Flubendazole
Appearance
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (November 2014) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.007 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
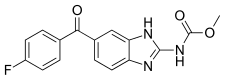
| Formula | C16H12FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 313.28 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 260 °C (500 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Flubendazole is an anthelmintic. Its brand name is Flutelmium which is a paste manufactured by Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. used by veterinarians for protection against internal parasites and worms in dogs and cats. Other brand names are Flubenol, Biovermin, and Flumoxal.[1]
It is also available for human use to treat worm infections. It is available OTC (without prescription) in Europe. Flubendazole-treated grit is used on UK grouse-shooting moors to reduce impact on the bird numbers from strongyle worm. Evidence of high worm burden is required before a veterinarian can dispense and sell the product, known as 'medicated grit'.[2]
See also
- Etibendazole (ditto albeit ethanediol cyclic ketal).
References
- ^ US Patent 5824336 - Chewable flubendazole tablets for companion animals
- ^ "Best practice use of medicated grit". Game and Wildlife Conservation Trust. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
