From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pharmaceutical drug
Pharmaceutical compound
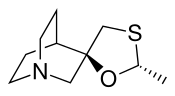
Cevimeline (trade name Evoxac ) is a synthetic analog of the natural alkaloid muscarine with a particular agonistic effect on M1 and M3 receptors . It is used in the treatment of dry mouth and Sjögren's syndrome .
Cevimeline is used in the treatment of xerostomia (dry mouth)[ 1] [ 2] Sjögren's syndrome .[ 1] [ 2]
Known side effects include nausea , vomiting , diarrhea , excessive sweating , rash , headache , runny nose , cough , drowsiness , hot flashes , blurred vision , and difficulty sleeping .[ 3]
Contraindications include asthma and angle closure glaucoma .[citation needed
Mechanism of action [ edit ] Cevimeline is a cholinergic agonist.[ 2] M1 and M3 receptors .[ 2] 3 receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system , cevimeline stimulates secretion by the salivary glands , thereby alleviating dry mouth.
Pilocarpine — a similar parasympathomimetic medication for dry mouth (xerostomia )Bethanechol — a similar muscarinic parasympathomimetic with longer-lasting effect
mAChRs Tooltip Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Agonists Antagonists
3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate 4-DAMP Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol )Abediterol AF-DX 250 AF-DX 384 Ambutonium bromide Anisodamine Anisodine Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine , buclizine , captodiame , chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine) , cinnarizine , clemastine , cyproheptadine , dimenhydrinate , dimetindene , diphenhydramine , doxylamine , meclizine , mequitazine , perlapine , phenindamine , pheniramine , phenyltoloxamine , promethazine , propiomazine , triprolidine )AQ-RA 741 Atropine Atropine methonitrate Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine , fluperlapine , olanzapine (+fluoxetine ), rilapine , quetiapine , tenilapine , zotepine )Benactyzine Benzatropine (benztropine) Benzilone Benzilylcholine mustard Benzydamine Bevonium BIBN 99 Biperiden Bornaprine Camylofin CAR-226,086 CAR-301,060 CAR-302,196 CAR-302,282 CAR-302,368 CAR-302,537 CAR-302,668 Caramiphen Cimetropium bromide Clidinium bromide Cloperastine CS-27349 Cyclobenzaprine Cyclopentolate Darifenacin DAU-5884 Desfesoterodine Dexetimide DIBD Dicycloverine (dicyclomine) Dihexyverine Difemerine Diphemanil metilsulfate Ditran Drofenine EA-3167 EA-3443 EA-3580 EA-3834 Emepronium bromide Etanautine Etybenzatropine (ethybenztropine) Fenpiverinium Fentonium bromide Fesoterodine Flavoxate Glycopyrronium bromide (+beclometasone/formoterol , +indacaterol , +neostigmine )Hexahydrodifenidol Hexahydrosiladifenidol Hexbutinol Hexocyclium Himbacine HL-031,120 Homatropine Imidafenacin Ipratropium bromide (+salbutamol )Isopropamide J-104,129 Hyoscyamine Mamba toxin 3 Mamba toxin 7 Mazaticol Mebeverine Meladrazine Mepenzolate Methantheline Methoctramine Methylatropine Methylhomatropine Methylscopolamine Metixene Muscarinic toxin 7 N-Ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate N-Methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate Nefopam Octatropine methylbromide (anisotropine methylbromide) Orphenadrine Otenzepad (AF-DX 116) Otilonium bromide Oxapium iodide Oxitropium bromide Oxybutynin Oxyphencyclimine Oxyphenonium bromide PBID PD-102,807 PD-0298029 Penthienate Pethidine pFHHSiD Phenglutarimide Phenyltoloxamine Pipenzolate bromide Piperidolate Pirenzepine Piroheptine Pizotifen Poldine Pridinol Prifinium bromide Procyclidine Profenamine (ethopropazine) Propantheline bromide Propiverine Quinidine 3-Quinuclidinyl thiochromane-4-carboxylate Revefenacin Rociverine RU-47,213 SCH-57,790 SCH-72,788 SCH-217,443 Scopolamine (hyoscine) Scopolamine butylbromide (hyoscine butylbromide) Silahexacyclium Sofpironium bromide Solifenacin SSRIs Tooltip Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (e.g., femoxetine , paroxetine )Telenzepine Terodiline Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin , mirtazapine )Tiemonium iodide Timepidium bromide Tiotropium bromide Tiquizium bromide Tofenacin Tolterodine Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline (+perphenazine ), amitriptylinoxide , butriptyline , cidoxepin , clomipramine , desipramine , desmethyldesipramine , dibenzepin , dosulepin (dothiepin) , doxepin , imipramine , lofepramine , nitroxazepine , northiaden (desmethyldosulepin) , nortriptyline , protriptyline , quinupramine , trimipramine )Tridihexethyl Trihexyphenidyl Trimebutine Tripitamine (tripitramine) Tropacine Tropatepine Tropicamide Trospium chloride Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , chlorprothixene , cyamemazine (cyamepromazine) , loxapine , mesoridazine , thioridazine )Umeclidinium bromide (+vilanterol )WIN-2299 Xanomeline Zamifenacin
Precursors (and prodrugs )