Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations: Difference between revisions
Revert vandalism - you just deleted the dates that HAD sources, and gave an edit summary that was clearly intended to obfuscate, which can only be considered vandalism: please desist |
|||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Australia|{{flagicon|Australia}} [[Australia]]}} |
| {{sort|Australia|{{flagicon|Australia}} [[Australia]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| align=right| 20,555,300 |
| align=right| 20,555,300 |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Bangladesh|{{flagicon|Bangladesh}} [[Bangladesh] |
| {{sort|Bangladesh|{{flagicon|Bangladesh}} [[Bangladesh]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1972-04-18</span>[[18 April]] [[1972]] |
| <span style="display:none">1972-04-18</span>[[18 April]] [[1972]] |
||
| Asia |
| Asia |
||
| align=right| 148,384,000 |
| align=right| 148,384,000 |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Cameroon|{{flagicon|Cameroon}} [[Cameroon]]}} |
| {{sort|Cameroon|{{flagicon|Cameroon}} [[Cameroon]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1995-11- |
| <span style="display:none">1995-11-13†</span>[[13 November]] [[1995]] |
||
| Africa |
| Africa |
||
| align=right| 16,322,000 |
| align=right| 16,322,000 |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Canada|{{flagicon|Canada}} [[Canada]]}} |
| {{sort|Canada|{{flagicon|Canada}} [[Canada]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| North America |
| North America |
||
| align=right| 32,654,500 |
| align=right| 32,654,500 |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Cyprus|{{flagicon|Cyprus}} [[Cyprus]]}} |
| {{sort|Cyprus|{{flagicon|Cyprus}} [[Cyprus]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1961-08-16†</span>[[16 August]] [[1961]] |
|||
| <span style="display:none">1961-03-13</span>[[13 March]] [[1961]]<ref>{{cite journal |last=McIntyre |first=W. David |authorlink=W. David McIntyre |year=2000 |month=January |title=Britain and the creation of the Commonwealth Secretariat |journal=Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=pp. 135–158 |id=10.1080/03086530008583082 }}</ref> |
|||
| Europe / Asia |
| Europe / Asia |
||
| align=right| 818,200 |
| align=right| 818,200 |
||
| |
|||
| Gained independence from the [[United Kingdom]] on [[18 August]] [[1960]]. |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Dominica|{{flagicon|Dominica}} [[Dominica]]}} |
| {{sort|Dominica|{{flagicon|Dominica}} [[Dominica]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1978-11-03</span>[[3 November]] [[1978]] |
| <span style="display:none">1978-11-03</span>[[3 November]] [[1978]] |
||
| North America |
| North America |
||
| align=right| {{sort|79,000|{{ref|1|[ |
| align=right| {{sort|79,000|{{ref|1|[A]}}79,000}} |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
| <span style="display:none">1979-07-12</span>[[12 July]] [[1979]] |
| <span style="display:none">1979-07-12</span>[[12 July]] [[1979]] |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| align=right| {{sort|99,000|{{ref|2|[ |
| align=right| {{sort|99,000|{{ref|2|[B]}}99,000}} |
||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Mozambique|{{flagicon|Mozambique}} [[Mozambique]]}} |
| {{sort|Mozambique|{{flagicon|Mozambique}} [[Mozambique]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1995-11- |
| <span style="display:none">1995-11-13†</span>[[13 November]] [[1995]] |
||
| Africa |
| Africa |
||
| align=right| 19,792,000 |
| align=right| 19,792,000 |
||
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Nauru|{{flagicon|Nauru}} [[Nauru] |
| {{sort|Nauru|{{flagicon|Nauru}} [[Nauru]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1968-11-01†</span>[[1 November]] [[1968]] |
| <span style="display:none">1968-11-01†</span>[[1 November]] [[1968]] |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| Line 194: | Line 194: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|New Zealand|{{flagicon|New Zealand}} [[New Zealand]]}} |
| {{sort|New Zealand|{{flagicon|New Zealand}} [[New Zealand]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| align=right| 4,147,972 |
| align=right| 4,147,972 |
||
| Line 217: | Line 217: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Saint Kitts and Nevis|{{flagicon|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} [[Saint Kitts and Nevis] |
| {{sort|Saint Kitts and Nevis|{{flagicon|Saint Kitts and Nevis}} [[Saint Kitts and Nevis]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1983-09-19</span>[[19 September]] [[1983]] |
| <span style="display:none">1983-09-19</span>[[19 September]] [[1983]] |
||
| North America |
| North America |
||
| Line 232: | Line 232: | ||
| <span style="display:none">1979-10-27</span>[[27 October]] [[1979]] |
| <span style="display:none">1979-10-27</span>[[27 October]] [[1979]] |
||
| North America |
| North America |
||
| align=right| {{sort|119,000|{{ref|1|[ |
| align=right| {{sort|119,000|{{ref|1|[A]}}119,000}} |
||
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a [[Special membership of the Commonwealth of Nations|special member]] from [[27 October]] [[1979]] until [[1 June]] [[1985]]. |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a [[Special membership of the Commonwealth of Nations|special member]] from [[27 October]] [[1979]] until [[1 June]] [[1985]]. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 242: | Line 242: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Seychelles|{{flagicon|Seychelles}} [[Seychelles]]}} |
| {{sort|Seychelles|{{flagicon|Seychelles}} [[Seychelles]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1976-06- |
| <span style="display:none">1976-06-29†</span>[[29 June]] [[1976]] |
||
| Africa |
| Africa |
||
| align=right| 81,000 |
| align=right| 81,000 |
||
| Line 265: | Line 265: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|South Africa|{{flagicon|South Africa}} [[South Africa]]}} |
| {{sort|South Africa|{{flagicon|South Africa}} [[South Africa]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| Africa |
| Africa |
||
| align=right| 47,423,000 |
| align=right| 47,423,000 |
||
| Line 299: | Line 299: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Tuvalu|{{flagicon|Tuvalu}} [[Tuvalu] |
| {{sort|Tuvalu|{{flagicon|Tuvalu}} [[Tuvalu]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1978-10-01</span>[[1 October]] [[1978]] |
| <span style="display:none">1978-10-01</span>[[1 October]] [[1978]] |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| Line 312: | Line 312: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|United Kingdom|{{flagicon|United Kingdom}} [[United Kingdom]]}} |
| {{sort|United Kingdom|{{flagicon|United Kingdom}} [[United Kingdom]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| Europe |
| Europe |
||
| align=right| 60,209,500 |
| align=right| 60,209,500 |
||
| The Parliament of the United Kingdom enacted the [[Statute of Westminster 1931]]. |
| The Parliament of the United Kingdom enacted the [[Statute of Westminster 1931]]. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Vanuatu|{{flagicon|Vanuatu}} [[Vanuatu] |
| {{sort|Vanuatu|{{flagicon|Vanuatu}} [[Vanuatu]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1980-07-30</span>[[30 July]] [[1980]] |
| <span style="display:none">1980-07-30</span>[[30 July]] [[1980]] |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| Line 329: | Line 329: | ||
| |
| |
||
|} |
|} |
||
{{note|1}}A. |
{{note|1}}A. The population figure is based on 2004 estimates.<br> |
||
{{note|2}}B. The population figure is based on |
{{note|2}}B. The population figure is based on 2005 estimates.<br> |
||
{{note|3}}C. The population figure is based on 2005 estimates. |
|||
==Suspended members== |
==Suspended members== |
||
| Line 342: | Line 340: | ||
! Notes |
! Notes |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|{{sort|Fiji|{{flagicon|Fiji}} [[Fiji] |
|{{sort|Fiji|{{flagicon|Fiji}} [[Fiji]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1970-10-10</span>[[10 October]] [[1970]] |
| <span style="display:none">1970-10-10</span>[[10 October]] [[1970]] |
||
| Oceania |
| Oceania |
||
| Line 348: | Line 346: | ||
| Left in 1987; rejoined in 1997; suspended on [[6 June]] [[2000]];<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2000 |month=July |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=89 |issue=355 |pages=pp. 311–55 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530050083406 }}</ref> readmitted on [[20 December]] [[2001]];<ref name="Commonwealth Update Apr 2002">{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2002 |month=April |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=91 |issue=364 |pages=pp. 131–59 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530220144148 }}</ref> resuspended on [[8 December]] [[2006]] because of the [[2006 Fijian coup d'état]].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2007 |month=February |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=96 |issue=388 |pages=pp. 2–28 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530701189734 }}</ref> |
| Left in 1987; rejoined in 1997; suspended on [[6 June]] [[2000]];<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2000 |month=July |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=89 |issue=355 |pages=pp. 311–55 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530050083406 }}</ref> readmitted on [[20 December]] [[2001]];<ref name="Commonwealth Update Apr 2002">{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2002 |month=April |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=91 |issue=364 |pages=pp. 131–59 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530220144148 }}</ref> resuspended on [[8 December]] [[2006]] because of the [[2006 Fijian coup d'état]].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ingram |first=Derek |authorlink=Derek Ingram (journalist) |year=2007 |month=February |title=Commonwealth Update |journal=[[The Round Table Journal|The Round Table]] |volume=96 |issue=388 |pages=pp. 2–28 |url= |accessdate=2008-12-20 |quote= |doi=10.1080/00358530701189734 }}</ref> |
||
|} |
|} |
||
{{note|4}}A. Not a member of the [[Commonwealth Foundation]].<br> |
|||
==Former members== |
==Former members== |
||
| Line 360: | Line 356: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Ireland|{{flagicon|Ireland}} [[Irish Free State]]/[[Republic of Ireland|Ireland]]}} |
| {{sort|Ireland|{{flagicon|Ireland}} [[Irish Free State]]/[[Republic of Ireland|Ireland]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| Europe |
| Europe |
||
| <span style="display:none">1949-04-18]]</span>[[18 April]] [[1949]] |
| <span style="display:none">1949-04-18]]</span>[[18 April]] [[1949]] |
||
| Line 372: | Line 368: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| {{sort|Newfoundland|{{flagicon|Newfoundland}} [[Dominion of Newfoundland|Newfoundland]]}} |
| {{sort|Newfoundland|{{flagicon|Newfoundland}} [[Dominion of Newfoundland|Newfoundland]]}} |
||
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span> |
| <span style="display:none">1931-12-11</span>N/A - One of the original [[Dominion]]s |
||
| North America |
| North America |
||
| <span style="display:none">1934-02-16</span>[[16 February]] [[1934]] |
| <span style="display:none">1934-02-16</span>[[16 February]] [[1934]] |
||
Revision as of 04:56, 15 June 2009
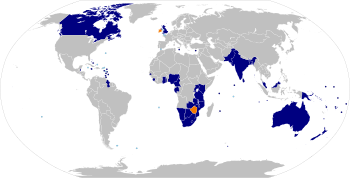
The Commonwealth of Nations is a voluntary association of 53 independent sovereign states, most of them are former British colonies, or dependencies of these colonies. No one government in the Commonwealth exercises power over the others, as in a political union. Rather, the relationship is one of an international organisation through which countries with diverse social, political, and economic backgrounds are regarded as equal in status, and co-operate within a framework of common values and goals, as outlined in the Singapore Declaration.[1] These include the promotion of democracy, human rights, good governance, the rule of law, individual liberty, egalitarianism, free trade, multilateralism, and world peace, and are carried out through multilateral projects and meetings, as well as the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.[2] The symbol of this free association is Queen Elizabeth II, known for this purpose as Head of the Commonwealth. This position, however, does not imbue her with any political or executive power over any Commonwealth member states; the position is purely symbolic, and it is the Commonwealth Secretary-General who is the chief executive of the organisation.[3]
The Commonwealth was first officially formed in 1931 when the Statute of Westminster gave legal recognition to the independence of dominions. Known as the "British Commonwealth", the first members were the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, the Irish Free State and Dominion of Newfoundland, although Australia and New Zealand did not adopt the statute until 1942 and 1947 respectively.[4] In 1949, the London Declaration was signed and marked the birth of the modern Commonwealth and the renaming to its present name.[5]
Presently, there are 53 states that are members of the Commonwealth of Nations which consists of over 1.9 billion people. Three members are in Europe, twelve in North America, one in South America, eighteen in Africa, eight in Asia, and eleven in Oceania. There is one suspended member, Fiji, and six former members, four of which no longer exist.
Current members
All table information based on figures provided by the Commonwealth of Nations Secretariat members list, most population figures are based on 2007 estimates, unless otherwise noted.[6]
Note: The table can be sorted alphabetically or chronologically using the ![]() icon.
icon.
| Country | Joined | Continent | Population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 November 1981 | North America | 81,000 | ||
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | Oceania | 20,555,300 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931, although the statute was not adopted in Australia until 1942.[7] | |
| 10 July 1973 | North America | 323,000 | ||
| 18 April 1972 | Asia | 148,384,000 | Gained independence from Pakistan in 1971.[8] | |
| 30 November 1966 | North America | 279,000 | ||
| 21 September 1981 | North America | 287,730 | ||
| 30 September 1966 | Africa | 1,765,000 | ||
| 1 January 1984 | Asia | 374,000 | ||
| 13 November 1995 | Africa | 16,322,000 | ||
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | North America | 32,654,500 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931.[9] | |
| 16 August 1961 | Europe / Asia | 818,200 | ||
| 3 November 1978 | North America | [A]79,000 | ||
| 18 February 1965 | Africa | 1,517,000 | ||
| 6 March 1957 | Africa | 22,113,000 | ||
| 7 February 1974 | North America | 103,000 | ||
| 26 May 1966 | South America | 751,000 | ||
| 15 August 1947 | Asia | 1,100,000,000 | ||
| 6 August 1962 | North America | 2,651,000 | ||
| 12 December 1963 | Africa | 34,256,000 | ||
| 12 July 1979 | Oceania | [B]99,000 | ||
| 4 October 1966 | Africa | 1,795,000 | ||
| 6 July 1964 | Africa | 12,884,000 | ||
| 16 September 1963 | Asia | 27,356,000 | Joined as the Federation of Malaya in 1957; reformed as Malaysia with its federation in 1963 with Singapore (became a separate member in 1965), Sabah, and Sarawak.[10] | |
| 9 July 1982 | Asia | 329,000 | Gained independence from the United Kingdom on 26 July 1965.[11] Maldives was a special member from 9 July 1982 until 20 July 1985.[12] | |
| 21 September 1964 | Europe | 402,668 | ||
| 12 March 1968 | Africa | 1,245,000 | ||
| 13 November 1995 | Africa | 19,792,000 | ||
| 21 March 1990 | Africa | 2,031,000 | ||
| 1 November 1968 | Oceania | 14,000 | Nauru is a special member. The nation was a special member from 1 November 1968 until 1 May 1999, when it became a full member,[13] before reverting back to special status in January 2006.[14] | |
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | Oceania | 4,147,972 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931, although the Statute was not adopted in New Zealand until 1947.[15] | |
| 1 October 1960 | Africa | 132,796,000 | Suspended in 1995, readmitted in 1999.[16] | |
| 14 August 1947 | Asia | 158,352,000 | Left in 1972, rejoined 1989; suspended in 1999, readmitted in 2004; suspended in 2007,[17] readmitted in 2008.[18] | |
| 16 September 1975 | Oceania | 5,887,000 | ||
| 19 September 1983 | North America | 43,000 | ||
| 22 February 1979 | North America | 161,000 | ||
| 27 October 1979 | North America | [A]119,000 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a special member from 27 October 1979 until 1 June 1985. | |
| 28 August 1970 | Oceania | 185,000 | ||
| 29 June 1976 | Africa | 81,000 | ||
| 27 April 1961 | Africa | 5,525,000 | ||
| 15 October 1965 | Asia | 4,326,000 | First joined as part of Malaysia on 16 September 1963. | |
| 7 July 1978 | Oceania | 478,000 | ||
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | Africa | 47,423,000 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Left on 31 May 1961, rejoined on 1 June 1994.[19] | |
| 4 February 1948 | Asia | 20,743,000 | ||
| 6 September 1968 | Africa | 1,032,000 | ||
| 26 April 1964 | Africa | 38,329,000 | Merger of Tanganyika and Zanzibar.[20] | |
| 4 June 1970 | Oceania | 102,000 | ||
| 31 August 1962 | North America | 1,305,000 | ||
| 1 October 1978 | Oceania | 12,000 | Tuvalu was a special member from 1 October 1978 until 1 September 2000.[21] | |
| 9 October 1962 | Africa | 28,816,000 | ||
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | Europe | 60,209,500 | The Parliament of the United Kingdom enacted the Statute of Westminster 1931. | |
| 30 July 1980 | Oceania | 211,000 | ||
| 24 October 1964 | Africa | 11,668,000 |
^ A. The population figure is based on 2004 estimates.
^ B. The population figure is based on 2005 estimates.
Suspended members
| Country | Joined | Continent | Population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 October 1970 | Oceania | 848,000 | Left in 1987; rejoined in 1997; suspended on 6 June 2000;[22] readmitted on 20 December 2001;[23] resuspended on 8 December 2006 because of the 2006 Fijian coup d'état.[24] |
Former members
| Country | Joined | Continent | Left | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | Europe | 18 April 1949 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Left after passing the Republic of Ireland Act in 1949.[8][25] | |
| 31 August 1957 | Asia | 16 September 1963 | Entered into Malaysia on 16 September 1963.[8] | |
| N/A - One of the original Dominions | North America | 16 February 1934 | One of the original Dominions at the time of the Statute of Westminster 1931 (although the Statute was never adopted by Newfoundland). Government suspended on 16 February 1934, joined Canada on 31 March 1949.[25] | |
| 9 December 1961 | Africa | 26 April 1964 | Merged with Zanzibar to form Tanzania on 26 April 1964.[20] | |
| 10 December 1963 | Africa | 26 April 1964 | Merged with Tanganyika to form Tanzania on 26 April 1964.[20] | |
| 1 October 1980 | Africa | 7 December 2003 | Suspended on 19 March 2002.[23] Withdrew voluntarily on 7 December 2003.[26] |
References
- General
- The Commonwealth
- "Members". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- "Commonwealth of Nations". Commonwealth of Nations. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- "The Commonwealth". Directgov. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- Specific
- ^ "FAQs". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "Singapore Declaration of Commonwealth Principles 1971". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-06-12.
- ^ "Head of the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "The Commonwealth–History–Dominion Status". Commonwealth of Nations. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "The Commonwealth–History–Modern Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "Members". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Australia". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ a b c "Wind of Change". Commonwealth of Nations. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Canada - History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Malaysia - History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Maldives - History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "The Maldives and the Commonwealth". Republic of Maldives. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- ^ "Nauru Accedes to Full Membership of the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. 12 April 1999. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- ^ "Nauru–History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "New Zealand- History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Nigeria". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Pakistan suspended from the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. 2007-11-22. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ^ "Commonwealth lifts Pakistan suspension". Commonwealth Secretariat. 2008-05-12. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ^ "South Africa". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ a b c "Tanzania - History". Commonwealth Secretariat. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Tuvalu Accedes to Full Membership of the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. 14 August 2000. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- ^ Ingram, Derek (2000). "Commonwealth Update". The Round Table. 89 (355): pp. 311–55. doi:10.1080/00358530050083406.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b Ingram, Derek (2002). "Commonwealth Update". The Round Table. 91 (364): pp. 131–59. doi:10.1080/00358530220144148.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Ingram, Derek (2007). "Commonwealth Update". The Round Table. 96 (388): pp. 2–28. doi:10.1080/00358530701189734.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b "Dominion Status". Commonwealth of Nations. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- ^ "Editorial: CHOGM 2003, Abuja, Nigeria". The Round Table. 93 (373): pp. 3–6. 2004. doi:10.1080/0035853042000188139.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
