran, Iran." Water Conservation, Reuse, and Recycling: Proceedings of the Iranian-American Workshop. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press.
- ^ Martin, Andrew (2008-08-10). "Farming in Israel, without a drop to spare". New York Times.
External links
- Interactive Diagram of Wastewater Treatment – "Go with the Flow" – Water Environment Federation, (available in English and Spanish and French).
- [ Improved Modelling of Wastewater Treatment Primary Clarifier Using Hybrid Anns]https://pureapps2.hw.ac.uk/portal/files/2687114/IJCSAI10061_20121228_164131_8693_9362.pdf


