Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders are the peoples of the Pacific Islands.
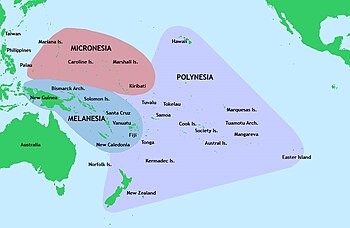
Pacific Islander regions
According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, the Pacific islands consist of three regions:
Polynesia
The islands scattered across a triangle covering the east-central region of the Pacific Ocean. The triangle is bound by the Hawaiian Islands in the north, New Zealand in the west, and Easter Island in the east. The rest of Polynesia includes the Samoan islands (American Samoa and Samoa), the Cook Islands, French Polynesia (Tahiti and The Society Islands, Marquesas Islands, Austral Islands, and the Tuamotu Archipelago), Niue Island, Tokelau and Tuvalu, Tonga, Wallis and Futuna, and Pitcairn Island.
Melanesia
The island of New Guinea, the Bismarck and Louisiade archipelagos, the Admiralty Islands, Bougainville Island, Maluku Islands, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, the Santa Cruz Islands (part of the Solomon Islands), New Caledonia and Loyalty Islands, Vanuatu (formerly New Hebrides), Fiji, Norfolk Island, and various smaller islands.
Micronesia
The islands of Kiribati, Nauru, the Marianas (Guam and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands), the Republic of the Marshall Islands, Palau, and the Federated States of Micronesia (Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae, all in the Caroline Islands).
The Pacific islands may also refer to any of the other islands in the Pacific Ocean.
Ethnolinguistics
Ethnolinguistically, those Pacific islanders who reside in Oceania are divided into two different ethnic classifications.
- Austronesian language peoples
- Austronesian peoples who speak the Oceanian languages, numbering about 2.3 million, who occupy Polynesia, Micronesia, and most of the smaller islands of Melanesia.
- Papuan language peoples
- Papuan peoples, those who speak the Papuan languages, who number about 7 million, and reside on the island of New Guinea and a few of the smaller islands of Melanesia located off the northeast coast of New Guinea.[1]
Usage of phrase by country
Australia
In Australia the term South Sea Islander was used to describe Australian descendants of people from the more than 80 islands in the western Pacific who had been brought to Australia to work on the sugar fields of Queensland,[2] in the 19th century called Kanakas. The Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901 was enacted to restrict entry of Pacific Islanders to Australia and to authorise their deportation. In the legislation Pacific Islanders were defined as:
"Pacific Island Labourer" includes all natives not of European extraction of any island except the islands of New Zealand situated in the Pacific Ocean beyond the Commonwealth [of Australia] as constituted at the commencement of this Act.[3]
In 2008 a Pacific Seasonal Worker Pilot Scheme was announced as a three-year pilot scheme.[4] The scheme provides visas for workers from Kiribati, Tonga, Vanuatu and Papua New Guinea to work in Australia.[5] The pilot scheme includes one country each from Melanesia (Vanuatu), Polynesia (Tonga) and Micronesia (Kiribati), countries which already send workers to New Zealand under its seasonal labour scheme. Australia's pilot scheme also includes Papua New Guinea.[6][7]
New Zealand
Local usage in New Zealand uses "Pacific islander" (or "Pasifika") to distinguish those who have emigrated from one of these areas in modern times from the indigenous New Zealand Māori, who are also Polynesian, but arrived in New Zealand centuries earlier.
In 2013 7.4 percent of the New Zealand population identified with one or more Pacific ethnic groups, although 62.3 percent of these were born in New Zealand. Those with a Samoan background make up the largest proportion, followed by Cook Islands Maori, Tongan, and Niuean.[8]
Some smaller island populations such as Niue and Tokelau have the majority of their nationals living in New Zealand (Smelt, and Lin, 1998).
To celebrate the diverse Pacific island cultures, the Auckland region hosts several Pacific island festivals. Two of the major ones are Polyfest, which showcases performances of the secondary school cultural groups in the Auckland region, and Pasifika, a festival that celebrates Pacific island heritage through traditional food, music, dance, and entertainment.
United States
According to the U.S. Bureau of the Census, Population Estimates Program (PEP), a "Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander" is "A person having origins in any of the original peoples of Hawaii, Guam, Samoa, or other Pacific islands. It includes people who indicate their race as 'Native Hawaiian', 'Guamanian or "Chamorro', 'Samoan', and 'Other Pacific Islander' or provide other detailed Pacific Islander responses."[9]
According to the Office of Management and Budget, "Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander" refers to a person having origins in any of the original peoples of Hawaii, Guam, Samoa, or other Pacific Islands.
The term Pacific Islands American is used for ethnic Pacific islander residents in U.S. states, and in the territories of the United States in the region.[10]
List of Pacific peoples
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2008) |
- Austronesian-speaking peoples
- Polynesians
- Western Polynesian-Melanesian region
- Northeast & South Polynesian region
- Melanesians
- Micronesians
- Marshallese
- Palauans
- Carolinians
- Chamorros
- Chuukese
- Yapese
- Kosraens
- Pohnpeians
- Nauruans
- Polynesians
See also
- Asian American and Pacific Islander Policy Research Consortium
- Pacific Islands Americans
- Indigenous peoples of Oceania
- Indigenous Australians
- Australian Aborigines
- Taiwanese Aborigines
- Tasmanian Aborigines
- Blackbirding
References
- ^ "Pacific Islands on Encyclopædia Britannica".
- ^ "South Sea Islander Project". ABC Radio Regional Production Fund. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2004. Retrieved 2008-08-27.
Recognition for Australian South Sea Islanders (ASSI) has been a long time coming. It was not until 1994 that the federal government recognized them as a distinct ethnic group with their own history and culture and not until September 2000 that the Queensland government made a formal statement of recognition.
- ^ "Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901 (Cth)" (PDF). Documenting a Democracy. National Archives of Australia. 1901. Retrieved 2008-08-27.
- ^ Australian Institute of Criminology: Australia's Pacific Seasonal Worker Pilot Scheme: Managing vulnerabilities to exploitation
- ^ "Pacific guestworker scheme to start this year". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2008-08-17.
- ^ "Seasonal Worker Pilot Scheme is more proof of Australia's new Pacific focus" (Press release). The Hon Duncan Kerr SC MP; Parliamentary Secretary for Pacific Island Affairs. 2008-08-20.
- ^ Australian classification standards code Pacific islanders, Oceanians, South Sea islanders, and Australasians all with code 1000, i.e., identically. This coding can be broken down into the finer classification of 1,100 Australian Peoples; 1,200 New Zealand peoples; 1,300 Melanesian and Papuan; 1,400 Micronesian; 1,500 Polynesian. There is no specific coding therefore for "Pacific islander"."Australian Standard Classification of Cultural and Ethnic Groups (ASCCEG) - 2nd edition" (pdf - 136 pages). Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2005-07-07. Retrieved 2008-08-27.
- ^ "Pacific peoples ethnic group", 2013 Census, Statistics New Zealand
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20130403171145/http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/meta/long_RHI525211.htm. Archived from the original on April 3, 2013. Retrieved March 27, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gary Y. Okihiro, American History Unbound: Asians and Pacific Islanders (University of California Press, 2015). xiv, 499 pp.
Further reading
- Lal, B., & Fortune, K. (Eds.). (2000). The Pacific Islands: An encyclopedia. Honolulu, HI: University of Hawaii Press.
- Okihiro, Gary Y. American History Unbound: Asians and Pacific Islanders (University of California Press, 2015). xiv, 499 pp.
- Smelt, R., & Lin, Y. (1998). Cultures of the world: New Zealand. Tarrytown, NY: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark
- Thomas, Nicholas, Islanders: The Pacific in the Age of Empire, Yale University Press, 2010. ISBN 978-0-300-12438-5
External links
- Statistics New Zealand . Retrieved March 21, 2013.
