Ohio State Highway Patrol
This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. (May 2022) |
| Ohio State Highway Patrol | |
|---|---|
| Patch of Ohio State Highway Patrol Patch of Ohio State Highway Patrol | |
 Badge of Ohio State Highway Patrol | |
| Abbreviation | OSHP |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | 1933 |
| Employees | 2,402 (as of 2014) [1] |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | Ohio, USA |
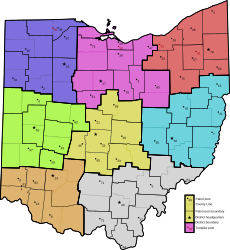 | |
| Ohio State Highway Patrol districts and posts | |
| Size | 44,825 square miles (116,100 km2) |
| Population | 11,689,442 (July 1, 2018) |
| General nature | |
| Operational structure | |
| Headquarters | Columbus, Ohio |
| Troopers | 1,598 (as of 2014) [1] |
| Civilian Members | 804 (as of 2014)[1] |
| Agency executive |
|
| Parent agency | Ohio Department of Public Safety |
| Districts | 9 |
| Website | |
| http://statepatrol.ohio.gov/ | |
The Ohio State Highway Patrol is a division of the Ohio Department of Public Safety and has the primary responsibility of traffic enforcement in the state of Ohio.
Divisions
Operationally, the Patrol is divided into units whose varying tasks complement the mission of the Patrol to provide safe roadways throughout the state. Operational units include the Office of Field Operations, units specializing in Aviation, a Special Response Team, Crash reconstruction, Inspections, Mobile Field Force, and Criminal Patrol; Human Resource Management, includes Labor Relations, Career Development and the Administrative Investigation Unit; Office of Investigative Services, includes statewide investigation of crimes occurring on state owned or leased property, crime lab, polygraph services, executive protection for the governor, criminal intelligence and computer crime unit; License and Commercial Standards, which provide for oversight of driver's license and commercial vehicle regulations throughout the state;[2]
The Patrol also has administrative offices which include the Offices of Technology and Communication Services, Finance and Logistics Services, Strategic Services and Recruitment and Training.[3]
The Patrol maintains 55 posts, each administered by one of ten districts and responsible for one, two, or three of Ohio's 88 counties or the Ohio Turnpike.[4] The Berea/Turnpike District operates from four posts on the Ohio Turnpike. Since the turnpike opened in 1955, the Ohio Turnpike Commission has contracted with the Ohio State Highway Patrol to provide law enforcement and assistance to disabled or stranded motorists. They are the only law enforcement agency with jurisdiction on the turnpike.[citation needed]
Enforcement activities
The Patrol divides the duties of road troopers between traffic enforcement and criminal patrol, with emphasis placed on apprehension of criminals using the state's highways, drug interdiction in particular. Arrests for illegal drugs exceeded 8,400 during the first three quarters of 2017, an increase of 10% over 2016. Recently the Patrol created a mission statement entitled "LifeStat 1.0", detailing the strategic goals for the Patrol.[5] One of the primary goals of this document was the reduction of traffic crash deaths in Ohio to one per 100 million vehicle miles traveled by the end of 2007;[6] the goal was ambitious: the rate reduced to 1.13 in 2007, 1.10 in 2008.[7] According to the Patrol, its 1,400 Troopers made over 1.4 million professional stops in 2006, with 60 percent being non-enforcement stops to help, assist or educate motorists. Twenty-five percent of enforcement-related stops in 2006 was for either aggressive driving or for an OVI offense. The Patrol arrested 26,187 drivers for OVI in 2006, and cited 133,650 drivers for aggressive driving.[8]
Organization
- Superintendent – Colonel
- Assistant Superintendent – Lieutenant Colonel
- Assistant Superintendent – Lieutenant Colonel
- Administrative Staff
- Public Affairs Unit
- Office of Personnel – Major
- Administrative Investigations Unit
- Employee Evaluation & Development
- Employee Relations
- Staffing Services
- Professional Standards Section
- Recruitment
- Regional Training
- Training Academy
- Office of Strategic Services – Major
- The Hub
- Communication Center
- Dispatch Operations
- Criminal Intel Unit
- Finance and Logistics
- Information Technology – LEADS
- Technology and Communication Services
- The Hub
- Office of Special Operations – Major
- Investigations
- Ohio Investigative Unit
- Crime Lab
- Criminal Patrol
- Office of Field Operations – Major
- Aviation
- Capitol Operations
- Crash Reconstruction
- Executive Protection Unit
- Government Affairs
- Licensing and Commercial Standards
- Special Response Team
- Office of Planning and Analysis – Major
- Administrative Audits
- Auxiliary
- Central Records
- Crime Laboratory
- Historical Preservation Unit
- Ohio Traffic Safety Office
- Photographic Services
- Policy Development/Accreditation
- Risk Management Unit
- Special Events Unit
- Statistical Analysis
- Traffic Safety/FARS
Ranks
| Title | Insignia | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Colonel | The Rank of Colonel is held by the OSHP Superintendent. | |
| Lieutenant Colonel | The Rank of Lieutenant Colonel is held by the OSHP Assistant Superintendent.. | |
| Major | Majors are in Command of a single OSHP Office. | |
| Captain | Captains are in Command of a District. | |
| Staff Lieutenant | Staff Lieutenants Serve as Assistant District Commanders. | |
| Lieutenant | Lieutenants are in Command of a Post. | |
| Sergeant | Sergeants Serve as Assistant Post Commanders. | |
| Trooper / Enforcement Agent | No insignia |
Staffing
Troopers
The Patrol has a strength of approximately 1,600 Troopers and Enforcement Agents.
Support staff
The OSHP maintains nearly 1,000 support personnel, including load limit inspectors, motor vehicle inspectors, motor carrier enforcement inspectors, dispatchers, electronics technicians, and civilian specialists..
Auxiliary
The Patrol also maintains an all-volunteer Auxiliary which was created during World War II to supplement staffing lost to the war effort.[9][10]
Police officers
The OSHP also maintains a force of State of Ohio Police Officers mostly located in the Columbus, Ohio area, who provide security police services to the Ohio Department of Transportation and the Ohio Expo Center and State Fairgrounds as well as perform security police functions at special events on state property.[11] State of Ohio Police Officers provide general police services and enforces appropriate laws, rules, regulations, and procedures at selected state facilities. Officers assist in the apprehension and arrest of criminal violators, conduct investigations of suspicious persons and incidents, and assist the public whenever needed. Preliminary qualifications include: United States citizen, Valid driver's license, 21 years of age or older, High school diploma or G.E.D., and OPOTA Certification.[12]
History
The Ohio State Highway Patrol was founded in 1933 under the command of Colonel Lynn Black. Originally, the Highway Patrol used solid black cars with the Flying Wheel on the door. In 1966, white cruisers made their appearance on the Ohio Turnpike. By 1972 all Ohio State Highway Patrol cruisers were white, which they remained until 1982 when they moved to sterling silver. The silver cars remained until 1991. In 1992, they moved to dark grey cruisers marked with the famous "flying wheel" insignia on the doors and a yellow stripe running the length of the car to make patrol cars more visible to motorists, in the hopes of avoiding trooper deaths related to accidents in Northern Ohio's strong winter storms. However, in 2002, the decision was made to transition the force back to white colored patrol vehicles with larger lightbars in response to a number of incidents where troopers were killed by inattentive motorists.[citation needed] Marked cruisers are once again silver in color. The emergency lighting system is now all blue with two red lights in the grille. The Patrol utilizes a variety of vehicles, including Dodge Chargers, Ford Explorers, and Chevrolet Tahoes. The OSHP remains to this day a highly respected organization, having gained CALEA accreditation. The state patrol made the first state wide radio.
As of 2019, Troopers carry the SIG Sauer P320 which replaced the SIG Sauer P226 DAO (Double-Action Only) in .40 S&W, which had been in service since the early 2000s. The pistol prior to the P226 was the Beretta 96 .40 S&W pistol which is a .40 caliber version of the Beretta 92.
In the line of duty
During the history of the Patrol, 41 Troopers have died in performance of their duties.[13]
| Incident | |
|---|---|
| Aircraft accident | 2 |
| Animal related | 1 |
| Automobile crash | 13 |
| Electrocuted | 1 |
| Gunfire | 3 |
| Heart attack | 1 |
| Motorcycle crash | 4 |
| Struck by train | 2 |
| Struck by vehicle | 7 |
| Vehicle pursuit | 3 |
| Vehicular assault | 4 |
Demographics
The OSHP demographics are:[14]
- Male: 91%
- Female: 9%
- White: 86%
- African-American/Black: 11%
- Hispanic: 3%
Auxiliary

The Patrol Auxiliary was created in 1942 when many Troopers entered service with the United States military due to World War II. Originally, members of the Auxiliary were required to be members of the American Legion because they were previous war veterans who were unlikely to be drafted.[15]
Today, volunteer Auxiliary members ride on patrol with Troopers, assist at crash scenes, natural disasters and emergency sites, provide highway safety displays, and patrol the Ohio State Fair.[16]
See also
- List of law enforcement agencies in Ohio
- State police
- State patrol
- Highway patrol
- Mark Dailey – former patrolman and Canadian newscaster
References
- ^ a b c "Dispatch Politics". Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- ^ "Ohio State Highway Patrol-Organizational Units". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Archived from the original on 2007-01-02. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Ohio State Highway Patrol-Organizational Units". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Archived from the original on 2007-01-01. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ "Patrol commissions 41 new troopers". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ "LifeStat 1.0" (PDF). Ohio State Highway Patrol. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-01-02. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ "Ohio Department of Public Safety". State of Ohio. Archived from the original on 2006-10-23. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ "Traffic Safety Facts" (PDF). NHTSA. December 2009.
Table 3: Total Alcohol-Impaired Fatalities and the Corresponding Fatality Rates per 100 Million VMT, 2007–2008. Ohio 1.13 (2007), 1.10 (2008)
- ^ "2006 Ohio Roads Safest on Record". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ "Ohio State Highway Patrol About Us". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Archived from the original on 2007-01-02. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Join OSHP!".
- ^ "OSHP - Training". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- ^ "Join OSHP!".
- ^ "Honoring all the Fallen Members of the Ohio State Highway Patrol". The Officer Down Memorial Page. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Law Enforcement Management and Administrative Statistics, 2000: Data for Individual State and Local Agencies with 100 or More Officers" (PDF). United States Department of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-04. Retrieved 2007-04-11.
- ^ "Patrol Auxiliary". Ohio State Highway Patrol. Archived from the original on 2007-01-02. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Ohio State Highway Patrol Auxiliary". Volunteers in Police Service. Retrieved 2007-01-08.