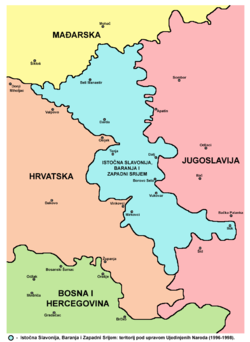
Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia (1995–1998)
Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995–1998 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Status | Self-proclaimed entity | ||||||||
| Capital | Vukovar | ||||||||
| Government | Republic | ||||||||
| Chairman | |||||||||
• 1995–1996 | Borislav Držajić | ||||||||
| President | |||||||||
• 1995–1996 | Slavko Dokmanović | ||||||||
• 1996–1998 | Goran Hadžić | ||||||||
| Historical era | Breakup of Yugoslavia | ||||||||
• Collapse of the RSK | August 1995 | ||||||||
• UNTAES administration | 15 January 1996 | ||||||||
• Reintegrated into Croatia | 15 January 1998 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 2,600 km2 (1,000 sq mi) | |||||||||
| Currency | Krajina dinar de jure Yugoslav dinar de facto Deutsche Mark de facto | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia (Template:Lang-sr / Istočna Slavonija, Baranja i Zapadni Srem; Template:Lang-hr) was a short-lived Serb parallel entity in the territory of Croatia. It encompassed the same territory as the SAO Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia formed in 1990, which had been merged into the Republic of Serbian Krajina. When the latter entity was dissolved with the end of the Croatian War of Independence in 1995, this territory remained in place for another three years.
After the Erdut Agreement, the territory was reintegrated into Croatia within UN peacekeeping mission UNTAES. The Joint Council of Municipalities, a sui generis inter-municipal legal body created during the process of reintegration, aligns the interests of the Serb community in the area.
History
Origins
Eastern Slavonia, Baranja, and Western Syrmia was formed out of the only part of the rebel Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) that was not overrun by Croatian government forces in August 1995. After Operation Storm in August 1995, by which the majority of the Republic of Serbian Krajina was restored to Croatian control, Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia became a de facto self-governing territory. Immediately upon completion of Operation Storm, U.S. President Bill Clinton, within the framework of an initiative to end the war in Bosnia, said that there must be "...a long-term plan for a sustainable solution to the situation in Eastern Slavonia ... based on Croatian sovereignty and the principles outlined in the Z-4 plan".[1] Croatia in this period hesitated between a diplomatic or military solution, but due to strong pressure from the international community, the possibility of military intervention was rejected.[1] In November 1995, local Serb leaders signed the Erdut Agreement, by which the eventual re-integration of this region into Croatia was agreed-upon.[1] The Erdut agreement was reached as part of negotiations at the Dayton Agreement conference.[1] Nevertheless, as of 2007 the Croatian negotiating team had not accepted the Z-4 plan proposed by President Bill Clinton as a basis for negotiations.[1]
Erdut Agreement and establishment of UNTAES

By the Erdut Agreement, Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia was replaced by the United Nations Transitional Administration for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) on 15 January 1996. The goal of the UNTAES mission was the creation of a transitional period during which the UNTAES peacekeepers would oversee a peaceful reintegration of the territory into Croatia. During the 1995–1998 period, the territory was called "Danube Krajina" (Podunavska Krajina) by Serbs, and "Croatian Danube" or "Croatian Podunavlje" (Hrvatsko Podunavlje) by Croats. Within the framework of reintegration in 1996 and under pressure from the international community, an abolition decision was passed for those who participated in rebellion.[1] One of the main tasks for the new United Nations mission was to create conditions for the return of Croats who were expelled during the war in this region.[1] Also, they wanted to avoid a new wave of emigration of ethnic Serbs community in Serbia that was seen after Operation Storm.
In 1998, the UNTAES mission was complete and the territory was formally returned to Croatia. It was sometimes called Podunavska Krajina ("Danube Krajina") by Serbs or Hrvatsko Podunavlje (Croatian Danube) by Croats. The name often used for it between 1995 and 1998 was Syrmia-Baranja Oblast (Serbian/Croatian: Sremsko-baranjska oblast/Srijemsko-baranjska oblast). Sometimes, the shortened name Eastern Slavonia (Serbian/Croatian: Istočna Slavonija) was also used as a designation for this region.[1]
Local authorities until the end of reintegration

After Operation Flash, representatives of Republika Srpska and Republic of Serbian Krajina announced that they would implement unification of these two entities.[2] In response to this, local Serb leaders in Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia founded a body called the Coordinating Committee that opposed unification, arguing that it would just deepen the crisis and damage Belgrade's intentions to achieve peace in Bosnia.[2] Authorities of the Republic of Serbian Krajina in Knin declared the goal of the Coordinating Committee to be the secession of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia from Republic of Serbian Krajina, claiming that there is now no power in Knin, but instead in Belgrade.[2] This statement became a reality once Operation Storm was completed because western parts of Republic of Serbian Krajina no longer existed. During the Croatian military actions Flash and Storm on western parts of Krajina, the army in Eastern Slavonia did not act against the Croatian Army.[2] However, local Serbs representatives strongly condemned the actions of the Croatian Army. After these events, and institution was established that was called the National Council Syrmia-Baranja Oblast and the region's name was changed to Syrmia-Baranja Oblast.[2] Since the region was keen to maintain continuity with the Republic of Serbian Krajina for future negotiations, the region also established the National Council of Republic of Serbian Krajina of Syrmia-Baranja Oblast.[2] In 1996 in Ilok, there was a proposal to abolish the District Assembly because there were no conditions for its work.[2] However, this proposal was rejected.[2] The District Assembly was a body with 50 members elected in elections.[2] In 1997 in Vukovar, the Independent Democratic Serb Party was established.[2] That same year, the Joint Council of Municipalities was founded, and by the end of reintegration, all the other entities were abolished and replaced by Croatian institutions.[2]
Local Serb population and Serbs from other parts of Croatia
The local Serb population did not regard the plans to reunite the region with Croatia with approval. At the end of June 1996, NGOs in the region organized a petition that asked that the region remain a special area with independent executive, legislative and judiciary. The petition was signed by 50,000 residents of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia.[2] The petition was then sent to the United Nations.[2] In 1997 in Vukovar, protests were organized in which the local population called for the establishment of autonomous Serbian institutions after the completion of reintegration.[2] The protests gathered between 5,000 and 12,000 participants.[2] At the protests, protesters expressed opposition to the partition of the region in two Croatian counties (Vukovar-Syrmia County and Osijek-Baranja). That question was posed in a referendum in which, according to the Electoral Commission, voter turnout was 77.40%; 99.01% of voters voted for the integrity of the region within Croatia.[2] Nonetheless, it did not prevent the decision and the region was divided. Representatives of United Nations missions in the region said that the referendum was irrelevant because such an option was never considered.[2]
Croats from the region

The majority of ethnic Croats from Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia were expelled from the region in conflicts in the early nineties. The persecution of 150 locals of Ćelije in the village of Trpinja municipality in July 1991 was the first mass exodus of the population in the Croatian War.[3] Although one of the tasks of the first United Nations mission UNPROFOR was to create conditions for the return of refugees, little had been done on that issue before signing Erdut Agreement.[1] This prompted refugees to organize themselves in new communities in Croatia. These refugees from the region that are now living in Croatia organized regional clubs, refugee organizations and exhibitions.[1] In addition, newspapers and other publications were published in other parts of Croatia, which included Vukovarske Novine (Vukovar Newspaper), Hrvatski Tovarnik (Croatian Tovarnik), Iločki list (Ilok magazine), Lovaski list (Lovas magazine), Baranjske novine (Baranja newspaper), Vukovarac () and Zov Srijema (Syrmia Calls).[1] There also were organized protests against UNPROFOR and blockades of official UNPROFOR crossings between region and Croatia.[1] By the end of UNTAES mandate, only two Catholic churches in region still were in regular function.[4]
Events after the completion of reintegration
Upon the completion of the reintegration at the territory of the former Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia, the Joint Council of Municipalities was established as a result of the Erdut Agreement. However, this unit can not legally be linked as the successor of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia, but instead as a new legal institution. In the former capital Vukovar, the consulate general of the Republic of Serbia was opened in 1998. A large number of Serbian minority institutions in the area were established or continued to work, such as the Eparchy of Osječko polje and Baranja, Radio Borovo, the Association for Serbian language and literature in the Republic of Croatia, the Independent Democratic Serb Party, and others. Croatia and Serbia still have open border disputes in this area around the two islands on the Danube – the Island of Vukovar and the Island of Šarengrad.
Geography
The territory of former Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia is part of the Central European Pannonian Basin. The eastern border of the region was mostly the Danube river, while approximately one third of the western border was the Drava river. The Kopački rit natural preserve was located near the confluence of Drava and Danube, and it formed a major geographical barrier – there were no road or rail connections between Baranja and the southern parts of the territory, except through Serbia.
Other boundaries were not natural boundaries: the border with Hungary in the north had existed since the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, the eastern border with FR Yugoslavia partly existed since the Kingdom of Slavonia (on the Danube) and was partly set with the formation of SFR Yugoslavia, while the border with the rest of Croatia in the west and south was formed after the fronts were settled in the first phase of the Croatian War of Independence.
Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia on its territory had 124 settlements, and with its 193,510 inhabitants, it was the largest Serbian Autonomous Oblast by population created on the territory of Croatia.[3]
Eastern Slavonia is a mostly flat area, with the best type of soil where agriculture is highly developed, particularly on wheat fields. It also has several forests as well as vineyards.
The Đeletovci Oil Fields are located between the villages of Đeletovci, Banovci and Nijemci.
Traffic over the Brotherhood and Unity Highway (today the A3) was interrupted with the formation of the ESBWS. The water transport over the Danube river continued unobstructed. The Drava river was not navigated at the time. The railway line between Zagreb and Belgrade and the transport between Budapest and Sarajevo were also closed.
Government
Presidents of the Coordinating Committee
- Slavko Dokmanović (7 August 1995 – 1996)
- Goran Hadžić (1996 – 15 January 1998)
Chairmen of the Executive Committee
- Borislav Držajić (7 August 1995 – 1996)
- Vojislav Stanimirović (1996 – 15 January 1998)
See also
Further reading
- The Thorny Issue of Ethnic Autonomy in Croatia: Serb Leaders and Proposals for Autonomy, Nina Caspersen, London School of Economics and Political Science (https://web.archive.org/web/20110302211937/http://www.ecmi.de/fileadmin/downloads/publications/JEMIE/2003/nr3/Focus3-2003_Caspersen.pdf)
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Bing, Albert (2007). "Put do Erduta-Položaj Hrvatske u međunarodnoj zajednici 1994.-1995. i reintegracija hrvatskog Podunavlja". Scrinia Slavonica. 7. Zagreb: Hrvatski institut za povijest: 371–404.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Barić, Nikica (2011). "Srpska oblast Istočna Slavonija, Baranja i Zapadni Srijem – od "Oluje" do dovršetka mirne reintegracije hrvatskog Podunavlja (prvi dio)". Scrinia Slavonica. 11. Zagreb: Hrvatski institut za povijest: 393–451.
- ^ a b Živić, Dražen (2003). "Prognano stanovništvo iz hrvatskog Podunavlja i problemi njegovog povratka (1991.-2001.)". Hrvatski Geografski Glasnik. 65 (1). Zagreb: 63–81. doi:10.21861/HGG.2003.65.01.04.
- ^ Derek Boothby (January–March 2004). "The Political Challenges of Administering Eastern Slavonia". Global Governance. 10 (1). Global Governance: A Review of Multilateralism and International Organizations: 37–51. JSTOR 27800508.
- States and territories established in 1995
- States and territories disestablished in 1998
- Republic of Serbian Krajina
- History of Baranya (region)
- History of Syrmia
- History of Slavonia
- Former Slavic countries
- History of the Serbs of Croatia
- Serbian nationalism in Croatia
- 1995 establishments in Europe
- 1998 disestablishments in Europe


