Luni River: Difference between revisions
Io Herodotus (talk | contribs) |
Rescuing 2 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.3.2.4) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.rajirrigation.gov.in/3bluni.htm Luni Basin (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080326193503/http://www.rajirrigation.gov.in/3bluni.htm Luni Basin (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)] |
||
* [http://www.rajirrigation.gov.in/3rivers5.htm Luni tributaries (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080419033829/http://www.rajirrigation.gov.in/3rivers5.htm Luni tributaries (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)] |
||
{{coord|24|39|N|71|11|E|display=title|region:IN_type:river_source:GNS-enwiki}} |
{{coord|24|39|N|71|11|E|display=title|region:IN_type:river_source:GNS-enwiki}} |
||
Revision as of 22:22, 27 May 2017
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2012) |
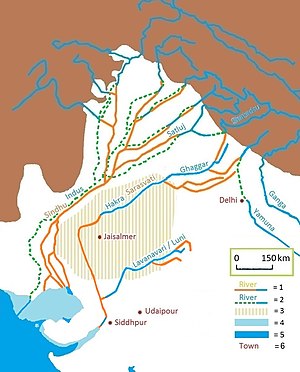
The Luni is an endorheic river of western Rajasthan state, India. It originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range, near Ajmer, passes through the southeastern portion of the Thar Desert, and ends in the marshy lands of Rann of Kutch in Gujarat, after travelling a distance of 495 km. It is first known as Sagarmati, then after passing Govindgarh, it meets its tributary Sarsuti, which originates from Pushkar Lake, and from then on it gets its name Luni.[1]
In 1892, Maharaja Jaswant Singh of Jodhpur constructed Jaswant Sagar in Pichiyak village between Bilara and Bhavi of Jodhpur district. It is one of the largest artificial lakes in India, and irrigates more than 12,000 acres (49 km2).[1]
Etymology
The Luni is also known as the Lavanaravi or Lavanavati, which means "salt river" in Sanskrit, due high salinity of its water.[1]
Overview
The Luni River basin is 37,363 km², which includes all or part of the Ajmer, Barmer, Jalore, Jodhpur, Nagaur, Pali, and Sirohi districts of Rajasthan and the Banaskantha and Patan districts of northern Gujarat. Its major tributaries are the Sukri, Mithri, Bandi, Khari, Jawai, Guhiya and Sagi from the left, and the Jojari River from the right.
The Luni River begins near Ajmer in the Pushkar valley of the western Aravalli Range at an elevation of about 550m. At this point, the river is also known as the Sagarmati. The river then flows in the southwest direction through the hills and plains of the Marwar region in Rajasthan. The river flows south-west and enters the Thar Desert before dissipating into the Rann of Kutch, traversing a total of 495 km. In spite of the high salinity, it is a major river in the region and serves as a primary source of irrigation. The Luni is not saline until it reaches Balotra, where high salt content in the soil impacts the river.
The Luni may have been the southern portion of the historic Ghaggar-Hakra river channel.
References
- ^ a b c Luni River The Imperial Gazetteer of India, 1909, v. 16, p. 211-212.
External links
- Luni Basin (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)
- Luni tributaries (Department of Irrigation, Government of Rajasthan)
24°39′N 71°11′E / 24.650°N 71.183°E
