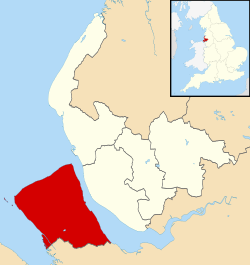
Metropolitan Borough of Wirral
The Metropolitan Borough of Wirral is a metropolitan borough of Merseyside, in North West England. It has a population of 322,453 (2022),[3] and encompasses 62 square miles (161 km2) of the northern part of the Wirral Peninsula. Major settlements include Birkenhead, Wallasey, Bebington, Heswall, Hoylake and West Kirby. Wirral is England's westernmost metropolitan borough, faced by the city of Liverpool to the northeast over the River Mersey.
Geography
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2020) |
Bordering is the River Mersey to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and the River Dee to the west; the borough of Cheshire West and Chester occupies the remainder of the Wirral Peninsula and borders the borough of Wirral to the south.
History
[edit]The borough was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, as a merger of the county boroughs of Birkenhead and Wallasey, along with the municipal borough of Bebington and the urban districts of Hoylake and Wirral.
Economy
[edit]This is a chart of trend of regional gross value added of Wirral at current basic prices published (pp. 240–253) by Office for National Statistics with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling.
| Year | Regional Gross Value Added4 | Agriculture1 | Industry2 | Services3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2,089 | 10 | 674 | 1,405 |
| 2000 | 2,609 | 5 | 814 | 1,789 |
| 2003 | 3,020 | 9 | 755 | 2,256 |
^1 includes hunting and forestry
^2 includes energy and construction
^3 includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured
^4 Components may not sum to totals due to rounding
Plans were announced in 2006 for a £4.5bn development around the docklands to be called Wirral Waters.[5] The development is a mixture of industrial, office, residential and leisure facilities. Planning permission was granted in 2010 and work began on the site in 2011, with development work potentially lasting for 30 years.[6]
Education
[edit]When the borough was set up in 1974, it inherited comprehensive systems from the former County Boroughs of Birkenhead and Wallasey. In the part of Wirral formerly administered by Cheshire County Council, it inherited a selective system of grammar and secondary modern non-Roman Catholic schools and a comprehensive Roman Catholic school (St John Plessington Catholic College).
Until the implementation of the Education Reform Act 1988, education in Wirral continued to be organised in four areas; Birkenhead, Wallasey and the former parts of Cheshire known for education purposes as "Bebington" and "Deeside". However this Act introduced "open enrolment", allowing parents from anywhere in the borough, and outside it, to apply for a place for their child at any secondary school. As a result, significant numbers of pupils from the former "comprehensive areas" attend schools in the former "selective areas" and vice versa. The distinction between different types of school was to an extent masked, as all secondary modern and most comprehensive schools were named "High School". As a further result of this Act, St Anselm's College and Upton Hall School, both within the Birkenhead education area, became the only independent schools in the country to become state funded grant-maintained schools, retaining selective admissions policies to become Roman Catholic grammar schools.
A further change came as a result of the School Standards and Framework Act 1998, which effectively changed secondary modern schools into comprehensives as schools were no longer permitted to select by examination failure. In summary, Wirral now has a state secondary sector made up of 16 comprehensive schools (of which two are Roman Catholic) and 6 grammar schools (of which two are Roman Catholic).
Local government
[edit]Liverpool City Region Combined Authority
[edit]The Metropolitan Borough of Wirral is one of the six constituent local government districts of the Liverpool City Region. Since 1 April 2014, some of the borough's responsibilities have been pooled with neighbouring authorities within the metropolitan area and subsumed into the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority.
The combined authority has effectively become the top-tier administrative body for the local governance of the city region and the leader of Wirral Borough Council, along with the five other leaders from neighbouring local government districts, take strategic decisions over economic development, transport, employment and skills, tourism, culture, housing and physical infrastructure.
As of July 2015, negotiations are currently taking place between the UK national government and the combined authority over a possible devolution deal to confer greater powers on the region. Discussions include whether to introduce an elected 'Metro Mayor' to oversee the entire metropolitan area.[7]
Wirral Borough Council Composition
[edit]
After the local elections in 2008 the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral was governed by a Labour Party/Liberal Democrat coalition, the second and third largest parties on the council respectively. Steve Foulkes of Labour was leader of the council. The Conservative Party was the largest party represented, and was in opposition with its leader Jeff Green being leader of the opposition.
After the local elections in 2010 the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral was governed by a Conservative Party/Liberal Democrat coalition, which reflected the coalition at national level.[8] The Conservative Party, continuing to be the largest party represented on the council increased its number of seats by 2 to 27 and has now entered into coalition government with the Liberal Democrats as the leading coalition partner with the leader of the Conservatives, Jeff Green, becoming the new leader of the council. The Labour Party increased its representation on the council by 4 to 24 and remained the second largest party though they are now in opposition with their leader, Steve Foulkes, who was leader of the council now leader of the opposition. The Liberal Democrats lost 4 seats decreasing their tally to 15 remaining the third largest party on the council but continuing to participate in the governing of the council as the junior coalition partner to the Conservatives. The one independent represented on the council lost their seat.
After the local elections in 2011 the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral was governed by a minority Labour Party administration. Foulkes was leader of the council with Phil Davies as deputy leader. The Liberal Democrats lost a councillor who switched to Labour, Steve Niblock shortly after the elections. There are now no independents on Wirral Council. Labour have 36 seats, Conservatives have 23 and the Liberal Democrats 7.
In February 2012 the Conservatives and Liberal Democrats defeated the Labour administration in a motion of no confidence and the two parties governed again until the May election.[9] Labour made gains in May 2012, gaining majority control of the council for the first time since local elections in 2002 saw Labour become a minority. Wirral is led by Phil Davies.
In 2014, the Green Party gained their first seat on the council, defeating Labour in their typically safe seat of Birkenhead and Tranmere. They retained it in 2018 with an increased vote share, albeit with a reduced majority.
Political makeup
[edit]| Year | Party | Ref. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | GRN | LAB | LIB | OTH | |||||||
| LDM | |||||||||||
| 1973 | 29 | 0 | 24 | 13 | 0 | [10] | |||||
| 1974 | 29 | 0 | 24 | 13 | 0 | ||||||
| 1975 | 36 | 0 | 21 | 9 | 0 | ||||||
| 37 | 0 | 21 | 8 | 0 | |||||||
| 1976 | 42 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1977 | 42 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1978 | 45 | 0 | 16 | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| 1979 | 40 | 0 | 20 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1980 | 37 | 0 | 23 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1981 | 37 | 0 | 23 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1982 | 35 | 0 | 25 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1983 | 34 | 0 | 24 | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| 1984 | 34 | 0 | 24 | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| 1985 | 34 | 0 | 24 | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| 1986 | 30 | 0 | 26 | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| 1987 | 29 | 0 | 27 | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| 1988 | 24 | 0 | 32 | 10 | 0 | ||||||
| 24 | 0 | 29 | 10 | 3 | |||||||
| 1989 | 24 | 0 | 29 | 10 | 3 | ||||||
| 1990 | 23 | 0 | 33 | 7 | 3 | ||||||
| 23 | 0 | 33 | 8 | 2 | |||||||
| 1991 | 24 | 0 | 34 | 7 | 1 | ||||||
| 1992 | 29 | 0 | 31 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1993 | 29 | 0 | 31 | 6 | 0 | ||||||
| 1994 | 28 | 0 | 30 | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| 1995 | 22 | 0 | 36 | 8 | 0 | ||||||
| 1996 | 16 | 0 | 41 | 9 | 0 | ||||||
| 1997 | 16 | 0 | 41 | 9 | 0 | ||||||
| 1998 | 16 | 0 | 41 | 8 | 1 | ||||||
| 1999 | 16 | 0 | 42 | 8 | 0 | [11] | |||||
| 17 | 0 | 39 | 10 | 0 | [10] | ||||||
| 2000 | 20 | 0 | 34 | 12 | 0 | ||||||
| 2001 | 20 | 0 | 34 | 12 | 0 | ||||||
| 20 | 0 | 33 | 12 | 1 | [12] | ||||||
| 2002 | 20 | 0 | 32 | 12 | 2 | ||||||
| 20 | 0 | 31 | 14 | 1 | [13] | ||||||
| 2003 | 23 | 0 | 26 | 16 | 1 | [14] | |||||
| 2004 | 21 | 0 | 26 | 19 | 0 | [15] | |||||
| 20 | 0 | 26 | 19 | 1 | [16] | ||||||
| 2005 | 21 | 0 | 26 | 18 | 1 | [17] | |||||
| 2006 | 21 | 0 | 26 | 19 | 0 | [18] | |||||
| 2007 | 21 | 0 | 25 | 20 | 0 | [19] | |||||
| 21 | 0 | 25 | 19 | 1 | [20] | ||||||
| 20 | 0 | 25 | 29 | 2 | [21] | ||||||
| 2008 | 24 | 0 | 21 | 20 | 1 | [22] | |||||
| 2009 | 25 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 1 | [23] | |||||
| 2010 | 27 | 0 | 24 | 15 | 0 | [24] | |||||
| 2011 | 27 | 0 | 29 | 10 | 0 | [25] | |||||
| 27 | 0 | 30 | 9 | 0 | [26] | ||||||
| 2012 | 22 | 0 | 37 | 7 | 0 | [27] | |||||
| 2013 | 23 | 0 | 36 | 7 | 0 | [28] | |||||
| 22 | 0 | 37 | 7 | 0 | [29] | ||||||
| 22 | 0 | 37 | 6 | 1 | [30] | ||||||
| 2014 | 21 | 1 | 38 | 6 | 0 | [31] | |||||
| 2015 | 21 | 1 | 39 | 5 | 0 | [32] | |||||
| 2016 | 21 | 1 | 38 | 5 | 1 | [33] | |||||
| 21 | 1 | 39 | 5 | 0 | [34] | ||||||
| 2017 | 21 | 1 | 39 | 5 | 0 | ||||||
| 2018 | 21 | 1 | 39 | 5 | 0 | [35] | |||||
| 21 | 1 | 38 | 5 | 1 | [36] | ||||||
| 21 | 1 | 37 | 5 | 2 | [37] | ||||||
| 2019 | 22 | 3 | 32 | 6 | 3 | [38] | |||||
Members of Parliament
[edit]Places of interest
[edit]Wirral Council maintains five designated Local Nature Reserves: Bidston Moss, Dibbinsdale, Heswall Dales, Hilbre Island and Thurstaston Common.[39] It also operates the Merseyside part of Wirral Country Park, which was the first country park to be established in Britain.[40]
Twin towns – sister cities
[edit]The Metropolitan Borough of Wirral is twinned or has sister city relationships with:
- Lorient, France[41]
- Gennevilliers, France[41]
- Midland, Texas, United States
- Reno, Nevada, United States[42]
- Sibiu, Romania, Romania[43]
Freedom of the Borough
[edit]The following people, military units, organisations and groups have received the Freedom of the Borough of Wirral.[44]
Individuals
[edit]- Lieutenant Commander Ian Edward Fraser: 1993.
- Joseph Lynch: 1996.
- Raymond Holmes: 2005.
- Reverend David Urquhart: 2006.
- Michael Chan, Baron Chan: 2006.
- Stephen Maddox: 2010.
- Police Constable David Phillips: 21 May 2016.[45]
- Frank Field, Baron Field of Birkenhead: 16 February 2022.[46][47][48]
- Paul O'Grady: 8 June 2023. (Awarded Posthumously)[49]
- Glenda Jackson: 9 October 2023. (Awarded Posthumously)[50]
Military units
[edit]- The Cheshire Regiment: 1996.
- The Royal Marines: 1998.
- 1st Battalion The Mercian Regiment: 2009.
- 234 (Wirral) Transport Squadron, RLC (Volunteers): 18 February 2012.
- 107 (Lancashire and Cheshire) Field Squadron (Volunteers): 18 February 2012.
- HMS Astute, RN: 6 July 2015.
- Wallasey Sea Cadet Corps: 6 July 2015.
Organisations and groups
[edit]- The 96 people killed at the Hillsborough disaster: 15 September 2017.[56]
- Andrew Devine (97th Hillsborough Victim): 21 March 2021.[57]
References
[edit]- ^ "Councillors and committees". Wirral Council. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
- ^ "Mid-Year Population Estimates, UK, June 2022". Office for National Statistics. 26 March 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ a b "Mid-Year Population Estimates, UK, June 2022". Office for National Statistics. 26 March 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ a b UK Census (2021). "2021 Census Area Profile – Wirral Local Authority (E08000015)". Nomis. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "BBC - Liverpool - Capital of Culture - Wirral's skyline to rival New York". www.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ "Approval for £4.5bn Wirral waterfront regeneration". BBC News. 29 November 2010. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ Liam Murphy (22 July 2015). "Liverpool city region to decide on devolution demands by end of summer". Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ Phibbs, Harry (25 May 2010). "Conservatives take over Wirral Council". Conservativehome.blogs.com. Retrieved 11 December 2010.
- ^ Murphy, Liam (14 February 2012). "Jeff Green is new leader of Wirral council after Labour group is kicked out". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 17 February 2012. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ a b "Council compositions". The Elections Centre. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Lib Dem councillor switches sides". Wirral Globe. 17 June 1998. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^ "Second councillor quits". Wirral Globe. 12 February 2002. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^ "Local Election - 02 May 2002". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Local Election - 01 May 2003". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Local Election - 10 June 2004". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "No respect for mayor". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "Why I jumped ship to join the Tories". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "Local Election - 4 May 2006". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Local Election - 03 May 2007". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Councillors also have a 'third duty'".
- ^ "Another one bites the dust". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "Election Result for 1 May 2008 2002". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "BREAKING NEWS: Labour councillor Denis Knowles quits and joins Tories at Wallasey Town Hall". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "Election Result for 6 May 2010". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Election Result for 5 May 2011". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Wirral Lib Dem Steve Niblock defects to Labour Party". BBC News.
- ^ "Election Result for 3 May 2012". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Conservative victory in Wirral by-elections". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "UPDATED: Labour victory in Wirral Council by-election". Wirral Globe.
- ^ "Wirral councillor Mark Johnson quits Liberal Democrat Party". Liverpool Echo.
- ^ "Election Result for 22 May 2014". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Election Result for 7 May 2015". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Seven things to talk about after the Wirral local elections". Liverpool Echo. 6 May 2016. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ "Election results by party, Local election - Thursday, 5 May 2016". Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council. 5 May 2016.
- ^ "Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council Election 2018 Results". BBC News.
- ^ "Wirral councillor quits party blaming hard left 'parasites'". Labour Uncut. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "Senior Labour politician quits party after 40 years citing 'absolute aggression' of 'hard-left clique'". Liverpool Echo. 25 October 2018. Retrieved 25 October 2018.
- ^ "Election results by wards". Metropolitan Borough of Wirral. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^ "Wirral Local Nature Reserves". Wirral council. Archived from the original on 12 February 2011. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ "Wirral Country Park". Wirral.gov.uk. Retrieved 11 November 2017.
- ^ a b "British towns twinned with French towns". Archant Community Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 5 July 2013. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- ^ Murphy, Liam (28 September 2015). "Wirral and Reno twinned - but what have they got in common?". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ Murphy, Liam. "Wirral and Sibiu twinned- but what have they got in common?".
- ^ "Civic recognition and awards". Metropolitan Borough of Wirral. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ "Killed PC Dave Phillips receives freedom of Wirral". BBC News. 21 May 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ Riches, Chris (17 February 2022). "Terminally ill ex-MP Lord Frank Field awarded freedom of town he served for 40 years". The Mirror. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ Morgan, George (16 February 2022). "Borough honours Frank Field with Freedom of Wirral". The Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ "Lord Field: Veteran politician awarded Freedom of Wirral". BBC News. 17 February 2022. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Millar, Will (8 June 2023). "Paul O'Grady: Comedian given freedom of the borough in posthumous honour from Wirral Council". The Edinburgh Evening News. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ "Glenda Jackson posthumously awarded freedom of Wirral". BBC News Liverpool. 10 October 2023. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ "Decision – Freedom of Entry". 2 February 2012.
- ^ "Consideration form" (PDF). democracy.wirral.gov.uk. 2 February 2012. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ "Submariners proudly parade as HMS Astute receives Freedom of Wirral – Royal Navy". royalnavy.mod.uk.
- ^ "UPDATED: Councillors vote in favour of granting HMS Astute and Wallasey Sea Cadets freedom of the borough". Wirral Globe. 6 July 2015.
- ^ "Civic recognition and awards – www.wirral.gov.uk". Government of the United Kingdom.
- ^ Thomas, Joe (15 September 2017). "Hillsborough 96 to be awarded freedom of Wirral in tribute to victims and campaigners". The Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ Manning, Craig (11 March 2022). "Freedom of Wirral for 97th victim of Hillsborough Disaster". The Wirral Globe. Retrieved 11 March 2022.