Gun violence in the United States: Difference between revisions
→Public policy: Copy-edits. |
Rescuing 5 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.6beta3) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
Between 1987 and 1990, [[David McDowall (criminologist)|McDowall]] et al. found that guns were used in defense during a crime incident 64,615 times annually (258,460 times total over the whole period).<ref name="mcdowall">{{cite journal |title=The Incidence of Defensive Firearm Use by US Crime Victims, 1987 through 1990 |author=McDowall, David, Brian Wiersema |journal=[[American Journal of Public Health]] |year=1994 |volume=84 |pages=1982–1984 |pmid=7998641 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.84.12.1982 |issue=12 |pmc=1615397}}</ref> This equated to two times out of 1,000 criminal incidents (0.2%) that occurred in this period, including criminal incidents where no guns were involved at all.<ref name="mcdowall"/> For violent crimes, [[assault]], [[robbery]], and [[rape]], guns were used 0.83% of the time in self-defense.<ref name="mcdowall"/> Of the times that guns were used in self-defense, 71% of the crimes were committed by strangers, with the rest of the incidents evenly divided between offenders that were acquaintances or persons well known to the victim.<ref name="mcdowall"/> In 28% of incidents where a gun was used for self-defense, victims fired the gun at the offender.<ref name="mcdowall"/> In 20% of the self-defense incidents, the guns were used by [[police officer]]s.<ref name="mcdowall"/> During this same period, 1987 to 1990, there were 46,319 gun homicides,<ref>{{cite book |title=Uniform Crime Reports, 1987-1990 |publisher=[[Federal Bureau of Investigation]]}}</ref> and the [[National Crime Victimization Survey]] estimated that 2,628,532 nonfatal crimes involving guns occurred.<ref name="mcdowall"/> |
Between 1987 and 1990, [[David McDowall (criminologist)|McDowall]] et al. found that guns were used in defense during a crime incident 64,615 times annually (258,460 times total over the whole period).<ref name="mcdowall">{{cite journal |title=The Incidence of Defensive Firearm Use by US Crime Victims, 1987 through 1990 |author=McDowall, David, Brian Wiersema |journal=[[American Journal of Public Health]] |year=1994 |volume=84 |pages=1982–1984 |pmid=7998641 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.84.12.1982 |issue=12 |pmc=1615397}}</ref> This equated to two times out of 1,000 criminal incidents (0.2%) that occurred in this period, including criminal incidents where no guns were involved at all.<ref name="mcdowall"/> For violent crimes, [[assault]], [[robbery]], and [[rape]], guns were used 0.83% of the time in self-defense.<ref name="mcdowall"/> Of the times that guns were used in self-defense, 71% of the crimes were committed by strangers, with the rest of the incidents evenly divided between offenders that were acquaintances or persons well known to the victim.<ref name="mcdowall"/> In 28% of incidents where a gun was used for self-defense, victims fired the gun at the offender.<ref name="mcdowall"/> In 20% of the self-defense incidents, the guns were used by [[police officer]]s.<ref name="mcdowall"/> During this same period, 1987 to 1990, there were 46,319 gun homicides,<ref>{{cite book |title=Uniform Crime Reports, 1987-1990 |publisher=[[Federal Bureau of Investigation]]}}</ref> and the [[National Crime Victimization Survey]] estimated that 2,628,532 nonfatal crimes involving guns occurred.<ref name="mcdowall"/> |
||
McDowall's study for the ''[[American Journal of Public Health]]'' contrasted with a 1995 study by [[Gary Kleck|Kleck]] and Gertz, who found that 2.45 million crimes were thwarted each year in the U.S. using guns, and in most cases, the potential victim never fired a shot.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Kleck|first1=Gary|last2=Gertz|first2=Marc|title=Armed Resistance to Crime: The Prevalence and Nature of Self-Defense with a Gun|journal=[[The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology]]|date=Autumn 1995|volume=86|issue=1|pages=150|doi=10.2307/1144004}}</ref> The results of the Kleck studies have been cited many times in scholarly and popular media.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Firearms and the killing threshold (Letter) |author=Suter, E.A. |journal=[[New England Journal of Medicine]] |year=1992 |volume=326 |page=1159 |pmid=1552925 |issue=17 | doi = 10.1056/NEJM199204233261712 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=The value of civilian handgun possession as a deterrent to crime or a defense against crime |author=Kates, D.B. |journal=[[American Journal of Criminal Law]] |year=1991 |volume=18 |pages=113–167 |id={{NCJ|132948}}}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Go ahead, make our day |publisher=[[The New Republic]] |date=February 22, 1988 |pages=7–9}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Do guns save lives? |publisher=[[Time Magazine]] |date=August 12, 1988 |pages=25–26}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Are we "a nation of cowards"? |publisher=[[Newsweek]] |date=November 15, 1993 |pages=93–94}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Hold your fire: gun control won't stop rising violence |author=Kopel, D.B. |publisher=Policy Review |year=1993 |volume=63 |pages=58–65 |id={{NCJ|153748}}}}</ref><ref name="medlit">{{cite web |url=http://teapot.usask.ca/cdn-firearms/Suter/med-lit.html |title=Guns in the Medical Literature - A Failure of Peer Review |author=Edgar A. Suter, MD}}</ref> The methodology of the Kleck and Gertz study has been criticized by some researchers.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cook|first1=Philip J.|last2=Ludwig|first2=Jens|last3=Hemenway|first3=David|title=The gun debate's new mythical number: How many defensive uses per year?|journal=[[Journal of Policy Analysis and Management]]|date=Summer 1997|volume=16|issue=3|pages=463–469|doi=10.1002/(SICI)1520-6688(199722)16:3<463::AID-PAM6>3.0.CO;2-F|url=http://home.uchicago.edu/ludwigj/papers/JPAM_Cook_Ludwig_Hemenway_2007.pdf}}</ref> |
McDowall's study for the ''[[American Journal of Public Health]]'' contrasted with a 1995 study by [[Gary Kleck|Kleck]] and Gertz, who found that 2.45 million crimes were thwarted each year in the U.S. using guns, and in most cases, the potential victim never fired a shot.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Kleck|first1=Gary|last2=Gertz|first2=Marc|title=Armed Resistance to Crime: The Prevalence and Nature of Self-Defense with a Gun|journal=[[The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology]]|date=Autumn 1995|volume=86|issue=1|pages=150|doi=10.2307/1144004}}</ref> The results of the Kleck studies have been cited many times in scholarly and popular media.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Firearms and the killing threshold (Letter) |author=Suter, E.A. |journal=[[New England Journal of Medicine]] |year=1992 |volume=326 |page=1159 |pmid=1552925 |issue=17 | doi = 10.1056/NEJM199204233261712 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=The value of civilian handgun possession as a deterrent to crime or a defense against crime |author=Kates, D.B. |journal=[[American Journal of Criminal Law]] |year=1991 |volume=18 |pages=113–167 |id={{NCJ|132948}}}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Go ahead, make our day |publisher=[[The New Republic]] |date=February 22, 1988 |pages=7–9}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Do guns save lives? |publisher=[[Time Magazine]] |date=August 12, 1988 |pages=25–26}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Are we "a nation of cowards"? |publisher=[[Newsweek]] |date=November 15, 1993 |pages=93–94}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Hold your fire: gun control won't stop rising violence |author=Kopel, D.B. |publisher=Policy Review |year=1993 |volume=63 |pages=58–65 |id={{NCJ|153748}}}}</ref><ref name="medlit">{{cite web |url=http://teapot.usask.ca/cdn-firearms/Suter/med-lit.html |title=Guns in the Medical Literature - A Failure of Peer Review |author=Edgar A. Suter, MD |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070813232423/http://teapot.usask.ca/cdn-firearms/Suter/med-lit.html |archivedate=2007-08-13 |df= }}</ref> The methodology of the Kleck and Gertz study has been criticized by some researchers.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cook|first1=Philip J.|last2=Ludwig|first2=Jens|last3=Hemenway|first3=David|title=The gun debate's new mythical number: How many defensive uses per year?|journal=[[Journal of Policy Analysis and Management]]|date=Summer 1997|volume=16|issue=3|pages=463–469|doi=10.1002/(SICI)1520-6688(199722)16:3<463::AID-PAM6>3.0.CO;2-F|url=http://home.uchicago.edu/ludwigj/papers/JPAM_Cook_Ludwig_Hemenway_2007.pdf}}</ref> |
||
== Suicides == |
== Suicides == |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
== Homicides == |
== Homicides == |
||
[[File:Ushomicidesbyweapon.svg|thumb|right|325px|Homicides by weapon type, 1976-2004.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://bjs.ojp.usdoj.gov/content/homicide/weapons.cfm |title=Homicide trends in the U.S. - Weapons used |publisher=[[Bureau of Justice Statistics]]}}</ref>]] |
[[File:Ushomicidesbyweapon.svg|thumb|right|325px|Homicides by weapon type, 1976-2004.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://bjs.ojp.usdoj.gov/content/homicide/weapons.cfm |title=Homicide trends in the U.S. - Weapons used |publisher=[[Bureau of Justice Statistics]]}}</ref>]] |
||
[[File:Homoffendersbyage.svg|thumb|right|325px|Homicide offenders by age, 1976-2004<ref name="bjs-age">{{cite web |url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/teens.htm |title=Homicide trends in the U.S. - Age trends |publisher=[[Bureau of Justice Statistics]]}}</ref>]] |
[[File:Homoffendersbyage.svg|thumb|right|325px|Homicide offenders by age, 1976-2004<ref name="bjs-age">{{cite web |url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/teens.htm |title=Homicide trends in the U.S. - Age trends |publisher=[[Bureau of Justice Statistics]] |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20061115183053/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/teens.htm |archivedate=2006-11-15 |df= }}</ref>]] |
||
[[File:DChomicides.jpg|thumb|right|325px|Gun and overall homicides in [[Crime in Washington, D.C.|Washington, D.C.]] are concentrated in crime hot spots located in neighborhoods (including [[Shaw, Washington, D.C.|Shaw]], [[Sursum Corda Cooperative|Sursum Corda]], [[Trinidad, Washington, D.C.|Trinidad]], [[Anacostia]], and [[Congress Heights]]) with [[Socioeconomics|socio-economic]] disadvantage, while homicide is rare in other neighborhoods.]] |
[[File:DChomicides.jpg|thumb|right|325px|Gun and overall homicides in [[Crime in Washington, D.C.|Washington, D.C.]] are concentrated in crime hot spots located in neighborhoods (including [[Shaw, Washington, D.C.|Shaw]], [[Sursum Corda Cooperative|Sursum Corda]], [[Trinidad, Washington, D.C.|Trinidad]], [[Anacostia]], and [[Congress Heights]]) with [[Socioeconomics|socio-economic]] disadvantage, while homicide is rare in other neighborhoods.]] |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
In the 19th century gun violence played a role in [[civil disorder]] such as the [[Haymarket riot]].<ref name="friedman-ch8">{{cite book|author=Friedman, Lawrence M.|year=1993|chapter=Chapter 8: Lawful Law and Lawless Law: Forms of American Violence|title=Crime and Punishment in American History|publisher=[[Basic Books]]|isbn=0-465-01461-5}}</ref> Homicide rates in cities such as [[Philadelphia]] were significantly lower in the 19th century than in modern times.<ref>{{cite book|author=Lane, Roger|year=1999|title=Violent Death in the City: Suicide, Accident, and Murder in Nineteenth-Century Philadelphia|publisher=[[Ohio State University Press]]|isbn=0-8142-5021-1}}</ref> |
In the 19th century gun violence played a role in [[civil disorder]] such as the [[Haymarket riot]].<ref name="friedman-ch8">{{cite book|author=Friedman, Lawrence M.|year=1993|chapter=Chapter 8: Lawful Law and Lawless Law: Forms of American Violence|title=Crime and Punishment in American History|publisher=[[Basic Books]]|isbn=0-465-01461-5}}</ref> Homicide rates in cities such as [[Philadelphia]] were significantly lower in the 19th century than in modern times.<ref>{{cite book|author=Lane, Roger|year=1999|title=Violent Death in the City: Suicide, Accident, and Murder in Nineteenth-Century Philadelphia|publisher=[[Ohio State University Press]]|isbn=0-8142-5021-1}}</ref> |
||
During the 1980s and early 1990s, homicide rates surged in cities across the United States (see graphs at right).<ref>{{cite web|author=Fox, James Alan, Marianne W. Zawitz|title=Homicide trends in the United States|url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/homtrnd.htm#contents |
During the 1980s and early 1990s, homicide rates surged in cities across the United States (see graphs at right).<ref>{{cite web|author=Fox, James Alan, Marianne W. Zawitz|title=Homicide trends in the United States|url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/homtrnd.htm#contents|publisher=[[Bureau of Justice Statistics]]|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20061113234843/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/homicide/homtrnd.htm#contents|archivedate=2006-11-13|df=}}</ref> Handgun homicides accounted for nearly all of the overall increase in the homicide rate, from 1985 to 1993, while homicide rates involving other weapons declined during that time frame.<ref name="NAS-ch3">{{cite book |author=Committee on Law and Justice |year=2004 |chapter=Chapter 3 |title=Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review|url=http://www.nap.edu/books/0309091241/html/53.html|publisher=[[National Academy of Science]]|isbn=0-309-09124-1}}</ref> The rising trend in homicide rates during the 1980s and early 1990s was most pronounced among lower income and especially unemployed males. Youths and [[Hispanic]] and [[African American]] males in the U.S. were the most represented, with the injury and death rates tripling for black males aged 13 through 17 and doubling for black males aged 18 through 24.<ref name=GVRC-Cook2000/><ref name="bjs-age"/> The rise in [[crack cocaine]] use in cities across the U.S. is often cited as a factor for increased gun violence among youths during this time period.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Cork, Daniel |year=1999 |title=Examining Time-Space Interaction in City-Level Homicide Data: Crack Markets and the Diffusion of Guns Among Youth |journal=[[Journal of Quantitative Criminology]] |volume=15 |pages=379–406 |doi=10.1023/A:1007540007803 |id={{NCJ|180974}} |issue=4}}</ref><ref>{{cite conference |
||
|author=Grogger, Jeff, Mike Willis|year=1998 |title=The Introduction of Crack Cocaine and the Rise of Urban Crime Rates |booktitle=National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper No. 6352 |publisher=[[National Bureau of Economic Research]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Blumstein, Alfred |year=1995 |title=Youth Violence, Guns and the Illicit-Drug Industry |journal=[[Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology]] |volume=86 |issue=1 |pages=10–36 |doi=10.2307/1143998 |id={{NCJ|162687}} |publisher=The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology (1973-), Vol. 86, No. 1 |jstor=1143998}}</ref> |
|author=Grogger, Jeff, Mike Willis|year=1998 |title=The Introduction of Crack Cocaine and the Rise of Urban Crime Rates |booktitle=National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper No. 6352 |publisher=[[National Bureau of Economic Research]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Blumstein, Alfred |year=1995 |title=Youth Violence, Guns and the Illicit-Drug Industry |journal=[[Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology]] |volume=86 |issue=1 |pages=10–36 |doi=10.2307/1143998 |id={{NCJ|162687}} |publisher=The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology (1973-), Vol. 86, No. 1 |jstor=1143998}}</ref> |
||
| Line 291: | Line 291: | ||
=== Project Safe Neighborhoods === |
=== Project Safe Neighborhoods === |
||
[[Project Safe Neighborhoods]] (PSN) is a national strategy for reducing gun violence that builds on the strategies implemented in Operation Ceasefire and [[Project Exile]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/BJA/html/PSNFactS.pdf |title=Project Safe Neighborhoods - Fact Sheet |author=U.S. Department of Justice |date=May 13, 2003 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120304014743/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/BJA/html/PSNFactS.pdf |archivedate=March 4, 2012 |df= }}</ref> PSN was established in 2001, with support from the [[George W. Bush administration|Bush administration]], channelled through the [[United States Attorney|United States Attorney's Offices]] in the [[United States Department of Justice]]. The [[Federal government of the United States|Federal government]] has spent over [[United States dollar|US$]]1.5 billion since the program's inception on the hiring of [[prosecutor]]s, and providing assistance to state and local jurisdictions in support of training and community outreach efforts.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.psn.gov/about/faqs.html |title=Project Safe Neighborhoods: FAQs |publisher=[[U.S. Department of Justice]]}}</ref><ref name="NAS-ch9">{{cite book |title=Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review |year=2004 |publisher=[[National Academy of Science]] |author=Committee on Law and Justice |chapter=Chapter 9 |isbn=0-309-09124-1}}</ref> |
[[Project Safe Neighborhoods]] (PSN) is a national strategy for reducing gun violence that builds on the strategies implemented in Operation Ceasefire and [[Project Exile]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/BJA/html/PSNFactS.pdf |title=Project Safe Neighborhoods - Fact Sheet |author=U.S. Department of Justice |date=May 13, 2003 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120304014743/http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/BJA/html/PSNFactS.pdf |archivedate=March 4, 2012 |df= }}</ref> PSN was established in 2001, with support from the [[George W. Bush administration|Bush administration]], channelled through the [[United States Attorney|United States Attorney's Offices]] in the [[United States Department of Justice]]. The [[Federal government of the United States|Federal government]] has spent over [[United States dollar|US$]]1.5 billion since the program's inception on the hiring of [[prosecutor]]s, and providing assistance to state and local jurisdictions in support of training and community outreach efforts.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.psn.gov/about/faqs.html |title=Project Safe Neighborhoods: FAQs |publisher=[[U.S. Department of Justice]] |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20060929130910/http://www.psn.gov/about/faqs.html |archivedate=2006-09-29 |df= }}</ref><ref name="NAS-ch9">{{cite book |title=Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review |year=2004 |publisher=[[National Academy of Science]] |author=Committee on Law and Justice |chapter=Chapter 9 |isbn=0-309-09124-1}}</ref> |
||
=== Americans for Responsible Solutions === |
=== Americans for Responsible Solutions === |
||
| Line 329: | Line 329: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [http://www.ncjrs.gov/App/Topics/Topic.aspx?topicid=87 Gun violence] - National Criminal Justice |
* [http://www.ncjrs.gov/App/Topics/Topic.aspx?topicid=87 Gun violence] - National Criminal Justice |
||
* [http://www.quandl.com/society/us-violent-crime US Violent Crime] - Data on US Violent Crime |
* [https://archive.is/20130201035550/http://www.quandl.com/society/us-violent-crime US Violent Crime] - Data on US Violent Crime |
||
* [http://www.gunviolencearchive.org/ Gun Violence Archive] - Data on each verified gun related incident, with annual statistics |
* [http://www.gunviolencearchive.org/ Gun Violence Archive] - Data on each verified gun related incident, with annual statistics |
||
*[http://www.report-us.org Report US] Anti-gun violence activist art project, Eileen Boxer (2016) |
*[http://www.report-us.org Report US] Anti-gun violence activist art project, Eileen Boxer (2016) |
||
Revision as of 02:55, 26 October 2017

Gun violence in the United States results in tens of thousands of deaths and injuries annually.[1] In 2013, there were 73,505 nonfatal firearm injuries (23.2 injuries per 100,000 U.S. citizens),[2][3] and 33,636 deaths due to "injury by firearms" (10.6 deaths per 100,000 U.S. citizens).[4] These deaths consisted of 11,208 homicides,[5] 21,175 suicides,[4] 505 deaths due to accidental or negligent discharge of a firearm, and 281 deaths due to firearms use with "undetermined intent".[4] Of the 2,596,993 total deaths in the US in 2013, 1.3% were related to firearms.[1][6] The ownership and control of guns are among the most widely debated issues in the country.
In 2010, 67% of all homicides in the U.S. were committed using a firearm.[7] In 2012, there were 8,855 total firearm-related homicides in the US, with 6,371 of those attributed to handguns.[8] In 2012, 64% of all gun-related deaths in the U.S. were suicides.[9] In 2010, there were 19,392 firearm-related suicides, and 11,078 firearm-related homicides in the U.S.[10] In 2010, 358 murders were reported involving a rifle while 6,009 were reported involving a handgun; another 1,939 were reported with an unspecified type of firearm.[11]
Firearms were used to kill 13,286 people in the U.S. in 2015, excluding suicide.[12] Approximately 1.4 million people have been killed using firearms in the U.S. between 1968 and 2011, equivalent to a top 10 largest U.S. city in 2016, falling between the populations of San Antonio and Dallas, Texas.[12]
Compared to 22 other high-income nations, the U.S. gun-related murder rate is 25 times higher.[13] Although it has half the population of the other 22 nations combined, the U.S. had 82 percent of all gun deaths, 90 percent of all women killed by guns, 91 percent of children under 14 and 92 percent of young people between ages 15 and 24 killed by guns.[13] In 2010, gun violence cost U.S. taxpayers approximately $516 million in direct hospital costs.[14]
Gun violence is most common in poor urban areas and frequently associated with gang violence, often involving male juveniles or young adult males.[15][16] Although mass shootings have been covered extensively in the media, mass shootings account for a small fraction of gun-related deaths[17] and the frequency of these events steadily declined between 1994 and 2007, rising between 2007 and 2013.[18][19]
Legislation at the federal, state, and local levels has attempted to address gun violence through a variety of methods, including restricting firearms purchases by youths and other "at-risk" populations, setting waiting periods for firearm purchases, establishing gun buyback programs, law enforcement and policing strategies, stiff sentencing of gun law violators, education programs for parents and children, and community-outreach programs. Despite widespread concern about the impacts of gun violence on public health, Congress has prohibited the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) from conducting research that advocates in favor of gun control.[20] The CDC has interpreted this ban to extend to all research on gun violence prevention, and so has not funded any research on this subject since 1996.[21]
Gun ownership
The Congressional Research Service in 2009 estimated there were 310 million firearms in the U.S., not including weapons owned by the military. Of these, 114 million were handguns, 110 million were rifles, and 86 million were shotguns.[22] In that same year, the Census bureau stated the population of people in the U.S. at 306 million.[23]
Accurate figures for civilian gun ownership are difficult to determine.[24] While the number of guns in civilian hands has been on the increase, the percentage of Americans and American households who claim to own guns has been in long-term decline, according to the General Social Survey. It found that gun ownership by households has declined steadily from about half, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, down to 32% in 2015. The percentage of individual owners declined from 31% in 1985 to 22% in 2014.[25] However, the Gallup organization has been performing similar polls for the same interval, and finds that household ownership of firearms was approximately the same in 2013 as it was in 1970 - 43%, and individual ownership numbers rose from 27% in 2000, to 29% in 2013.[24] Pew found that fewer Americans are dying as a result of gun violence: In 1993, there were seven homicides using firearms for every 100,000; by 2013, that figure had fallen to 3.6.[26]
What the Pew research does not account for though, is that household firearms ownership hit a high again in the 1993-1994 timeframe where household gun ownership exceeded 50% according to Gallup polls. The Gallup polls further show that household firearm ownership currently exceeds 40% and that the long-term trend is a sharp decline in polling for stricter gun control laws. Lastly, Gallup polling has consistently been over 65% against, when asking whether there should be bans on possession of handguns.[27]
Gun ownership figures are generally estimated via polling, by such organizations as the General Social Survey (GSS), Harris Interactive, and Gallup. There are significant disparities in the results across polls by different organizations, calling into question their reliability.[28] In Gallup's 1972 survey, 43% reported having a gun in their home, while GSS's 1973 survey resulted in 49% reporting a gun in the home; in 1993, Gallup's poll results were 51%, while GSS's 1994 poll showed 43%.[29] In 2012, Gallup's survey showed 47% of Americans reporting having a gun in their home,[30] while the GSS in 2012 reports 34%.[29]
In 1997, estimates were approximately 44 million gun owners in the United States. These owners possessed approximately 192 million firearms, of which an estimated 65 million were handguns.[31] A National Survey on Private Ownership and Use of Firearms (NSPOF), conducted in 1994, indicated that Americans owned 192 million guns: 36% rifles, 34% handguns, 26% shotguns, and 4% other types of long guns.[31] Most firearm owners owned multiple firearms, with the NSPOF survey indicating 25% of adults owned firearms.[31] In the U.S., 11% of households reported actively being involved in hunting,[citation needed] with the remaining firearm owners having guns for self-protection and other reasons. Throughout the 1970s and much of the 1980s, the rate of gun ownership in the home ranged from 45-50%.[29] Rapid increases in gun purchases characterized by exceptionally large crowds accruing at gun vendors and gun shows is consistently observed due to the possibility of increased gun control following highly publicized mass murders.[32][33][34][35][36]
Gun ownership also varied across geographic regions, ranging from 25% rates of ownership in the Northeastern United States to 60% rates of ownership in the East South Central States.[37] A Gallup poll (2004) indicated that 49% of men reported gun ownership, compared to 33% of women, and 44% of whites owned a gun, compared to only 24% of nonwhites.[38] More than half of those living in rural areas (56%) owned a gun, compared with 40% of suburbanites and 29% of those in urban areas.[38] More than half (53%) of Republicans owned guns, compared with 36% of political independents and 31% of Democrats.[38] One criticism of the GSS survey and other proxy measures of gun ownership, is that they do not provide adequate macro-level detail to allow conclusions on the relationship between overall firearm ownership and gun violence.[39] Kleck compared various survey and proxy measures and found no correlation between overall firearm ownership and gun violence.[40][41] In contrast, studies by David Hemenway and his colleagues, which used GSS data and the fraction of suicides committed with a gun as a proxy for gun ownership rates, found a strong positive association between gun ownership and homicide in the United States.[42][43] Similarly, a 2006 study by Philip J. Cook and Jens Ludwig, which also used the percent of suicides committed with a gun as a proxy, found that gun prevalence increased homicide rates. This study also found that the elasticity of this effect was between +0.1 and +0.3.[44]
Self-protection
The effectiveness and safety of guns used for personal defense is debated. Studies place the instances of guns used in personal defense as low as 65,000 times per year, and as high as 2.5 million times per year. Under President Clinton, the Department of Justice conducted a survey in 1994 that placed the usage rate of guns used in personal defense at 1.5 million times per year, but noted this was likely to be an overestimate.[41]
Between 1987 and 1990, McDowall et al. found that guns were used in defense during a crime incident 64,615 times annually (258,460 times total over the whole period).[45] This equated to two times out of 1,000 criminal incidents (0.2%) that occurred in this period, including criminal incidents where no guns were involved at all.[45] For violent crimes, assault, robbery, and rape, guns were used 0.83% of the time in self-defense.[45] Of the times that guns were used in self-defense, 71% of the crimes were committed by strangers, with the rest of the incidents evenly divided between offenders that were acquaintances or persons well known to the victim.[45] In 28% of incidents where a gun was used for self-defense, victims fired the gun at the offender.[45] In 20% of the self-defense incidents, the guns were used by police officers.[45] During this same period, 1987 to 1990, there were 46,319 gun homicides,[46] and the National Crime Victimization Survey estimated that 2,628,532 nonfatal crimes involving guns occurred.[45]
McDowall's study for the American Journal of Public Health contrasted with a 1995 study by Kleck and Gertz, who found that 2.45 million crimes were thwarted each year in the U.S. using guns, and in most cases, the potential victim never fired a shot.[47] The results of the Kleck studies have been cited many times in scholarly and popular media.[48][49][50][51][52][53][54] The methodology of the Kleck and Gertz study has been criticized by some researchers.[55]
Suicides
There were 19,392 firearm-related suicides in the U.S. in 2010.[10] The U.S. Department of Justice reports that approximately 60% of all adult firearm deaths are by suicide, 61% more than deaths by homicide.[56] In the U.S., firearms remain the most common method of suicide, accounting for 51% of all suicides committed in 2006.[57] One study found that military veterans used firearms in about 67% of suicides in 2014.[58] Firearms are the most lethal method of suicide, with a lethality rate 2.6 times higher than suffocation (the second-most lethal method).[59]
A 1992 case-control study in the New England Journal of Medicine showed an association between estimated household firearm ownership and suicide rates, finding that individuals living in a home where firearms are present are more likely to commit suicide than those individuals who do not own firearms, by a factor of 3 or 4.[1][60] A 2006 study by researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health found a significant association between changes in estimated household gun ownership rates and suicide rates in the United States among men, women, and children.[61] A 2007 study by the same research team found that in the United States, estimated household gun ownership rates were strongly associated with overall suicide rates and gun suicide rates, but not with non-gun suicide rates.[62] A 2013 study reproduced this finding, even after controlling for different underlying rates of suicidal behavior by states.[63] A 2015 study also found a strong association between estimated gun ownership rates in American cities and rates of both overall and gun suicide, but not with non-gun suicide.[64] Correlation studies comparing different countries do not always find a statistically significant effect.[65]: 30 A 2016 cross-sectional study showed a strong association between estimated household gun ownership rates and gun-related suicide rates among men and women in the United States. The same study found a strong association between estimated gun ownership rates and overall suicide rates, but only in men.[66] During the 1980s and early 1990s, there was a strong upward trend in adolescent suicides with guns[67]: 29 as well as a sharp overall increase in suicides among those age 75 and over.[68]
David Hemenway, professor of health policy at Harvard University's School of Public Health, and director of the Harvard Injury Control Research Center and the Harvard Youth Violence Prevention Center, stated
Differences in overall suicide rates across cities, states and regions in the United States are best explained not by differences in mental health, suicide ideation, or even suicide attempts, but by availability of firearms. Many suicides are impulsive, and the urge to die fades away. Firearms are a swift and lethal method of suicide with a high case-fatality rate.[13]
Homicides


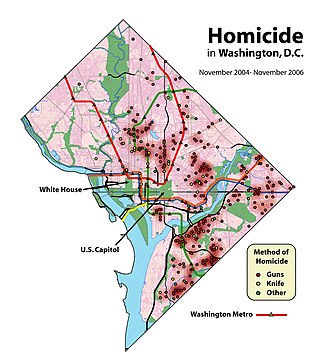
According to the FBI, in 2012, there were 8,897 total firearm-related homicides in the US, with 6,404 of those attributed to handguns.[8] The Centers for Disease Control reports that there were 11,078 firearm-related homicides in the U.S. in 2010.[10] The FBI breaks down the gun-related homicides in 2010 by weapon: 6,009 involved a handgun, 358 involved a rifle, and 1,939 involved an unspecified type of firearm.[11] In 2005, 75% of the 10,100 homicides committed using firearms in the U.S. were committed using handguns, compared to 4% with rifles, 5% with shotguns, and the rest with unspecified firearms.[71]
In the United States, states with higher gun ownership rates have higher rates of overall and gun homicides, but not higher rates of non-gun homicides.[72][73][74] Higher gun availability is positively associated with homicide rates.[75][76][77] There is evidence, however, that gun ownership has less of an effect on rates of gun homicide than it does on gun suicide.[78] In the U.S. in 2011, 67 percent of homicide victims were killed using a firearm: 66 percent of single-victim homicides and 79 percent of multiple-victim homicides.[79]
In the 19th century gun violence played a role in civil disorder such as the Haymarket riot.[80] Homicide rates in cities such as Philadelphia were significantly lower in the 19th century than in modern times.[81] During the 1980s and early 1990s, homicide rates surged in cities across the United States (see graphs at right).[82] Handgun homicides accounted for nearly all of the overall increase in the homicide rate, from 1985 to 1993, while homicide rates involving other weapons declined during that time frame.[39] The rising trend in homicide rates during the 1980s and early 1990s was most pronounced among lower income and especially unemployed males. Youths and Hispanic and African American males in the U.S. were the most represented, with the injury and death rates tripling for black males aged 13 through 17 and doubling for black males aged 18 through 24.[67][70] The rise in crack cocaine use in cities across the U.S. is often cited as a factor for increased gun violence among youths during this time period.[83][84][85]
Prevalence of homicide and violent crime is higher in statistical metropolitan areas of the U.S. than it is in non-metropolitan counties;[86] the vast majority of the U.S. population lives in statistical metropolitan areas.[87] In metropolitan areas, the homicide rate in 2013 was 4.7 per 100,000 compared with 3.4 in non-metropolitan counties.[88] More narrowly, the rates of murder and non-negligent manslaughter are identical in metropolitan counties and non-metropolitan counties.[89] In U.S. cities with populations greater than 250,000, the mean homicide rate was 12.1 per 100,000.[90] According to FBI statistics, the highest per capita rates of gun-related homicides in 2005 were in D.C. (35.4/100,000), Puerto Rico (19.6/100,000), Louisiana (9.9/100,000), and Maryland (9.9/100,000).[91] In 2017, according to the Associated Press, Baltimore broke a record for homicides.[92]
In 2005, the 17 through 24 age group remains significantly over-represented in violent crime statistics, particularly homicides involving firearms.[93] In 2005, 17- through 19-year-olds were 4.3% of the overall population of the U.S.[94] This same age group accounted for 11.2% of those killed in firearm homicides.[95] This age group also accounted for 10.6% of all homicide offenses.[96] The 20- through 24-year-old age group accounted for 7.1% of the population,[94] while accounting for 22.5% of those killed in firearm homicides.[95] The 20 through 24 age group also accounted for 17.7% of all homicide offenses.[96] Those under age 17 are not overrepresented in homicide statistics. In 2005, 13- through 16-year-olds accounted for 6% of the overall population of the U.S., but only accounted for 3.6% of firearm homicide victims,[95] and 2.7% of overall homicide offenses.[96]
People with a criminal record were also more likely to die as homicide victims.[67] Between 1990 and 1994, 75% of all homicide victims age 21 and younger in the city of Boston had a prior criminal record.[97] In Philadelphia, the percentage of those killed in gun homicides that had prior criminal records increased from 73% in 1985 to 93% in 1996.[67][98] In Richmond, Virginia, the risk of gunshot injury is 22 times higher for those males involved with crime.[99]
The likelihood that a death will result is significantly increased when either the victim or the attacker has a firearm.[100][101] For example, the mortality rate for gunshot wounds to the heart is 84%, compared to 30% for people who sustain stab wounds to the heart.[102]
The U.S. is ranked 4th out of 34 developed nations for the highest incidence rate of homicides committed with a firearm, according to Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) data. Mexico, Turkey, Estonia are ranked ahead of the U.S. in incidence of homicides. A U.S. male aged 15–24 is 70 times more likely to be killed with a gun than their counterpart in the eight (G-8) largest industrialized nations in the world (United Kingdom, France, Germany, Japan, Canada, Italy, Russia).[103] In a broader comparison of 218 countries the U.S. is ranked 111.[104] In 2010, the U.S.' homicide rate is 7 times higher than the average for populous developed countries in the OECD, and its firearm-related homicide rate was 25.2 times higher.[105] In 2013 the United States' firearm-related death rate was 10.64 deaths for every 100,000 inhabitants, a figure very close to Mexico's 11.17, although in Mexico firearm deaths are predominantly homicides whereas in the United States they are predominantly suicides.[106] (Although Mexico has ostensibly strict gun laws, the laws restricting carry are often unenforced, and the laws restricting manufacture and sale are often circumvented by trafficking from the United States and other countries.[107]) Canada and Switzerland each have much looser gun control regulation than the majority of developed nations, although significantly more than in the United States, and have firearm death rates of 2.22 and 2.91 per 100,000 citizens, respectively. By comparison Australia, which imposed sweeping gun control laws in response to the Port Arthur massacre in 1996, has a firearm death rate of 0.86 per 100,000, and in the United Kingdom the rate is 0.26. In the year of 2014, thousands of Americans were killed by guns. There was a total of 8,124 gun homicides.[108] In 2015, there were 372 mass shootings and 33,636 deaths due to firearms in the U.S, while guns were used to kill about 50 people in the U.K.[103] More people are typically killed with guns in the U.S. in a day (about 85) than in the U.K. in a year.[103]
Deadly mass shootings have resulted in considerable coverage by the media. These shootings have represented 1% of all deaths using gun between 1980 and 2008.[109] Although mass shootings have been covered extensively in the media, mass shootings account for a small fraction of gun-related deaths[17] and the frequency of these events had steadily declined between 1994 and 2007. Between 2007 and 2013, the rate of active shooter incidents per year in the US has increased.[18][19]
Handguns figured in the Virginia Tech massacre, Binghamton shootings, 2009 Fort Hood shooting, Oikos University shooting, and 2011 Tucson shooting. The Aurora theater shooting and the Columbine High School massacre were committed by assailants armed with multiple weapons.
Accidental and negligent injuries
The perpetrators and victims of accidental and negligent gun discharges may be of any age. Over 120 children 15 years old or younger were killed in gun accidents in 1998.[110] Accidental injuries are most common in homes where guns are kept for self-defense.[110] The injuries are self-inflicted in half of the cases.[110] On January 16, 2013, President Obama issued 23 Executive Orders on Gun Safety,[111] one of which was for the Center for Disease Control (CDC) to research causes and possible prevention of gun violence. The five main areas of focus were gun violence, risk factors, prevention/intervention, gun safety and how media and violent video games influence the public. They also researched the area of accidental firearm deaths. According to this study not only have the number of accidental firearm deaths been on the decline over the past century but they now account for less than 1% of all unintentional deaths, half of which are self-inflicted.[112]
Violent crime
In the United States, areas with higher levels of gun ownership also have higher rates of gun assault and gun robbery.[72]
U.S. presidential assassinations and attempts
At least eleven assassination attempts with firearms have been made on U.S. presidents (over one-fifth of all presidents); four were successful, three with handguns and one with a rifle.
Abraham Lincoln survived an earlier attack,[113] but was killed using a .44-caliber Derringer pistol fired by John Wilkes Booth.[114] James A. Garfield was shot two times and mortally wounded by Charles J. Guiteau using a .44-caliber revolver on July 2, 1881. He would die of pneumonia the same year on September 19. On September 6, 1901, William McKinley was fatally wounded by Leon Czolgosz when he fired twice at point-blank range using a .32-caliber revolver. Despite only being struck by one of the bullets and receiving immediate surgical treatment, McKinley died 8 days later of gangrene infection.[114] John F. Kennedy was killed by Lee Harvey Oswald with a bolt-action rifle on November 22, 1963.[115]
Andrew Jackson, Harry S. Truman, and Gerald Ford (the latter twice) survived assassination attempts involving firearms unharmed.[116][117][118]
Ronald Reagan was critically wounded in the March 30, 1981 assassination attempt by John Hinckley, Jr. with a .22-caliber revolver. He remains the only U.S. President to survive being shot while in office.[119] Former president Theodore Roosevelt was shot and wounded right before delivering a speech during his 1912 presidential campaign. Despite bleeding from his chest, Roosevelt refused to go to a hospital until he delivered the speech.[120] On February 15, 1933, Giuseppe Zangara attempted to assassinate president-elect Franklin Delano Roosevelt, who was giving a speech from his car in Miami, Florida.[121] Although Roosevelt was unharmed, Chicago mayor Anton Cermak died in that attempt, and several other bystanders received non-fatal injuries.[122]
Response to these events has resulted in federal legislation to regulate the public possession of firearms. For example, the attempted assassination of Franklin Roosevelt contributed to passage of the National Firearms Act of 1934,[122] and the Kennedy assassination (along with others) resulted in the Gun Control Act of 1968. The GCA is a federal law signed by President Lyndon Johnson that broadly regulates the firearms industry and firearms owners. It primarily focuses on regulating interstate commerce in firearms by largely prohibiting interstate firearms transfers except among licensed manufacturers, dealers, and importers. The assassination attempt on Ronald Reagan largely contributed to the passage of the Firearm Owners Protection Act in 1986.[123]
Other violent crime
A quarter of robberies of commercial premises in the U.S. are committed with guns.[124] Fatalities are three times as likely in robberies committed with guns than where other, or no, weapons are used,[124][125][126] with similar patterns in cases of family violence.[127] Criminologist Philip J. Cook hypothesized that if guns were less available, criminals might commit the same crime, but with less-lethal weapons.[128] He finds that the level of gun ownership in the 50 largest U.S. cities correlates with the rate of robberies committed with guns, but not with overall robbery rates.[129][130] He also finds that robberies in which the assailant uses a gun are more likely to result in the death of the victim, but less likely to result in injury to the victim.[131] A significant number of homicides are the consequence of an unintended escalation of another crime in which firearms are present, with no initial intent to kill.[126][132] Overall robbery and assault rates in the U.S. are comparable to those in other developed countries, such as Australia and Finland, with much lower levels of gun ownership.[128][132] A strong association exists between the availability of illegal guns and violent crime rates, but not between legal gun availability and violent crime rates.[133]
- See also Assault with a deadly weapon
Offenders
Considering mass shooting alone (four people shot dead in a public place), nearly all were male. About 47% were white, 12% black, and 6% Asian (1982-2016).[134][135] However, this definition of "mass shooting" is contested by some.[136] The mass shootings have represented 1% of all deaths using gun between 1980 and 2008.[109]
Vectors
In 2015, Arizona State University researcher Sherry Towers said "National news media attention is like a 'vector' that reaches people who are vulnerable." She stated that disaffected people can become infected by the attention given other disturbed people who have become mass killers.[135]
Victims
African Americans were 55% of the victims of gun homicide in 2010, but 13% of the population. Non-Hispanic whites were 25% of victims but 65% of the population in 2010. Hispanics were 17% of victims and 16% of the population in 2010.[137]
According to the U.S. Bureau of Justice Statistics, from 1980 to 2008, 84% of white homicide victims were killed by white offenders and 93% of black homicide victims were killed by black offenders.[138]
Public policy
Public policy as related to preventing gun violence is an ongoing political and social debate regarding both the restriction and availability of firearms within the United States. Policy at the Federal level is/has been governed by the Second Amendment, National Firearms Act, Gun Control Act of 1968, Firearm Owners Protection Act, Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act, Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act, and the Domestic Violence Offender Act. Gun policy in the U.S. has been revised many times with acts such as the Firearm Owners Protection Act, which loosened provisions for gun sales while also strengthening automatic firearms law.[139]
At the federal, state and local level gun laws such as handgun bans have been overturned by the Supreme Court in cases such as District of Columbia v. Heller and McDonald v. Chicago. These cases hold that the Second Amendment protects an individual right to possess a firearm. Columbia v. Heller only addressed the issue on Federal enclaves, while McDonald v. Chicago addressed the issue as relating to the individual states.[140]

Gun control proponents often cite the relatively high number of homicides committed with firearms as reason to support stricter gun control laws.[141] Firearm laws are a subject of debate in the U.S., with firearms used for recreational purposes as well as for personal protection.[1] Gun rights advocates cite the use of firearms for self-protection, and to deter violent crime, as reasons why more guns can reduce crime.[142] Gun rights advocates also say criminals are the least likely to obey firearms laws, and so limiting access to guns by law-abiding people makes them more vulnerable to armed criminals.[45]
In an interview with Bill Simmons of HBO, President Obama said that gun control would be the "dominant" issue on his agenda in his last year of presidency.[2][143]
In a survey of 41 studies, half of the studies found a connection between gun ownership and homicide but these were usually the least rigorous studies. Only six studies controlled at least six statistically significant confounding variables, and none of them showed a significant positive effect. Eleven macro-level studies showed that crime rates increase gun levels (not vice versa). The reason that there is no opposite effect may be that most owners are noncriminals and that they may use guns to prevent violence.[144]
Access to firearms

U.S. policy aims to maintain the right of most people to own most types of firearms, while restricting access to firearms by people considered to present a higher risk of misuse.[128] Gun dealers in the U.S. are prohibited from selling handguns to those under the age of 21, and long guns to those under the age of 18.[128] There are also restrictions on selling guns to people not resident in the state.[128] In 2017, the National Safety Council released a state ranking on firearms access indicators such as background checks, waiting periods, safe storage, training, and sharing of mental health records with the NICS database to restrict firearm access.[146]
Assuming access to guns, the top ten guns involved in crime in the U.S. show a definite trend to favor handguns over long guns. The top ten guns used in crime, as reported by the ATF in 1993, were the Smith & Wesson .38 Special and .357 revolvers; Raven Arms .25 caliber, Davis P-380 .380 caliber, Ruger .22 caliber, Lorcin L-380 .380 caliber, and Smith & Wesson semi-automatic handguns; Mossberg and Remington 12 gauge shotguns; and the Tec DC-9 9 mm handgun.[145] An earlier 1985 study of 1,800 incarcerated felons showed that criminals preferred revolvers and other non-semi-automatic firearms over semi-automatic firearms.[147] In Pittsburgh a change in preferences towards pistols occurred in the early 1990s, coinciding with the arrival of crack cocaine and the rise of violent youth gangs.[148] Background checks in California from 1998 to 2000 resulted in 1% of sales being initially denied.[149] The types of guns most often denied included semiautomatic pistols with short barrels and of medium caliber.[149]
Among juveniles (minors under the age of 16, 17, or 18, depending on legal jurisdiction) serving in correctional facilities, 86% had owned a gun, with 66% acquiring their first gun by age 14.[16] There was also a tendency for juvenile offenders to have owned several firearms, with 65% owning three or more.[16] Juveniles most often acquired guns illegally from family, friends, drug dealers, and street contacts.[16] Inner city youths cited "self-protection from enemies" as the top reason for carrying a gun.[16] In Rochester, New York, 22% of young males have carried a firearm illegally, most for only a short time.[150] There is little overlap between legal gun ownership and illegal gun carrying among youths.[150]
Firearms market
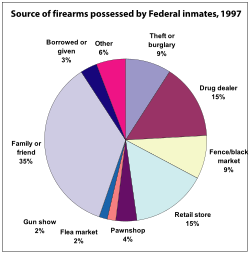

Gun rights advocates complain that policy aimed at the supply side of the firearms market is based on limited research.[1] One consideration is that only 60-70% of firearms sales in the U.S. are transacted through federally licensed firearm dealers, with the remainder taking place in the "secondary market", in which previously owned firearms are transferred by non-dealers.[31][152][153][154] Access to secondary markets is generally less convenient to purchasers, and involves such risks as the possibility of the gun having been used previously in a crime.[67]: 119 Unlicensed private sellers were permitted by law to sell privately owned guns at gun shows or at private locations in 24 states as of 1998.[155] Regulations that limit the number of handgun sales in the primary, regulated market to one handgun a month per customer have been shown to be effective at reducing illegal gun trafficking by reducing the supply into the secondary market.[156] Taxes on firearm purchases are another means for government to influence the primary market.[157]
Criminals tend to obtain guns through multiple illegal pathways, including gun traffickers, who tend to provide criminals with relatively few guns.[158] Federally licensed firearm dealers in the primary (new and used gun) market are regulated by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF). Firearm manufacturers are required to mark all firearms manufactured with serial numbers. This allows the ATF to trace guns involved in crimes back to their last Federal Firearms License (FFL) reported change of ownership transaction, although not past the first private sale involving any particular gun. A report by the ATF released in 1999 found that 0.4% of federally licensed dealers sold half of the guns used criminally in 1996 and 1997.[159][160] This is sometimes done through "straw purchases."[159] State laws, such as those in California, that restrict the number of gun purchases in a month may help stem such "straw purchases."[159] States with gun registration and licensing laws are generally less likely to have guns initially sold there used in crimes.[161] Similarly, crime guns tend to travel from states with weak gun laws to states with strict gun laws.[162][163][164] An estimated 500,000 guns are stolen each year, becoming available to prohibited users.[152][157] During the ATF's Youth Crime Gun Interdiction Initiative (YCGII), which involved expanded tracing of firearms recovered by law enforcement agencies,[165] only 18% of guns used criminally that were recovered in 1998 were in possession of the original owner.[166] Guns recovered by police during criminal investigations were often sold by legitimate retail sales outlets to legal owners, and then diverted to criminal use over relatively short times ranging from a few months to a few years,[97][166][167] which makes them relatively new compared with firearms in general circulation.[157][168]
Federal legislation
The first Federal legislation related to firearms was the Second Amendment to the United States Constitution ratified in 1791. For 143 years, this was the only major Federal legislation regarding firearms. The next Federal firearm legislation was the National Firearms Act of 1934, which created regulations for the sale of firearms, established taxes on their sale, and required registration of some types of firearms such as machine guns.[169]
In the aftermath of the Robert F. Kennedy and Martin Luther King Jr. assassinations, the Gun Control Act of 1968 was enacted. This Act regulated gun commerce, restricting mail order sales, and allowing shipments only to licensed firearm dealers. The Act also prohibited sale of firearms to felons, those under indictment, fugitives, illegal aliens, drug users, those dishonorably discharged from the military, and those in mental institutions.[128] The law also restricted importation of so-called Saturday night specials and other types of guns, and limited the sale of automatic weapons and semi-automatic weapon conversion kits.[159]
The Firearm Owners Protection Act, also known as the McClure-Volkmer Act, was passed in 1986. It changed some restrictions in the 1968 Act, allowing federally licensed gun dealers and individual unlicensed private sellers to sell at gun shows, while continuing to require licensed gun dealers to require background checks.[159] The 1986 Act also restricted the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms from conducting repetitive inspections, reduced the amount of record-keeping required of gun dealers, raised the burden of proof for convicting gun law violators, and changed restrictions on convicted felons from owning firearms.[159]
In the years following the passage of the Gun Control Act of 1968, people buying guns were required to show identification and sign a statement affirming that they were not in any of the prohibited categories.[128] Many states enacted background check laws that went beyond the federal requirements.[170] The Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act passed by Congress in 1993 imposed a waiting period before the purchase of a handgun, giving time for, but not requiring, a background check to be made.[171] The Brady Act also required the establishment of a national system to provide instant criminal background checks, with checks to be done by firearms dealers.[172] The Brady Act only applied to people who bought guns from licensed dealers, whereas felons buy some percentage of their guns from black market sources.[167] Restrictions, such as waiting periods, impose costs and inconveniences on legitimate gun purchasers, such as hunters.[157]

The Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act, enacted in 1994, included the Federal Assault Weapons Ban, and was a response to public concern over mass shootings.[173] This provision prohibited the manufacture and importation of some semiautomatic firearms with certain features relevant to military use such as a folding stock, pistol grip, flash suppressor, and magazines holding more than ten rounds.[173] A grandfather clause was included that allowed firearms manufactured before 1994 to remain legal. A short-term evaluation by University of Pennsylvania criminologists Christopher S. Koper and Jeffrey A. Roth did not find any clear impact of this legislation on gun violence.[174] Given the short study time period of the evaluation, the National Academy of Sciences advised caution in drawing any conclusions.[157] In September 2004, the assault weapon ban expired, with its sunset clause.[175]
The Domestic Violence Offender Gun Ban, the Lautenberg Amendment, prohibited anyone previously convicted of a misdemeanor or felony crime of domestic violence from shipment, transport, ownership and use of guns or ammunition.[176] This law also prohibited the sale or gift of a firearm or ammunition to such a person. It was passed in 1996, and became effective in 1997. The law does not exempt people who use firearms as part of their duties, such as police officers or military personnel with applicable criminal convictions; they may not carry firearms.[177]
In the immediate aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, police and National Guard units in New Orleans confiscated firearms from private citizens in an attempt to prevent violence. In reaction, Congress passed the Disaster Recovery Personal Protection Act of 2006 in the form of an amendment to Department of Homeland Security Appropriations Act, 2007. Section 706 of the Act prohibits federal employees and those receiving federal funds from confiscating legally possessed firearms during a disaster.[178]
On Jan. 5, 2016, President Obama unveiled his new strategy to curb gun violence in America. His proposals focus on new background check requirements that are intended to enhance the effectiveness of the National Instant Criminal Background Check System (NICS), and greater education and enforcement efforts of existing laws at the state level.[179][180] In an interview with Bill Simmons of HBO, President Obama also confirmed that gun control will be the "dominant" issue on his agenda in his last year of presidency.[181][182]
State legislation
Right-to-carry

All 50 U.S. states allow for the Right-to-carry firearms, with forty-two states generally requiring a state-issued permit in order to carry concealed weapons in public and the remaining eight states generally allowing individuals to carry concealed weapons in public without a permit. Right-to-carry laws expanded in the 1990s as homicide rates from gun violence in the U.S. increased, largely in response to incidents such as the Luby's shooting of 1991 in Texas which directly resulted in the passage of a carrying concealed weapon, or CCW, law in Texas in 1995.[183] As Rorie Sherman, staff reporter for the National Law Journal wrote in an article published on April 18, 1994, "It is a time of unparalleled desperation about crime. But the mood is decidedly 'I'll do it myself' and 'Don't get in my way.'"[184]
The result was laws, or the lack thereof, that permitted persons to carry firearms openly, known as open carry, often without any permit required, in 22 states by 1998.[185] Laws that permitted persons to carry concealed handguns, sometimes termed a concealed handgun license, CHL, or concealed pistol license, CPL in some jurisdictions instead of CCW, existed in 34 states in the U.S. by 2004.[1] Since then, the number of states with CCW laws has increased; as of 2014[update], all 50 states have some form of CCW laws on the books.[186][187]
Economist John Lott has argued that right-to-carry laws create a perception that more potential crime victims might be carrying firearms, and thus serve as a deterrent against crime.[188] Lott's study has been criticized for not adequately controlling for other factors, including other state laws also enacted, such as Florida's laws requiring background checks and waiting period for handgun buyers.[189] When Lott's data was re-analyzed by some researchers, the only statistically significant effect of concealed-carry laws found was an increase in assaults,[189] with similar findings by Jens Ludwig.[190] Lott and Mustard's 1997 study has also been criticized by Paul Rubin and Hashem Dezhbakhsh for inappropriately using a dummy variable; Rubin and Dezhbakhsh reported in a 2003 study that right-to-carry laws have much smaller and more inconsistent effects than those reported by Lott and Mustard, and that these effects are usually not crime-reducing.[191] Since concealed-carry permits are only given to adults, Philip J. Cook suggested that analysis should focus on the relationship with adult and not juvenile gun incident rates.[128] He found no statistically significant effect.[128] A 2004 National Academy of Science survey of existing literature found that the data available "are too weak to support unambiguous conclusions" about the impact of right-to-carry laws on rates of violent crime.[1] NAS suggested that new analytical approaches and datasets at the county or local level are needed to adequately evaluate the impact of right-to-carry laws.[192] A 2014 study found that Arizona's SB 1108, which allowed adults in the state to concealed carry without a permit and without passing a training course, was associated with an increase in gun-related fatalities.[193] A 2015 NBER working paper found that the apparent effects of RTC laws on crime rates depend significantly on the assumptions made in the analysis.[194]
Child Access Prevention (CAP)
Child Access Prevention (CAP) laws, enacted by many states, require parents to store firearms safely, to minimize access by children to guns, while maintaining ease of access by adults.[195] CAP laws hold gun owners liable should a child gain access to a loaded gun that is not properly stored.[195] The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) claimed that, on average, one child died every three days in accidental incidents in the U.S. from 2000 to 2005.[196] In most states, CAP law violations are considered misdemeanors.[195] Florida's CAP law, enacted in 1989, permits felony prosecution of violators.[195] Research indicates that CAP laws are correlated with a reduction in unintentional gun deaths by 23%,[197] and gun suicides among those aged 14 through 17 by 11%.[198] A study by Lott did not detect a relationship between CAP laws and accidental gun deaths or suicides among those age 19 and under between 1979 and 1996.[199] However, two studies disputed Lott's findings.[198][200] A 2008 National Bureau of Economic Research working paper found that CAP laws are correlated with a reduction of non-fatal gun injuries among both children and adults by 30-40%.[195] In 2016 the American Academy of Pediatrics found that safe gun storage laws were associated with lower overall adolescent suicide rates.[201] Research also indicated that CAP laws were most highly correlated with reductions of non-fatal gun injuries in states where violations were considered felonies, whereas in states that considered violations as misdemeanors, the potential impact of CAP laws was not statistically significant.[202] All of these studies were correlational, and do not account for other potential contributing factors.
Local restrictions
Some local jurisdictions in the U.S. have more restrictive laws, such as Washington, D.C.'s Firearms Control Regulations Act of 1975, which banned residents from owning handguns, and required permitted firearms be disassembled and locked with a trigger lock. On March 9, 2007, a U.S. Appeals Court ruled the Washington, D.C. handgun ban unconstitutional.[203] The appeal of that case later led to the Supreme Court's ruling in District of Columbia v. Heller that D.C.'s ban was unconstitutional under the Second Amendment.
Despite New York City's strict gun control laws, guns are often trafficked in from other parts of the U.S., particularly the southern states.[160][204] Results from the ATF's Youth Crime Gun Interdiction Initiative indicate that the percentage of imported guns involved in crimes is tied to the stringency of local firearm laws.[165]
Prevention programs
Violence prevention and educational programs have been established in many schools and communities across the United States. These programs aim to change personal behavior of both children and their parents, encouraging children to stay away from guns, ensure parents store guns safely, and encourage children to solve disputes without resorting to violence.[205] Programs aimed at altering behavior range from passive (requiring no effort on the part of the individual) to active (supervising children, or placing a trigger lock on a gun).[205] The more effort required of people, the more difficult it is to implement a prevention strategy.[206][207] Prevention strategies focused on modifying the situational environment and the firearm itself may be more effective.[205] Empirical evaluation of gun violence prevention programs has been limited.[1] Of the evaluations that have been done, results indicate such programs have minimal effectiveness.[205]
Hotline
SPEAK UP is a national youth violence prevention initiative created by The Center to Prevent Youth Violence,[208] which provides young people with tools to improve the safety of their schools and communities. The SPEAK UP program is an anonymous, national hot-line for young people to report threats of violence in their communities or at school. The hot-line is operated in accordance with a protocol developed in collaboration with national education and law enforcement authorities, including the FBI. Trained counselors, with access to translators for 140 languages, collect information from callers and then report the threat to appropriate school and law enforcement officials.[209][210][non-primary source needed]
Gun safety parent counseling
One of the most widely used parent counseling programs is Steps to Prevent Firearm Injury program (STOP), which was developed in 1994 by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Brady Center to Prevent Gun Violence (the latter of which was then known as the Center to Prevent Handgun Violence).[205][211] STOP was superseded by STOP 2 in 1998, which has a broader focus including more communities and health care providers.[205] STOP has been evaluated and found not to have a significant effect on gun ownership or firearm storage practices by inner-city parents.[212] Marjorie S. Hardy suggests further evaluation of STOP is needed, as this evaluation had a limited sample size and lacked a control group.[205] A 1999 study found no statistically significant effect of STOP on rates of gun ownership or better gun storage.[211]
Children
Prevention programs geared towards children have also not been greatly successful.[205] Many inherent challenges arise when working with children, including their tendency to perceive themselves as invulnerable to injury,[213] limited ability to apply lessons learned,[214][215] their innate curiosity,[214] and peer pressure.
The goal of gun safety programs, usually administered by local firearms dealers and shooting clubs, is to teach older children and adolescents how to handle firearms safely.[205] There has been no systematic evaluation of the effect of these programs on children.[205] For adults, no positive effect on gun storage practices has been found as a result of these programs.[31][216] Also, researchers have found that gun safety programs for children may likely increase a child's interest in obtaining and using guns, which they cannot be expected to use safely all the time, even with training.[217]
One approach taken is gun avoidance, such as when encountering a firearm at a neighbor's home. The Eddie Eagle Gun Safety Program, administered by the National Rifle Association (NRA), is geared towards younger children from pre-kindergarten to sixth grade, and teaches kids that real guns are not toys by emphasizing a "just say no" approach.[205] The Eddie Eagle program is based on training children in a four-step action to take when they see a firearm: (1) Stop! (2) Don't touch! (3) Leave the area. (4) Go tell an adult. Materials, such as coloring books and posters, back the lessons up and provide the repetition necessary in any child-education program. The ineffectiveness of the "just say no" approach promoted by the NRA's Eddie the Eagle program was highlighted in an investigative piece by ABC's Diane Sawyer in 1999.[218] Sawyer's piece was based on academic studies conducted by Dr. Marjorie Hardy, assistant professor of psychology at Muhlenberg College in Allentown, Pennsylvania.[219] Dr. Hardy's study tracked the behavior of elementary age schoolchildren who spent a day learning the Eddie the Eagle four-step action plan from a uniformed police officer. The children were then placed into a playroom which contained a hidden gun. When the children found the gun, they did not run away from the gun, but rather, they inevitably played with it, pulled the trigger while looking into the barrel, or aimed the gun at a playmate and pulled the trigger. The study concluded that children's natural curiosity was far more powerful than the parental admonition to "Just say no".[220]
Community programs
Programs targeted at entire communities, such as community revitalization, after-school programs, and media campaigns, may be more effective in reducing the general level of violence that children are exposed to.[221][222] Community-based programs that have specifically targeted gun violence include Safe Kids/Healthy Neighborhoods Injury Prevention Program in New York City,[223][224] and Safe Homes and Havens in Chicago.[205] Evaluation of such community-based programs is difficult, due to many confounding factors and the multifaceted nature of such programs.[205] A Chicago-based program, "BAM" (Becoming a Man) has produced positive results, according to the University of Chicago Crime Lab, and is expanding to Boston in 2017.[225]
Intervention programs
Sociologist James D. Wright suggests that to convince inner-city youths not to carry guns "requires convincing them that they can survive in their neighborhood without being armed, that they can come and go in peace, that being unarmed will not cause them to be victimized, intimidated, or slain."[16] Intervention programs, such as CeaseFire Chicago, Operation Ceasefire in Boston and Project Exile in Richmond, Virginia during the 1990s, have been shown to be effective.[1][226] Other intervention strategies, such as gun "buy-back" programs have been demonstrated to be ineffective.[227]
Gun buyback programs
Gun "buyback" programs are a strategy aimed at influencing the firearms market by taking guns "off the streets".[227] Gun "buyback" programs have been shown to be effective to prevent suicides, but ineffective to prevent homicides[228][229] with the National Academy of Sciences citing theory underlying these programs as "badly flawed."[227] Guns surrendered tend to be those least likely to be involved in crime, such as old, malfunctioning guns with little resale value, muzzleloading or other black-powder guns, antiques chambered for obsolete cartridges that are no longer commercially manufactured or sold, or guns that individuals inherit but have little value in possessing.[230] Other limitations of gun buyback programs include the fact that it is relatively easy to obtain gun replacements, often of better guns than were relinquished in the buyback.[227] Also, the number of handguns used in crime (approximately 7,500 per year) is very small compared to the approximately 70 million handguns in the U.S.. (i.e., 0.011%).[227]
"Gun bounty" programs launched in several Florida cities have shown more promise. These programs involve cash rewards for anonymous tips about illegal weapons that lead to an arrest and a weapons charge. Since its inception in May 2007, the Miami program has led to 264 arrests and the confiscation of 432 guns owned illegally and $2.2 million in drugs, and has solved several murder and burglary cases.[231]
Operation Ceasefire
In 1995, Operation Ceasefire was established as a strategy for addressing youth gun violence in Boston. Violence was particularly concentrated in poor, inner-city neighborhoods including Roxbury, Dorchester, and Mattapan.[232] There were 22 youths (under the age of 24) killed in Boston in 1987, with that figure rising to 73 in 1990.[232] Operation Ceasefire entailed a problem-oriented policing approach, and focused on specific places that were crime hot spots—two strategies that when combined have been shown to be quite effective.[233][234][235] Particular focus was placed on two elements of the gun violence problem, including illicit gun trafficking[236] and gang violence.[232] Within two years of implementing Operation Ceasefire in Boston, the number of youth homicides dropped to ten, with only one handgun-related youth homicide occurring in 1999 and 2000[159] The Operation Ceasefire strategy has since been replicated in other cities, including Los Angeles.[237] Erica Bridgeford, spearheaded a "72-hour ceasefire" in August 2017, but the ceasefire was broken with a homicide. Councilman Brandon Scott, Mayor Catherine Pugh and others talked of community policing models that might work for Baltimore.[238][92]
Project Exile

Project Exile, conducted in Richmond, Virginia during the 1990s, was a coordinated effort involving federal, state, and local officials that targeted gun violence. The strategy entailed prosecution of gun violations in Federal courts, where sentencing guidelines were tougher. Project Exile also involved outreach and education efforts through media campaigns, getting the message out about the crackdown.[239] Research analysts offered different opinions as to the program's success in reducing gun crime. Authors of a 2003 analysis of the program argued that the decline in gun homicide was part of a "general regression to the mean" across U.S. cities with high homicide rates.[240] Authors of a 2005 study disagreed, concluding that Richmond's gun homicide rate fell more rapidly than the rates in other large U.S. cities with other influences controlled.[239][241]
Project Safe Neighborhoods
Project Safe Neighborhoods (PSN) is a national strategy for reducing gun violence that builds on the strategies implemented in Operation Ceasefire and Project Exile.[242] PSN was established in 2001, with support from the Bush administration, channelled through the United States Attorney's Offices in the United States Department of Justice. The Federal government has spent over US$1.5 billion since the program's inception on the hiring of prosecutors, and providing assistance to state and local jurisdictions in support of training and community outreach efforts.[243][244]
Americans for Responsible Solutions
Americans for Responsible Solutions was started in January 2013 as a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to "encourage elected officials to stand up for solutions to prevent gun violence and protect responsible gun ownership by communicating directly with the constituents that elect them."[245] The organization was announced on January 8, 2013 by Gabrielle "Gabby" Giffords, a former Democratic member of the United States House of Representatives for Arizona's 8th congressional district, and Mark Kelly, a retired American astronaut.[246] In an op-ed published in USA Today, Gifford and Kelly referred to the NRA lobby and sought to counter it by creating a lobby dedicated to responsible gun control measures.[247]
Research limitations
In the United States, research into firearms and violent crime is fraught with difficulties, associated with limited data on gun ownership and use,[37] firearms markets, and aggregation of crime data.[1] Research studies into gun violence have primarily taken one of two approaches: case-control studies and social ecology.[1] Gun ownership is usually determined through surveys, proxy variables, and sometimes with production and import figures. In statistical analysis of homicides and other types of crime which are rare events, these data tend to have poisson distributions, which also presents methodological challenges to researchers. With data aggregation, it is difficult to make inferences about individual behavior.[248] This problem, known as ecological fallacy, is not always handled properly by researchers; this leads some to jump to conclusions that their data do not necessarily support.[249]
In 1996 the NRA lobbied Congressman Jay Dickey (R-Ark.) to include budget provisions that prohibited the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) from advocating or promoting gun control and that deleted $2.6 million from the CDC budget, the exact amount the CDC had spent on firearms research the previous year. The ban was later extended to all research funded by the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). According to an article in Nature, this made gun research more difficult, reduced the number of studies, and discouraged researchers from even talking about gun violence at medical and scientific conferences. In 2013, after the December 2012 Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting, President Barack Obama ordered the CDC to resume funding research on gun violence and prevention, and put $10 million in the 2014 budget request for it.[250] Prior to this, U.S. public funding directed towards gun violence prevention was less than $2 million annually, a disproportionately low total compared to public funding totals for other leading public health burdens with respect to potential years of life lost.[251]
See also
- Crime in the United States
- Firearm death rates in the United States by state
- Gun violence and gun control in Texas
- Sullivan Law of 1911, one of the broadest and oldest existing gun control laws in the United States.
- Index of gun politics articles
- "Thoughts and prayers"
Notes and references
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k National Research Council (2004). "Executive Summary". In Wellford, Charles F.; Pepper, John V.; Petrie, Carol V. (eds.). Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. ISBN 978-0-309-09124-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Priorities for Research to Reduce the Threat of Firearm-Related Violence". The National Academies Press. 2013. Retrieved 28 June 2016.
- ^ and, Institute of Medicine (5 June 2013). "Priorities for Research to Reduce the Threat of Firearm-Related Violence". doi:10.17226/18319.
- ^ a b c https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr64/nvsr64_02.pdf Page 84, Table 18 (accessed July 31, 2016)
- ^ FastStats: Mortality - All firearm deaths. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/homicide.htm (accessed July 27, 2015).
- ^ https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr64/nvsr64_02.pdf Page 5 (accessed July 31, 2016)
- ^ Homicides by firearms UNODC. Retrieved: 28 July 2012.
- ^ a b "Expanded Homicide Data Table 8". FBI.gov. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ Wintemute, Garen J. (18 March 2015). "The Epidemiology of Firearm Violence in the Twenty-First Century United States". Annual Review of Public Health. 36 (1). Annual Reviews: 5–19. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031914-122535.
- ^ a b c "10 Leading Causes of Injury Death by Age Group Highlighting Violence-Related Injury Deaths, United States" (PDF). National Vital Statistics System. National Center for Health Statistics, CDC. 2010.
- ^ a b "FBI — Expanded Homicide Data Table 8". Fbi.gov. 2011-07-25. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ a b "Guns in the US: The statistics behind the violence". BBC News. 5 January 2016.
- ^ a b c "How U.S. gun deaths compare to other countries". CBS. October 7, 2017.
- ^ Howell, Embry M. (September 13, 2013). "The Hospital Costs of Firearm Assaults". Urban Institute. Retrieved 12 September 2015.
- ^ Bjerregaard, Beth, Alan J. Lizotte (1995). "Gun Ownership and Gang Membership". Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 86 (1). The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology (1973-), Vol. 86, No. 1: 37–58. doi:10.2307/1143999. JSTOR 1143999. NCJ 162688.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f Wright, James D., Joseph F. Sheley, and M. Dwayne Smith (1993). "Kids, Guns, and Killing Fields". Society. 30 (1). NCJ 140211.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Priorities for Research to Reduce the Threat of Firearm-Related Violence. The National Academies Press. ISBN 978-0-309-28438-7.
- ^ a b Duwe, Grant (January 4, 2013). "Seven Mass Shootings in 2012 Most since 1999". The Washington Times (Washington, DC). Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ^ a b "FBI Confirms Rise in Mass Shootings in Us". 24 September 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Zwillich, Todd. "Quietly, Congress extends a ban on CDC research on gun violence". Public Radio International (PRI). Retrieved 12 September 2015.
- ^ Rubin, Rita (26 April 2016). "Tale of 2 Agencies: CDC Avoids Gun Violence Research But NIH Funds It". JAMA. 315 (16): 1689. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.1707.
- ^ "Gun control offers no cure-all in America - NBC Politics". Nbcpolitics.nbcnews.com. 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- ^ "Census Bureau Projects U.S. Population of 305.5 Million on New Year's Day". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- ^ a b Bialik, Carl (23 March 2013). "Guns Present Polling Conundrum".
- ^ "Number of households with guns on the decline, study shows".
- ^ Max Ehrenfreund: We’ve had a massive decline in gun violence in the United States. Here's why. - Wonk blog, December 3, 2015
- ^ "Guns Gallup Historical Trends". www.gallup.com. Jan 6–10, 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ Bialik, Carl. "Guns Present Polling Conundrum". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 21 June 2014.
- ^ a b c "Why Own a Gun? Protection Is Now Top Reason". Pew ResearchCenter for the People & the Press. Retrieved 21 June 2014.
- ^ "Self Reported gun ownership highest since 1993". Retrieved 2014-06-21.
- ^ a b c d e Cook, Philip J.; Ludwig, Jens (May 1997). "Guns in America: National survey on private ownership and use of firearms" (PDF). National Institute of Justice.
- ^ Lach, Eric. "A History of the Rifle used in the Sandy Hook Massacre". TPM. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ Isikoff, Michael. "Authorities establish timeline of gun purchases in Connecticut school shooting". NBC NEWS.
- ^ McDaniel, Chris. "Yuma gun show draws big crowd". YumaSun.com.
- ^ Gross, Daniel. "This Gun Kills Kids -- and Reaps Profits". The Daily Beast.
- ^ Kopel, Dave. "The AR-15 and the Second Amendment: No Respoect". NRA.
- ^ a b Azrael, Deborah, Philip J. Cook, Matthew Miller (2004). "State and Local Prevalence of Firearms Ownership Measurement, Structure, and Trends". Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 20 (1): 43–62. doi:10.1023/B:JOQC.0000016699.11995.c7. NCJ 205033.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Carlson, Darren K. "Americans and Guns: Danger or Defense?". 2004 Poll report. Gallup. Retrieved 23 December 2012.
- ^ a b Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 3". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Kleck, Gary (2004). "Measures of Gun Ownership Levels of Macro-Level Crime and Violence Research" (PDF). Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency. 41 (1). Sage Publications: 3–36. doi:10.1177/0022427803256229. NCJ 203876. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-20.
Studies that attempt to link the gun ownership of individuals to their experiences as victims (e.g., Kellermann, et al. 1993) do not effectively determine how an individual's risk of victimization is affected by gun ownership by other people, especially those not living in the gun owner's own household.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Travis, Jeremy (May 1997). "Guns in America: National Survey on Private Ownership and Use of Firearms". National Institute of Justice.
- ^ Miller, Matthew; Azrael, Deborah; Hemenway, David (December 2002). "Rates of Household Firearm Ownership and Homicide Across US Regions and States, 1988–1997". American Journal of Public Health. 92 (12): 1988–1993. doi:10.2105/AJPH.92.12.1988. PMC 1447364. PMID 12453821.
- ^ Miller, Matthew; Hemenway, David; Azrael, Deborah (February 2007). "State-level homicide victimization rates in the US in relation to survey measures of household firearm ownership, 2001–2003". Social Science & Medicine. 64 (3): 656–664. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.09.024.
- ^ Cook, Philip J.; Ludwig, Jens (January 2006). "The social costs of gun ownership". Journal of Public Economics. 90 (1–2): 379–391. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.02.003.
- ^ a b c d e f g h McDowall, David, Brian Wiersema (1994). "The Incidence of Defensive Firearm Use by US Crime Victims, 1987 through 1990". American Journal of Public Health. 84 (12): 1982–1984. doi:10.2105/AJPH.84.12.1982. PMC 1615397. PMID 7998641.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Uniform Crime Reports, 1987-1990. Federal Bureau of Investigation.
- ^ Kleck, Gary; Gertz, Marc (Autumn 1995). "Armed Resistance to Crime: The Prevalence and Nature of Self-Defense with a Gun". The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 86 (1): 150. doi:10.2307/1144004.
- ^ Suter, E.A. (1992). "Firearms and the killing threshold (Letter)". New England Journal of Medicine. 326 (17): 1159. doi:10.1056/NEJM199204233261712. PMID 1552925.
- ^ Kates, D.B. (1991). "The value of civilian handgun possession as a deterrent to crime or a defense against crime". American Journal of Criminal Law. 18: 113–167. NCJ 132948.
- ^ "Go ahead, make our day". The New Republic. February 22, 1988. pp. 7–9.
- ^ "Do guns save lives?". Time Magazine. August 12, 1988. pp. 25–26.
- ^ "Are we "a nation of cowards"?". Newsweek. November 15, 1993. pp. 93–94.
- ^ Kopel, D.B. (1993). "Hold your fire: gun control won't stop rising violence". 63. Policy Review: 58–65. NCJ 153748.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Edgar A. Suter, MD. "Guns in the Medical Literature - A Failure of Peer Review". Archived from the original on 2007-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Cook, Philip J.; Ludwig, Jens; Hemenway, David (Summer 1997). "The gun debate's new mythical number: How many defensive uses per year?" (PDF). Journal of Policy Analysis and Management. 16 (3): 463–469. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6688(199722)16:3<463::AID-PAM6>3.0.CO;2-F.
- ^ "Bureau of Justice Statistics Keyfacts at a Glance". Bjs.ojp.usdoj.gov. 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ "U.S.A. Suicide: 2006 Official Final Data" (PDF). American Association of Suicidology.
- ^ Office of Suicide Prevention (3 August 2016). Suicide Among Veterans and Other Americans 2001–2014 (PDF). U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
- ^ Shenassa, E D (1 February 2003). "Lethality of firearms relative to other suicide methods: a population based study". Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. 57 (2): 120–124. doi:10.1136/jech.57.2.120.
- ^ Kellerman, Arthur L.; Rivara, Frederick P. (August 13, 1992). "Suicide in the Home in Relation to Gun Ownership". The New England Journal of Medicine. 327 (7). Massachusetts Medical Society: 467–472. doi:10.1056/NEJM199208133270705. PMID 1308093.
- ^ Miller, M (1 June 2006). "The association between changes in household firearm ownership and rates of suicide in the United States, 1981-2002". Injury Prevention. 12 (3): 178–182. doi:10.1136/ip.2005.010850.
- ^ Miller, M; Lippmann, SJ; Azrael, D; Hemenway, D (April 2007). "Household firearm ownership and rates of suicide across the 50 United States". The Journal of Trauma. 62 (4): 1029–34, discussion 1034-5. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000198214.24056.40. PMID 17426563.
- ^ Miller, M; Barber, C; White, RA; Azrael, D (15 September 2013). "Firearms and suicide in the United States: is risk independent of underlying suicidal behavior?". American Journal of Epidemiology. 178 (6): 946–55. doi:10.1093/aje/kwt197. PMID 23975641.
- ^ Miller, Matthew; Warren, Molly; Hemenway, David; Azrael, Deborah (April 2015). "Firearms and suicide in US cities". Injury Prevention. 21 (e1): e116–e119. doi:10.1136/injuryprev-2013-040969.
- ^ Miller, Matthew; Hemenway, David (2001). "Firearm Prevalence and the Risk of Suicide: A Review" (PDF). Harvard Health Policy Review. 2 (2). Exploring Policy in Health Care (EPIHC): 29–37.
One study found a statistically significant relationship between estimated gun ownership levels and suicide rate across 14 developed nations (e.g. where survey data on gun ownership levels were available), but the association lost its statistical significance when additional countries were included.
- ^ Siegel, Michael; Rothman, Emily F. (July 2016). "Firearm Ownership and Suicide Rates Among US Men and Women, 1981–2013". American Journal of Public Health. 106 (7): 1316–1322. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303182. PMC 4984734. PMID 27196643.
- ^ a b c d e Cook, Philip J.; Ludwig, Jens (2000). Gun Violence: The Real Costs. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195137934. OCLC 45580985.
- ^ Ikeda, Robin M.; Gorwitz, Rachel; James, Stephen P.; Powell, Kenneth E.; Mercy, James A. (1997). "Fatal Firearm Injuries in the United States 1962-1994". Violence Surveillance Summary. 3. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
- ^ "Homicide trends in the U.S. - Weapons used". Bureau of Justice Statistics.
- ^ a b "Homicide trends in the U.S. - Age trends". Bureau of Justice Statistics. Archived from the original on 2006-11-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Expanded Homicide Data Table 7 - Murder Victims by Weapon". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2001–2005. Archived from the original on 2010-04-12.
- ^ a b Monuteaux, Michael C.; Lee, Lois K.; Hemenway, David; Mannix, Rebekah; Fleegler, Eric W. (August 2015). "Firearm Ownership and Violent Crime in the U.S.". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 49 (2): 207–214. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2015.02.008.
- ^ Siegel, Michael; Ross, Craig S; King, Charles (December 2014). "Examining the relationship between the prevalence of guns and homicide rates in the USA using a new and improved state-level gun ownership proxy". Injury Prevention. 20 (6). BMJ Group: 424–426. doi:10.1136/injuryprev-2014-041187.
- ^ Gius, Mark (13 November 2009). "The effect of gun ownership rates on homicide rates: a state-level analysis". Applied Economics Letters. 16 (17): 1687–1690. doi:10.1080/13504850701675508.
- ^ McDowall, David (June 1991). "Firearm Availability and Homicide Rates in Detroit, 1951-1986". Social Forces. 69 (4): 1085. doi:10.2307/2579303.
- ^ Duggan, Mark (October 2001). "More Guns, More Crime". Journal of Political Economy. 109 (5): 1086–1114. doi:10.1086/322833.
- ^ Hepburn, Lisa M; Hemenway, David (July 2004). "Firearm availability and homicide: A review of the literature". Aggression and Violent Behavior. 9 (4): 417–440. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(03)00044-2.
- ^ Kaplan, Mark S.; Geling, Olga (May 1998). "Firearm suicides and homicides in the United States: regional variations and patterns of gun ownership". Social Science & Medicine. 46 (9): 1227–1233. doi:10.1016/S0277-9536(97)10051-X.
- ^ Cooper, Alexia; Smith, Erica L. (December 30, 2013). "Homicide in the U.S. Known to Law Enforcement, 2011". bjs.gov. U.S. Bureau of Justice Statistics. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Friedman, Lawrence M. (1993). "Chapter 8: Lawful Law and Lawless Law: Forms of American Violence". Crime and Punishment in American History. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-01461-5.
- ^ Lane, Roger (1999). Violent Death in the City: Suicide, Accident, and Murder in Nineteenth-Century Philadelphia. Ohio State University Press. ISBN 0-8142-5021-1.
- ^ Fox, James Alan, Marianne W. Zawitz. "Homicide trends in the United States". Bureau of Justice Statistics. Archived from the original on 2006-11-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cork, Daniel (1999). "Examining Time-Space Interaction in City-Level Homicide Data: Crack Markets and the Diffusion of Guns Among Youth". Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 15 (4): 379–406. doi:10.1023/A:1007540007803. NCJ 180974.
- ^ Grogger, Jeff, Mike Willis (1998). "The Introduction of Crack Cocaine and the Rise of Urban Crime Rates". National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper No. 6352. National Bureau of Economic Research.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Blumstein, Alfred (1995). "Youth Violence, Guns and the Illicit-Drug Industry". Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 86 (1). The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology (1973-), Vol. 86, No. 1: 10–36. doi:10.2307/1143998. JSTOR 1143998. NCJ 162687.
- ^ "Crime in the U.S. 2013".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-04-17. Retrieved 2016-05-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Crime in the United States in 2013, table 2". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2013.
- ^ "Crime in the United States in 2013, table 16". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2013.
- ^ "Rate: Number of Crimes per 100,000 Inhabitants by Population Group". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2005.
- ^ "Murder, Types of Weapons Used Percent Distribution within Region". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2005.
- ^ a b Linderman, Juliet (August 4, 2017). "Residents propose 3-day cease fire". Associated Press. ABC News.
- ^ Butts, Jeffrey A., Howard N. Snyder (November 2006). "Too Soon to Tell: Deciphering Recent Trends in Youth Violence". Issue Brief. Chapin Hall Center for Children, University of Chicago.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "American Fact Finder". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ a b c "Expanded Homicide Data Table 3, Murder Victims by Age by Weapon". 2005.
- ^ a b c "Expanded Homicide Data Table 3, Murder Offenders by Age, Sex, and Race". 2005.
- ^ a b Kennedy, David M.; Piehl, Anne M.; Braga, Anthony A. (1996). "Youth Violence in Boston: Gun Markets, Serious Youth Offenders, and a Use-reduction Strategy". Law and Contemporary Problems. 59 (1). Duke University School of Law: 147–196. doi:10.2307/1192213. JSTOR 1192213. NCJ 169549.
- ^ McGonigal, Michael D.; Cole, John; Schwab, C. William; Kauder, Donald R.; Rotondo, Michael F.; Angood, Peter B. (199). "Urban Firearm Deaths: A Five-Year Perspective". Journal of Trauma. 35 (4): 532–6. doi:10.1097/00005373-199310000-00006. PMID 8411275.

- ^ McLaughlin, Colleen R., Jack Daniel, Scott M. Riener, Dennis E. Waite; et al. "Factors Associated with Assault-Related Firearm Injuries in Male Adolescents". Working paper. Virginia Department of Juvenile Justice.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^
Cook, Philip J., Mark H. Moore (1995). "Gun Control". In Wilson, James Q.; Joan Petersilia (eds.). Crime. Institute of Contemporary Studies Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zimring, Franklin E. (March 2004). "Firearms, Violence, and the Potential Impact of Firearms Control". The Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics. 32 (1): 34–37. doi:10.1111/j.1748-720X.2004.tb00446.x.
Gun assaults are seven times as likely to kill as all other kinds of criminal assault, and about five times as likely to kill as are knives, the next most deadly weapon that is frequently used in criminal attacks.
- ^ Asensio J.A.; J. Murray; D. Demetriades; et al. (1998). "Penetrating cardiac injuries: A prospective study of variables predicting outcome". Journal of the American College of Surgery. 186 (1): 24–34. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(97)00144-0. PMID 9449597.
- ^ a b c "Stopping Gun Violence: Time for Innovative Solutions". Forbes. July 8, 2016.
- ^ "Global Study on Homicide 2013: Trends, Contexts, Data" (PDF). www.unodc.org (report). Vienna, Austria: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). 2014.
- ^ Grinshteyn, E; Hemenway, D (March 2016). "Violent Death Rates: The US Compared with Other High-income OECD Countries, 2010". The American Journal of Medicine. 129 (3): 266–73. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.10.025. PMID 26551975.
- ^ "Guns and Suicide: the Hidden Toll". Harvard University.
- ^ "Mexico: Dynamics of the Gun Trade". Stratfor.
- ^ Quealy, Kevin; Sanger-Katz, Margot (2016-06-13). "Compare These Gun Death Rates: The U.S. Is in a Different World". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-10-03.
- ^ a b Parker, Kathleen (September 19, 2013). "Here we go again: After another mass shooting we have same debate". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 9A. Retrieved September 19, 2013.
- ^ a b c Lott, John R.; Whitley, John E. (2001). "Safe-Storage Gun Laws: Accidental Deaths, Suicides, and Crime" (PDF). Journal of Law and Economics. 44 (2): 659–689. doi:10.1086/338346.
- ^ Ungar, Rick. "Here Are The 23 Executive Orders On Gun Safety Signed Today By The President".
- ^ " Priorities for Research to Reduce the Threat of Firearm-Related Violence ." Priorities for Research to Reduce the Threat of Firearm-Related Violence . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2013 .
- ^ Gienapp, William E (2002). Abraham Lincoln and Civil War America. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515100-8.
- ^ a b Koller, Larry (1957). Handguns. Random House. p. 4.
- ^ "Report of the President's Commission on the Assassination of President Kennedy, Chapter 4". Archives.gov. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ Ward, John William (1962). Andrew Jackson. Oxford University Press. p. 114. ISBN 0-19-500699-2.
- ^ Donovan, Robert J. (1996). Tumultuous Years. University of Missouri Press. p. 291. ISBN 0-393-01619-6.
- ^ Winget, Mary Mueller (2007). Gerald R. Ford. Twenty-First Century Books. p. 86. ISBN 0-8225-1509-1.
- ^ "Ronald Reagan's Life, 1979-1982". PBS. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
- ^ Miller, Nathan (1993). Theodore Roosevelt. HarperCollins. p. 530. ISBN 0-688-06784-0.
- ^ "Franklin D. Roosevelt Assassination Attempt - FBI Freedom of Information Act Files - Miami Public Pages". Digital.library.miami.edu. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- ^ a b Weaver, Greg S. (2002). "Firearm Deaths, Gun Availability, and Legal Regulatory Changes: Suggestions from the Data". The Journal of Criminal Law & Criminology. 92 (3/4 (Spring-Summer)). Chicago, Illinois: Northwestern University School of Law: 823–842. doi:10.2307/1144246. JSTOR 1144246.
- ^ Attempted assassination of Ronald Reagan§Aftermath
- ^ a b Cook, Philip J. (1987). "Robbery Violence". Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 70 (2). NCJ 108118.
- ^ Kleck, Gary, K. McElrath (1991). "The Effects of Weaponry on Human Violence". Social Forces. 69 (3). Social Forces, Vol. 69, No. 3: 669–692. doi:10.2307/2579469. JSTOR 2579469. NCJ 134329.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Zimring, Franklin E. (1972). "The Medium is the Message: Firearm Caliber as a Determinant of Death from Assault". Journal of Legal Studies. 1: 97–123. doi:10.1086/467479. NCJ 47874.
- ^ Saltzman, L., J.A. Mercy; et al. (1992). "Weapon Involvement and Injury Outcomes in Family and Intimate Assaults". Journal of the American Medical Association. 267 (22): 3043–3047. doi:10.1001/jama.267.22.3043. PMID 1588718.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i Cook, Philip J.; Ludwig, Jens (2000). "How Guns Matter". Gun Violence: The Real Costs. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195137934. OCLC 45580985.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Cook, Philip J. (1979). "The Effect of Gun Availability on Robbery and Robbery Murder: A Cross-Section Study of Fifty Cities". Policy Studies Review Annual. 3: 743–781.
- ^ Kleck, Gary (1997). Targeting guns: Firearms and their control. Aldine de Gruyter. ISBN 0-202-30569-4.
- ^ Cook, Philip J. (January 1983). "The Influence of Gun Availability on Violent Crime Patterns". Crime and Justice. 4: 49–89. doi:10.1086/449086.
- ^ a b Zimring, Franklin E., Gordon Hawkins (1997). Crime Is Not the Problem: Lethal Violence in America. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-513105-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stolzenberg, L.; D'Alessio, S. J. (1 June 2000). "Gun Availability and Violent Crime: New Evidence from the National Incident-Based Reporting System". Social Forces. 78 (4). Oxford University Press: 1461–1482. doi:10.1093/sf/78.4.1461.
- ^ "US Mass Shootings, 1982-2016: Data From Mother Jones' Investigation". Mother Jones. June 12, 2016.
- ^ a b "The killing contagion". The Week: 11. September 11, 2015.
- ^ "How Redditors Are Changing the Way Media Counts Mass Shootings". 8 October 2015.
- ^ "Blacks Suffer Disproportionate Share of Firearm Homicide Deaths". Pew Research Center. May 21, 2013.
- ^ "Homicide Trends in the United States, 1980-2008" (PDF). U.S. Bureau of Justice Statistics. November 2011.
- ^ "Library of Congress Record". Library of Congress.
- ^ Barnes, Robert (2009-10-01). "Justices to Decide if State Gun Laws Violate Rights". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2010-02-19.
the 5 to 4 opinion in District of Columbia v. Heller did not address the question of whether the Second Amendment extends beyond the federal government and federal enclaves such as Washington.
- ^ Kassirer, Jerome P. (1991). "Firearms and the killing threshold. (Editorial)". New England Journal of Medicine. 325 (23): 1647–1651. doi:10.1056/NEJM199112053252311. PMID 1944455.
- ^ Baker, James Jay (July 1992). "Second amendment message in Los Angeles". American Rifleman: 32–34.
- ^ Boyer, Dave (17 November 2015). "Obama says gun control to be top issue of final year". The Washington Times. Retrieved 14 January 2016.
- ^ The Impact of Gun Ownership Rates on Crime Rates: A Methodological Review of the Evidence, Gary Kleck, Journal of Criminal Justice 43 (2015) 40–48.
- ^ a b LaPierre, Wayne (1994). Guns, Crime, and Freedom. Regnery Publishing. p. 58. ISBN 0-89526-477-3.
- ^ National Safety Council (2017). The State of Safety - A State-by-State Report. Itasca, IL. pg. 27 accessed at: http://www.nsc.org/NSCDocuments_Advocacy/State-of-Safety/State-Report.pdf
- ^ James D. Wright; Peter H. Rossi (1986). ARMED AND CONSIDERED DANGEROUS: A Survey of Felons and their Firearms. Aldine de Gruyter. ISBN 0-202-30543-0.
- ^ Cohen, Jacqueline, Wilpen Gorr, Piyusha Singh (December 2002). "Guns and Youth Violence: An Examination of Crime Guns in One City". Final report. National Institute of Justice/Carnegie Mellon University.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Wright, M.A., G.J. Wintemute, B E Claire (2005). "People and guns involved in denied and completed handgun sales". Injury Prevention. 11 (4): 247–250. doi:10.1136/ip.2005.008482. PMC 1730243. PMID 16081756.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Lizotte, Alan J., Gregory J. Howard, Marvin D. Krohn, Terence P. Thornberry (1997). "Patterns of Illegal Gun Carrying Among Urban Young Males". Valparaiso University Law Review. 31 (2).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Federal Firearm Offenders, 1992-98" (PDF). Bureau of Justice Statistics.
- ^ a b Cook, Philip J., S.Molliconi, T.B. Cole (1995). "Regulating Gun Markets". Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 86 (1). The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology (1973-), Vol. 86, No. 1: 59–92. doi:10.2307/1144000. JSTOR 1144000. NCJ 162689.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wright, James D., Peter H. Rossi (1994). Armed and Considered Dangerous: A Survey of Felons and Their Firearms. Aldine de Gruyter. ISBN 0-202-30543-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ash, Peter, Arthur L. Kellermann; et al. (1996). "Gun Acquisition and Use by Juvenile Offenders". Journal of the American Medical Association. 275 (22): 1754–1758. doi:10.1001/jama.275.22.1754. PMID 8637174.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Boston T. Party (Kenneth W. Royce) (1998). Boston on Guns & Courage. Javelin Press. pp. 3:15. ISBN 1-888766-04-2.
- ^ Weil, Douglas S., Rebecca C. Knox (1996). "Effects of Limiting Handgun Purchases on Interstate Transfer of Firearms". Journal of the American Medical Association. 275 (22): 1759–1761. doi:10.1001/jama.275.22.1759. PMID 8637175.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 4". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Braga, Anthony A.; Wintemute, Garen J.; Pierce, Glenn L.; Cook, Philip J.; Ridgeway, Greg (6 June 2012). "Interpreting the Empirical Evidence on Illegal Gun Market Dynamics". Journal of Urban Health. 89 (5): 779–793. doi:10.1007/s11524-012-9681-y.
- ^ a b c d e f g Rushefsky, Mark E. (2002). "Chapter 7: Criminal Justice: To Ensure Domestic Tranquility". Public Policy in the United States: At the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century. M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 0-7656-0647-X.
- ^ a b Butterfield, Fox (July 1, 1999). "Gun Flows to Criminals Laid to Tiny Fraction of Dealers". The New York Times.
- ^ Webster, D W (1 September 2001). "Relationship between licensing, registration, and other gun sales laws and the source state of crime guns". Injury Prevention. 7 (3): 184–189. doi:10.1136/ip.7.3.184.
- ^ Knight, Brian (November 2013). "State Gun Policy and Cross-State Externalities: Evidence from Crime Gun Tracing". American Economic Journal: Economic Policy. 5 (4): 200–229. doi:10.1257/pol.5.4.200.
- ^ Kahane, Leo H. (July 2013). ", Understanding the Interstate Export of Crime Guns: A Gravity Model Approach". Contemporary Economic Policy. 31 (3): 618–634. doi:10.1111/j.1465-7287.2012.00324.x.
- ^ Coates, Michael; Pearson-Merkowitzz, Shanna (June 2017). "Policy Spillover and Gun Migration: The Interstate Dynamics of State Gun Control Policies". Social Science Quarterly. 98 (2): 500–512. doi:10.1111/ssqu.12422.
- ^ a b "Youth Crime Gun Interdiction Initiative (1998)". Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
- ^ a b Cook, Philip J., Anthony A. Braga (2001). "Comprehensive firearms tracing: Strategic and investigative uses of new data on firearms markets". Arizona Law Review. 43: 277–309.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Wachtel, J. (1998). "Sources of crime guns in Los Angeles, California". Policing: An International Journal of Police Strategies & Management. 21 (2): 220–239. doi:10.1108/13639519810220127. NCJ 174254.
- ^ Pierce, G.L., A.A. Braga, C. Koper, J. McDevitt, D. Carlson, J. Roth, A. Saiz (2001). The Characteristics and Dynamics of Gun Markets: Implications for a Supply-Side Enforcement Strategy (Final Report) (PDF). Center for Criminal Justice Policy Research, Northeastern University and the National Institute of Justice.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Friedman, Lawrence M. (1993). Crime and Punishment in American History. Basic Books. p. 267. ISBN 0-465-01461-5.
- ^ Cook, Philip J., James Blose (1981). "State Programs for Screening Handgun Buyers". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. May 1981: 80–91. doi:10.1177/000271628145500108. NCJ 79101.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ The background check provision has been challenged on grounds that it violates the Tenth Amendment of the Constitution. In the 1997 case, Printz v. United States, the Supreme Court voided that part of the Brady Act. (Rushefsky, 2002)
- ^ "Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act" (PDF). Congress of the United States/Government Printing Office.
- ^ a b Roth, Jeffrey A., Christopher S. Koper (1999). Impacts of the 1994 Assault Weapons Ban: 1994–96 (PDF). National Institute of Justice.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Koper, Christopher S., Jeffrey A. Roth (2001). "The impact of the 1994 federal assault weapon ban on gun markets: An assessment of short-term primary and secondary market effects". Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 18 (3): 239–266. doi:10.1023/A:1016055919939. NCJ 196844.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lawrence, Jill (September 12, 2004). "Federal ban on assault weapons expires". USA Today.
- ^ This was ex post facto, in the opinion of Representative Bob Barr.[1] House of Representatives, Subcommittee on Crime, Committee on the Judiciary, March 5, 1997
- ^ "Domestic Violence Offender Gun Ban Fact Sheet" (asp). National Center for Women & Policing. Retrieved 2007-02-05.
- ^ "House Report 109-699 - Making Appropriations For The Department Of Homeland Security For The Fiscal Year Ending September 30, 2007, And For Other Purposes". The Library of Congress - THOMAS Home - Bills, Resolutions.
- ^ "Obama on gun control: 'We need a change in attitude' - CNNPolitics.com". CNN. Retrieved 2016-01-14.
- ^ "President Obama's 2015 Executive Actions on Gun Control". www.ncsl.org. Retrieved 2016-01-19.
- ^ Boyer, David (17 November 2015). "Obama says gun control to be top issue of final year". The Washington Times. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
- ^ Simmons, Bill (17 November 2015). "President Obama and Bill Simmons: The GQ Interview". GQ Magazine. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
- ^ "Guns in America, Part II". San Antonio Express-News. Archived from the original on June 15, 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ LaPierre, Wayne (1994). Guns, Crime, and Freedom. Regnery Publishing. p. 98. ISBN 0-89526-477-3.
- ^ Boston T. Party (Kenneth W. Royce) (1998). "Chapter 3". Boston on Guns & Courage. Javelin Press. pp. 3:15. ISBN 1-888766-04-2.
- ^ "'Conceal and carry' begins in Wisconsin". KARE. Associated Press. November 1, 2011.
- ^ IL Firearm Concealed Carry Act. Illinois State Police https://www.ccl4illinois.com/ccw/Public/AboutTheAct.aspx.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Lott, Jr., John R., David B. Mustard (1997). "Crime, Deterrence, and Right-to-Carry Concealed Handguns". Journal of Legal Studies. 26 (1): 1–68. doi:10.1086/467988. NCJ 174718.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Black, Dan, Daniel Nagin (1998). "Do 'Right to Carry' Laws Reduce Violent Crime?". Journal of Legal Studies. 27 (1): 209–219. doi:10.1086/468019. NCJ 177169.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ludwig, Jens (1998). "Concealed-Gun-Carrying Laws and Violent Crime: Evidence from State Panel Data". International Review of Law and Economics. 18 (3): 239–254. doi:10.1016/S0144-8188(98)00012-X.
- ^ Rubin, Paul H; Dezhbakhsh, Hashem (June 2003). "The effect of concealed handgun laws on crime: beyond the dummy variables". International Review of Law and Economics. 23 (2): 199–216. doi:10.1016/S0144-8188(03)00027-9.
- ^ Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 6". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Ginwalla, Rashna; Rhee, Peter; Friese, Randall; Green, Donald J.; Gries, Lynn; Joseph, Bellal; Kulvatunyou, Narong; Lubin, Dafney; O’Keeffe, Terence; Vercruysse, Gary; Wynne, Julie; Tang, Andrew (March 2014). "Repeal of the concealed weapons law and its impact on gun-related injuries and deaths". Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 76 (3): 569–575. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000000141.
- ^ Manski, Charles; Pepper, John (2015). "How Do Right-To-Carry Laws Affect Crime Rates? Coping With Ambiguity Using Bounded-Variation Assumptions". NBER working paper.
- ^ a b c d e DeSimone, Jeff, Sara Markowitz (September 2005). "The Effect of Child Access Prevention Laws on Non-Fatal Gun Injuries". NBER Working Paper No. 11613. National Bureau of Economic Research.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Boy finds forgotten gun, accidentally shoots self in head". CNN. April 21, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Cummings, Peter, David C. Grossman, Frederick P. Rivara, Thomas D. Koepsell (1997). "State Gun Safe Storage Laws and Child Mortality Due to Firearms". Journal of the American Medical Association. 278 (13): 1084–1086. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03550130058037. PMID 9315767.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Webster, Daniel, John Vernick; et al. (2004). "Association between Youth-Focused Firearm Laws and Youth Suicides". Journal of the American Medical Association. 292 (5): 594–601. doi:10.1001/jama.292.5.594. PMID 15292085.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lott, John, John E. Whitley (2001). "Safe-Storage Gun Laws: Accidental Deaths, Suicides, and Crime" (PDF). Journal of Law and Economics. 44 (2): 659–689. doi:10.1086/338346.
It is frequently assumed that safe-storage laws reduce accidental gun deaths and total suicides. We find no support that safe-storage laws reduce either juvenile accidental gun deaths or suicides.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ruddel, Rick; Mays, G. Larry (October 2004). "Risky Behavior, Juveniles, Guns, and Unintentional Firearms Fatalities". Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice. 2: 342–358. doi:10.1177/1541204004267782. Retrieved April 6, 2015.
- ^ American Academy of Pediatrics (2016). State Advocacy Focus: Safe Storage of Firearms. Accessed at: https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/state-advocacy/Documents/Safe%20Storage.pdf
- ^ Webster, D.W., M. Starnes (2000). "Reexamining the association between child access prevention gun laws and unintentional shooting deaths of children". Pediatrics. 106 (6): 1466–1469. doi:10.1542/peds.106.6.1466. PMID 11099605.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Federal Appeals Court Strikes Down D.C. Handgun Ban" Bloomberg News, March 9, 2007
- ^ Wintemute, Garen (2000). "Guns and Gun Violence". In Blumstein, Alfred; Joel Wallman (eds.). The Crime Drop in America. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Hardy, Marjorie S. (2002). "Behavior-Oriented Approaches to Reducing Gun Violence". The Future of Children. 12 (2). Woodrow Wilson School / The Brookings Institution: 101–118. doi:10.2307/1602741. NCJ 196785.
- ^ Christophersen, E.R. (1993). "Improving compliance in childhood injury control". Developmental aspects of health compliance behavior. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. pp. 219–231.
- ^ Williams, A.F. (1982). "Passive and active measures for controlling disease and injury". Health Psychology. 1: 399–409. doi:10.1037/h0090242.
- ^ "The Center to Prevent Youth Violence". Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ [2] Archived January 5, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "What is SPEAK UP?". Archived from the original on October 4, 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Oatis, PJ; Fenn Buderer, NM; Cummings, P; Fleitz, R (March 1999). "Pediatric practice based evaluation of the Steps to Prevent Firearm Injury program". Injury Prevention. 5 (1): 48–52. PMID 10323570.
- ^ Oatis, Pamela J., Nancy M. Fenn Buderer, Peter Cummings, Rosemarie Fleitz (1999). "Pediatric practice based evaluation of the Steps to Prevent Firearm Injury program". Injury Prevention. 5 (1): 48–52. doi:10.1136/ip.5.1.48. PMC 1730460. PMID 10323570.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Benthin, A., P. Slovic, H. Severan (1993). "A psychometric study of adolescent risk perception". Journal of Adolescence. 16 (2): 153–168. doi:10.1006/jado.1993.1014. PMID 8376640.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Hyson, M.C., G.G. Bollin (1990). "Children's appraisal of home and neighborhood risks: Questions for the 1990s". Children's Environments Quarterly. 7 (3): 50–60.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Coppens, N.M. (1985). "Cognitive development and locus of control as predictors of preschoolers' understanding of safety and prevention". Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology. 6: 43–55. doi:10.1016/0193-3973(85)90015-2.
- ^ Hemenway, D., S. Solnek, D.R. Azrael (1995). "Firearm training and storage". Journal of the American Medical Association. 273 (1): 46–50. doi:10.1001/jama.273.1.46. PMID 7996649.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wilson, M.H., S.P. Baker, S.P. Teret; et al. (1991). Saving children: A guide to injury prevention. Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sawyer, Diane (21 May 1999). "20/20 Classic: Kids and Guns". ABC News. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ Holman, Virginia. "Is There a Gun in the House?". Parents Magazine. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- ^ Patten, Peggy (2000). "Saying No to Guns: It's Not Enough. An Interview with Marjorie Hardy" (PDF). Parent News [Online]. 6 (4).
- ^ Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry, Committee on Preventative Psychiatry (1999). "Violent behavior in children and youth: Preventative intervention from a psychiatric perspective". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 38 (3): 235–241. doi:10.1097/00004583-199903000-00008.
- ^ Arrendondo, S., T. Aultman-Bettride, T.P. Johnson; et al. (1999). Preventing youth handgun violence: A national study with trends and patterns for the state of Colorado. Center for the Study and Prevention of Violence.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Davidson, L.L., M S Durkin, L Kuhn, P O'Connor, B Barlow, M C Heagarty (1994). "The impact of the Safe Kids/Healthy Neighborhoods Injury Prevention Program in Harlem, 1988 through 1991". American Journal of Public Health. 84 (4): 580–586. doi:10.2105/AJPH.84.4.580. PMC 1614780. PMID 8154560.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Klassen, T.P., I.M. MacKay, A.W. Moher, A. I. Jones (2000). "Community-based prevention interventions". The Future of Children. 10 (1). The Future of Children, Vol. 10, No. 1: 83–110. doi:10.2307/1602826. JSTOR 1602826.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Group Therapy Is Saving Lives in Chicago". POLITICO Magazine. Retrieved 2017-09-22.
- ^ Braga, Anthony A., David M. Kennedy, Elin J. Waring, Anne M. Piehl (2001). "Problem-Oriented Policing, Deterrence, and Youth Violence: An Evaluation of Boston's Operation Ceasefire". Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency. 38 (3). NCJ 189562.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e National Research Council (2004). Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Callahan, Charles M.; Rivara, Frederick P.; Koepsell, Thomas D. (1994). "Money for Guns: Evaluation of the Seattle Gun Buy-Back Program". Public Health Reports. 109 (4). National Center for Biotechnology Information: 472–477. PMC 1403522. PMID 8041845.
- ^ Rosenfeld, Richard (1996). "Gun buy-backs: Crime control or community mobilization?". In Plotkin, Martha R. (ed.). Under Fire: Gun Buy-Backs, Exchanges, and Amnesty Programs. Police Executive Research Forum. NCJ 161877.
- ^ Kennedy, David M.; Piehl, Anne M.; Braga, Anthony A. (1996). "Gun buy-backs: Where do we stand and where do we go?". In Plotkin, Martha R. (ed.). Under Fire: Gun Buy-Backs, Exchanges, and Amnesty Programs. Police Executive Research Forum. NCJ 161877.
- ^ "Gun Bounty Program Makes Big Bust In South Miami-Dade". CBS Local Media. May 26, 2010. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- ^ a b c Kennedy, David M., Anthony A. Braga, Anne M. Piehl (2001). Reducing Gun Violence: The Boston Gun Project's Operation Ceasefire (PDF).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Braga, Anthony A., David L. Weisburd; et al. (1999). "Problem-oriented policing in violent crime places: A randomized controlled experiment". Criminology. 7 (3): 541–580. doi:10.1111/j.1745-9125.1999.tb00496.x. NCJ 178770.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weisburd, D., L. Green (1995). "Policing drug hot spots: The Jersey City drug market analysis experiment". Justice Quarterly. 12 (4): 711–735. doi:10.1080/07418829500096261. NCJ 167667.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sherman, L.W., D. Rogan (1995). "Effects of gun seizures on gun violence: "Hot spots" patrol in Kansas City". Justice Quarterly. 12 (4): 673–694. doi:10.1080/07418829500096241. NCJ 167665.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Braga, Anthony A., Glenn L. Pierce (2005). "Disrupting Illegal Firearms Markets in Boston: The Effects of Operation Ceasefire on the Supply of New Handguns to Criminals". Criminology and Public Policy. 4 (4). NCJ 212303.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ National Institute of Justice (February 2005). Research Report: Reducing Gun Violence - Operation Ceasefire in Los Angeles (PDF).
- ^ "Homicide in Baltimore breaks 'ceasefire' meant to reduce violence". Reuters. No. August 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Raphael, Stephen, Jens Ludwig (2003). "Prison Sentence Enhancements: The Case of Project Exile". In Ludwig, Jens; Philip I. Cook (eds.). Evaluating Gun Policy: Effects on Crime and Violence. Brookings Institution Press. NCJ 203345.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Prison Sentence Enhancements: The Case of Project Exile, in Evaluating Gun Policy by Jens Ludwig and Steven Raphael 251 (2003)
- ^ Did Ceasefire, Compstat, and Exile Reduce Homicide? by Richard Rosenfeld 4 Crimonology & Pub. Pol'y 419 (2005)
- ^ U.S. Department of Justice (May 13, 2003). "Project Safe Neighborhoods - Fact Sheet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Project Safe Neighborhoods: FAQs". U.S. Department of Justice. Archived from the original on 2006-09-29.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 9". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ "'Enough,' Says Giffords As She Launches Campaign For New Gun Laws". NPR. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^ "Giffords and Kelly: Fighting Gun Violence". USA Today. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Une ex-élue du congrès américain, rescapée d'une fusillade, face au lobby des armes à feu" (in French). Libération. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 1". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Committee on Law and Justice (2004). "Chapter 2". Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. National Academy of Science. ISBN 0-309-09124-1.
- ^ Wadman, Meredith (April 24, 2013). "Firearms research: The gun fighter". Nature. 496. Nature Publishing Group: 412–415. doi:10.1038/496412a. PMID 23619673.
- ^ "Access Denied: How the Gun Lobby is Depriving Police, Policy Makers, and the Public of the Data We Need to Prevent Gun Violence". Mayors Against Illegal Guns. January 2013. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
External links
- Gun violence - National Criminal Justice
- US Violent Crime - Data on US Violent Crime
- Gun Violence Archive - Data on each verified gun related incident, with annual statistics
- Report US Anti-gun violence activist art project, Eileen Boxer (2016)
- The Accessibility of Firearms and Risk for Suicide and Homicide Victimization Among Household Members - Anglemyer, Horvath, and Rutherford (2014)
- Guns in the Home and Risk of a Violent Death in the Home - Dahlberg, Ikeda, and Kresnow (2004)
