Template:Syrian civil war infobox: Difference between revisions
JuznaAfrika (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Croatia denied being involved in the arms shipment. |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Authenticity and Development Front|AD Front]] |
* [[Authenticity and Development Front|AD Front]] |
||
* [[Sham Legion]] |
* [[Sham Legion]] |
||
'''Supported by:'''<br><!-- DO NOT ADD COUNTRIES PROVIDING NON-LETHAL SUPPORT. THIS WAS AGREED UPON AT THE TALK PAGE. !-->{{flag|Qatar}}<br>{{flag|Saudi Arabia|name=Saudi Arabia}}<br>{{flag|Turkey}}<ref name="TurkeyAssad">{{cite web|last=Epatko|first=Larisa|title=Syria and Turkey: A Complex Relationship|url=http://www.pbs.org/newshour/rundown/2012/11/syria-and-turkey.html|publisher=PBS NEWSHOUR|accessdate=15 November 2012|date=November 15, 2012}}</ref><ref name=SyriaRebelsTurkey>{{cite web|title=Training of moderate Syrian rebels 'allowed in Turkey'|url=http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-29591916|website=bbc.com|publisher=BBC News|accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref><br>{{Flag|United States}}<ref>{{cite news|title=U.S. weapons reaching Syrian rebels|url=http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2013-09-11/world/41972742_1_lethal-aid-syrian-rebels-chemical-weapons|newspaper=Washington Post|date=September 11, 2013}}</ref><br>{{Flag|France}}<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.enca.com/hollande-confirms-french-delivery-arms-syrian-rebels|title=Hollande confirms French delivery of arms to Syrian rebels|date=2014-08-21|accessdate=2015-01-16}}</ref><br>{{flag|Libya}}{{Ref label|libya|Ω}}<ref>{{cite web|last=Sherlock|first=Ruth|title=Libya's new rulers offer weapons to Syrian rebels|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/syria/8917265/Libyas-new-rulers-offer-weapons-to-Syrian-rebels.html|work=The Daily Telegraph|accessdate=25 May 2014}}</ref |
'''Supported by:'''<br><!-- DO NOT ADD COUNTRIES PROVIDING NON-LETHAL SUPPORT. THIS WAS AGREED UPON AT THE TALK PAGE. !-->{{flag|Qatar}}<br>{{flag|Saudi Arabia|name=Saudi Arabia}}<br>{{flag|Turkey}}<ref name="TurkeyAssad">{{cite web|last=Epatko|first=Larisa|title=Syria and Turkey: A Complex Relationship|url=http://www.pbs.org/newshour/rundown/2012/11/syria-and-turkey.html|publisher=PBS NEWSHOUR|accessdate=15 November 2012|date=November 15, 2012}}</ref><ref name=SyriaRebelsTurkey>{{cite web|title=Training of moderate Syrian rebels 'allowed in Turkey'|url=http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-29591916|website=bbc.com|publisher=BBC News|accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref><br>{{Flag|United States}}<ref>{{cite news|title=U.S. weapons reaching Syrian rebels|url=http://articles.washingtonpost.com/2013-09-11/world/41972742_1_lethal-aid-syrian-rebels-chemical-weapons|newspaper=Washington Post|date=September 11, 2013}}</ref><br>{{Flag|France}}<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.enca.com/hollande-confirms-french-delivery-arms-syrian-rebels|title=Hollande confirms French delivery of arms to Syrian rebels|date=2014-08-21|accessdate=2015-01-16}}</ref><br>{{flag|Libya}}{{Ref label|libya|Ω}}<ref>{{cite web|last=Sherlock|first=Ruth|title=Libya's new rulers offer weapons to Syrian rebels|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/syria/8917265/Libyas-new-rulers-offer-weapons-to-Syrian-rebels.html|work=The Daily Telegraph|accessdate=25 May 2014}}</ref> |
||
---- |
---- |
||
{{flagicon image|Flag of Jabhat al-Nusra.jpg}} [[al-Nusra Front]]<br> |
{{flagicon image|Flag of Jabhat al-Nusra.jpg}} [[al-Nusra Front]]<br> |
||
Revision as of 18:27, 14 June 2015
| Syrian Civil War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab Spring and Arab Winter Spillover of the Iraqi insurgency | |||||||||
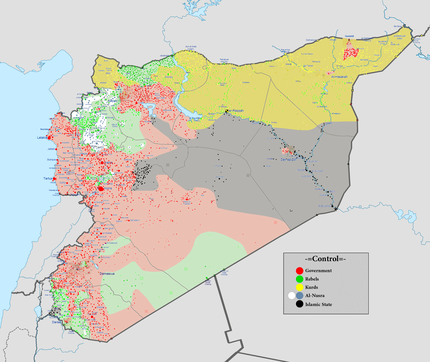 Current military situation: Red: government, Green: rebels, Yellow: Kurds (Rojava), Grey: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, White: al-Nusra Front (for a more detailed map, see Cities and towns during the Syrian Civil War). | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Main belligerents | |||||||||
|
Allied militias Supported by: |
(SRCC)
Supported by:
|
See: Rojava conflict | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Syrian Armed Forces: 178,000[30]
General Security Directorate: 8,000[32] National Defense Force: 80,000[33] Iran: 15,000[34] Ba'ath Brigades: 7,000[35][36] al-Abbas brigade: 10,000[37] (8,000 Iraqis)[38] Hezbollah: 3,000–5,000[39] Syrian Resistance: 2,000[40] |
FSA: 40,000–50,000[41] Islamic Front: 40,000–70,000[42] Ajnad al-Sham Union: up to 15,000 Army of Mujahedeen: 5,000[44]–12,000[45] Sham Legion:2,000+[46] al-Nusra Front: 13,000[47][48] Muhajirin wa-Ansar: 7,000 Jabhat Ansar al-Din 1,500+ | 31,500[49]–100,000[50] |
People's Protection Units (YPG): 65,000[51] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Syrian Government:
49,106–84,106 soldiers killed[53][54] 2,844 killed[53] |
72,363–113,363 fighters killed[‡] |
7,377–9,078 killed (per SOHR; certain events January 2014–May 2015)[57] 4,800+ killed (per SAA; conflict with the Syrian gov. September–December 2014)[58] | 1,236–1,405 fighters killed[59] | ||||||
|
69,494[53]–84,268[60] (2,996 foreign) civilian deaths documented by opposition Total killed: 130,000 captured or missing overall[62] 4.5 million (UN, Sep 2013) – 5.1 million (iDMC, Sep 2013) internally displaced[63][64][65] * Also aligned with Syrian opposition forces[69][70][71] Ω Due to the ongoing Second Libyan Civil War, there are two governments in charge of the country. The Council of Deputies (Tobruk) is the government aiding the Syrian opposition. ‡ Number includes Kurdish and ISIL fighters, whose deaths are also listed in their separate columns[72][53][54] | |||||||||
References
- ^ Ariel Ben Solomon (31 May 2013). "Report: Yemen Houthis fighting for Assad in Syria". Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 5 June 2013.
- ^ Galpin, Richard (10 January 2012). "Russian arms shipments bolster Syria's embattled Assad". News. BBC. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ "Russian military presence in Syria poses challenge to US-led intervention". The Guardian, 23 December 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^
- "Report: Iran, North Korea Helping Syria Resume Building Missiles". Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- Ryall, Julian (6 June 2013). "Syria: North Korean military 'advising Assad regime'". The Telegraph. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- "North Korea violating sanctions, according to UN report". The Telegraph. 3 July 2012. Retrieved 6 October 2012.
- ^ Epatko, Larisa (November 15, 2012). "Syria and Turkey: A Complex Relationship". PBS NEWSHOUR. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- ^ "Training of moderate Syrian rebels 'allowed in Turkey'". bbc.com. BBC News. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- ^ "U.S. weapons reaching Syrian rebels". Washington Post. September 11, 2013.
- ^ "Hollande confirms French delivery of arms to Syrian rebels". 2014-08-21. Retrieved 2015-01-16.
- ^ Sherlock, Ruth. "Libya's new rulers offer weapons to Syrian rebels". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 25 May 2014.
- ^ "Free Syrian Army fires military chief". Al Jazeera English. 16 February 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ^ "U.N. withdraws staffers as violence rages in Syria". Edition.cnn.com. 25 May 2013.
- ^ Mroue, Bassem; Suzan Fraser (2012-12-08). "Syria Rebels Create New Unified Military Command". The Huffington Post. AP. Archived from the original on 2012-12-08. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d "Leading Syrian rebel groups form new Islamic Front". BBC. 22 November 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- ^ "Bombing kills head of Syrian rebel group". Al Arabiya News.
- ^ Top Syrian rebel commander dies from wounds (Reuters), 18 November 2013
- ^ a b Nic Robertson and Paul Cruickshank (5 March 2015). "Source: Syrian warplanes kill leaders of al-Nusra". CNN.
- ^ "An internal struggle: Al Qaeda's Syrian affiliate is grappling with its identity". Brookings Institute. 31 May 2015. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ Counter Extremism Project (2014). "Executive Summary: Sami al-Oraidi". Counter Extremism Project.
- ^ "An internal struggle: Al Qaeda's Syrian affiliate is grappling with its identity". Brookings Institute. 31 May 2015. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ "Who's who in the Nusra Front?". al-Araby. 15 December 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "ISIS reportedly kills Al Nusrah Front's commander for Idlib province". The Long War Journal. 16 April 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Condemns Terrorist Attacks in Iraq and Pledges to Help Combat al Qaeda". United States Department of State. 10 August 2013.
- ^ http://www.businessinsider.com/report-a-former-physics-teacher-is-now-leading-isis-2015-4
- ^ http://www.ibtimes.com/if-isis-leader-abu-bakr-al-baghdadi-killed-who-caliph-islamic-state-group-1721638
- ^ "Military Skill and Terrorist Technique Fuel Success of ISIS". The New York Times. 27 August 2014. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
- ^ "Top ISIS Leaders are Revealed". Alarabiya. 13 February 2014.
- ^ "Al Huffington Post Algérie : Abou Khattab, kurde, jihadiste et chef des opérations du Daech contre Kobané". Al Huffington Post. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State's commanders killed in Kobane". ARA News.
- ^ Tarek Radwan. "Kurdish-Arab Rebel Alliance May be Key to Obama's Syrian Strategy". Atlantic Council.
- ^ "Syria military strength". Global Fire Power. 4 January 2015.
- ^ Barnard, Anne; Saad, Hwaida; Schmitt, Eric (28 April 2015). "An Eroding Syrian Army Points to Strain". New York Times. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ^ "Syria's diminished security forces". AFP. 28 August 2013. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ ISIS’ Iraq offensive could trigger Hezbollah to fill gap left in Syria The Daily Star, 16 June 2014
- ^ "Iran sends 15,000 fighters to Syria". The Daily Star. 4 June 2015.
- ^ "«كتائب البعث» إلى شوارع دمشق". Al Akhbar. 14 January 2014.
- ^ Aron Lund (13 January 2014). "The Baath Battalions Move Into Damascus". Carnegie Endowment.
- ^ Syrian war widens Sunni-Shia schism as foreign jihadis join fight for shrines retrieved 5 June 2013
- ^ Maria Abi-Habib (18 June 2014). "Shiite Militias Decamping From Syria to Fight in Iraq". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ "From Qusair to Yabrud: Shiite foreign fighters in Syria - Al-Monitor: the Pulse of the Middle East". Al-Monitor.
- ^ Albayrak, Aydin. "Mihraç Ural, a man with a long history of terrorism". Today's Zaman. Retrieved 3 August 2013.
- ^ Cockburn, Patrick (11 December 2013). "West suspends aid for Islamist rebels in Syria, underlining their disillusionment with those forces opposed to President Bashar al-Assad". The Independent.
- ^ "Front to Back". Foreign Policy.
- ^ "Syria crisis: Guide to armed and political opposition". BBC. 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Factbox: Syria's rebel groups". Reuters. 9 January 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ "Al Qaida rebels leave mass grave behind as they desert base in Syria". McClatchy. 6 January 2014. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ [1]
- ^ "Syria crisis: Spooked by rebel gains, Jordan doubles down on Islamic State". 4 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ^ "Syria Direct: News Update 3-25-15". 4 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State fighter estimate triples - CIA". BBC. 12 September 2014.
- ^ "War with Isis: Islamic militants have army of 200,000, claims senior Kurdish leader". The Independent. 18 November 2014.
- ^ "Will the Islamic State last through 2015?". Today's Zaman. Retrieved 4 January 2015.
- ^ Mutlu Civiroglu (11 August 2013). "Kurdish Commander: Jihadi Groups in Syria Have Hijacked FSA". Rudaw.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "320,000 people killed since the beginning of the Syrian Revolution". 9 June 2015.
- ^ a b c "More than 110 dead, thousands of regime forces during the 41 months". Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- ^ "David Cameron Offers 'Safe Passage' For Syria's Bashar Al-Assad, But Not To Britain (PICTURES)". Huffington Post. 6 November 2012.
- ^ "Syria: Opposition, almost 11,500 civilians killed". Ansamed.ansa.it. 2010-01-03. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ^ 2,196 killed in the inter-rebel conflict by late June 2014,[2] 139 executed,[3] 5 killed during the 2014 American rescue mission in Syria, 456–586 killed in the 2014 Eastern Syria offensive, 1,443–2,978 killed in the Siege of Kobanî (not including airstrikes), 389–425 killed during the Al-Hasakah offensive (February–March 2015), 280 killed (Northeastern Syria; 6-28 May 2015),[4] 150 killed during the Palmyra offensive (2015), 102 killed during the Al-Hasakah city offensive (May–June 2015), and 2,217 killed due to the American-led intervention in Syria, a total of 7,377–9,078 reported killed
- ^ "Syrian Army Kills Nearly 5,000 IS Militants in Three Months: Source". sputniknews.com. 25 December 2014.
- ^ 15 killed (31 October 2012),[5] 25 killed (19 November 2012),[6] 379 killed (2013),[7] 537–706 killed (2014),[8][9][10] 280 killed (2015),[11][12][13][14][15] total of 1,236–1,405 reported killed
- ^ "Violations Documenting Center". Violations Documenting Center. 8 June 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "Syrian Rebels And Government Reach Truce In Besieged Area". AP. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- ^ "Syria's Meltdown Requires a U.S.-Led Response". Washington Institute for Near East Policy. 22 March 2013.
- ^ "Syrian Refugees in Lebanon," The New York Times, September 5, 2013: UN says: 6.5 million displaced, of whom 2 million fled out of the country
- ^ "Syria: A full-scale displacement and humanitarian crisis with no solutions in sight"., iDMC, Sep 2013: 5.1 million internally displaced ("forced to flee their homes because their lives were at danger, but did not cross international borders")
- ^ "Dispatch: Syria's Internally Displaced Depend on Handouts"., UN, Feb 2013: 2.5 million internally displaced
- ^ "Syrian refugees top three million mark: UN". SBS News. AAP. 2013-11-29. Retrieved 2014-01-03.
- ^ "Most US Airstrikes in Syria Target a City That's Not a "Strategic Objective"". Mother Jones.
- ^ At least 20,000 civilians displaced during the Al-Hasakah offensive (February–March 2015); 5,000+ in the Khabur Valley region,[16] and 15,000+ in the Tell Hamis region[17]
- ^ Bronstein, Scott; Griffin, Drew (26 September 2014). "Syrian rebel groups unite to fight ISIS". CNN. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
Under the agreement, moderate Muslim rebel groups fighting under the Supreme Military Council of Syria agreed to form an alliance with the predominantly Christian Syriac Military Council.
- ^ Cousins, Sophie (22 December 2014). "Remaining Christians in Syria fight to save their land". USA Today. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ahmad, Rozh (23 September 2014). "A glimpse into the world of Syria's Christian "Sutoro" fighters (video)". Your Middle East. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
The regime wants us to be puppets, deny our ethnicity and demand an Arab-only state.
- ^ "More than 215,000 killed in Syria since 2011". 3news.co.nz.
