From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Tolgabide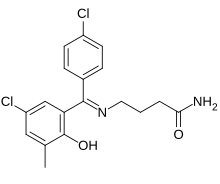 |
|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
| Legal status |
|
|---|
|
4-{[(E)-(3-Chloro-5-methyl-6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]amino}butanamide
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C18H18Cl2N2O2 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 365.25 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
Cc1cc(cc(c1O)/C(=N/CCCC(=O)N)/c2ccc(cc2)Cl)Cl
|
InChI=1S/C18H18Cl2N2O2/c1-11-9-14(20)10-15(18(11)24)17(22-8-2-3-16(21)23)12-4-6-13(19)7-5-12/h4-7,9-10,24H,2-3,8H2,1H3,(H2,21,23)/b22-17+ Key:AOAFGVWKONLQRN-OQKWZONESA-N
|
Tolgabide (INN; development code SL-81.0142) is a drug which was patented by Synthélabo as an anticonvulsant but was never marketed.[1] It is an analogue of progabide and acts similarly to it as a prodrug of GABA, and therefore as an indirect agonist of the GABA receptors.[1][2]
See also
References
|
|---|
| Ionotropic | | GABAATooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A receptor |
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., drinking alcohol, 2M2B)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, cholesterol, THDOC)
- Niacin
- Niacinamide
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, diethyl ether, paraldehyde, sevoflurane)
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α3IA
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., apalutamide, bicalutamide, enzalutamide, flutamide, nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
|
|---|
| GABAA-ρTooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid A-rho receptor | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Metabotropic | | GABABTooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid B receptor | |
|---|
|
|---|
|

