Pristina: Difference between revisions
{{pp-dispute}} |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|subdivision_name = {{flag|Kosovo}} |
|subdivision_name = {{flag|Kosovo}} |
||
|subdivision_type2 = District |
|subdivision_type2 = District |
||
|subdivision_name2 = [[District of |
|subdivision_name2 = [[District of Pristina]] |
||
|image_flag = |
|image_flag = |
||
|image_flag_size = 130px |
|image_flag_size = 130px |
||
|Flag_legend = [[Flag of |
|Flag_legend = [[Flag of Pristina|City flag]] |
||
|image_shield = prishtinalogo.jpg |
|image_shield = prishtinalogo.jpg |
||
|image_map = Prishtinë 2006.PNG |
|image_map = Prishtinë 2006.PNG |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|timezone = [[CET]] |
|timezone = [[CET]] |
||
|utc_offset =+1 |
|utc_offset =+1 |
||
|website = [http://www.prishtina-komuna.org/ |
|website = [http://www.prishtina-komuna.org/ Pristina Municipality] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:BoroRamizi.jpg|thumb|256px|The "Palace of Youth" building]] |
|[[Image:BoroRamizi.jpg|thumb|256px|The "Palace of Youth" building]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:Rilindja.jpg|right|256px|thumb|The building of the former "Rilindja" newspaper, also the tallest in |
|[[Image:Rilindja.jpg|right|256px|thumb|The building of the former "Rilindja" newspaper, also the tallest in Pristina.]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:Townletpeyton.jpg|right|256px|thumb|"Townlet Peyton" district to the north of Bill Clinton boulevard.]] |
|[[Image:Townletpeyton.jpg|right|256px|thumb|"Townlet Peyton" district to the north of Bill Clinton boulevard.]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:Dardaniapr.JPG|right|256px|thumb|Dardania, the most densely-populated district of |
|[[Image:Dardaniapr.JPG|right|256px|thumb|Dardania, the most densely-populated district of Pristina.]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:Prishtina maj 2005.jpg|right|256px|thumb|[[United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo|UNMIK]] Head Quarters - |
|[[Image:Prishtina maj 2005.jpg|right|256px|thumb|[[United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo|UNMIK]] Head Quarters - Pristina.]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:nenatereze1.jpg|right|256px|thumb|[[Mother Teresa]] Boulevard.]] |
|[[Image:nenatereze1.jpg|right|256px|thumb|[[Mother Teresa]] Boulevard.]] |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|[[Image:Kosovo government.jpg|thumb|256px|Kosovar Government Central Building (Formerly a bank, damaged in the [[Kosovo War|1999 war]], now fully renovated).]] |
|[[Image:Kosovo government.jpg|thumb|256px|Kosovar Government Central Building (Formerly a bank, damaged in the [[Kosovo War|1999 war]], now fully renovated).]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Image:Bibloteka Kombëtare e Kosovës.jpg|right|256px|thumb|National Public Library in |
|[[Image:Bibloteka Kombëtare e Kosovës.jpg|right|256px|thumb|National Public Library in Pristina.]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|<!-- Image with unknown copyright status removed: [[Image:200501271331450.Pamje e qytetit.JPG|right|256|thumb|Old |
|<!-- Image with unknown copyright status removed: [[Image:200501271331450.Pamje e qytetit.JPG|right|256|thumb|Old Pristina.]] --> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |
||
|} |
|} |
||
<!-- Commented out because image was deleted: [[Image:oldprishtina.jpg|right|240px|thumb|Old Picture of |
<!-- Commented out because image was deleted: [[Image:oldprishtina.jpg|right|240px|thumb|Old Picture of Pristina.]] --> |
||
''' |
'''Pristina''', also spelled '''Pristina''' ( [[Albanian language|Albanian]]: ''Prishtinë'' or ''Prishtina'', {{Audio|Prishtina.ogg|listen}} , [[Serbian language|Serbian]]: Приштина, ''Priština'') is the capital and the largest city of [[Kosovo]], a [[International reaction to the 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence|partially recognized]] country in the [[Balkans]] that declared independence from [[Serbia]] on [[February 17]] [[2008]]. It is the administrative center of the homonymous municipality and [[District of Pristina|district]]. |
||
It is estimated that the current population of the city stands between 500,000<ref name="OSCE profile">[[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe|OSCE]] {{PDF|[http://www.osce.org/documents/mik/2007/10/1199_en.pdf municipal profile of |
It is estimated that the current population of the city stands between 500,000<ref name="OSCE profile">[[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe|OSCE]] {{PDF|[http://www.osce.org/documents/mik/2007/10/1199_en.pdf municipal profile of Pristina]}}, October 2007. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.</ref> and 600,000.<ref name="UK profile">[http://www.fco.gov.uk/servlet/Front?pagename=OpenMarket/Xcelerate/ShowPage&c=Page&cid=1007029394365&a=KCountryProfile&aid=1019233722672 UK Foreign & Commonwealth Office Country Profiles: Kosovo]. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.</ref> The city has a majority [[Albanians|Albanian]] population, alongside other smaller communities including [[Turks]], [[Serbs]], [[Bosniaks]], [[Roma people|Roma]] and others. The territory's interim government and the [[United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo]] (UNMIK) have their headquarters in the city. It is the administrative, educational, cultural center of Kosovo. The city is home to the [[University of Pristina]] and has an international airport, [[Pristina International Airport]], with the [[IATA airport code]] of PRN and [[International Civil Aviation Organization|ICAO]] code LYPR (temporarily BKPR while UNMIK in effect). |
||
The inhabitants of this city are called ''Prishtinali'' or ''Prishtinas'' in Albanian and ''Prištinci'' (Приштинци) or ''Prištevci'' (Приштевци) in Serbian. |
The inhabitants of this city are called ''Prishtinali'' or ''Prishtinas'' in Albanian and ''Prištinci'' (Приштинци) or ''Prištevci'' (Приштевци) in Serbian. |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
Pristina lies in these geographical coordinates 42° 40' 0" North and 21° 10' 0" East Pristina covers 572 km2. Pristina lies in the Northeastern part of Kosovo close to the "silver mountains". It has a good geographical position because it lies in the continental "roadcrosses" |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
===Early history=== |
===Early history=== |
||
In [[Roman Empire|Roman]] times a large town called ''[[Ulpiana]]'' existed 15 kilometres (9 miles) to the south of modern-day |
In [[Roman Empire|Roman]] times a large town called ''[[Ulpiana]]'' existed 15 kilometres (9 miles) to the south of modern-day Pristina. This city was destroyed but was restored by the [[List of Byzantine Emperors|Emperor]] [[Justinian I]]. Today the town of [[Lipljan]] stands on the site of the Roman city, and remains of the old city can still be seen. |
||
After the fall of Rome, |
After the fall of Rome, Pristina grew from the ruins of the former Roman city. The city was located at a junction of roads leading in all directions throughout the [[Balkans]]. For this reason Pristina rose to become an important trading centre on the main trade routes across south-eastern Europe. |
||
Pristina came to be of great importance to the medieval Serbian state, and served as the capital of King [[Stefan Uroš II Milutin of Serbia|Milutin]] ([[1282]]-[[1321]]) and other Serbian rulers from the [[House of Nemanjić|Nemanjić]] and [[House of Branković|Branković]] dynasties until the [[Battle of Kosovo]] in [[1389]], when an invading [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] army decisively defeated the Balkans coalition army. In the following decades the area gradually came under Ottoman control, there was an Ottoman law-court in Pristina in [[1423]]. The whole of Serbia was subsequently conquered by the Ottoman Empire in [[1459]]. |
|||
The oldest Albanian writer [[Pjetër Bogdani]] came from |
The oldest Albanian writer [[Pjetër Bogdani]] came from Pristina. He published his book ''Cuneus Profetarum'' (Alb: ''Ceta e Profeteve'' roughly ''Vanguard of the Prophets'') in 1555. During the Ottoman Empire, Pristina became increasingly Ottoman in character following the conversion to [[Islam]] of many of its inhabitants, both Albanians and Slavs. |
||
From the [[1870s]] onwards Albanians in the region formed the [[League of Prizren]] to resist Ottoman rule, and a provisional government was formed in [[1881]]. In [[1912]] |
From the [[1870s]] onwards Albanians in the region formed the [[League of Prizren]] to resist Ottoman rule, and a provisional government was formed in [[1881]]. In [[1912]] Pristina along with the rest of Kosovo was briefly included in the newly independent state of [[Albania]]. But the following year the [[Great Powers]] forced Albania to cede the region to the [[Kingdom of Serbia]]. In [[1918]] Kosovo became a part of the newly formed [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes|Yugoslavia]], though without any of the autonomy that the region later enjoyed. |
||
Before [[World War II]], |
Before [[World War II]], Pristina was an ethnically mixed town with large communities of Albanians and Serbs. Many Albanians were deported to Turkey as a consequence of the ethnic cleaning program applied by the Serbs. Muslim Albanians were identified as Turks and thus forcibly evicted from their ancestors' homes. The Albanians were sent to Turkey, where the Turkish government enforced them to accept new Turkish names and settle the Turkish provinces formerly inhabited by [[Greeks]] and [[Armenians]]. |
||
The Second World War saw the decline of |
The Second World War saw the decline of Pristina's [[Serb]]ian community as well as a large-scale settling of Albanians in the town. Between [[1941]] and [[1945]] Pristina was incorporated into the [[Italy|Italian]]-occupied [[Greater Albania]]. |
||
=== |
===Pristina after World War II=== |
||
In [[1946]], |
In [[1946]], Pristina became the capital of the Socialist Autonomous Region of Kosovo. Between [[1953]] and 1999, the population increased from around 24,000 to over 300,000. All of the national communities of the city increased over this period, but the greatest increase was among the Albanian population, a large number of whom had moved from Mountains areas to settle in the city. The Albanian population increased from around 9,000 in 1953 to nearly 76,000 in [[1981]]. The Serbian and Montenegrin population increased too but by a far more modest number, from just under 8,000 in 1953 to around 21,000 by 1981. By the start of the 1980s, Albanians constituted over 70% of the city's population. |
||
Although Kosovo was under the rule of local Albanian members of the Communist Party, economic decline and political instability in the late 1960s and at the start of the 1980s led to outbreaks of nationalist unrest. In November [[1968]], student demonstrations and riots in [[Belgrade]] spread to |
Although Kosovo was under the rule of local Albanian members of the Communist Party, economic decline and political instability in the late 1960s and at the start of the 1980s led to outbreaks of nationalist unrest. In November [[1968]], student demonstrations and riots in [[Belgrade]] spread to Pristina, but were put down by the Yugoslav security forces. Some of the demands of the students were nonetheless met by the [[Josip Broz Tito|Tito]] government, including the establishment in [[1970]] of the [[University of Pristina]] as an independent institution. This ended a long period when the institution had been run as an outpost of [[Belgrade University]] and gave a major boost to Albanian-language education and culture in Kosovo. The Albanians were also allowed to use the Albanian flag. |
||
In March 1981, students at |
In March 1981, students at Pristina University rioted over poor food in their university canteen. This seemingly trivial dispute rapidly spread throughout Kosovo and took on the character of a national revolt, with massive popular demonstrations in Pristina and other Kosovo towns. The Communist Yugoslav presidency quelled the disturbances by sending in riot police and the army and proclaiming a state of emergency, with several people being killed in clashes and thousands subsequently being imprisoned or disciplined. |
||
=== |
===Pristina in the Kosovo War and afterwards=== |
||
[[Image:prishtinalogo.jpg|thumb|left|City's emblem.]] |
[[Image:prishtinalogo.jpg|thumb|left|City's emblem.]] |
||
Following the reduction of Kosovo's autonomy by [[President of Serbia|Serbian President]] [[Slobodan Milošević]] in [[1990]], a harshly repressive regime was imposed throughout Kosovo by the Serbian government with Albanians largely being purged from state industries and institutions. University of |
Following the reduction of Kosovo's autonomy by [[President of Serbia|Serbian President]] [[Slobodan Milošević]] in [[1990]], a harshly repressive regime was imposed throughout Kosovo by the Serbian government with Albanians largely being purged from state industries and institutions. University of Pristina was seen as a hotbed of Albanian nationalism and was duly purged: 800 lecturers were sacked and 22,500 of the 23,000 students expelled. In response, the Kosovo Albanians set up a "shadow government" under the authority of the [[Democratic League of Kosovo]] (LDK), led by the writer [[Ibrahim Rugova]]. Although the city was formally controlled by Serbs appointed by the Milošević government, the LDK established parallel structures, funded by private contributions, to provide free services such as health care and education that were largely denied to the Albanian population. |
||
The LDK's role meant that when the [[Kosovo Liberation Army]] began to attack Serbian and Yugoslav forces from 1996 onwards, |
The LDK's role meant that when the [[Kosovo Liberation Army]] began to attack Serbian and Yugoslav forces from 1996 onwards, Pristina remained largely calm until the outbreak of the [[Kosovo War]] in March [[1999]]. The city was placed under a state of emergency at the end of March and large areas were sealed off. After [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation|NATO]] began air strikes against Yugoslavia on [[March 24]] 1999, widespread violence broke out in Pristina. Serbian and Yugoslav forces shelled several districts and, in conjunction with paramilitaries, conducted large-scale expulsions of ethnic Albanians accompanied by widespread looting. Many of those expelled were directed onto trains apparently brought to Pristina's main station for the express purpose of taking them to the border of the [[Republic of Macedonia]], where they were forced into exile. The [[United States Department of State]] estimated in May 1999 that between 100,000-120,000 people had been driven out of Pristina by government forces and [[paramilitary|paramilitaries]]. |
||
Several strategic targets in |
Several strategic targets in Pristina were attacked by NATO during the war, but physical damage appears to have largely been restricted to a few specific neighborhoods shelled by Yugoslav security forces. At the end of the war, most of the city's 40,000<ref>[http://www.euronews.net/index.php?article=468126&lng=1&option=1 EuroNews Serbs in Kosovo vote in Gracanica and Mitrovica published February 3, 2008 accessed February 3, 2008]</ref> Serbs fled. The few who remained were subjected to harassment and violence in revenge by Albanian gangs, which reduced Pristina's Serb population still further. Other national groups accused of collaboration with the Serbian war effort by Albanians – notably the [[Roma people|Roma]] – were also driven out. According to the [[United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees]], by August 1999 fewer than 2,000 Serbs were left in the city. The number reportedly fell even further after the March [[2004 unrest in Kosovo]]. In early 2008 only a few dozen Serbs remained in Pristina, most of whom were elderly people.<ref>[http://www.euronews.net/index.php?article=468126&lng=1&option=1 EuroNews Serbs in Kosovo vote in Gracanica and Mitrovica published February 3, 2008 accessed February 3, 2008]</ref> |
||
== Economy == |
== Economy == |
||
The number of registered businesses in |
The number of registered businesses in Pristina is currently at 8,725, with a total of 75,089 employees. The exact number of businesses is unknown due to the fact that not all are registered. |
||
<!-- Comment statistics as it is poorly arranged and not cited. Please rearrange the statistics, cite it, and re-insert it back into the main article. Thanks. |
<!-- Comment statistics as it is poorly arranged and not cited. Please rearrange the statistics, cite it, and re-insert it back into the main article. Thanks. |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
[[Image:Kosovo museum.jpg|left|thumb|250px|The museum of Kosovo]] |
[[Image:Kosovo museum.jpg|left|thumb|250px|The museum of Kosovo]] |
||
The '''Museum of Kosovo''' is located in an Austro-Hungarian inspired building originally built for the regional administration of the Ottoman [[Vilayet of Kosovo]]. From 1945 until 1975 it served as headquarters for the [[Yugoslav National Army]]. In 1963 it was sold to the Kosovo Museum. From 1999 until 2002, the [[European Agency for Reconstruction]] had its main office in the museum building. The Kosovo Museum has an extensive collection of archaeological and ethnological artifacts, including the Neolithic ''Goddess on the Throne'' terracotta, unearthed near |
The '''Museum of Kosovo''' is located in an Austro-Hungarian inspired building originally built for the regional administration of the Ottoman [[Vilayet of Kosovo]]. From 1945 until 1975 it served as headquarters for the [[Yugoslav National Army]]. In 1963 it was sold to the Kosovo Museum. From 1999 until 2002, the [[European Agency for Reconstruction]] had its main office in the museum building. The Kosovo Museum has an extensive collection of archaeological and ethnological artifacts, including the Neolithic ''Goddess on the Throne'' terracotta, unearthed near Pristina in 1960<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6718105.stm Kosovo contest for state symbols], by Nick Thorpe, ''BBC'', Pristina, 4 June 2007. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.</ref> and depicted in the city's emblem. |
||
The '''Clock Tower''' (''Sahat Kulla'') dates back to the 19th century. Following a fire, the tower has been reconstructed using bricks. The original bell was brought to Kosovo from [[Moldovia]]. It bore an inscription reading "this bell was made in 1764 for ''Jon Moldova Rumen''." In 2001, the original bell was stolen. The same year, French KFOR troops replaced the old clock mechanism with an electric one. Given Kosovo's electricity problems the tower is struggling to keep time. |
The '''Clock Tower''' (''Sahat Kulla'') dates back to the 19th century. Following a fire, the tower has been reconstructed using bricks. The original bell was brought to Kosovo from [[Moldovia]]. It bore an inscription reading "this bell was made in 1764 for ''Jon Moldova Rumen''." In 2001, the original bell was stolen. The same year, French KFOR troops replaced the old clock mechanism with an electric one. Given Kosovo's electricity problems the tower is struggling to keep time. |
||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
== Sport == |
== Sport == |
||
[[Image:Prishtinë SQ.JPG|left|256px|thumb|''Stadiumi i Qytetit'' - City's Football Stadium.]] |
[[Image:Prishtinë SQ.JPG|left|256px|thumb|''Stadiumi i Qytetit'' - City's Football Stadium.]] |
||
Basketball is one of the most popular sports in |
Basketball is one of the most popular sports in Pristina since 2000. In this sport Pristina is represented by two teams. Football is also very popular. Pristina's representatives [[KF Prishtina]] plays its home games in the city's stadium. |
||
[[Handball]] is also very popular. |
[[Handball]] is also very popular. Pristina's representatives are recognized internationally and play international matches. |
||
== Demographics == |
== Demographics == |
||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
* The [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]] conducted their first census in 1486; there were 392 families then. |
* The [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]] conducted their first census in 1486; there were 392 families then. |
||
* In 1487, an [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] census was conducted in the domain of the [[House of Branković]]. |
* In 1487, an [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] census was conducted in the domain of the [[House of Branković]]. Pristina had together with Vucitrn 412 [[Christianity|Christian]] households and 94 [[Islam|Muslim]] housing. |
||
* The Ottomans conducted an official census in [[Rumelia]] in 1569; listing 692 families |
* The Ottomans conducted an official census in [[Rumelia]] in 1569; listing 692 families |
||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
* The Ottomans conducted in 1902 an official population census in the [[Viyalet of Kosovo]]; enlisting around 18,000 citizens in some 3,760 families. |
* The Ottomans conducted in 1902 an official population census in the [[Viyalet of Kosovo]]; enlisting around 18,000 citizens in some 3,760 families. |
||
=== |
=== Pristina District between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Serbia === |
||
In 1912, a German scholar by the name of conducted an estimate within the |
In 1912, a German scholar by the name of conducted an estimate within the Pristina District just before the [[First Balkan War|Balkan War]]{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. The population of the entire district was: |
||
:* ''67%'' [[Albanians|Albanian]] |
:* ''67%'' [[Albanians|Albanian]] |
||
:* ''30%'' [[Serbs|Serbian]] |
:* ''30%'' [[Serbs|Serbian]] |
||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
:* 2,504 [[Muslims by nationality|Muslims]] (''2%'') |
:* 2,504 [[Muslims by nationality|Muslims]] (''2%'') |
||
According to the last census in [[1991]] (boycotted by the Albanian majority), the population of the |
According to the last census in [[1991]] (boycotted by the Albanian majority), the population of the Pristina municipality was 199,654, including 77.63% Albanians, 15.43% Serbs and Montenegrins, 1.72% Muslims by nationality, and others.<ref>[http://www.anem.org.yu/mape/ops/dg90263-en.htm Statistic data for the municipality of Pristina - grad]</ref> This census cannot be considered accurate as it is based on previous records and estimates. |
||
In 2004 it was estimated that the population exceeded half a million, and that [[Albanians]] form around ''98%'' of it. The Serbian population in the city has fallen significantly since 1999, many of the city's Serbs having fled or been expelled following the end of the war. In early 1999 |
In 2004 it was estimated that the population exceeded half a million, and that [[Albanians]] form around ''98%'' of it. The Serbian population in the city has fallen significantly since 1999, many of the city's Serbs having fled or been expelled following the end of the war. In early 1999 Pristina had about 230,000 inhabitants. There were more than 40,000 Serbs and about 6,500 Romas with the remainder being Albanians. |
||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" rules="all" width="75%%" style="clear:all; margin:5px 0 1em 1em; border-style: solid; border-width: 1px; border-collapse:collapse; font-size:95%; empty-cells:show" |
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" rules="all" width="75%%" style="clear:all; margin:5px 0 1em 1em; border-style: solid; border-width: 1px; border-collapse:collapse; font-size:95%; empty-cells:show" |
||
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
| 564,800 |
| 564,800 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|colspan="10" align=left style="background:#FFEBCD;"|<small>Source: {{PDFlink|[http://www.osce.org/documents/mik/2005/12/1199_en.pdf OSCE |
|colspan="10" align=left style="background:#FFEBCD;"|<small>Source: {{PDFlink|[http://www.osce.org/documents/mik/2005/12/1199_en.pdf OSCE Pristina municipal profile]|511 [[Kibibyte|KiB]]<!-- application/pdf, 523986 bytes -->}}, June 2006, page 2 (Table 1.1).</br> |
||
1. IDP: [[Internally displaced person]].</br> |
1. IDP: [[Internally displaced person]].</br> |
||
2. Others include Montenegrins, Muslim Slavs, Turks, etc.</br> |
2. Others include Montenegrins, Muslim Slavs, Turks, etc.</br> |
||
| Line 257: | Line 257: | ||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[District of |
* [[District of Pristina]] |
||
* [[Kosovo War]] |
* [[Kosovo War]] |
||
* [[University of |
* [[University of Pristina]] |
||
* [[Bregu i Diellit]] |
* [[Bregu i Diellit]] |
||
* [[Pristina City Stadium]] |
* [[Pristina City Stadium]] |
||
| Line 267: | Line 267: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.inyourpocket.com/kosovo/pristina/en/ |
* [http://www.inyourpocket.com/kosovo/pristina/en/ Pristina In Your Pocket city guide] |
||
* {{wikitravelpar|Pristina}} |
* {{wikitravelpar|Pristina}} |
||
* [http://www.uni-pr.edu/ University of |
* [http://www.uni-pr.edu/ University of Pristina] |
||
* [http://www.airportpristina.com/ |
* [http://www.airportpristina.com/ Pristina Airport] |
||
* [http://www.rrethi.com Interactive map of |
* [http://www.rrethi.com Interactive map of Pristina] |
||
{{coor title dm|42|40|N|21|10|E|type:city(500,000)_region:CS}}. |
{{coor title dm|42|40|N|21|10|E|type:city(500,000)_region:CS}}. |
||
| Line 277: | Line 277: | ||
{{Municipalities of the Republic of Kosovo}} |
{{Municipalities of the Republic of Kosovo}} |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Pristina| ]] |
||
[[Category:Cities, towns and villages in Kosovo|Pristina]] |
[[Category:Cities, towns and villages in Kosovo|Pristina]] |
||
[[ar:برشتينا]] |
[[ar:برشتينا]] |
||
[[az:Priştina]] |
[[az:Priştina]] |
||
[[zh-min-nan: |
[[zh-min-nan:Pristina]] |
||
[[bs: |
[[bs:Pristina]] |
||
[[br: |
[[br:Pristina]] |
||
[[bg:Прищина]] |
[[bg:Прищина]] |
||
[[cs: |
[[cs:Pristina]] |
||
[[da:Pristina]] |
[[da:Pristina]] |
||
[[de: |
[[de:Pristina]] |
||
[[et: |
[[et:Pristina]] |
||
[[es:Pristina]] |
[[es:Pristina]] |
||
[[eo:Priŝtino]] |
[[eo:Priŝtino]] |
||
| Line 296: | Line 296: | ||
[[ko:프리슈티나]] |
[[ko:프리슈티나]] |
||
[[hr:Priština]] |
[[hr:Priština]] |
||
[[id: |
[[id:Pristina]] |
||
[[it:Pristina]] |
[[it:Pristina]] |
||
[[he:פרישטינה]] |
[[he:פרישטינה]] |
||
[[ka:პრიშტინა]] |
[[ka:პრიშტინა]] |
||
[[kw:Prishtina]] |
[[kw:Prishtina]] |
||
[[lv: |
[[lv:Pristina]] |
||
[[lt: |
[[lt:Pristina]] |
||
[[hu:Prishtina]] |
[[hu:Prishtina]] |
||
[[ms: |
[[ms:Pristina]] |
||
[[nl:Pristina]] |
[[nl:Pristina]] |
||
[[ja:プリシュティナ]] |
[[ja:プリシュティナ]] |
||
[[no: |
[[no:Pristina]] |
||
[[nn: |
[[nn:Pristina]] |
||
[[pms:Prìstina]] |
[[pms:Prìstina]] |
||
[[pl:Prisztina]] |
[[pl:Prisztina]] |
||
[[pt: |
[[pt:Pristina]] |
||
[[ro:Priştina]] |
[[ro:Priştina]] |
||
[[ru:Приштина]] |
[[ru:Приштина]] |
||
[[sq:Prishtina]] |
[[sq:Prishtina]] |
||
[[simple: |
[[simple:Pristina]] |
||
[[sk: |
[[sk:Pristina]] |
||
[[sl: |
[[sl:Pristina]] |
||
[[sr:Приштина]] |
[[sr:Приштина]] |
||
[[sh: |
[[sh:Pristina]] |
||
[[fi: |
[[fi:Pristina]] |
||
[[sv: |
[[sv:Pristina]] |
||
[[vi: |
[[vi:Pristina]] |
||
[[tr:Priştine]] |
[[tr:Priştine]] |
||
[[uk:Приштина]] |
[[uk:Приштина]] |
||
Revision as of 13:33, 7 March 2008
Editing of this article by new or unregistered users is currently disabled until editing disputes have been resolved. This protection is not an endorsement of the current version. See the protection policy and protection log for more details. If you cannot edit this article and you wish to make a change, you can submit an edit request, discuss changes on the talk page, request unprotection, log in, or create an account. |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2008) |
This template is a customized wrapper for {{[[Template:{{{1}}}|{{{1}}}]]}}. Any field from {{[[Template:{{{1}}}|{{{1}}}]]}} can work so long as it is added to this template first. Questions? Just ask here or over at [[Template talk:{{{1}}}]]. |
|
Pristina Prishtina/ë Приштина Priština | |
|---|---|
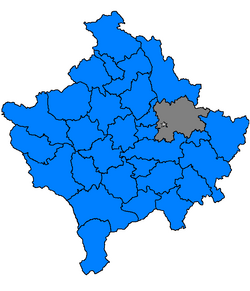 | |
| Country | |
| District | District of Pristina |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Isa Mustafa |
| Elevation | 652 m (2,139 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 500,000 - 600,000 |
| • Density | 661/km2 (1,710/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| Area code | +381 38 |
| Website | Pristina Municipality |
|-
|
|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|-
|

|- | |- | |}
Pristina, also spelled Pristina ( Albanian: Prishtinë or Prishtina, , Serbian: Приштина, Priština) is the capital and the largest city of Kosovo, a partially recognized country in the Balkans that declared independence from Serbia on February 17 2008. It is the administrative center of the homonymous municipality and district.
It is estimated that the current population of the city stands between 500,000[1] and 600,000.[2] The city has a majority Albanian population, alongside other smaller communities including Turks, Serbs, Bosniaks, Roma and others. The territory's interim government and the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) have their headquarters in the city. It is the administrative, educational, cultural center of Kosovo. The city is home to the University of Pristina and has an international airport, Pristina International Airport, with the IATA airport code of PRN and ICAO code LYPR (temporarily BKPR while UNMIK in effect).
The inhabitants of this city are called Prishtinali or Prishtinas in Albanian and Prištinci (Приштинци) or Prištevci (Приштевци) in Serbian.
Geography
Pristina lies in these geographical coordinates 42° 40' 0" North and 21° 10' 0" East Pristina covers 572 km2. Pristina lies in the Northeastern part of Kosovo close to the "silver mountains". It has a good geographical position because it lies in the continental "roadcrosses"
History
Early history
In Roman times a large town called Ulpiana existed 15 kilometres (9 miles) to the south of modern-day Pristina. This city was destroyed but was restored by the Emperor Justinian I. Today the town of Lipljan stands on the site of the Roman city, and remains of the old city can still be seen.
After the fall of Rome, Pristina grew from the ruins of the former Roman city. The city was located at a junction of roads leading in all directions throughout the Balkans. For this reason Pristina rose to become an important trading centre on the main trade routes across south-eastern Europe.
Pristina came to be of great importance to the medieval Serbian state, and served as the capital of King Milutin (1282-1321) and other Serbian rulers from the Nemanjić and Branković dynasties until the Battle of Kosovo in 1389, when an invading Ottoman army decisively defeated the Balkans coalition army. In the following decades the area gradually came under Ottoman control, there was an Ottoman law-court in Pristina in 1423. The whole of Serbia was subsequently conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1459.
The oldest Albanian writer Pjetër Bogdani came from Pristina. He published his book Cuneus Profetarum (Alb: Ceta e Profeteve roughly Vanguard of the Prophets) in 1555. During the Ottoman Empire, Pristina became increasingly Ottoman in character following the conversion to Islam of many of its inhabitants, both Albanians and Slavs.
From the 1870s onwards Albanians in the region formed the League of Prizren to resist Ottoman rule, and a provisional government was formed in 1881. In 1912 Pristina along with the rest of Kosovo was briefly included in the newly independent state of Albania. But the following year the Great Powers forced Albania to cede the region to the Kingdom of Serbia. In 1918 Kosovo became a part of the newly formed Yugoslavia, though without any of the autonomy that the region later enjoyed.
Before World War II, Pristina was an ethnically mixed town with large communities of Albanians and Serbs. Many Albanians were deported to Turkey as a consequence of the ethnic cleaning program applied by the Serbs. Muslim Albanians were identified as Turks and thus forcibly evicted from their ancestors' homes. The Albanians were sent to Turkey, where the Turkish government enforced them to accept new Turkish names and settle the Turkish provinces formerly inhabited by Greeks and Armenians.
The Second World War saw the decline of Pristina's Serbian community as well as a large-scale settling of Albanians in the town. Between 1941 and 1945 Pristina was incorporated into the Italian-occupied Greater Albania.
Pristina after World War II
In 1946, Pristina became the capital of the Socialist Autonomous Region of Kosovo. Between 1953 and 1999, the population increased from around 24,000 to over 300,000. All of the national communities of the city increased over this period, but the greatest increase was among the Albanian population, a large number of whom had moved from Mountains areas to settle in the city. The Albanian population increased from around 9,000 in 1953 to nearly 76,000 in 1981. The Serbian and Montenegrin population increased too but by a far more modest number, from just under 8,000 in 1953 to around 21,000 by 1981. By the start of the 1980s, Albanians constituted over 70% of the city's population.
Although Kosovo was under the rule of local Albanian members of the Communist Party, economic decline and political instability in the late 1960s and at the start of the 1980s led to outbreaks of nationalist unrest. In November 1968, student demonstrations and riots in Belgrade spread to Pristina, but were put down by the Yugoslav security forces. Some of the demands of the students were nonetheless met by the Tito government, including the establishment in 1970 of the University of Pristina as an independent institution. This ended a long period when the institution had been run as an outpost of Belgrade University and gave a major boost to Albanian-language education and culture in Kosovo. The Albanians were also allowed to use the Albanian flag.
In March 1981, students at Pristina University rioted over poor food in their university canteen. This seemingly trivial dispute rapidly spread throughout Kosovo and took on the character of a national revolt, with massive popular demonstrations in Pristina and other Kosovo towns. The Communist Yugoslav presidency quelled the disturbances by sending in riot police and the army and proclaiming a state of emergency, with several people being killed in clashes and thousands subsequently being imprisoned or disciplined.
Pristina in the Kosovo War and afterwards
Following the reduction of Kosovo's autonomy by Serbian President Slobodan Milošević in 1990, a harshly repressive regime was imposed throughout Kosovo by the Serbian government with Albanians largely being purged from state industries and institutions. University of Pristina was seen as a hotbed of Albanian nationalism and was duly purged: 800 lecturers were sacked and 22,500 of the 23,000 students expelled. In response, the Kosovo Albanians set up a "shadow government" under the authority of the Democratic League of Kosovo (LDK), led by the writer Ibrahim Rugova. Although the city was formally controlled by Serbs appointed by the Milošević government, the LDK established parallel structures, funded by private contributions, to provide free services such as health care and education that were largely denied to the Albanian population.
The LDK's role meant that when the Kosovo Liberation Army began to attack Serbian and Yugoslav forces from 1996 onwards, Pristina remained largely calm until the outbreak of the Kosovo War in March 1999. The city was placed under a state of emergency at the end of March and large areas were sealed off. After NATO began air strikes against Yugoslavia on March 24 1999, widespread violence broke out in Pristina. Serbian and Yugoslav forces shelled several districts and, in conjunction with paramilitaries, conducted large-scale expulsions of ethnic Albanians accompanied by widespread looting. Many of those expelled were directed onto trains apparently brought to Pristina's main station for the express purpose of taking them to the border of the Republic of Macedonia, where they were forced into exile. The United States Department of State estimated in May 1999 that between 100,000-120,000 people had been driven out of Pristina by government forces and paramilitaries.
Several strategic targets in Pristina were attacked by NATO during the war, but physical damage appears to have largely been restricted to a few specific neighborhoods shelled by Yugoslav security forces. At the end of the war, most of the city's 40,000[3] Serbs fled. The few who remained were subjected to harassment and violence in revenge by Albanian gangs, which reduced Pristina's Serb population still further. Other national groups accused of collaboration with the Serbian war effort by Albanians – notably the Roma – were also driven out. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, by August 1999 fewer than 2,000 Serbs were left in the city. The number reportedly fell even further after the March 2004 unrest in Kosovo. In early 2008 only a few dozen Serbs remained in Pristina, most of whom were elderly people.[4]
Economy
The number of registered businesses in Pristina is currently at 8,725, with a total of 75,089 employees. The exact number of businesses is unknown due to the fact that not all are registered.
Culture
The Museum of Kosovo is located in an Austro-Hungarian inspired building originally built for the regional administration of the Ottoman Vilayet of Kosovo. From 1945 until 1975 it served as headquarters for the Yugoslav National Army. In 1963 it was sold to the Kosovo Museum. From 1999 until 2002, the European Agency for Reconstruction had its main office in the museum building. The Kosovo Museum has an extensive collection of archaeological and ethnological artifacts, including the Neolithic Goddess on the Throne terracotta, unearthed near Pristina in 1960[5] and depicted in the city's emblem.
The Clock Tower (Sahat Kulla) dates back to the 19th century. Following a fire, the tower has been reconstructed using bricks. The original bell was brought to Kosovo from Moldovia. It bore an inscription reading "this bell was made in 1764 for Jon Moldova Rumen." In 2001, the original bell was stolen. The same year, French KFOR troops replaced the old clock mechanism with an electric one. Given Kosovo's electricity problems the tower is struggling to keep time.
Sport

Basketball is one of the most popular sports in Pristina since 2000. In this sport Pristina is represented by two teams. Football is also very popular. Pristina's representatives KF Prishtina plays its home games in the city's stadium.
Handball is also very popular. Pristina's representatives are recognized internationally and play international matches.
Demographics
Ottoman Empire
- The Ottomans conducted their first census in 1486; there were 392 families then.
- In 1487, an Ottoman census was conducted in the domain of the House of Branković. Pristina had together with Vucitrn 412 Christian households and 94 Muslim housing.
- The Ottomans conducted an official census in Rumelia in 1569; listing 692 families
- The Ottomans conducted an official census in Rumelia in 1669; listing some 2,060 families
- In 1685 the Ottomans officially conducted a population census in Rumelia; enlisting around 3,000 families.
- The Ottomans officially conducted a population census in 1689 in Rumelia; enlisting around 4,000 families.
- In 1850 the Ottomans officially conducted a population census in the Viyalet of Kosovo; enlisting around 12,000 citizens in around 3,000 families.
- The Ottomans conducted in 1902 an official population census in the Viyalet of Kosovo; enlisting around 18,000 citizens in some 3,760 families.
Pristina District between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Serbia
In 1912, a German scholar by the name of conducted an estimate within the Pristina District just before the Balkan War[citation needed]. The population of the entire district was:
Serbia and Kingdom of Yugoslavia
- The 1921 official population census conducted by the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes listed 14,338 citizens.
- The 1931 official population census organized by the Kingdom of Yugoslavia listed 18,358 inhabitants by mother tongues:
- Turkish - 7,573 (41%)
- Serbian - 5,738 (31%)
- Albanian - 2,351 (13%)
- other languages (Romani, Circassian etc.) - 2,651 (14%)
Socialist Yugoslavia

- The 1948 official population census of the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija organized by the government of the People's Republic of Serbia under the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia government recorded 19,631 citizens in 4,667 families.
- The 1953 official population census of the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija organized by the government of Serbia under the Yugoslav government recorded 24,229 citizens:
- 9,034 Albanians (37%)
- 7,951 Serbs and Montenegrins (33%)
- 4,726 Turks (20%)
- 2,518 Roma and others (10%)
- The 1961 official population census of the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija organized by the government of the Socialist Republic of Serbia under the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia government recorded 38,593 citizens in 9,095 families:
- 19,060 Albanians (49%)
- 14,695 Serbs and Montenegrins (38%)
- The 1971 official population census of the Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo organized by the government of the Socialist Republic of Serbia under the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia government 69,514 citizens in 14,813 families:
- 40,873 Albanians (59%)
- 19,767 Serbs and Montenegrins (28%)
- 4,119 Roma (6%)
- The 1981 official population census of the Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo organized by the government of the Socialist Republic of Serbia under the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia government 108,083 citizens in 21,017 families:
- 75,803 Albanians (70%)
- 21,067 Serbs and Montenegrins (19%)
- 5,101 Roma (5%)
- 2,504 Muslims (2%)
According to the last census in 1991 (boycotted by the Albanian majority), the population of the Pristina municipality was 199,654, including 77.63% Albanians, 15.43% Serbs and Montenegrins, 1.72% Muslims by nationality, and others.[6] This census cannot be considered accurate as it is based on previous records and estimates.
In 2004 it was estimated that the population exceeded half a million, and that Albanians form around 98% of it. The Serbian population in the city has fallen significantly since 1999, many of the city's Serbs having fled or been expelled following the end of the war. In early 1999 Pristina had about 230,000 inhabitants. There were more than 40,000 Serbs and about 6,500 Romas with the remainder being Albanians.
| Ethnic Composition, Including IDPs1 | |||||||||
| Year | Albanians | % | Serbs | % | Roma | % | Others2 | % | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 census3 | 161,314 | 78.7 | 27,293 | 13.3 | 6,625 | 3.2 | 9,861 | 4.8 | 205,093 |
| 19984 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 225,388 |
| February 2000 estimate5 | 550,000 | 97.4 | 12,000 | 2.2 | 1,000 | 0.1 | 1,800 | 0.3 | 564,800 |
| Source: Template:PDFlink, June 2006, page 2 (Table 1.1). 1. IDP: Internally displaced person. | |||||||||
Twin (Partner) Cities
See also
References
- ^ a b OSCE Template:PDF, October 2007. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.
- ^ a b UK Foreign & Commonwealth Office Country Profiles: Kosovo. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.
- ^ EuroNews Serbs in Kosovo vote in Gracanica and Mitrovica published February 3, 2008 accessed February 3, 2008
- ^ EuroNews Serbs in Kosovo vote in Gracanica and Mitrovica published February 3, 2008 accessed February 3, 2008
- ^ Kosovo contest for state symbols, by Nick Thorpe, BBC, Pristina, 4 June 2007. Retrieved on 21 February 2008.
- ^ Statistic data for the municipality of Pristina - grad

