1941 Philippine House of Representatives elections
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
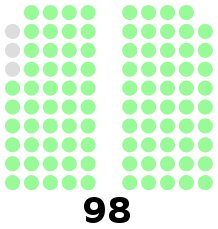
All 98 seats in the House of Representatives of the Philippines 50 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
The Elections for the House of Representatives of the Philippines were held on November 11, 1941, with the ruling Nacionalista Party retaining a majority of the seats. Still, the party was prevented a clean sweep when three independents were elected. The elected congressmen were supposed to serve from December 30, 1941 to December 30, 1945 but World War II intervenedied Imperial Japan invaded the Philippines on December 8, 1941 and set up a puppet Second Philippine Republic, which then organized the National Assembly of the Second Philippine Republic in which its members were elected in 1943.[1][2]
The Philippines was re-taken by the Allied Powers in 1945 and the acts of the Second Republic were nullified; elected representatives who survived the war and were not interred for collaboration with the Japanese served until those who won in elections that were held in 1946 took office.
Results
|
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Seats | +/– | |
| Nacionalista Party | 94 | −4 | |
| Popular Front | 2 | +1 | |
| Partido Democrata Nacional | 1 | +1 | |
| Young Philippines | 1 | +1 | |
| Total | 98 | 0 | |
| Source: Teehankee[3] and PCDSPO[4] | |||
See also
References
- ^ Philippine Electoral Almanac. The Presidential Communications Development and Strategic Planning Office. 2013. p. 17. Archived from the original on 2014-04-09.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Liang, Dapen. Philippine Parties & Politics: A Historical Study of National Experience in Democracy.
- ^ Teehankee, Julio (2002). "Electoral Politics in the Philippines" (PDF). In Croissant, Aurel (ed.). Electoral Politics in Southeast and East Asia. Singapore: Fiedrich-Ebert-Siftung. pp. 149–202 – via quezon.ph.
- ^ Presidential Communications Development & Strategic Planning Office (2015). Philippine Electoral Almanac (Revised and expanded ed.). Manila: Presidential Communications Development and Strategic Planning Office – via Internet Archive.
- The Presidents of the Senate of the Republic of the Philippines. ISBN 971-8832-24-6.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=,|chapterurl=, and|coauthors=(help) - Pobre, Cesar P. Philippine Legislature 100 Years. ISBN 971-92245-0-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=,|chapterurl=, and|coauthors=(help) - Teehankee, Julio. "Electoral Politics in the Philippines" (PDF). quezon.ph. Retrieved 2010-12-06.

