Ponatinib
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Iclusig |
| Other names | AP24534 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
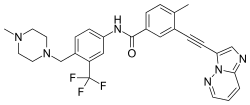
| Formula | C29H27F3N6O |
| Molar mass | 532.56 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ponatinib (trade name Iclusig, previously AP24534) is an Food and Drug Administration–approved oral drug candidate developed by ARIAD Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It is a multi-targeted tyrosine-kinase inhibitor.[1] Some forms of CML, those that have the T315I mutation, are resistant to current therapies such as imatinib. Ponatinib has been designed to be effective against these types of tumors.[2]
Oncologists have complained, however, that many patients can not afford the "astronomical" cost of $138,000 a year, which makes it one of the most expensive drugs in medicine, and far more expensive than what is needed to pay the development costs.[3][4]
The Food and Drug Administration temporarily suspended sales of the drug in the U.S. on 31 October 2013 because of “the risk of life-threatening blood clots and severe narrowing of blood vessels”.[5][6] This suspension was partially lifted on Dec. 20, 2013 with ponatinib being issued revised prescribing information, a new "Black Box Warning" and a "Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy" in place to better evaluate the risks and benefits of using the drug.
Approvals and indications
Ponatinib was approved by the US FDA on December 14, 2012, for patients with resistant or intolerant CML and Ph+ ALL, based on results of the PACE phase II trial reported days earlier at the annual ASH meeting.[7] Because the approval was under the FDA's accelerated approval program the applicant will be required to carry out additional studies.
Adverse effects
The United States Food and Drug Administration issued a partial clinical hold on new trial enrollment for Iclusig on 9 October 2013 due to an increased number of blood clots observed in patients taking the drug.[8] The EPIC trial was later cancelled on 18 October.[9]
Clinical trials
The PACE (Ponatinb Ph+ ALL and CML Evaluation) pivotal phase II trial started enrolling patients in September 2010 and is designed to provide definitive clinical data for regulatory approval in this setting. Good results were reported in Dec 2012.[7][10]
At the 2010 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, ARIAD announced from a Phase I study of ponatinib in patients with resistant and refractory chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). The study demonstrated that in chronic-phase CML patients treated with ponatinib, 66 percent of patients in the trial achieved a major cytogenetic response, including 100 percent of patients who also had a T315I mutation.[citation needed]
The EPIC (Evaluation of Ponatinib versus Imatinib in CML) phase-III trial began in June 2012 [11] and was halted on 18 October 2013.
Mechanism of action
The primary target for ponatinib is BCR-ABL, an abnormal tyrosine kinase that is the hallmark of CML and Ph+ ALL. CML is characterized by an excessive and unregulated production of white blood cells by the bone marrow due to a genetic abnormality that produces the BCR-ABL protein. After a chronic phase of production of too many white blood cells, CML typically evolves to more aggressive phases such as accelerated or blast crisis. Ph+ ALL is a subtype of acute lymphoblastic leukemia that carries the Ph+ chromosome that produces BCR-ABL. It has a more aggressive course than CML and is often treated with a combination of chemotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Because both of these diseases express the BCR-ABL protein, this would render them potentially susceptible to treatment with ponatinib. BCR-ABL is detected in 95% of patients with CML. Patients with CML currently receive front line therapies nilotinib and/or dasatinib though 22−33% of patients discontinue therapy by two years due to adverse events, treatment failure and other causes.[citation needed]
Discovery and origin
Ponatinib was designed using ARIAD’s computational and structure-based drug design platform to inhibit the enzymatic activity of BCR-ABL with very high potency and broad specificity. Ponatinib was intended to target not only native BCR-ABL, but also its isoforms that carry mutations that confer resistance to treatment with existing tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including especially the T315I mutation for which no effective therapy exists.[12]
The road to discovery can be linked to AP23464, one of the first of Ariad's ATP competitive dual Src/Abl inhibitors. AP23464 was identified using structure base drug design and focused synthetic libraries of trisubstituted purine analogs. The substance potently inhibits, on nanomolar scale, Src and Bcr-Abl kinases including many common imatinib resistant Bcr-Abl mutations. AP23464 does not inhibit the T315I mutation, however, whereas AP24534 (ponatinib) does.
See also
References
- ^ {{cite journal | author = Huang WS, Metcalf CA, Sundaramoorthi R, Wang Y, Zou D, Thomas RM, Zhu X, Cai L, Wen D, Liu S, Romero J, Qi J, Chen I, Banda G, Lentini SP, Das S, Xu Q, Keats J, Wang F, Wardwell S, Ning Y, Snodgrass JT, Broudy MI, Russian K, Zhou T, Commodore L, Narasimhan NI, Mohemmad QK, Iuliucci J, Rivera VM, Dalgarno DC, Sawyer TK, Clackson T, Shakespeare WC | title = Discovery of 3-[2-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-yl)ethynyl]-4-methyl-N-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzamide (AP24534), a potent, orally active pan-inhibitor of breakpoint cluster region-abelson (BCR-ABL) kinase including the T315I gatekeeper mutant | journal = J. Med. Chem. | volume = 53 | issue = 12 | pages = 4701–19 | year = 2010 | month = June | pmid = 20513156 | doi = 10.1021/jm100395q }}
- ^ O'Hare T, Shakespeare WC, Zhu X, Eide CA, Rivera VM, Wang F, Adrian LT, Zhou T, Huang WS, Xu Q, Metcalf CA, Tyner JW, Loriaux MM, Corbin AS, Wardwell S, Ning Y, Keats JA, Wang Y, Sundaramoorthi R, Thomas M, Zhou D, Snodgrass J, Commodore L, Sawyer TK, Dalgarno DC, Deininger MW, Druker BJ, Clackson T (2009). "AP24534, a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor for chronic myeloid leukemia, potently inhibits the T315I mutant and overcomes mutation-based resistance". Cancer Cell. 16 (5): 401–12. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.09.028. PMC 2804470. PMID 19878872.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pollack A (April 25, 2013). "Doctors Denounce Cancer Drug Prices of $100,000 a Year". New York Times.
- ^ "The price of drugs for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a reflection of the unsustainable prices of cancer drugs: from the perspective of a large group of CML experts". Blood. 121 (22): 4439–42. 2013. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-03-490003. PMID 23620577.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "FDA asks manufacturer of the leukemia drug Iclusig (ponatinib) to suspend marketing and sales". FDA Drug Safety Communication. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2013-10-31.
- ^ Grady D (2013-10-31). "Serious Danger of Blood Clots Halts Sale of Leukemia Drug". Business. New York Times.
- ^ a b Gever J (Dec 14, 2012). "Ponatinib Wins Early FDA Nod". Oncology/Hematology. MedPageToday.com.
- ^ Carroll J. "UPDATED: Ariad hammered on toxicity concerns for leukemia drug Iclusig". FierceBiotech.
- ^ "ARIAD Announces Discontinuation of the Phase 3 Epic Trial of Iclusig in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia".
- ^ Gever J (Dec 10, 2012). "Ponatinib Retains Luster in Leukemia". Oncology/Hematology. MedPageToday.com.
- ^ "Ponatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia".
- ^ Zhou T, Commodore L, Huang WS, Wang Y, Thomas M, Keats J, Xu Q, Rivera VM, Shakespeare WC, Clackson T, Dalgarno DC, Zhu X (2011). "Structural mechanism of the Pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor ponatinib (AP24534): lessons for overcoming kinase inhibitor resistance". Chem Biol Drug Des. 77 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.01054.x. PMID 21118377.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
