The Holocaust in Estonia: Difference between revisions
Replaced data from an erroneous source with updated info. |
|||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
A selection process was supervised by Ain Mere, chief of [[Security Police in Estonia (1942-1944)|Sicherheitspolizei]] in Estonia; those not selected for slave labor were sent by bus to an execution site near the camp. Usually able bodied men were selected to work on the [[oil shale]] mines in northeastern Estonia. Women, children, and old people would be executed on arrival. In the case ''Be 1.9.1942'' however, the only ones chosen for labor and to survive the war were a small group of young women who were taken through concentration camps in Estonia, Poland and Germany to [[Bergen-Belsen concentration camp|Bergen-Belsen]], where they were liberated.<ref>[http://www.bterezin.org.il/newsletter/dapey_59/eng59.doc From Ghetto Terezin to Lithuania and Estonia]</ref> Later the police<ref name="levandehistoria" /> in teams of 6 to 8 men<ref name="epl"/> would execute the Jews by [[machine gun]] fire, on other hand, during later investigation some guards of camp denied participation of police and said that execution was done by camp personnel<ref name="epl"/>. On the first day a total of 900 people were murdered in this way.<ref name="levandehistoria" /><ref name="epl"/> Gerrets told that he had fired a pistol at a victim who was still making noises in the pile of bodies.<ref name="levandehistoria" /><ref name="video" /> The whole operation was directed by [[Obersturmführer]] [[Heinrich Bergmann]] and [[Oberscharführer]] J. Geese.<ref name="epl">[http://www.epl.ee/?artikkel=316769 Jägala laager ja juutide hukkamine Kalevi-Liival] – [[Eesti Päevaleht]] March 30, 2006 {{et icon}}</ref><ref name="levandehistoria" /> |
A selection process was supervised by Ain Mere, chief of [[Security Police in Estonia (1942-1944)|Sicherheitspolizei]] in Estonia; those not selected for slave labor were sent by bus to an execution site near the camp. Usually able bodied men were selected to work on the [[oil shale]] mines in northeastern Estonia. Women, children, and old people would be executed on arrival. In the case ''Be 1.9.1942'' however, the only ones chosen for labor and to survive the war were a small group of young women who were taken through concentration camps in Estonia, Poland and Germany to [[Bergen-Belsen concentration camp|Bergen-Belsen]], where they were liberated.<ref>[http://www.bterezin.org.il/newsletter/dapey_59/eng59.doc From Ghetto Terezin to Lithuania and Estonia]</ref> Later the police<ref name="levandehistoria" /> in teams of 6 to 8 men<ref name="epl"/> would execute the Jews by [[machine gun]] fire, on other hand, during later investigation some guards of camp denied participation of police and said that execution was done by camp personnel<ref name="epl"/>. On the first day a total of 900 people were murdered in this way.<ref name="levandehistoria" /><ref name="epl"/> Gerrets told that he had fired a pistol at a victim who was still making noises in the pile of bodies.<ref name="levandehistoria" /><ref name="video" /> The whole operation was directed by [[Obersturmführer]] [[Heinrich Bergmann]] and [[Oberscharführer]] J. Geese.<ref name="epl">[http://www.epl.ee/?artikkel=316769 Jägala laager ja juutide hukkamine Kalevi-Liival] – [[Eesti Päevaleht]] March 30, 2006 {{et icon}}</ref><ref name="levandehistoria" /> |
||
| ⚫ | A German task force liquidated the [[Vaivara concentration camp]] in Klooga.<ref name=hiio>{{cite book|author=Riho Västrik, Meelis Maripuu|year=2006|pages=719–738|chapter=Vaivara concentration camp|editor=Toomas Hiio, Meelis Maripuu, & Indrek Paavle |title=Estonia 1940–1945: Reports of the [[Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity]]|location=Tallinn}}</ref> Survivors report that, during this period when Jewish slave labourers were visible, the Estonian population in part attempted to help the Jews by providing food and so on.<ref name="Birn">Birn, Ruth Bettina (2001), [http://journals.cambridge.org/production/action/cjoGetFulltext?fulltextid=81766 Collaboration with Nazi Germany in Eastern Europe: the Case of the Estonian Security Police]. ''[[Contemporary European History]]''10.2, 181–198. P. 190–191.</ref></blockquote> |
||
According to an article published by the journal "[[Contemporary European History]]" in 2001, |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
A number of foreign witnesses were heard at the [[Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia]], including five women, who had been transported on ''Be 1.9.1942'' from Theresienstadt.<ref name="levandehistoria" /> |
A number of foreign witnesses were heard at the [[Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia]], including five women, who had been transported on ''Be 1.9.1942'' from Theresienstadt.<ref name="levandehistoria" /> |
||
<blockquote>''"The accused Mere, Gerrets and Viik actively participated in crimes and mass killings that were perpetrated by the Nazi invaders on the territory of the [[Estonian SSR]]. In accordance with the Nazi racial theory, the [[Sicherheitspolizei]] and [[Sicherheitsdienst]] were instructed to exterminate the Jews and Gypsies. For that end in August–September 1941 Mere and his collaborators set up a death camp at Jägala, 30 km from Tallinn. Mere put Aleksander Laak in charge of the camp; Ralf Gerrets was appointed his deputy. On 5 September 1942 a train with approximately 1,500 Czechoslovak citizens arrived to the [[Raasiku]] railway station. Mere, Laak and Gerrets personally selected who of them should be executed and who should be moved to the Jägala death camp. More than 1,000 people, mostly children, the old, and the infirm, were translocated to a wasteland at Kalevi-Liiva where they were monstrously executed in a special pit. In mid-September the second troop train with 1,500 prisoners arrived to the railway station from Germany. Mere, Laak, and Gerrets selected another thousand victims that were condemned by them to extermination. This group of prisoners, which included nursing women and their new-born babies, were transported to Kalevi-Liiva where they were killed.<br /> |
<blockquote>''"The accused Mere, Gerrets and Viik actively participated in crimes and mass killings that were perpetrated by the Nazi invaders on the territory of the [[Estonian SSR]]. In accordance with the Nazi racial theory, the [[Sicherheitspolizei]] and [[Sicherheitsdienst]] were instructed to exterminate the Jews and Gypsies. For that end in August–September 1941 Mere and his collaborators set up a death camp at Jägala, 30 km from Tallinn. Mere put Aleksander Laak in charge of the camp; Ralf Gerrets was appointed his deputy. On 5 September 1942 a train with approximately 1,500 Czechoslovak citizens arrived to the [[Raasiku]] railway station. Mere, Laak and Gerrets personally selected who of them should be executed and who should be moved to the Jägala death camp. More than 1,000 people, mostly children, the old, and the infirm, were translocated to a wasteland at Kalevi-Liiva where they were monstrously executed in a special pit. In mid-September the second troop train with 1,500 prisoners arrived to the railway station from Germany. Mere, Laak, and Gerrets selected another thousand victims that were condemned by them to extermination. This group of prisoners, which included nursing women and their new-born babies, were transported to Kalevi-Liiva where they were killed.<br /> |
||
Revision as of 15:08, 22 April 2010
The Holocaust in Estonia refers to the Nazi crimes during the occupation of Estonia by Nazi Germany. There were, prior to the war, approximately 4,300 Estonian Jews. After the Soviet 1940 occupation about 10% of Jewish population were deported to Siberia along with other Estonians. About 75% of Estonian Jews, aware of the fate that awaited them from Nazi Germany, escaped to the Soviet Union; virtually all the remainder (between 950 and 1,000 people) were killed by Einsatzgruppe A and local collaborators before the end of 1941.[1] Roma people of Estonia were also murdered and enslaved by the Nazi occupiers.
Murder of Jewish population
Round-ups and killings of the remaining Jews began immediately by the extermination squad Einsatzkommando (Sonderkommando) 1A under Martin Sandberger, part of Einsatzgruppe A led by Walter Stahlecker, who followed the arrival of the first German troops in July 7, 1941. Arrests and executions continued as the Germans, with the assistance of local collaborators, advanced through Estonia. Estonia became a part of the Reichskommissariat Ostland. A Sicherheitspolizei (Security Police) was established for internal security under the leadership of Ain Mere in 1942. Estonia was declared Judenfrei quite early by the German occupation regime at the Wannsee Conference.[2] Jews that had remained in Estonia (921 according to Martin Sandberger, 929 according to Evgenia Goorin-Loov and 963 according to Walter Stahlecker) were killed.[3] Fewer than a dozen Estonian Jews are known to have survived the war in Estonia.[citation needed]
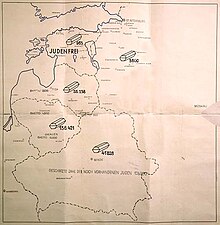
German policy towards the Jews in Estonia
The Estonian state archives contain death certificates and lists of Jews shot dated July, August, and early September 1941. For example the official death certificate of Ruvin Teitelbaum, born in Tapa pn January 17, 1907, states laconically in a form with item 7 already printed with only the date left blank: "7. By a decision of the Sicherheitspolizei on September 4, 1941, condemned to death, with the decision being carried out the same day in Tallinn." Teitelbaum's crime was "being a Jew" and thus constituting a "threat to the public order".
On September 11, 1941 an article entitled "Juuditäht seljal" – "A Jewish Star on the Back" appeared in the Estonian mass-circulation newspaper Postimees. It stated that Dr. Otto-Heinrich Drechsler, the High Commissioner of Ostland, had proclaimed ordinances in accordance with which all Jewish residents of Ostland from that day onward had to wear visible yellow six-pointed Star of David at least 10 cm. in diameter on the left side of their chest and back.
On the same day Regulations [4] issued by the Sicherheitspolizei were delivered to all local police departments proclaiming that the Nuremberg Laws were in force in Ostland, defining who is a Jew, and what Jews could and could not do. Jews were prohibited from changing their place of residence, walking along the sidewalk, using any means of transportation, going to theatres, museums, cinema, or school. The professions of lawyer, physician, notary, banker, or real estate agent were declared closed to Jews, as was the occupation of street hawker. The regulations also declared that the property and homes of Jewish residents were to be confiscated. The regulations emphasized that work to this ends was to be begun as soon as possible, and that lists of Jews, their addresses, and their property were to be completed by the police by September 20, 1941.
These regulations also provided for the establishment of a concentration camp near the south-eastern Estonian city of Tartu. A later decisions provided for the construction of a Jewish ghetto near the town of Harku, but this was never built, a small concentration camp being built there instead. The Estonian State Archives contain material pertinent to the cases of about 450 Estonian Jews. They were typically arrested either at home or in the street, taken to the local police station, and charged with the 'crime' of being Jews. They were either shot outright or sent to concentration camp and shot later. An Estonian woman, E. S. describes the arrest of her Jewish husband as follows[5]:

As my husband did not go out of the house, I was the one to go to town every day to see what was going on. I was very frighteend when I saw a poster at the corner of Vabaduse Square and Harju Street calling for people to show where the apartments of Jews were located. On that fatal day of September 13, I went out again because the weather was fine but I remember being very worried. I rushed home and when I got there and heard some voices in our apartment I had a foreboding that something bad had happened. There were two men in our apartment from the Selbstschutz who said they were taking my husband to the police station. I ran after them and went to the chief officer and asked for permission to see my husband. The chief officer said that he could not give me permission but added, in a low voice, that I should come the next morning when the prisoners would be taken to prison and perhaps I could see my husband in the corridor. I returned the next morning as I had been advised, and it was the last time I saw my husband. On September 15 I went to the German Sicherheitspolizei on Tõnismägi in an attempt to get information about my husband. I was told he had been shot. I asked the reason since he had not been a communist but a businessman, The answer was: "Aber er war doch ein Jude." [But he was a Jew.].
Concentration camps established for foreign Jews
With the invasion of the Baltic States, it was the intention of the Nazi government to use the Baltics countries as their main area of mass genocide. Consequently, Jews from countries outside the Baltics were shipped there to be killed. [6] and an estimated 10,000 Jews were killed in Estonia after having been deported to camps there from elsewhere in Eastern Europe. The Nazi regime also established 22 concentration and labor camps on occupied Estonian territory for foreign Jews. The largest, Vaivara concentration camp housed 1,300 prisoners at a time. These prisoners were mainly Jews, with smaller groups of Russians, Dutch, and Estonians.[7] Several thousand foreign Jews were killed at the Kalevi-Liiva camp. [2] Units of Estonian auxiliary police participated in the extermination of the Jews in Estonia and Pskov region of Russia and provided guards for concentration camps for Jews and Soviet POWs (Jägala, Vaivara, Klooga, Lagedi), where the prisoners were killed – despite the criminal activities in which numbers of policemen were engaged.[8] All members of Police Department B-IV did participate in such crimes.
From 1941 to 1943 Karl Linnas had commanded a Nazi concentration camp at Tartu, Estonia, where he directed and personally took part in the murder of thousands of men, women, and children who were herded into anti-tank ditches.
Concentration camps
KZ-Stammlager
- KZ Vaivara
KZ-Außenlager
- KZ Aseri
- KZ Auvere
- KZ Erides
- KZ Goldfields (Kohtla)
- KZ Ilinurme
- KZ Jewe
- KZ Kerestowo (Karstala-Korostell in Estonian Ingria)
- KZ Kiviöli
- KZ Kukruse
- KZ Kunda
- KZ Kuremaa
- KZ Lagedi

- KZ Lodensee (KZ Klooga; commandant SS-Untersturmführer Wilhelm Werle; September 1943 – September 1944. There were hold 2 000 – 3 000 prisoners, most of them the Lithuanian Jews. When the Red Army approached, SS-men shot the 2 500 prisoners on September 19, 1944 and burned most of the bodies. The less than 100 prisoners succeeded to hide, and survive. There is a monument on the place of the concentration camp.)
- KZ Narwa
- KZ Narwa-Hungerburg
- KZ Putki
- KZ Reval (Ülemiste?)
- KZ Saka
- KZ Sonda
- KZ Soski
- KZ Wiwikond
- KZ Ülenurme
Arbeits- und Erziehungslager
(Nazi terminology about 'extermination camp')
- AEL Jägala (August, 1942 – September 1943)
- AEL Murru
- AEL Reval
- Harku (243 Estonian Romani people were executed in the Harku concentration camp on October 27, 1942.[10])
- Lasnamäe vankila
- AEL Tartu (commandant Karl Linnas)
- AEL Turba (In Ellamaa[11])
Prisons
Other concentration camps
- Dvigatel[12]
- Essu
- Järvakandi
- Laitse
- Lavassaare[13]
- Lehtse
- Lelle[14] (1942 – May, 1943)
- Roela
- Sitsi (In Tallinn, at the end of Tööstuse Street where was 10 barracks; until September 17, 1944.[15])
- Vasalemma
- Vaste
This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. |
War crimes trials
Four Estonians most responsible for the murders at Kalevi-Liiva were accused at war crimes trials in 1961. Two were later executed, while the Soviet occupation authorities were unable to press charges against two who lived in exile. [16] There have been several known 7 ethnic Estonians: Ralf Gerrets, Ain-Ervin Mere, Jaan Viik, Juhan Jüriste, Karl Linnas, Aleksander Laak and Ervin Viks who have faced trials for crimes against humanity committed during the Nazi occupation in Estonia. The accused were charged with murdering up to 5000 German and Czechoslovakian Jews and Romani people near the Kalevi-Liiva concentration camp in 1942–1943. Ain-Ervin Mere, commander of the Estonian Security Police (Group B of the Sicherheitspolizei) under the Estonian Self-Administration, was tried in absentia.
Before the trial Mere was an active member of the Estonian community in England, contributing to Estonian language publications.[17] At the time of the trial he was however held in captivity, accused of murder. He was never deported[18] and died a free man in England in 1969. Ralf Gerrets, the deputy commandant at the Jägala camp. Jaan Viik, (Jan Wijk, Ian Viik), a guard at the Jägala labor camp was singled out for prosecution out of the hundreds of Estonian camp guards and police for his particular brutality.[19] He was testified as throwing small children into the air and shooting them. He did not deny the charge.[20] A fourth accused, camp commandant, Aleksander Laak (Alexander Laak) was discovered in Canada but committed suicide.
Transport of Jews to Estonia
According to testimony of the survivors, at least two transports with about 2,100–2,150 people[21], arrived at the railway station at Raasiku, one from Theresienstadt (Terezin) with Czechoslovakian Jews and one from Berlin with German citizens. Around 1,700–1,750 people, mainly Jews, not selected for work at the Jägala camp were taken to Kalevi-Liiva and shot.[21] Transport Be 1.9.1942 from Theresienstadt arrived at the Raasiku station on September 5, 1942, after a five day trip.[22][23] According to testimony by one of the accused, Gerrets, eight busloads of Estonian auxiliary police had arrived from Tallinn.[23]
Murder or slave labor for transported persons determined upon arrival
A selection process was supervised by Ain Mere, chief of Sicherheitspolizei in Estonia; those not selected for slave labor were sent by bus to an execution site near the camp. Usually able bodied men were selected to work on the oil shale mines in northeastern Estonia. Women, children, and old people would be executed on arrival. In the case Be 1.9.1942 however, the only ones chosen for labor and to survive the war were a small group of young women who were taken through concentration camps in Estonia, Poland and Germany to Bergen-Belsen, where they were liberated.[24] Later the police[23] in teams of 6 to 8 men[21] would execute the Jews by machine gun fire, on other hand, during later investigation some guards of camp denied participation of police and said that execution was done by camp personnel[21]. On the first day a total of 900 people were murdered in this way.[23][21] Gerrets told that he had fired a pistol at a victim who was still making noises in the pile of bodies.[23][20] The whole operation was directed by Obersturmführer Heinrich Bergmann and Oberscharführer J. Geese.[21][23]
A German task force liquidated the Vaivara concentration camp in Klooga.[25] Survivors report that, during this period when Jewish slave labourers were visible, the Estonian population in part attempted to help the Jews by providing food and so on.[26]
A number of foreign witnesses were heard at the Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia, including five women, who had been transported on Be 1.9.1942 from Theresienstadt.[23]
"The accused Mere, Gerrets and Viik actively participated in crimes and mass killings that were perpetrated by the Nazi invaders on the territory of the Estonian SSR. In accordance with the Nazi racial theory, the Sicherheitspolizei and Sicherheitsdienst were instructed to exterminate the Jews and Gypsies. For that end in August–September 1941 Mere and his collaborators set up a death camp at Jägala, 30 km from Tallinn. Mere put Aleksander Laak in charge of the camp; Ralf Gerrets was appointed his deputy. On 5 September 1942 a train with approximately 1,500 Czechoslovak citizens arrived to the Raasiku railway station. Mere, Laak and Gerrets personally selected who of them should be executed and who should be moved to the Jägala death camp. More than 1,000 people, mostly children, the old, and the infirm, were translocated to a wasteland at Kalevi-Liiva where they were monstrously executed in a special pit. In mid-September the second troop train with 1,500 prisoners arrived to the railway station from Germany. Mere, Laak, and Gerrets selected another thousand victims that were condemned by them to extermination. This group of prisoners, which included nursing women and their new-born babies, were transported to Kalevi-Liiva where they were killed.
In March 1943 the personnel of the Kalevi-Liiva camp executed about fifty Gypsies, half of which were under 5 years of age. Also were executed 60 Gypsy children of school age..."[19]
Eesti Omakaitse (Estonian Selbstschutz; approximately between 1000 and 1200 men) were directly involved in criminal acts, taking part in the round-up (and possibly killing) of 200 Roma people and 950 Jews.[8]
Roma people murdered
Few witnesses pointed out Heinrich Bergmann as the key figure behind the extermination of Estonian Roma people.
Sexual slavery
According to Soviet sources, camp commandant Laak used the women as sex slaves, killing at least one who refused to comply.[27]
Modern memorials

Since the reestablishment of the Estonian independence markers were put in place for the 60th anniversary of the mass executions that were carried out at the Lagedi, Vaivara and Klooga (Kalevi-Liiva) camps in September 1944. [28] On February 5, 1945 in Berlin, Ain Mere founded the Eesti Vabadusliit together with SS-Obersturmbannführer Harald Riipalu.[29] He was sentenced to the capital punishment during the Holocaust trials in Soviet Estonia but was not extradited by Great Britain and died there in peace. In 2002 the Government of the Republic of Estonia decided to officially commemorate the Holocaust. In the same year, the Simon Wiesenthal Center had provided the Estonian government with information on alleged Estonian war criminals, all former members of the 36th Estonian Police Battalion.
Collaborators
Organizations
- Einsatzgruppe A
- Estonian Auxiliary Police
- Omakaitse
- Ordnungspolizei
- Sonderkommando 1a
- Sicherheitspolizei
Bibliography
- 12000: Tartus 16.-20.jaanuaril 1962 massimõrvarite Juhan Jüriste, Karl Linnase ja Ervin Viksi üle peetud kohtuprotsessi materjale. Koostanud Karl Lemmik ja Ervin Martinson. Eesti Riiklik Kirjastus. 1962
- Ants Saar, Vaikne suvi vaikses linnas. Kirjastus Eesti Raamat. 1971
- Eesti vaimuhaigete saatus Saksa okupatsiooni aastail (1941–1944), Eesti Arst, nr. 3 Märts 2007
- Ervin Martinson. Elukutse – reetmine. Eesti Raamat 1970
- Ervin Martinson. Haakristi teenrid. Eesti Riiklik Kirjastus 1962
- Inimesed olge valvsad. Koostanud Vladimir Raudsepp. Eesti Riiklik Kirjastus 1961
- Pruun katk. Dokumentide kogumik fašistide kuritegude kohta okupeeritud Eesti NSV territooriumil. Koostanud Ervin Martinson ja A. Matsulevitš. Eesti Raamat 1969
- SS tegutseb. Dokumentide kogumik SS-kuritegude kohta. Eesti Riiklik Kirjastus 1963
References
- ^ Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity, Conclusions of the commission 1998
- ^ a b Museum of Tolerance Multimedia Learning Center
- ^ Küng, Andres, Communism and Crimes against Humanity in the Baltic states, A Report to the Jarl Hjalmarson Foundation seminar on April 13, 1999
- ^ ERA.F.R-89.N.1.S.1.L.2
- ^ Quoted in Eugenia Gurin-Loov, Holocaust of Estonian Jews 1941, Eesti Juudi Kogukond, Tallinn 1994: pg. 224
- ^ The Holocaust in the Baltics at University of Washington
- ^ Vaivara
- ^ a b Conclusions of the Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity
- ^ Quelle und weiterführende Hinweise. Siehe auch die Sechste Verordnung zur Durchführung des Bundesentschädigungsgesetzes (6. DV-BEG)
- ^ Mustlaste likvideerimine Tõrvas
- ^ Haakristi haardes.Tallinn 1979, lk 84
- ^ Haakristi haardes.Tallinn 1979, lk 68
- ^ Haakristi haardes.Tallinn 1979, lk 66
- ^ Haakristi haardes.Tallinn 1979, lk 64
- ^ Haakristi haardes.Tallinn 1979, lk 69
- ^ Estonia at Jewish Virtual Library
- ^ Estonian State Archives of the Former Estonian KGB (State Security Committee) records relating to war crime investigations and trials in Estonia, 1940–1987 (manuscript RG-06.026) – United States Holocaust Memorial Museum – document available on-line through this query page using document id RG-06.026 – Also available at Axis History Forum – This list includes the evidence presented at the trial. It list as evidence several articles by Mere in Estonian language newspapers published in London
- ^ Masses and Mainstream, 1963
- ^ a b Weiss-Wendt, Anton (2003). Extermination of the Gypsies in Estonia during World War II: Popular Images and Official Policies. Holocaust and Genocide Studies 17.1, 31–61.
- ^ a b Estonian policemen stand trial for war crimes – Video footage at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- ^ a b c d e f Jägala laager ja juutide hukkamine Kalevi-Liival – Eesti Päevaleht March 30, 2006 Template:Et icon
- ^ The Genocide of the Czech Jews
- ^ a b c d e f g De dödsdömda vittnar (Transport Be 1.9.1942) Template:Sv icon
- ^ From Ghetto Terezin to Lithuania and Estonia
- ^ Riho Västrik, Meelis Maripuu (2006). "Vaivara concentration camp". In Toomas Hiio, Meelis Maripuu, & Indrek Paavle (ed.). Estonia 1940–1945: Reports of the Estonian International Commission for the Investigation of Crimes Against Humanity. Tallinn. pp. 719–738.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Birn, Ruth Bettina (2001), Collaboration with Nazi Germany in Eastern Europe: the Case of the Estonian Security Police. Contemporary European History10.2, 181–198. P. 190–191.
- ^ Omakaitse omakohus – JERUUSALEMMA SÕNUMID Template:Et icon
- ^ Holocaust Markers, Estonia
- ^ Veebruari sündmused Template:Et icon
- ^ Alo Lõhmus, 1941. aasta suvesõda
- ^ Andrei Hvostov, Jakobsoni komisjon Augeiase tallis
External links
- Articles needing cleanup from March 2009
- Cleanup tagged articles without a reason field from March 2009
- Wikipedia pages needing cleanup from March 2009
- The Holocaust in Estonia
- Military history of Estonia during World War II
- World War II prisoners of war massacres
- World War II casualties
- Soviet–German War
- Eastern Front (World War II)
- Local participation in the Holocaust
