Duduk: Difference between revisions
→Television soundtracks: No evidence that this show exists |
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) WaybackMedic using AWB |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
Historically, the word {{lang|hy|[[wikt:ծիրանափող|ծիրանափող]]}}, {{IPA-hy|tsiɾɑnɑˈpʰoʁ|pron}}, (literally "[[apricot]] pipe")<ref>{{cite news|title=‘Dudukner Ensemble’ to Play in Watertown|url=http://www.armenianweekly.com/2012/09/12/dudukner-ensemble-to-play-in-watertown/|newspaper=[[Armenian Weekly]]|date=12 September 2012|author=Weekly Staff|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316203538/http://www.armenianweekly.com/2012/09/12/dudukner-ensemble-to-play-in-watertown/|archivedate=16 March 2014|quote=The duduk, known since antiquity as an “apricot pipe,” is a traditional woodwind instrument indigenous to Armenia.}}</ref> was used in [[Armenian language|Armenian]].<ref>{{cite news|last=Gasparyan|first=Djivan|title=Կբացվի դուդուկահարների դպրոց [A school for duduk players to be opened]|url=http://www.aravot.am/2004/10/30/319034/|newspaper=[[Aravot]]|date=30 October 2004|authorlink=Djivan Gasparyan |
Historically, the word {{lang|hy|[[wikt:ծիրանափող|ծիրանափող]]}}, {{IPA-hy|tsiɾɑnɑˈpʰoʁ|pron}}, (literally "[[apricot]] pipe")<ref>{{cite news|title=‘Dudukner Ensemble’ to Play in Watertown|url=http://www.armenianweekly.com/2012/09/12/dudukner-ensemble-to-play-in-watertown/|newspaper=[[Armenian Weekly]]|date=12 September 2012|author=Weekly Staff|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316203538/http://www.armenianweekly.com/2012/09/12/dudukner-ensemble-to-play-in-watertown/|archivedate=16 March 2014|quote=The duduk, known since antiquity as an “apricot pipe,” is a traditional woodwind instrument indigenous to Armenia.}}</ref> was used in [[Armenian language|Armenian]].<ref>{{cite news|last=Gasparyan|first=Djivan|title=Կբացվի դուդուկահարների դպրոց [A school for duduk players to be opened]|url=http://www.aravot.am/2004/10/30/319034/|newspaper=[[Aravot]]|date=30 October 2004|authorlink=Djivan Gasparyan|language=hy|quote=Ես ապացուցեցի, որ դուդուկի իսկական անունը ծիրանափող է, որի արմատները գալիս են Մուշից, Վանից, Գյումրիից, Էջմիածնից: <br> translation: "I proved that the real name of duduk is tsiranapogh, whose roots come from Mush, Van, Gyumri and Ejmiatsin.}}{{dead link|date=April 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref><ref name="encyclopedia.am"/> According to some sources, the word "duduk" ([[wikt:դուդուկ|դուդուկ]]) was put into wide circulation in Armenia in the 1920s, during the early Soviet period, thus largely replacing "tsiranapogh".<ref>{{cite news|last=Hovhannisyan|first=Hasmik|title=Դուդուկ. գյուղական քեֆերից մինչեւ հոլիվուդյան ֆիլմեր [Duduk: From Village Parties to Hollywood Films]|url=http://hetq.am/arm/news/10658/|newspaper=[[Hetq Online]]|date=10 July 2006|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316181828/http://hetq.am/arm/news/10658/|archivedate=16 March 2014|quote=Վարկածներից մեկն ասում է, որ դուդուկն ի սկզբանե կոչվել է ծիրանափող եւ դուդուկ դարձել է ռուսների «թեթեւ ձեռքով», 1920-ական թվականներին, որոնք դժվարանում էին արտասանել այս բարդ անունը, եւ այն ձեւափոխեցին ռուսական «դուդկա» բառից:}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|script-title=hy:Բրոնզե ականջ պետք է ունենաս, որ չհուզվես|url=http://www.azg.am/AM/error/2013021514|newspaper=[[Azg Daily]]|date=15 February 2013|authorlink=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316202659/http://www.azg.am/AM/error/2013021514|archivedate=16 March 2014|language=hy|quote=Միայն Հայաստանում է աճում այն ծիրանենին, որից երաժշտականՙ հոբոյին նման այս գործիքն են ստանում, եւ որը դարեր ի վեր հայերը ծիրանափող են անվանում: Ռուսներն այս բառը չեն կարողացել արտասանել, «դուդկա» անունն են տվել, այստեղից էլՙ դուդուկ ուրախ բառը:}}</ref> |
||
The word "duduk" (also spelled ''doudouk'') is a loanword ultimately derived from [[Turkish language|Turkish]] "düdük" which means whistle.<ref name=GSE>{{cite web|language=ru|url=http://bse.sci-lib.com/article034454.html|title=Дудук [Duduk]|publisher=''[[Great Soviet Encyclopedia]]''}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://feb-web.ru/feb/mas/mas-abc/05/ma145204.htm|language=ru|publisher=Russian language dictionary in 4 volumes. Volume 1|year=1999|title=Дудук [Duduk]}}</ref> The word ''dudka'' in Slavic languages is a diminutive of ''duda'' and is of native [[Proto-Slavic language|Proto-Slavic]] origin.<ref>[http://starling.rinet.ru/cgi-bin/response.cgi?root=/usr/local/share/starling/morpho&morpho=0&basename=\usr\local\share\starling\morpho\vasmer\vasmer&first=3601 “дуда”] in М. Фасмер (1986), ''Этимологический Словарь Русского Языка'' (Москва: Прогресс), 2-е изд. — Перевод с немецкого и дополнения О.Н. Трубачёва</ref> |
The word "duduk" (also spelled ''doudouk'') is a loanword ultimately derived from [[Turkish language|Turkish]] "düdük" which means whistle.<ref name=GSE>{{cite web|language=ru|url=http://bse.sci-lib.com/article034454.html|title=Дудук [Duduk]|publisher=''[[Great Soviet Encyclopedia]]''}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://feb-web.ru/feb/mas/mas-abc/05/ma145204.htm|language=ru|publisher=Russian language dictionary in 4 volumes. Volume 1|year=1999|title=Дудук [Duduk]}}</ref> The word ''dudka'' in Slavic languages is a diminutive of ''duda'' and is of native [[Proto-Slavic language|Proto-Slavic]] origin.<ref>[http://starling.rinet.ru/cgi-bin/response.cgi?root=/usr/local/share/starling/morpho&morpho=0&basename=\usr\local\share\starling\morpho\vasmer\vasmer&first=3601 “дуда”] in М. Фасмер (1986), ''Этимологический Словарь Русского Языка'' (Москва: Прогресс), 2-е изд. — Перевод с немецкого и дополнения О.Н. Трубачёва</ref> |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
* ''[[Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2]] '' (2011) by [[Alexandre Desplat]], in the track "Lily's Theme (Opening)" |
* ''[[Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2]] '' (2011) by [[Alexandre Desplat]], in the track "Lily's Theme (Opening)" |
||
* ''[[Hotel Rwanda]]'' (2004) main theme music <ref name=rwanda>"Hotel Rwanda Film Music"http://www.musicweb-international.com/film/2006/apr06/hotelrwanda.html</ref> |
* ''[[Hotel Rwanda]]'' (2004) main theme music <ref name=rwanda>"Hotel Rwanda Film Music"http://www.musicweb-international.com/film/2006/apr06/hotelrwanda.html</ref> |
||
* ''[[Hulk (film)|Hulk]]'' (2003) duduk by [[Pedro Eustache]] by [[Danny Elfman]]<ref>{{cite web|title=Hulk Editorial Review|url=http://www.filmtracks.com/titles/hulk.html|publisher=Filmtracks|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/ |
* ''[[Hulk (film)|Hulk]]'' (2003) duduk by [[Pedro Eustache]] by [[Danny Elfman]]<ref>{{cite web|title=Hulk Editorial Review|url=http://www.filmtracks.com/titles/hulk.html|publisher=Filmtracks|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20131521153100/http://www.filmtracks.com/titles/hulk.html |archivedate=16 March 2014 |date=8 June 2003}}</ref> |
||
* ''[[The Island (2005 film)|The Island]]'' (2005) by [[Steve Jablonsky]]<ref name="chrisbleth1" /> |
* ''[[The Island (2005 film)|The Island]]'' (2005) by [[Steve Jablonsky]]<ref name="chrisbleth1" /> |
||
* ''[[The Kite Runner (film)|The Kite Runner]]'' (2007) by [[Alberto Iglesias]]<ref name="chrisbleth1" /> |
* ''[[The Kite Runner (film)|The Kite Runner]]'' (2007) by [[Alberto Iglesias]]<ref name="chrisbleth1" /> |
||
Revision as of 17:05, 22 April 2016
It has been suggested that Balaban (instrument) be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since February 2015. |
Duduk - also known as ծիրանափող (tsiranapogh) in Armenian | |
| Classification | Wind instrument with double reed |
|---|---|
| Playing range | |
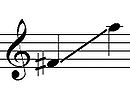 | |
| Musicians | |
| Gevorg Dabaghyan, Djivan Gasparyan, Pedro Eustache, Vache Sharafyan, Didier Malherbe | |
The duduk (doo-dook;[1] Template:Lang-hy)[2] is an ancient double-reed woodwind flute made of apricot wood. It is indigenous to Armenia.[3][4] It is commonly played in pairs: while the first player plays the song, the second plays a stready drone, and the sound of the two instruments together creates a richer, more haunting sound.
The unflattened reed and cylindrical body produce a sound closer to a clarinet than to more commonly known double-reeds. Unlike other double reed instruments like the oboe or shawm, the duduk has a very large reed proportional to its size. UNESCO proclaimed the Armenian duduk and its music as a Masterpiece of the Intangible Heritage of Humanity in 2005 and inscribed it in 2008.[5][6] Duduk music has been used in a number of films, most notably in The Russia House and Gladiator.
Variations of the duduk exist in Eastern Europe, the Middle East and Central Asia, including the balaban in Azerbaijan and Iran.[7]
Etymology
Historically, the word ծիրանափող, pronounced [tsiɾɑnɑˈpʰoʁ], (literally "apricot pipe")[8] was used in Armenian.[9][2] According to some sources, the word "duduk" (դուդուկ) was put into wide circulation in Armenia in the 1920s, during the early Soviet period, thus largely replacing "tsiranapogh".[10][11]
The word "duduk" (also spelled doudouk) is a loanword ultimately derived from Turkish "düdük" which means whistle.[12][13] The word dudka in Slavic languages is a diminutive of duda and is of native Proto-Slavic origin.[14]
This instrument is not to be confused with the northwestern Bulgarian folk instrument of the same name (see below, Balkan duduk).
Overview


The duduk is a double reed instrument with ancient origins, having existed since at least the fifth century, while there are Armenian scholars who believe it existed more than 1,500 years before that.[15] The earliest instruments similar to the duduk's present form are made of bone or entirely of cane. Today, the duduk is exclusively made of wood with a large double reed, with the body made from aged apricot wood.[16]
The particular tuning depends heavily on the region in which it is played. In the twentieth century, the Armenian duduk began to be standardized diatonic in scale and single-octave in range. Accidentals, or chromatics are achieved using fingering techniques. The instrument's body also has different lengths depending upon the range of the instrument and region. The reed (Armenian: եղեգն, eġegn), is made from one or two pieces of cane in a duck-bill type assembly. Unlike other double-reed instruments, the reed is quite wide, helping to give the duduk both its unique, mournful sound, as well as its remarkable breath requirements. The duduk player is called dudukahar (դուդուկահար) in Armenian.
The performer uses air stored in his cheeks to keep playing the instrument while he inhales air into his lungs. This “circular” breathing technique is commonly used with all the double-reed instruments in the Middle East.[7]
Duduk "is invariably played with the accompaniment of a second dum duduk, which gives the music an energy and tonic atmosphere, changing the scale harmoniously with the principal duduk."[17]
History
Armenian musicologists cite evidence of the duduk's use as early as 1200 BC, though Western scholars suggest it is 1,500 years old.[18] Variants of the duduk can be found in Armenia and the Caucasus. The history of the Armenian duduk music is dated to the reign of the Armenian king Tigran the Great, who reigned from 95–55 B.C.[19] According to ethnomusicologist Dr. Jonathan McCollum, the instrument is depicted in numerous Armenian manuscripts of the Middle Ages, and is "actually the only truly Armenian instrument that's survived through history, and as such is a symbol of Armenian national identity ... The most important quality of the duduk is its ability to express the language dialectic and mood of the Armenian language, which is often the most challenging quality to a duduk player."[20]
Balkan duduk
While "duduk" most commonly refers to the double reed instrument described on this page, by coincidence there is a different instrument of the same name played in northwestern Bulgaria. This is a blocked-end flute resembling the Serbian frula, known also as kaval or kavalče in a part of Macedonia,[21] and as duduk (дудук) in northwest Bulgaria.[22][23] Made of maple or other wood, it comes in two sizes: 700–780 millimetres (28–31 in) and 240–400 millimetres (9.4–15.7 in) (duduce). The blocked end is flat. Playing this type of duduk is fairly straightforward and easy, [citation needed] and its sound is clean and pleasant.
In popular culture
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2014) |
The sound of the duduk has become known to wider audiences through its use in popular film soundtracks. Starting with Peter Gabriel's score for Martin Scorsese's The Last Temptation of Christ, the duduk's archaic and mournful sound has been employed in a variety of genres to depict such moods. Djivan Gasparyan played the duduk in Gladiator, Syriana, and Blood Diamond, among others.[24] The duduk was also used extensively in Battlestar Galactica.[25] The duduk was also used in the series Avatar: The Last Airbender. Its computer-altered sound was given to the fictitious Tsungi horn, played by a number of the characters. The sound of the duduk was used in The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe. A Lullaby that Mr. Tumnus plays on a fictitious double flute.[26]
The 2010 Eurovision Song Contest entry from Armenia "Apricot Stone", which finished 7th in the final, featured prominent duduk played by Djivan Gasparyan. In the indie-rock genre, the French-American band Deleyaman is the first alternative music band to have featured the duduk on all of their albums with Gerard Madilian as a permanent member in their line-up.
Film soundtracks
The duduk has been used in a number of films, especially "to denote otherworldliness, loneliness, and mourning or to supply a Middle Eastern/Central Asian atmosphere."[27]
- Ararat (2002) by Mychael Danna
- Avatar (2009) by James Horner, in the track Shutting Down Grace's Lab
- Bedtime Stories (2008) by Rupert Gregson-Williams[28]
- Brotherhood of the Wolf (2001) by Joseph LoDuca
- Chilean Gothic (film) (2000) by Fractal
- Constantine (2005) by Brian Tyler, Klaus Badelt, in the track Circle of Hell
- The Crow (1994) by Graeme Revell featuring the duduk player Djivan Gasparyan
- Dead Man Walking (film) (1995) by David Robbins
- Elektra (2005) by Christophe Beck[28]
- Gladiator (2000) by Djivan Gasparyan in the track Duduk of the North[29]
- Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2 (2011) by Alexandre Desplat, in the track "Lily's Theme (Opening)"
- Hotel Rwanda (2004) main theme music [30]
- Hulk (2003) duduk by Pedro Eustache by Danny Elfman[31]
- The Island (2005) by Steve Jablonsky[28]
- The Kite Runner (2007) by Alberto Iglesias[28]
- The Last Temptation of Christ (1988) by Peter Gabriel, featuring the duduk player Vatche Hovsepian
- The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (2005) by Harry Gregson-Williams, in the track A Narnia Lullaby[32]
- Munich duduk by Pedro Eustache (2005) by John Williams
- Mayrig (1991) by Omar Al Sharif
- Next (2007) by Mark Isham[28]
- The Passion of The Christ (2004) by Mel Gibson, composer John Debney duduks by Pedro Eustache and Chris Bleth
- Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End (2007) by Hans Zimmer[28]
- Rendition (2007) by Paul Hepker and Mark Kilian, duduk by Pedro Eustache
- Ronin (1998) by Elia Cmiral
- Syriana (2005) by Alexandre Desplat, duduks by Djivan Gasparyan and Pedro Eustache
- The Russia House (1990) by Jerry Goldsmith
- Vantage Point (2008) by Atli Orvarsson[28]
- Wanted (2008) by Danny Elfman[28]
- Warriors of Heaven and Earth (2003) by A. R. Rahman[33]
- You Don't Mess with the Zohan (2008) by Rupert Gregson-Williams[28]


Television soundtracks
- Angel by Rob Kral[28]
- Avatar: The Last Airbender The character Zuko, Iroh and the band "Flamey-Os" play a fictional instrument called a "Tsungi Horn" and its sound is actually a duduk electronically modulated to resemble a brass instrument[citation needed]
- Battlestar Galactica (2004 TV series) by Bear McCreary. Its tracks "Two Funerals", "Starbuck on the Red Moon", "Escape from the Farm", "Colonial Anthem, "Black Market", "Something Dark is Coming", "Martial Law", "Prelude to War" feature the duduk.[34][35][36] Roslin's theme was set to lyrics a second time for the third season premiere "Occupation", this time in Armenian.
- Buffy the Vampire Slayer by Christophe Beck, Tomas Wanker, Rob Dunkin, Douglas Stevens[28]
- Castle by Robert Duncan[28]
- Children of Dune by Brian Tyler in the tracks "Dune Messiah", "The Throne of Alia", "The Preacher At Arrakeen", "Farewell"[37]
- CSI: New York by Bill Brown[28]
- Firefly by Greg Edmonson[28]
- Game of Thrones by Ramin Djawadi features the instrument in Daenerys Targaryen's theme[38]
- JAG by Steve Bramson[28]
- The Mummy Who Would Be King by Gil Talmi, Andrew Gross[28]
- Over There by Ed Rogers[28]
- The Pacific by Blake Neely and Geoff Zanelli[28]
- Path to 9/11 by John Cameron[28]
- The Shield features the Armenian song Hayots Aghoonak by Seda Garibyan
- Rome by Jeff Beal[39]
- Spartacus by Randy Miller. Track Second Thought
- Star Trek: Enterprise by Paul Baillargeon[28]
- Yu-Gi-Oh! by Wayne Sharpe
- Xena: Warrior Princess by Joseph Loduca
Video game scores
- 'Shards of the Exodar' in World of Warcraft: The Burning Crusade by Derek Duke, Glenn Stafford and Russell Brower
- 'Dalaran' in World of Warcraft: Wrath of the Lich King by Derek Duke, Glenn Stafford and Russell Brower
- Civilization V by Michael Curran[40][41]
- Dark Void by Bear McCreary[28]
- Dota 2 by Jason Hayes
- F.E.A.R. by Nathan Grigg
- God of War III by Gerard Marino
- Mass Effect by Jack Wall[42]
- Myst III: Exile by Jack Wall
- Myst IV: Revelation by Jack Wall[28]
- Outcast by Lennie Moore in the track Oriental Spirit
- Prince of Persia: The Two Thrones by Inon Zur[28]
- Uncharted 2 by Greg Edmonson[28]
- 'Croft Manor Theme' in Tomb Raider Legend by Troels Brun Folmann
- * The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim (2011) by Jeremy Soule in the track Tundra
Popular music
The duduk also appears in songs:
- "Prelude & Nostalgia" by Yanni (from the 1997 album Tribute)
- "Come Talk to Me" by Peter Gabriel (from the 1992 album Us)
- "Zachem Ya" by t.A.T.u. (from the 2001 album 200 Po Vstrechnoy)
- "Jenny Wren" by Paul McCartney (2005)
- "All That I Am" by Rob Thomas (from the 2006 album ...Something to Be)
- "Touching the Void" by Soulfly (from the 2008 album Conquer)
- "Castles in the Sand" by Deleyaman (2014) [43]
- "Rooftop Runner" by fRecord (2014) [44]
- "Soulfly X" by Soulfly (from the 2015 album Archangel)
Anime soundtracks
- Tales from Earthsea by Tamiya Terashima, in the tracks "The Trip", "The Spider" and "Violent Robbery/The Seduction of the Undead".[45]
See also
References
- ^ Journal of the American Musical Instrument Society. 32. American Musical Instrument Society: 183. 2006.
...the duduk (pronounced doo-dook)...
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b "Երաժշտական գործիքներ [Musical instruments]" (in Armenian). Armenian Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
Հայաստանում փողային գործիքների շարքում առանձնահատուկ է դուդուկը (կոչվում է նաև ծիրանափող), որը պատրաստվում է վայրի ծիրանենու կամ տանձենու փայտից:
- ^ Stokes, Jamie, ed. (2008). Peoples of Africa and the Middle East, Volume 1. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-8160-7158-6.
One of the oldest indigenous Armenian instruments is the duduk, a woodwind instrument usually made from apricot wood, with a double reed mouthpiece.
- ^ "Armenian duduk and other Armenian folk instruments" (PDF). UNESCO. June 2003. p. 32. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
Duduk is considered to be the most Armenian of all folk instruments for its Armenian origin and honest expression. It has a 1500 – year history and is native to Armenia although there are its variants played in Turkey, Georgia and Azerbaijan.
- ^ "Sounds of Armenian duduk". UNESCO. November 2012. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
Duduk and its music were inscribed on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2008 (originally proclaimed in 2005). The duduk, or "dziranapogh" in Armenian, is a double-reed woodwind instrument made of apricot wood, conventionally called the "Armenian oboe".
- ^ "Duduk and its music". UNESCO. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ a b Albright, Ch. (15 December 1988). "BĀLĀBĀN". Encyclopaedia Iranica. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
- ^ Weekly Staff (12 September 2012). "'Dudukner Ensemble' to Play in Watertown". Armenian Weekly. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
The duduk, known since antiquity as an "apricot pipe," is a traditional woodwind instrument indigenous to Armenia.
- ^ Gasparyan, Djivan (30 October 2004). "Կբացվի դուդուկահարների դպրոց [A school for duduk players to be opened]". Aravot (in Armenian).
Ես ապացուցեցի, որ դուդուկի իսկական անունը ծիրանափող է, որի արմատները գալիս են Մուշից, Վանից, Գյումրիից, Էջմիածնից:
[dead link]
translation: "I proved that the real name of duduk is tsiranapogh, whose roots come from Mush, Van, Gyumri and Ejmiatsin. - ^ Hovhannisyan, Hasmik (10 July 2006). "Դուդուկ. գյուղական քեֆերից մինչեւ հոլիվուդյան ֆիլմեր [Duduk: From Village Parties to Hollywood Films]". Hetq Online. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
Վարկածներից մեկն ասում է, որ դուդուկն ի սկզբանե կոչվել է ծիրանափող եւ դուդուկ դարձել է ռուսների «թեթեւ ձեռքով», 1920-ական թվականներին, որոնք դժվարանում էին արտասանել այս բարդ անունը, եւ այն ձեւափոխեցին ռուսական «դուդկա» բառից:
- ^ Բրոնզե ականջ պետք է ունենաս, որ չհուզվես. Azg Daily (in Armenian). 15 February 2013.
Միայն Հայաստանում է աճում այն ծիրանենին, որից երաժշտականՙ հոբոյին նման այս գործիքն են ստանում, եւ որը դարեր ի վեր հայերը ծիրանափող են անվանում: Ռուսներն այս բառը չեն կարողացել արտասանել, «դուդկա» անունն են տվել, այստեղից էլՙ դուդուկ ուրախ բառը:
{{cite news}}:|archive-date=requires|archive-url=(help); External link in|authorlink= - ^ "Дудук [Duduk]" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Дудук [Duduk]" (in Russian). Russian language dictionary in 4 volumes. Volume 1. 1999.
- ^ “дуда” in М. Фасмер (1986), Этимологический Словарь Русского Языка (Москва: Прогресс), 2-е изд. — Перевод с немецкого и дополнения О.Н. Трубачёва
- ^ World Music: Africa, Europe and the Middle East. 1999. p. 334. ISBN 9781858286358.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Andrea L. Stanton, Edward Ramsamy, Peter J. Seybolt, ed. (2012). Cultural Sociology of the Middle East, Asia, and Africa: An Encyclopedia. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications. p. 167. ISBN 9781412981767.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ [1] Duduk Info at Ethnicinstruments.co.uk
- ^ Encyclopedia.com:DJIVAN GASPARYAN
- ^ "The roots of Armenian duduk music go back to the times of the Armenian king Tigran the Great (95-55 BC)": "The Duduk and its Music. UNESCO. Accessed February 8, 2010.
- ^ Turpin, Andy (12 February 2010). "Nothing Sounds Armenian Like a Duduk: ALMA Lecture". Armenian Weekly. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ www.macedoniadirect.com/instruments/supelki.htm
- ^ "Дудук : Horo.bg - българският сайт за народни хора, песни, танци, обичаи, фолклор" (in Bulgarian). Horo.bg. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ For a detailed description of the instrument (in Bulgarian), see http://www.bgjourney.com/Bit%20t%20Kultura/Old%20gloss/Old%20gloss%20Du.html
- ^ Gasparian article at imdb.com
- ^ Duduk article from composer Bear McCreary's Battlestar Galactica site
- ^ Harry Gregson-Williams Talks Narnia & Narnian Lullaby Clip
- ^ Hung, Eric (2011). Leonard, Kendra Preston (ed.). Buffy, Ballads, and Bad Guys Who Sing: Music in the Worlds of Joss Whedon. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press. p. 259. ISBN 9780810877658.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x "Chris Bleth Movie Credits". Chrisbleth.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
- ^ Gladiator by Hans Zimmer and Lisa Gerrard
- ^ "Hotel Rwanda Film Music"http://www.musicweb-international.com/film/2006/apr06/hotelrwanda.html
- ^ Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Date_validation at line 986: bad argument #3 to 'format' (string expected, got nil).
- ^ Brennan, Mike (2 December 2005). "The Chronicles of Narnia Review". Archived from the original on 16 March 2014.
These include the use of the duduk as Mr. Tumnus' pipe in "A Narnia Lullaby"...
- ^ Savita Gautham. "inese rhapsody". The Hindu. Retrieved 2003-10-23.
- ^ "Instruments of Battlestar Galactica: Duduk". Bearmccreary.com. 2006-09-28. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
- ^ Runner, Blade (2004-02-26). "Duduk: The Instrument That Makes Hollywood Cry". Galactica-station.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
- ^ "Battlestar Galactica: Season Two". Musicweb-international.com. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
- ^ "Children of Dune". Cinemusic.net. Archived from the original on November 15, 2009. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "'Game of Thrones' Composer Ramin Djawadi: 'I'm Just Trying to Create Something Magical' (Q&A)". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved 2013-12-27.
- ^ http://www.soundtrack.net/content/article/?id=201
- ^ "Civ5in". Michaelcurran.net. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ "Rome - Augustus Caesar War - "Ancient Roman Melody Fragments" by Geoff Knorr". ISSUU. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ Bloodworth, Daniel (2012-04-09). "BackTrack: Composing Mass Effect – Jack Wall Interview, Part 1 | Side Mission". GameTrailers. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ "Deleyaman on last.fm". Archived from the original on 26 January 2015.
- ^ "fRecord on last.fm". Archived from the original on 26 January 2015.
- ^ Benoit Basirico (2005-11-14). "Gedo Senki (Les Contes de Terremer)". Cinezik.org. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
Further reading
- Nercessian, Andy (2001). The Duduk and National Identity in Armenia. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9781461672722.
External links
- EthnicInstruments.co.uk
- Jenewein Duduks
- Armenian Duduk
- Duduk Music
- Professional duduk, shvi and blul by Master Karen
- Duduk.ca
- Duduk.com, including Duduk Forum
- Duduk YahooGroup
- ArmenianInstruments.com, including duduk scores

