From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Tigestol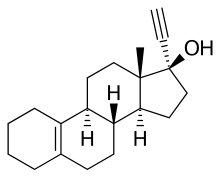 |
|
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17R)-17-ethynyl-13-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ol
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C20H28O |
|---|
| Molar mass | 284.443 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
CC12CCC3C(C1CCC2(C#C)O)CCC4=C3CCCC4
|
InChI=InChI=1S/C20H28O/c1-3-20(21)13-11-18-17-9-8-14-6-4-5-7-15(14)16(17)10-12-19(18,20)2/h1,16-18,21H,4-13H2,2H3/t16-,17-,18+,19+,20+/m1/s1 Key:DHOKBGHAEUVRMO-SLHNCBLASA-N
|
Tigestol (INN, USAN), also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5(10)-en-17β-ol,[1] is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was developed by Organon in the 1960s but was never marketed.[2][3][4][5] It is an isomer of the related 19-nortestosterone derivative progestins lynestrenol and cingestol.[6]
References
|
|---|
| PRTooltip Progesterone receptor | | Agonists |
- Testosterone derivatives: Progestins: 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone
- 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate
- 17α-Allyl-19-nortestosterone
- Allylestrenol
- Altrenogest
- Chloroethynylnorgestrel
- Cingestol
- Danazol
- Desogestrel
- Dienogest
- Ethinylandrostenediol
- Ethisterone
- Ethynerone
- Etonogestrel
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Gestodene
- Gestrinone
- Levonorgestrel
- Levonorgestrel esters (e.g., levonorgestrel butanoate)
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Metynodiol
- Metynodiol diacetate
- Norelgestromin
- Norethisterone (norethindrone)
- Norethisterone esters (e.g., norethisterone acetate, norethisterone enanthate)
- Noretynodrel
- Norgesterone
- Norgestimate
- Norgestrel
- Norgestrienone
- Norvinisterone
- Oxendolone
- Quingestanol
- Quingestanol acetate
- Tibolone
- Tigestol
- Tosagestin; Anabolic–androgenic steroids: 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone
- 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone dodecylcarbonate
- 19-Nor-5-androstenediol
- 19-Nor-5-androstenedione
- 19-Nordehydroepiandrosterone
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Bolandione
- Dimethisterone
- Dienedione
- Dienolone
- Dimethandrolone
- Dimethandrolone buciclate
- Dimethandrolone dodecylcarbonate
- Dimethandrolone undecanoate
- Dimethyldienolone
- Dimethyltrienolone
- Ethyldienolone
- Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol)
- Methyldienolone
- Metribolone (R-1881)
- Methoxydienone (methoxygonadiene)
- Mibolerone
- Nandrolone
- Nandrolone esters (e.g., nandrolone decanoate, nandrolone phenylpropionate)
- Norethandrolone
- Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethandrolone, normethisterone)
- RU-2309
- Tetrahydrogestrinone
- Trenbolone (trienolone)
- Trenbolone esters (e.g., trenbolone acetate, trenbolone enanthate)
- Trendione
- Trestolone
- Trestolone acetate
|
|---|
Mixed
(SPRMsTooltip Selective progesterone receptor modulators) | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
|
|---|
mPRTooltip Membrane progesterone receptor
(PAQRTooltip Progestin and adipoQ receptor) | |
|---|
|

