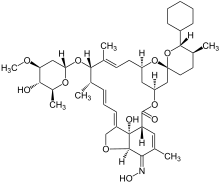
Selamectin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Revolution, Stronghold, Revolt |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.250.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H63NO11 |
| Molar mass | 769.973 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Selamectin (trade names Revolution and Stronghold manufactured by Zoetis, and Revolt manufactured by Aurora Pharmaceuticals, among others) is a topical parasiticide and anthelminthic used on dogs and cats. It treats and prevents infections of heartworms, fleas, ear mites, sarcoptic mange (scabies), and certain types of ticks in dogs, and prevents heartworms, fleas, ear mites, hookworms, and roundworms in cats. It is structurally related to ivermectin and milbemycin. Selamectin is not approved for human use.
Usage
The drug is applied topically. It is isopropyl alcohol based, packaged according to its varying dosage sizes and applied once monthly. It is not miscible in water. [1]
Mode of action
Selamectin disables parasites by activating glutamate-gated chloride channels at muscle synapses. Selamectin activates the chloride channel without desensitization, allowing chloride ions to enter the nerve cells and causing neuromuscular paralysis, impaired muscular contraction, and eventual death.
The substance fights both internal and surface parasitic infection. Absorbed into the body through the skin and hair follicles, it travels through the bloodstream, intestines, and sebaceous glands; parasites ingest the drug when they feed on the animal's blood or secretions.
Side effects
Selamectin has been found to be safe and effective in a 2003 review.[2]
Selamectin has high safety ratings, with less than 1% of pets displaying side effects[citation needed]. In cases where side-effects do occur, they most often include passing irritation or hair loss at the application site. Symptoms beyond these (such as drooling, rapid breathing, lack of coordination, vomiting, or diarrhea) could be due to shock as a result of selamectin killing heartworms or other vulnerable parasites present at high levels in the bloodstreams of dogs.[citation needed] This would be a reaction due to undetected or underestimated infections prior to using the medication, rather than an actual allergic reaction to the drug itself.
Similar products
Main rival products for dogs include ivermectin (trade names Stromectol, Ivermec and others) or milbemycin oxime (Interceptor) for heartworms, imidacloprid and moxidectin (Advocate), fipronil (Frontline) or lufenuron (Program) for fleas, or the combination milbemycin oxime/lufenuron (Sentinel) for both.
References
- ^ "Revolt Topical - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com.
- ^ Pipano E (2003). "Recent Developments In The Control Of Ectoparasites And Endoparasites Of Dogs And Cats With Selamectin". Israel Journal of Veterianry Medicine. 58 (2–3). Archived from the original on April 14, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
