33rd G8 summit: Difference between revisions
m Undid revision 280662769 by 122.163.218.174 (talk)rv? |
Lucy-marie (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Composition of summit leaders== |
==Composition of summit leaders== |
||
The composition of the G8 summit is a perennial topic. The G8 summits after 1997 considered the [[President of the European Commission]] as a permanently welcome participant in all meetings and decision-making, which means that this G8 summit has nine essential participants.<ref name="reuters_what"/> |
The composition of the G8 summit is a perennial topic. The G8 summits after 1997 considered the [[President of the European Commission]] as a permanently welcome participant in all meetings and decision-making, which means that this G8 summit has nine essential participants.<ref name="reuters_what"/> |
||
===Permanent G8 |
===Permanent G8 participants=== |
||
[[Image:33rdG8Leaders.jpg|thumb|300px|G8 "family photo" at the Heiligendamm summit. From left are: Prime Minister [[Stephen Harper]] of Canada; Prime Minister [[Tony Blair]] of the United Kingdom; [[José Manuel Durão Barroso]], President of the European Commission; President [[Nicolas Sarkozy]] of France; President [[Vladimir Putin]] of Russia; Prime Minister [[Shinzo Abe]] of Japan; Chancellor [[Angela Merkel]] of Germany; Prime Minister [[Romano Prodi]] of Italy, and President [[George W. Bush]] of the United States.]] |
[[Image:33rdG8Leaders.jpg|thumb|300px|G8 "family photo" at the Heiligendamm summit. From left are: Prime Minister [[Stephen Harper]] of Canada; Prime Minister [[Tony Blair]] of the United Kingdom; [[José Manuel Durão Barroso]], President of the European Commission; President [[Nicolas Sarkozy]] of France; President [[Vladimir Putin]] of Russia; Prime Minister [[Shinzo Abe]] of Japan; Chancellor [[Angela Merkel]] of Germany; Prime Minister [[Romano Prodi]] of Italy, and President [[George W. Bush]] of the United States.]] |
||
This was the first G8 summit for Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and French President Nicolas Sarkozy, and the final one for British Prime Minister Tony Blair, Italian Prime Minister Romano Prodi and Russian President Vladimir Putin. |
This was the first G8 summit for Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and French President Nicolas Sarkozy, and the final one for British Prime Minister Tony Blair, Italian Prime Minister Romano Prodi and Russian President Vladimir Putin. |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* {{flagicon|United Kingdom}} '''[[United Kingdom]]''' [[Tony Blair]], [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|Prime Minister]] |
* {{flagicon|United Kingdom}} '''[[United Kingdom]]''' [[Tony Blair]], [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|Prime Minister]] |
||
* {{flagicon|USA}} '''[[United States]]''' [[George W. Bush]], [[President of the United States|President]] |
* {{flagicon|USA}} '''[[United States]]''' [[George W. Bush]], [[President of the United States|President]] |
||
+ |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
===Invited (partial participation)=== |
===Invited (partial participation)=== |
||
| Line 54: | Line 52: | ||
* [[Image:Flag of WHO.svg|22px|WHO]] '''[[World Health Organization]]''' [[Margaret Chan]], Director-General. |
* [[Image:Flag of WHO.svg|22px|WHO]] '''[[World Health Organization]]''' [[Margaret Chan]], Director-General. |
||
* <!-- Image with inadequate rationale removed: [[Image:Wto logo.png|22px]] -->'''[[World Trade Organization]]''' [[Pascal Lamy]], Director-General. |
* <!-- Image with inadequate rationale removed: [[Image:Wto logo.png|22px]] -->'''[[World Trade Organization]]''' [[Pascal Lamy]], Director-General. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Priorities== |
==Priorities== |
||
Revision as of 21:26, 10 April 2009
| 33rd G8 Summit | |
|---|---|
| File:G8 Heiligendamm 2007.png 33rd G8 Summit official logo | |
| Host country | Germany |
| Dates | June 6 – June 8, |
The 33rd G8 summit took place at Kempinski Grand Hotel in Heiligendamm in the old Duchy of Mecklenburg in the Northern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern on the Baltic Coast.[1] The group of eight leaders met together from June 6 to June 8 2007.The locations of previous G8 summits to have been hosted by Germany include: Bonn (1978, 1985); Munich (1992) and Cologne (1999).
Overview
The Group of Seven (G7) was an unofficial forum which brought together the heads of the richest industrialized countries: France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada starting in 1976. The G8, meeting for the first time in 1997, was formed with the addition of Russia.[2] In addition, the President of the European Commission has been formally included in summits since 1981.[3] The summits were not meant to be linked formally with wider international institutions; and in fact, a mild rebellion against the stiff formality of other international meetings was a part of the genesis of cooperation between France's President Giscard d'Estaing and Germany's Chancellor Helmut Schmidt as they conceived the initial summit of the Group of Six (G6) in 1975.[4]
The G8 summits during the twenty-first century have inspired widespread debates, protests and demonstrations; and the two- or three-day event becomes more than the sum of its parts, elevating the participants, the issues and the venue as focal points for activist pressure.[5]
Composition of summit leaders
The composition of the G8 summit is a perennial topic. The G8 summits after 1997 considered the President of the European Commission as a permanently welcome participant in all meetings and decision-making, which means that this G8 summit has nine essential participants.[3]
Permanent G8 participants

This was the first G8 summit for Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and French President Nicolas Sarkozy, and the final one for British Prime Minister Tony Blair, Italian Prime Minister Romano Prodi and Russian President Vladimir Putin.
 Canada Stephen Harper, Prime Minister
Canada Stephen Harper, Prime Minister France Nicolas Sarkozy, President
France Nicolas Sarkozy, President Germany Angela Merkel, Chancellor[6]
Germany Angela Merkel, Chancellor[6] Italy Romano Prodi, Prime Minister
Italy Romano Prodi, Prime Minister Japan Shinzo Abe, Prime Minister
Japan Shinzo Abe, Prime Minister Russia Vladimir Putin, President
Russia Vladimir Putin, President United Kingdom Tony Blair, Prime Minister
United Kingdom Tony Blair, Prime Minister United States George W. Bush, President
United States George W. Bush, President
Invited (partial participation)
The leaders of a number of non-G8 countries were invited to attend and participate in the summit.
G8+5
The G8 plus the five largest emerging economies has come to be known as G8+5.
 Brazil Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, President.
Brazil Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, President. China Hu Jintao, President.
China Hu Jintao, President. India Manmohan Singh, Prime Minister.
India Manmohan Singh, Prime Minister. Mexico Felipe Calderón, President.
Mexico Felipe Calderón, President. South Africa Kgalema Motlanthe, President.
South Africa Kgalema Motlanthe, President.
Heads of international organizations
Leaders of the major international organizations, such as the United Nations, WTO, OECD, World Bank, the African Union and the International Energy Agency, have also been invited to participate in the outreach sessions.
- African Union John Kufuor, AU Commission Chairman; Alpha Oumar Konaré, AU Chairman.
 Commonwealth of Independent States Nursultan Nazarbayev, Executive Secretary
Commonwealth of Independent States Nursultan Nazarbayev, Executive Secretary International Atomic Energy Agency Mohamed ElBaradei, Director General
International Atomic Energy Agency Mohamed ElBaradei, Director General United Nations Ban Ki-moon, Secretary-General
United Nations Ban Ki-moon, Secretary-General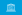 UNESCO Koichiro Matsuura, Director General.
UNESCO Koichiro Matsuura, Director General.- World Bank Paul Wolfowitz, President.
 World Health Organization Margaret Chan, Director-General.
World Health Organization Margaret Chan, Director-General.- World Trade Organization Pascal Lamy, Director-General.
 European Union Jose Manuel Barroso, Commission President[6]
European Union Jose Manuel Barroso, Commission President[6]
Priorities

Traditionally, the host country of the G8 summit sets the agenda for negotiations, which take place primarily amongst multi-national civil servants in the weeks before the summit itself, leading to a joint declaration which all countries can agree to sign.[7] In any event, security for the world leaders and for the venue remained a high priority throughout.
Issues
The summit was intended as a venue for resolving differences among its members. As a practical matter, the summit was also conceived as an opportunity for its members to give each other mutual encouragement in the face of difficult economic decisions.[4]
Schedule and Agenda
At the end of the 32nd G8 summit in Russia, German Chancellor Angela Merkel reported that the agenda of the G8 summit in 2007 had not been determined, but "the struggle against poverty across the globe will be a priority."[8]
According to the official German Presidency website, the summit's motto was "Growth and Responsibility," focusing on "Investition, Innovation und Nachhaltigkeit (Investment, Innovation and Sustainability)", and "Africa: good governance, sustainable investment, peace and security".[9] Transparency of the financial markets, intellectual property and energy efficiency will also be on the agenda, as well as talks about climate change.
On April 13, 2007, Oil Change International released a reported leaked draft of the economic communique.[10] The G8 financial ministers began pre-summit meetings on 30 May 2007.[11]
Citizens' responses and authorities' counter-responses
Protesters and demonstrations



As with all recent G8 summits, the event drew large protests, part of the anti-globalization movement (a term not generally used by its supporters). However, because of the isolated location of the summit, protests were much smaller than in previous years. On December 29, 2006, anonymous protesters splattered the Kempinski hotel with red and black paintbombs; the combination of red and black is a common symbol of the anarchist movement for flags, banners, stickers etc. For the 33rd G8 summit, the local police expected about 100,000 protesters from all parts of Germany and other countries. Preparations were nervous on both sides: 16,000 policemen and over 1,000 soldiers were deployed to protect the interests of the G8 heads of state and government, a 12 kilometer-long steel fence was built around Heiligendamm for the price of €12.4 million (approx. $16.6 million), and ATTAC Germany chartered three trains to get as many discontented citizens as possible from the farther parts of Germany and nearby countries to the year's biggest unified demonstration against G8,[12] along with numerous buses organized by various groups and political parties. The main demonstration took place June 2, 2007 in the nearby city of Rostock and was the starting event for a week of protests and blockades. Organizers spoke of up to 80,000 participants, while police put the figure at an estimated 25,000.[13] Towards the end of the June 2 protest, violent clashes occurred between protesters and the police, essentially limited to a small area at the harbor. Initially, these drew wide media overstatement, with initial reports claiming nearly 1000 people injured (433 German police officers, 30–33 of them requiring hospitalisation,[14] and 520 protesters, 20 requiring hospitalisation[15]). Later, these figures were disputed,[16] and the number of police requiring hospitalization was corrected to 2.[17] According to police estimates, 2,000 autonomists led the riots, setting fire to a total of 3 cars and setting up make-shift barricades; many peaceful protesters fled the action and ensuing police response in panic.[18] Over 1,000 protesters were detained, and nine of them were tried and condemned during the summit [19]. Hundreds were expelled [19]. According to the European Democratic Lawyers NGO:
The evidence collected in this manner was absolutely inconsistent and as previously noted everybody detained was released after brief periods of time. In fact it all amounts to an illegal system of mass-indexing and psychological terrorism. The police were aware that the judicial authority would not have confirmed these arrests but proceeded equally with a different objective. The aim was not to arrest presumed offenders but the indexing of a great number of demonstrators, the psychological intimidation of the protesters and the creation of false records to be used in other occasions.[19]
A protest also occurred on 2 June 2007 on the river bank opposite the Houses of Parliament in London, principally a reminder of the G8's previous (and, as the protestors saw them, unfulfilled) promises on debt relief, entitled "G8 – The World Can't Wait" and "Wake Up To Poverty". It was a static protest, with small marches converging on in from Lambeth Park and Methodist Central Hall, on a route starting at the foot of Victoria Tower, along the riverbank of Victoria Tower Gardens, the north side of Lambeth Bridge, and the southern riverbank opposite Parliament as far as (but not including) Westminster Bridge. This principally involved the protesters setting off alarm clocks at 2pm as a "wakeup call" to the G8, and passed without incident.[20]
The protesters had little effect on the leaders of the top industrialized nations because they couldn't get close enough to disturb the windswept quiet of Heiligendamm's streets.[21]
Accomplishments
The G8 summit is an international event which is observed and reported by news media, but the G8's continuing relevance after more than 30 years is somewhat unclear.[22] More than one analyst suggests that a G-8 summit is not the place to flesh out the details of any difficult or controversial policy issue in the context of a three-day event. Rather, the meeting offers an opportunity to bring a range of complex and sometimes inter-related issues. The G8 summit brings leaders together "not so they can dream up quick fixes, but to talk and think about them together."[23] [8]
Global warming
In a non-binding communiqué issued on Thursday June 7, it was announced that the G8 nations would 'aim to at least halve global CO2 emissions by 2050'. The details which would enable this salutatory goal to be achieved were left to be negotiated.[24]
It was anticipated that the G8 Environment ministers would work together within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in a process that would also include the major emerging economies. Groups of countries would also be able to reach additional agreements on achieving the goal outside and in parallel with the United Nations process.[25]
The G8 also announced their desire to use the proceeds from the auction of emission rights and other financial tools to support climate protection projects in developing countries.[25]
The agreement was welcomed by British Prime Minister Tony Blair as 'a major, major step forward'.[26] French president Nicolas Sarkozy would have preferred a binding figure for emissions reduction to have been set.[27] This was apparently blocked by U.S. President George W. Bush until the other major greenhouse gas emitting countries, like India and China, make similar commitments.[28]
Missile defence system

En route to the summit, U.S. president George Bush attempted to assuage Russian concerns over U.S. plans to construct a missile defence system in Poland (see US missile defense complex in Poland) and the Czech Republic with remarks appearing to invite Russian participation in the project. At the summit, Russian president Vladimir Putin responded by suggesting that the radar installments for the proposed missile defence system be placed in Azerbaijan. Bush, in turn, responded by describing Putin's ideas as "an interesting suggestion".
G8+5 Institutionalisation
Chancellor Angela Merkel announced the establishment of the "Heiligendamm Process" through which the full institutionalisation of the permanent dialogue between the G8 countries and the 5 greatest emerging economies will be implemented.
This process puts an end to the enlargement debate of the G8 into a hypothetical G9, G11, etc. since Merkel declared "The objective is the cohesion of all these countries into a single group which will be called G8+5".
Controversed video of Sarkozy
Contrary to French TV, the Belgian TV network diffused a video of French President Nicolas Sarkozy who appeared to be drunk after a chat with Russian head of state Vladimir Putin [29].
Infrastructure Consortium for Africa
The Infrastructure Consortium for Africa (ICA) was established at the 31st G8 summit at Gleneagles, Scotland in the United Kingdom in 2005. Since that time, the ICA’s annual meeting is traditionally hosted by the country holding the Presidency of the G8 -- in Russia in 2007.[30]
Location

Heiligendamm is situated on the Baltic near the city Rostock, and is the oldest seaside resort in Germany[31], developed in 1793 as the seaside meeting place of nobility and high society close to Frederick Francis I, Duke of Mecklenburg. It was selected as the location for the G8 summit due to its isolated location, in anticipation of protests such as those in Gleneagles and St Petersburg. The summit site was fenced off by 12 km long barrier, costing an approximate EUR 12.4 million.[32]
Heiligendamm, known as "White Town by the Sea", also used to be the summer getaway of the Russian imperial family, who also were related to the Dukes of Mecklenburg. For the occasion of the G8 summit, a former summer residence of the imperial family was demolished to make space for a media centre.[32]
Business opportunity
For some, the G8 summit became a profit-generating event; as for example, the official G8 Summit magazines which have been published under the auspices of the host nations for distribution to all attendees since 1998.[33]
Security precautions included a $17 million, 8-foot-high, 7.5-mile-long fence topped with barbed and razor wire, which encompassed the landward access to the resort;[34] but no protests were reported from the suppliers of the fencing materials.
See also
Notes
- ^ Bradley, Kimberly. "A Spa Town Reclaims Its Glory," New York Times. June 3, 2007.
- ^ Saunders, Doug. "Weight of the world too heavy for G8 shoulders," Globe and Mail (Toronto). July 5, 2008.
- ^ a b Reuters: "Factbox: The Group of Eight: what is it?", July 3, 2008.
- ^ a b Reinalda, Bob and Bertjan Verbeek. (1998). Autonomous Policy Making by International Organizations, p. 205.
- ^ "Influencing Policy on International Development: G8," BOND (British Overseas NGOs for Development). 2008.
- ^ a b Angela Merkel attended as German Chancellor and as the President of the European Council
- ^ G8 Information Centre: Prospective agenda
- ^ a b
"German Chancellor holds news conference on results of G8 summit". G8Russia. 2006-07-17. Retrieved 2006-07-19.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Official Agenda, g-8.de
- ^ Template:PDFlink, draft of February 2007
- ^ "Ministers in talks for G8 summit", BBC News, 30 May 2007
- ^ Press release of the demonstration consortium, 24 April 2007
- ^ "An Orgy of Violence as G8 Approaches; German City Rocked by Violent Riots," Der Spiegel. JUne 2, 2007.
- ^ Yahoo.de News: Zahl der verletzten Polizisten in Rostock auf 433 gestiegen
- ^ Yahoo.de News: Organisatoren zählen 520 verletzte Demonstranten nach Krawallen
- ^ Focus online: Rostock-Krawalle: Zahl der Verletzten zweifelhaft
- ^ junge Welt: Kampf um die Köpfe
- ^ German city rocked by violent riots - SPIEGEL.de international edition
- ^ a b c European Democratic Lawyers (EDL): Press statement (in English)
- ^ "Wakeup call" demonstration
- ^ Landler, Mark. "Thousands of Protesters Foil Some German Security Measures and Clash With the Police," New York Times. June 7, 2007.
- ^ Lee, Don. "On eve of summit, G-8's relevance is unclear," Los Angeles Times. July 6, 2008.
- ^ Feldman, Adam. "What's Wrong With The G-8," Forbes (New York). July 7, 2008.
- ^ Landler, Mark and Judy Dempsey. [http://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/08/world/europe/08climate.html?scp=3&sq=Heiligendamm%20&st=cse "U.S. Compromise on Global Warming Plan Averts Impasse at Group of 8 Meeting,"} New York Times. June 8, 2007.
- ^ a b Breakthrough on climate protection, G8 Summit 2007 Heiligendamm, published 2007-06-07, accessed 2007-06-07
- ^ PM hails G8 climate change step Guardian Unlimited, published 2007-06-07, accessed 2007-06-07
- ^ Sarkozy says would have preferred climate change target to be binding, Forbes, published 2007-06-07, accessed 2007-06-07
- ^ G8 leaders agree "substantial" greenhouse gas cuts, Reuters, published 2007-06-07, accessed 2007-06-07
- ^ The Controversed Video of Sarkozy in the G8, Le Monde, 10 June 2007 (with links to the video)
- ^ "Meeting to Discuss Crisis Impact in Africa's Infrastructure Development," Afrol News. March 2, 2009.
- ^ "Heiligendamm - First German Seaside Resort". Retrieved 2006-07-19.
- ^ a b Heiligendamm Prepares for the G8 Summit. Deutsche Welle, 17 February 2007. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ Prestige Media: "official" G8 Summit magazine
- ^ Landler, Mark. "Thousands of Protesters Foil Some German Security Measures and Clash With the Police," New York Times. June 7, 2007.
References
- Bayne, Nicholas and Robert D. Putnam. (2000). Hanging in There: The G7 and G8 Summit in Maturity and Renewal. Aldershot, Hampshire, England: Ashgate Publishing. 10-ISBN 0-754-61185-X; 13-ISBN 978-0-754-61185-1; OCLC 43186692
- Reinalda, Bob and Bertjan Verbeek. (1998). Autonomous Policy Making by International Organizations. London: Routledge. 10-ISBN 0-415-16486-9; 13-ISBN 978-0-415-16486-3
External links
- Official G8 website: Heiligendamm summit, 2007; n.b., no official website is created for any G7 summit prior to 1995 -- see the 21st G7 summit.
- University of Toronto: G8 Research Group, G8 Information Centre
General
- Official website of the related anti G8 demonstration / English version (less extensive)
- MODEL G8 YOUTH SUMMIT 2007, G8-Simulation, Berlin - May 2007
- Reported "leaked draft" of Economic Communique
- Reported "leaked draft" of Global Warming Communique (with US Government redlining)
- G8 TV - daily video stream from the G8
- 33rd G8 summit: Issues and controversies (BBC)
- Internationalist Review: The Presence of the Past - How German fear of terrorism in the 1970s might restrict criticism of the G8 today
Security
In the media
- May 31, 2007, Agence France-Presse: Bush pushes new climate change plan
- May 14, 2007, BBC: US seeks G8 climate text changes
