Arsenic: Difference between revisions
Luckas-bot (talk | contribs) m r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding ia:Arsenico |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===Isotopes=== |
===Isotopes=== |
||
{{Main|Isotopes of arsenic}} |
{{Main|Isotopes of arsenic}} |
||
Naturally occurring arsenic is composed of one stable [[isotope]], <sup>75</sup>As.<ref name="NUBASE">{{cite journal| first = Audi| last = Georges|title = The NUBASE Evaluation of Nuclear and Decay Properties| journal = Nuclear Physics A| volume = 729| pages = |
Naturally occurring arsenic is composed of one stable [[isotope]], <sup>75</sup>As.<ref name="NUBASE">{{cite journal| first = Audi| last = Georges|title = The NUBASE Evaluation of Nuclear and Decay Properties| journal = Nuclear Physics A| volume = 729| pages = 3f-life]] of 80.3 days. Isotopes that are lighter than the stable <sup>75</sup>As tend to decay by [[beta decay|β<sup>+</sup> decay]], and those that are heavier tend to decay by [[beta decay|β<sup>-</sup> decay]], with some exceptions. |
||
At least 10 [[nuclear isomer]]s have been described, ranging in atomic mass from 66 to 84. The most stable of arsenic's isomers is <sup>68m</sup>As with a half-life of 111 seconds.<ref name="NUBASE"/> |
At least 10 [[nuclear isomer]]s have been described, ranging in atomic mass from 66 to 84. The most stable of arsenic's isomers is <sup>68m</sup>As with a half-life of 111 seconds.<ref name="NUBASE"/> fatso |
||
===Chemistry=== |
===Chemistry=== |
||
Revision as of 15:27, 5 December 2011
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allotropes | grey (most common), yellow, black (see Allotropes of arsenic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | metallic grey | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(As) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point | 887 K (615 °C, 1137 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | grey: 5.782 g/cm3[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 5.22 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 1090 K, 3628 kPa[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 1673 K, ? MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | grey: 24.44 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 34.76 kJ/mol (?) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.64 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: −3, +3, +5 −2,? −1,? 0,[5] +1,[6] +2,[7] +4? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 119 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 119±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 185 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | grey: rhombohedral (hR2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
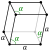
| Lattice constants | ar = 413.15 pm α = 54.133° pm ah = 375.99 pm ch = 1054.58 pm (at 20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 5.6 µm/(m⋅K)[8] (at r.t.) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 50.2 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 333 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −5.5×10−6 cm3/mol[10] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 8 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 22 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 1440 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-38-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Arabic alchemists (before AD 815) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arsenic /[invalid input: 'icon']ˈɑːrs[invalid input: 'i-']nɪk/ is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.[12]
Arsenic is a metalloid. It can exist in various allotropes, although only the grey form has important use in industry. The main use of metallic arsenic is for strengthening alloys of copper and especially lead (for example, in car batteries). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices, and the optoelectronic compound gallium arsenide is the most common semiconductor in use after doped silicon.
A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites, and are arsenic-tolerant. Arsenic is notoriously poisonous to multicellular life because of the interaction of arsenic ions with protein thiols. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides (treated wood products), herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining, however, as many of these compounds are being phased out.[13] Arsenic poisoning from naturally occurring arsenic compounds in drinking water remains a problem in many parts of the world.
Characteristics
Physical characteristics

The three most common allotropes are metallic grey, yellow and black arsenic, with grey being the most common.[14] Grey arsenic (α-As, space group R3m No. 166) adopts a double-layered structure consisting of many interlocked ruffled six-membered rings. Because of weak bonding between the layers, grey arsenic is brittle and has a relatively low Mohs hardness of 3.5. Nearest and next-nearest neighbors form a distorted octahedral complex, with the three atoms in the same double-layer being slightly closer than the three atoms in the next.[15] This relatively close packing leads to a high density of 5.73 g/cm3.[16] Grey arsenic is a semimetal, but becomes a semiconductor with a bandgap of 1.2–1.4 eV if amorphized.[17] Yellow arsenic is soft and waxy, and somewhat similar to tetraphosphorus (P
4). Both have four atoms arranged in a tetrahedral structure in which each atom is bound to each of the other three atoms by a single bond. This unstable allotrope, being molecular, is the most volatile, least dense and most toxic. Solid yellow arsenic is produced by rapid cooling of arsenic vapour, As
4. It is rapidly transformed into the grey arsenic by light. The yellow form has a density of 1.97 g/cm3.[16] Black arsenic is similar in structure to red phosphorus.[16]
Isotopes
Naturally occurring arsenic is composed of one stable isotope, 75As.Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).

Compounds
Arsenic compounds resemble in some respects those of phosphorus, which occupies the same group (column) of the periodic table. Arsenic is less commonly observed in the pentavalent state, however. The most common oxidation states for arsenic are: −3 in the arsenides, such as alloy-like intermetallic compounds; and +3 in the arsenites, arsenates(III), and most organoarsenic compounds. Arsenic also bonds readily to itself as seen in the square As3−
4 ions in the mineral skutterudite. In the +3 oxidation state, arsenic is typically pyramidal, owing to the influence of the lone pair of electrons.
Inorganic
Arsenic forms colourless, odourless, crystalline oxides As2O3 ("white arsenic") and As2O5, which are hygroscopic and readily soluble in water to form acidic solutions. Arsenic(V) acid is a weak acid. Its salts are called arsenates, e.g., Paris Green (copper(II) acetoarsenite), calcium arsenate, and lead hydrogen arsenate. The latter three have been used as agricultural insecticides and poisons. The protonation steps between the arsenate and arsenic acid are similar to those between phosphate and phosphoric acid. However, arsenite and arsenous acid contain arsenic bonded to three oxygen and not hydrogen atoms, in contrast to phosphite and phosphonic acid, which contains a non-acidic P-H bond. Arsenous acid is genuinely tribasic, whereas phosphonic acid is not.
A broad variety of sulfur compounds of arsenic are known. Orpiment (As2S3) and realgar (As4S4) are somewhat abundant and were formerly used as painting pigments. Other sulfides include As4S3 and As4S10. Arsenic has a formal oxidation state of +2 in As4S4, which features As-As bonds so that the total covalency of As is still in fact three.[18]
The trifluoride, trichloride, tribromide, and triiodide of arsenic(III) are well known, whereas only AsF5 is the main pentahalide. Arsenic pentafluoride is stable at room temperature, whereas the pentachloride is stable only below −50 °C.[16]
Organoarsenic compounds

A large variety of organoarsenic compounds are known. Several were developed as chemical warfare agents during World War I, including vesicants such as lewisite and vomiting agents such as adamsite.[19][20][21] Cacodylic acid, which is of historic and practical interest, arises from the methylation of arsenic trioxide, a reaction that has no analogy in phosphorus chemistry.
Alloys
Arsenic is used as the group 5 element in the III-V semiconductors gallium arsenide, indium arsenide, and aluminium arsenide. The valence electron count of GaAs is the same as a pair of Si atoms, but the band structure is completely different, which results distinct bulk properties. Other arsenic alloys include the II-IV semiconductor cadmium arsenide.
Occurrence and production

Minerals with the formula MAsS and MAs2 (M = Fe, Ni, Co) are the dominant commercial sources of arsenic, together with realgar (an arsenic sulfide mineral) and native arsenic. An illustrative mineral is arsenopyrite (FeAsS), which is structurally related to iron pyrite. Many minor As-containing minerals are known. Arsenic also occurs in various organic forms in the environment.[22] Inorganic arsenic and its compounds, upon entering the food chain, are progressively metabolized to a less toxic form of arsenic through a process of methylation.[23]
Other naturally occurring pathways of exposure include volcanic ash, weathering of arsenic-containing minerals and ores, and dissolved in groundwater. It is also found in food, water, soil, and air.[24] The most common pathway of exposure for humans is ingestion, and the predominant source of arsenic in our diet is through seafood. An additional route of exposure is through inhalation.[25]

In 2005, China was the top producer of white arsenic with almost 50% world share, followed by Chile, Peru, and Morocco, according to the British Geological Survey and the United States Geological Survey.[26] Most operations in the US and Europe have closed for environmental reasons. The arsenic is recovered mainly as a side product from the purification of copper. Arsenic is part of the smelter dust from copper, gold, and lead smelters.[27]
On roasting in air of arsenopyrite, arsenic sublimes as arsenic(III) oxide leaving iron oxides,[22] while roasting without air results in the production of metallic arsenic. Further purification from sulfur and other chalcogens is achieved by sublimation in vacuum or in a hydrogen atmosphere or by distillation from molten lead-arsenic mixture.[28]
History

The word arsenic was borrowed from the Syriac word ܠܐ ܙܐܦܢܝܐ (al) zarniqa [29] and the Persian word زرنيخ Zarnikh, meaning "yellow orpiment", into Greek as arsenikon (Αρσενικόν). It is also related to the similar Greek word arsenikos (Αρσενικός), meaning "masculine" or "potent". The word was adopted in Latin arsenicum and Old French arsenic, from which the English word arsenic is derived.[29] Arsenic sulfides (orpiment, realgar) and oxides have been known and used since ancient times.[30] Zosimos (circa 300 AD) describes roasting sandarach (realgar) to obtain cloud of arsenic (arsenious oxide), which he then reduces to metallic arsenic.[31] As the symptoms of arsenic poisoning were somewhat ill-defined, it was frequently used for murder until the advent of the Marsh test, a sensitive chemical test for its presence. (Another less sensitive but more general test is the Reinsch test.) Owing to its use by the ruling class to murder one another and its potency and discreetness, arsenic has been called the Poison of Kings and the King of Poisons.[32]
During the Bronze Age, arsenic was often included in bronze, which made the alloy harder (so-called "arsenical bronze"[33]). Albertus Magnus (Albert the Great, 1193–1280) is believed to have been the first to isolate the element in 1250 by heating soap together with arsenic trisulfide.[12] In 1649, Johann Schröder published two ways of preparing arsenic.
Cadet's fuming liquid (impure cacodyl), often claimed as the first synthetic organometallic compound, was synthesized in 1760 by Louis Claude Cadet de Gassicourt by the reaction of potassium acetate with arsenic trioxide.[34]
In the Victorian era, "arsenic" ("white arsenic" trioxide) was mixed with vinegar and chalk and eaten by women to improve the complexion of their faces, making their skin paler to show they did not work in the fields. Arsenic was also rubbed into the faces and arms of women to "improve their complexion". The accidental use of arsenic in the adulteration of foodstuffs led to the Bradford sweet poisoning in 1858, which resulted in approximately 20 deaths.[35]
Applications
Agricultural

The toxicity of arsenic to insects, bacteria and fungi led to its use as a wood preservative.[36] In the 1950s a process of treating wood with chromated copper arsenate (also known as CCA or Tanalith) was invented, and for decades this treatment was the most extensive industrial use of arsenic. An increased appreciation of the toxicity of arsenic resulted in a ban for the use of CCA in consumer products; the European Union and United States initiated this process in 2004.[37][38] CCA remains in heavy use in other countries however, e.g. Malaysian rubber plantations.[13]
Arsenic was also used in various agricultural insecticides, termination and poisons. For example, lead hydrogen arsenate was a common insecticide on fruit trees,[39] but contact with the compound sometimes resulted in brain damage among those working the sprayers. In the second half of the 20th century, monosodium methyl arsenate (MSMA) and disodium methyl arsenate (DSMA) – less toxic organic forms of arsenic – have replaced lead arsenate in agriculture.
Arsenic is still added to animal food, in particular in the U.S. as a method of disease prevention[40][41] and growth stimulation. One example is roxarsone, which is used as a broiler starter by about 70% of the broiler growers since 1995.[42] The Poison-Free Poultry Act of 2009 proposes to ban the use of roxarsone in industrial swine and poultry production.[43]
Medical use
During the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries, a number of arsenic compounds have been used as medicines, including arsphenamine (by Paul Ehrlich) and arsenic trioxide (by Thomas Fowler). Arsphenamine as well as neosalvarsan was indicated for syphilis and trypanosomiasis, but has been superseded by modern antibiotics. Arsenic trioxide has been used in a variety of ways over the past 500 years, but most commonly in the treatment of cancer. The US Food and Drug Administration in 2000 approved this compound for the treatment of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia that is resistant to ATRA.[44] It was also used as Fowler's solution in psoriasis.[45] Recently new research has been done in locating tumours using arsenic-74 (a positron emitter). The advantages of using this isotope instead of the previously used iodine-124 is that the signal in the PET scan is clearer as the body tends to transport iodine to the thyroid gland producing a lot of noise.[46]
In subtoxic doses, soluble arsenic compounds act as stimulants, and were once popular in small doses as medicine by people in the mid-18th century.[16]
Alloys
The main use of metallic arsenic is for alloying with copper and especially lead. Lead components in car batteries are strengthened by the presence of a few percent of arsenic. Gallium arsenide is an important semiconductor material, used in integrated circuits. Circuits made from GaAs are much faster (but also much more expensive) than those made in silicon. Unlike silicon it is direct bandgap, and so can be used in laser diodes and LEDs to directly convert electricity into light.[13]
Military
After World War I, the United States built up a stockpile of 20000tons of lewisite (ClCH=CHAsCl2), a chemical weapon that is a vesicant (blister agent) and lung irritant. The stockpile was neutralized with bleach and dumped into the Gulf of Mexico after the 1950s.[47] During the Vietnam War the United States used Agent Blue, a mixture of sodium cacodylate and its acid form, as one of the rainbow herbicides to deprive the Vietnamese of valuable crops.
Other uses
- Copper acetoarsenite was used as a green pigment known under many names, including 'Paris Green' and 'Emerald Green'. It caused numerous arsenic poisonings. Scheele's Green, a copper arsenate, was used in the 19th century as a coloring agent in sweets.[48]
- Also used in bronzing and pyrotechnics.
- Up to 2% of arsenic is used in lead alloys for lead shots and bullets.[49]
- Arsenic is added in small quantities to alpha-brass to make it dezincification resistant. This grade of brass is used to make plumbing fittings or other items that are in constant contact with water.[50]
- Arsenic is also used for taxonomic sample preservation.
- Until recently arsenic was used in optical glass. Modern glass manufacturers, under pressure from environmentalists, have removed it, along with lead.[51]
Biological role
Bacteria

Some species of bacteria obtain their energy by oxidizing various fuels while reducing arsenate to arsenite. Under oxidative environmental conditions some bacteria use arsenite, which is oxidized to arsenate as fuel for their metabolism.[52] The enzymes involved are known as arsenate reductases (Arr).
In 2008, bacteria were discovered that employ a version of photosynthesis in the absence of oxygen with arsenites as electron donors, producing arsenates (just as ordinary photosynthesis uses water as electron donor, producing molecular oxygen). Researchers conjecture that, over the course of history, these photosynthesizing organisms produced the arsenates that allowed the arsenate-reducing bacteria to thrive. One strain PHS-1 has been isolated and is related to the γ-Proteobacterium Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii. The mechanism is unknown, but an encoded Arr enzyme may function in reverse to its known homologues.[53]
Heredity
Arsenic has been linked to epigenetic changes that are heritable changes in gene expression that occur without changes in DNA sequence and include DNA methylation, histone modification, and RNA interference. Toxic levels of arsenic cause significant DNA hypermethylation of tumour suppressor genes p16 and p53, thus increasing risk of carcinogenesis. These epigenetic events have been observed in in vitro studies with human kidney cells and in vivo tests with rat liver cells and peripheral blood leukocytes in humans.[54] Inductive coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is used to detect precise levels of intracellular arsenic and its other bases involved in epigenetic modification of DNA.[55] Studies investigating arsenic as an epigenetic factor will help in developing precise biomarkers of exposure and susceptibility.
The Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata) hyperaccumulates arsenic present in the soil into its leaves and has a proposed use in phytoremediation.[56]
Arsenic reported substituting for phosphorus as a building block of life
A NASA-funded astrobiology research team claimed on December 2, 2010 that the microbe strain GFAJ-1 of the Gammaproteobacteria (designated Halomonadaceae) group has the ability to substitute arsenic for at least part of the phosphorus in the molecules of its cells, including DNA and ATP.[57][58] Bacteria from Mono Lake, a naturally arsenic-rich site in California, were cultured in an environment high in arsenic but low in phosphorus. This finding has faced strong criticism from the scientific community, many scientists have argued that there is no evidence that arsenic is actually incorporated into biomolecules.[59][60] Independent confirmation of this finding has not yet been possible.
Biomethylation of arsenic
Inorganic arsenic and its compounds, upon entering the food chain, are progressively metabolised through a process of methylation.[61] For example, the mold Scopulariopsis brevicaulis produce significant amounts of trimethylarsine if inorganic arsenic is present.[62] The organic compound arsenobetaine is found in some marine foods such as fish and algae, and also in mushrooms in larger concentrations. The average person's intake is about 10–50 µg/day. Values about 1000 µg are not unusual following consumption of fish or mushrooms. But there is little danger in eating fish because this arsenic compound is nearly non-toxic.[63]
Environmental issues
Arsenic in drinking water
Widespread arsenic contamination of groundwater has led to a massive epidemic of arsenic poisoning in Bangladesh[64] and neighbouring countries. As of this writing, 42 major incidents around the world have been reported on groundwater arsenic contamination. It is estimated that approximately 57 million people are drinking groundwater with arsenic concentrations elevated above the World Health Organization's standard of 10 parts per billion. However, a study of cancer rates in Taiwan[65] suggested that significant increases in cancer mortality appear only at levels above 150 parts per billion. The arsenic in the groundwater is of natural origin, and is released from the sediment into the groundwater, owing to the anoxic conditions of the subsurface. This groundwater began to be used after local and western NGOs and the Bangladeshi government undertook a massive shallow tube well drinking-water program in the late twentieth century. This program was designed to prevent drinking of bacteria-contaminated surface waters, but failed to test for arsenic in the groundwater. Many other countries and districts in Southeast Asia, such as Vietnam and Cambodia have geological environments conducive to generation of high-arsenic groundwaters. Arsenicosis was reported in Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand in 1987, and the dissolved arsenic in the Chao Phraya River is suspected of containing high levels of naturally occurring arsenic, but has not been a public health problem owing to the use of bottled water.[66]
In the United States, arsenic is most commonly found in the ground waters of the southwest.[67] Parts of New England, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota and the Dakotas are also known to have significant[clarification needed] concentrations of arsenic in ground water. Increased levels of skin cancer have been associated with arsenic exposure in Wisconsin, even at levels below the 10 part per billion drinking water standard.[68] According to a recent film funded by the US Superfund, millions of private wells have unknown arsenic levels, and in some areas of the US, over 20% of wells may contain levels that exceed established limits.[69]
Low-level exposure to arsenic at concentrations found commonly in US drinking water compromises the initial immune response to H1N1 or swine flu infection according to NIEHS-supported scientists. The study, conducted in laboratory mice, suggests that people exposed to arsenic in their drinking water may be at increased risk for more serious illness or death in response to infection from the virus.[70]
Epidemiological evidence from Chile shows a dose-dependent connection between chronic arsenic exposure and various forms of cancer, in particular when other risk factors, such as cigarette smoking, are present. These effects have been demonstrated to persist below 50 parts per billion.[71]
Analyzing multiple epidemiological studies on inorganic arsenic exposure suggests a small but measurable risk increase for bladder cancer at 10 parts per billion.[72] According to Peter Ravenscroft of the Department of Geography at the University of Cambridge,[73] roughly 80 million people worldwide consume between 10 and 50 parts per billion arsenic in their drinking water. If they all consumed exactly 10 parts per billion arsenic in their drinking water, the previously cited multiple epidemiological study analysis would predict an additional 2,000 cases of bladder cancer alone. This represents a clear underestimate of the overall impact, since it does not include lung or skin cancer, and explicitly underestimates the exposure. Those exposed to levels of arsenic above the current WHO standard should weigh the costs and benefits of arsenic remediation.
Early (1973) evaluations of the removal of dissolved arsenic by drinking water treatment processes demonstrated that arsenic is very effectively removed by co-precipitation with either iron or aluminum oxides. The use of iron as a coagulant, in particular, was found to remove arsenic with efficiencies exceeding 90%.[74][75] Several adsorptive media systems have been approved for point-of-service use in a study funded by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S.EPA) and the National Science Foundation (NSF). A team of European and Indian scientists and engineers have set up six arsenic treatment plants in West Bengal based on in-situ remediation method (SAR Technology). This technology does not use any chemicals and arsenic is left as an insoluble form (+5 state) in the subterranean zone by recharging aerated water into the aquifer and thus developing an oxidation zone to support arsenic oxidizing micro-organisms. This process does not produce any waste stream or sludge and is relatively cheap.[76]
Another effective and inexpensive method to remove arsenic from contaminated well water is to sink wells 500 feet or deeper to reach purer waters. A recent 2011 study funded by the U.S. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences' Superfund Research Program shows that deep sediments can remove arsenic and take it out of circulation. Through this process called adsorption in which arsenic sticks to the surfaces of deep sediment articles, arsenic can be naturally removed from well water.[77]
Magnetic separations of arsenic at very low magnetic field gradients have been demonstrated in point-of-use water purification with high-surface-area and monodisperse magnetite (Fe3O4) nanocrystals. Using the high specific surface area of Fe3O4 nanocrystals the mass of waste associated with arsenic removal from water has been dramatically reduced.[78]
Epidemiological studies have suggested a correlation between chronic consumption of drinking water contaminated with arsenic and the incidence of all leading causes of mortality. The literature provides reason to believe arsenic exposure is causative in the pathogenesis of diabetes.
Wood preservation in the US
As of 2002, US-based industries consumed 19,600 metric tons of arsenic. Ninety percent of this was used for treatment of wood with chromated copper arsenate (CCA). In 2007, 50% of the 5,280 metric tons of consumption was still used for this purpose.[27][79] In the United States, the use of arsenic in consumer products was discontinued for residential, and general consumer construction on December 31, 2003 and alternative chemicals are now used, such as Alkaline Copper Quaternary, borates, copper azole, cyproconazole, and propiconazole.[80]
Although discontinued, this application is also one of the most concern to the general public. The vast majority of older pressure-treated wood was treated with CCA. CCA lumber is still in widespread use in many countries, and was heavily used during the latter half of the 20th century as a structural and outdoor building material. Although the use of CCA lumber was banned in many areas after studies showed that arsenic could leach out of the wood into the surrounding soil (from playground equipment, for instance), a risk is also presented by the burning of older CCA timber. The direct or indirect ingestion of wood ash from burnt CCA lumber has caused fatalities in animals and serious poisonings in humans; the lethal human dose is approximately 20 grams of ash. Scrap CCA lumber from construction and demolition sites may be inadvertently used in commercial and domestic fires. Protocols for safe disposal of CCA lumber do not exist evenly throughout the world; there is also concern in some quarters about the widespread landfill disposal of such timber.
Mapping of industrial releases in the US
One tool that maps releases of arsenic to particular locations in the United States[81] and also provides additional information about such releases is TOXMAP. TOXMAP is a Geographic Information System (GIS) from the Division of Specialized Information Services of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) that uses maps of the United States to help users visually explore data from the United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Toxics Release Inventory and Superfund Basic Research Programs. TOXMAP is a resource funded by the US Federal Government. TOXMAP's chemical and environmental health information is taken from NLM's Toxicology Data Network (TOXNET)[82] and PubMed, and from other authoritative sources.
Toxicity and precautions

Arsenic and many of its compounds are especially potent poisons. Many water supplies close to mines are contaminated by these poisons. Arsenic disrupts ATP production through several mechanisms. At the level of the citric acid cycle, arsenic inhibits lipoic acid, which is a cofactor for pyruvate dehydrogenase; and by competing with phosphate it uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, thus inhibiting energy-linked reduction of NAD+, mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis. Hydrogen peroxide production is also increased, which, it is speculated, has potential to form reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. These metabolic interferences lead to death from multi-system organ failure, it is presumed from necrotic cell death, not apoptosis. A post mortem reveals brick-red-coloured mucosa, owing to severe haemorrhage. Although arsenic causes toxicity, it can also play a protective role.[83]
Elemental arsenic and arsenic compounds are classified as "toxic" and "dangerous for the environment" in the European Union under directive 67/548/EEC. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) recognizes arsenic and arsenic compounds as group 1 carcinogens, and the EU lists arsenic trioxide, arsenic pentoxide and arsenate salts as category 1 carcinogens.
Arsenic is known to cause arsenicosis owing to its manifestation in drinking water, “the most common species being arsenate [HAsO42-; As(V)] and arsenite [H3AsO3 ; As(III)]”. The ability of arsenic to undergo redox conversion between As(III) and As(V) makes its availability in the environment more abundant. According to Croal, Gralnick, Malasarn and Newman, “[the] understanding [of] what stimulates As(III) oxidation and/or limits As(V) reduction is relevant for bioremediation of contaminated sites (Croal). The study of chemolithoautotrophic As(III) oxidizers and the heterotrophic As(V) reducers can help the understanding of the oxidation and/or reduction of arsenic.[84]
Treatment of chronic arsenic poisoning is easily accomplished. British anti-lewisite (dimercaprol) is prescribed in dosages of 5 mg/kg up to 300 mg each 4 hours for the first day. Then administer the same dosage each 6 hours for the second day. Then prescribe this dosage each 8 hours for eight additional days.[85] However the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) states that the long-term effects of arsenic exposure cannot be predicted.[25] Blood, urine, hair, and nails may be tested for arsenic; however, these tests cannot foresee possible health outcomes from the exposure.[25] Excretion occurs in the urine and long-term exposure to arsenic has been linked to bladder and kidney cancer in addition to cancer of the liver, prostate, skin, lungs and nasal cavity.[86]
Occupational exposure and arsenic poisoning may occur in persons working in industries involving the use of inorganic arsenic and its compounds, such as wood preservation, glass production, nonferrous metal alloys, and electronic semiconductor manufacturing. Inorganic arsenic is also found in coke oven emissions associated with the smelter industry.[87]
Biochemical basis of arsenic toxicity
The high affinity of arsenic(III) oxides for thiols is usually assigned as the cause of the high toxicity. Thiols, in the form of cysteine residues, are situated at the active sites of many important enzymes.[13]
See also
References
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Arsenic". CIAAW. 2013.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ Gokcen, N. A (1989). "The As (arsenic) system". Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams. 10: 11–22. doi:10.1007/BF02882166.
- ^ Abraham, Mariham Y.; Wang, Yuzhong; Xie, Yaoming; Wei, Pingrong; Shaefer III, Henry F.; Schleyer, P. von R.; Robinson, Gregory H. (2010). "Carbene Stabilization of Diarsenic: From Hypervalency to Allotropy". Chemistry: A European Journal. 16 (2): 432–5. doi:10.1002/chem.200902840. PMID 19937872.
- ^ Ellis, Bobby D.; MacDonald, Charles L. B. (2004). "Stabilized Arsenic(I) Iodide: A Ready Source of Arsenic Iodide Fragments and a Useful Reagent for the Generation of Clusters". Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (19): 5981–6. doi:10.1021/ic049281s. PMID 15360247.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Cverna, Fran (2002). ASM Ready Reference: Thermal properties of metals. ASM International. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-0-87170-768-0. pdf.
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2000). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (81 ed.). CRC press. ISBN 0849304814.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ a b Emsley, John (2001). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 43, 513, 529. ISBN 0-19-850341-5.
- ^ a b c d Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans Uwe Wolf. "Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Norman, Nicholas C (1998). Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth. Springer. p. 50. ISBN 9780751403893.
- ^ Biberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils; Holleman, Arnold Frederick (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. ISBN 9780123526519.
- ^ a b c d e Holleman, Arnold F. (1985). "Arsen". Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 675–681. ISBN 3110075113.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Otfried Madelung (2004). Semiconductors: data handbook. Birkhäuser. pp. 410–. ISBN 978-3-540-40488-0. Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- ^ "Arsenic: arsenic(II) sulfide compound data". WebElements.com. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Ellison, Hank D. (2007). Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849314346.
- ^ Girard, James (2010). Principles of Environmental Chemistry. Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN 9780763759391.
- ^ Somani, Satu M (2001). Chemical warfare agents: toxicity at low levels. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849308727.
- ^ a b Matschullat, Jörg (2000). "Arsenic in the geosphere — a review". The Science of the Total Environment. 249 (1–3): 297–312. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00524-0. PMID 10813460.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|issues=ignored (help) - ^ Reimer, K.J. (2010). "Organoarsenicals. Distribution and transformation in the environment". Metal ions in life sciences. 7. Cambridge: RSC publishing: 165–229. doi:10.1039/BK9781847551771-00165. ISBN 9781847551771. PMID 20877808.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Case Studies in Environmental Medicine (CSEM) Arsenic Toxicity Exposure Pathways" (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. Retrieved 2010-05-15.
- ^ a b c Arsenic. The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2009).
- ^ a b Brooks, William E. "Mineral Commodity Summaries 2007: Arsenic" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- ^ a b Brooks, William E. "Minerals Yearbook 2007: Arsenic" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-11-08.
- ^ Whelan, J. M.; Struthers, J. D.; Ditzenberger, J. A. (1960). "Separation of Sulfur, Selenium, and Tellurium from Arsenic". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 107 (12): 982–985. doi:10.1149/1.2427585.
- ^ a b "arsenic". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2010-05-15.
- ^ Bentley, Ronald; Chasteen, Thomas G. (2002). "Arsenic Curiosa and Humanity" (PDF). The Chemical Educator. 7 (2): 51. doi:10.1007/s00897020539a.
- ^ Holmyard John Eric (2007). Makers of Chemistry. Read Books. ISBN 1406732753.
- ^ Vahidnia, A.; Van Der Voet, G. B.; De Wolff, F. A. (2007). "Arsenic neurotoxicity – a review". Human & experimental toxicology. 26 (10): 823–32. doi:10.1177/0960327107084539. PMID 18025055.
- ^ Lechtman, H. (1996). "Arsenic Bronze: Dirty Copper or Chosen Alloy? A View from the Americas". Journal of Field Archaeology. 23 (4): 477–514. doi:10.2307/530550. JSTOR 530550.
- ^ Seyferth, Dietmar (2001). "Cadet's Fuming Arsenical Liquid and the Cacodyl Compounds of Bunsen". Organometallics. 20 (8): 1488–1498. doi:10.1021/om0101947.
- ^ Turner, Alan (1999). "Viewpoint: the story so far: An overview of developments in UK food regulation and associated advisory committees". British Food Journal. 101 (4): 274–283. doi:10.1108/00070709910272141.
- ^ Rahman, FA; Allan, DL; Rosen, CJ; Sadowsky, MJ (2004). "Arsenic availability from chromated copper arsenate (CCA)-treated wood". Journal of environmental quality. 33 (1): 173–80. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0173. PMID 14964372.
- ^ Lichtfouse, Eric (2004). "Electrodialytical Removal of Cu, Cr and As from Threaded Wood". Environmental Chemistry: Green Chemistry and Pollutants in Ecosystems. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 9783540228608.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Mandal, Badal Kumar; Suzuki, K. T. (2002). "Arsenic round the world: a review". Talanta. 58 (1): 201–235. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00268-0. PMID 18968746.
- ^ Peryea, F. J. (20–26 August). Historical use of lead arsenate insecticides, resulting in soil contamination and implications for soil remediation. 16th World Congress of Soil Science. Montpellier, France.
{{cite conference}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - ^ Nachman, Keeve E; Graham, Jay P.; Price, Lance B.; Silbergeld, Ellen K. (2005). "Arsenic: A Roadblock to Potential Animal Waste Management Solutions". Environmental Health Perspective. 113 (9): 1123–1124. doi:10.1289/ehp.7834.
- ^ "Arsenic. Section 5.3, p. 310" (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
- ^ Jones, F. T. (2007). "A Broad View of Arsenic". Poultry Science. 86 (1): 2–14. PMID 17179408.
- ^ Bottemiller, Helena (September 26, 2009). "Bill Introduced to Ban Arsenic Antibiotics in Feed". Food Safety News. Retrieved 2011-01-10.
- ^ Antman, Karen H. (2001). "The History of Arsenic Trioxide in Cancer Therapy". The oncologist. 6 (Suppl 2): 1–2. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.6-suppl_2-1. PMID 11331433.
- ^ Huet, P. M.; Guillaume, E.; Cote, J.; Légaré, A.; Lavoie, P.; Viallet, A. (1975). "Noncirrhotic presinusoidal portal hypertension associated with chronic arsenical intoxication". Gastroenterology. 68' (5 Pt 1): 1270–1277. PMID 1126603.
- ^ Jennewein, Marc; Lewis, M. A.; Zhao, D.; Tsyganov, E.; Slavine, N.; He, J.; Watkins, L.; Kodibagkar, V. D.; O'Kelly, S. (2008). "Vascular Imaging of Solid Tumors in Rats with a Radioactive Arsenic-Labeled Antibody that Binds Exposed Phosphatidylserine". Journal of Clinical Cancer. 14 (5): 1377–1385. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1516. PMID 18316558.
- ^ "Blister Agents". Code Red – Weapons of Mass Destruction. Retrieved 2010-05-15.
- ^ Timbrell, John (2005). "Butter Yellow and Scheele's Green". The Poison Paradox: Chemicals as Friends and Foes. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780192804952.
- ^ Guruswamy, Sivaraman (1999). "XIV. Ammunition". Engineering Properties and Applications of Lead Alloys. CRC Press. pp. 569–570. ISBN 9780824782474.
- ^ Davis, Joseph R; Handbook Committee, ASM International (2001-08-01). "Dealloying". Copper and copper alloys. p. 390. ISBN 9780871707260.
- ^ "Arsenic Supply Demand and the Environment". Pollution technology review 214: Mercury and arsenic wastes: removal, recovery, treatment, and disposal. William Andrew. 1993. p. 68. ISBN 9780815513261.
- ^ Stolz, John F.; Basu, Partha; Santini, Joanne M.; Oremland, Ronald S. (2006). "Arsenic and Selenium in Microbial Metabolism*". Annual Review of Microbiology. 60: 107–30. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142053. PMID 16704340.
- ^ Kulp, T. R; Hoeft, S. E.; Asao, M.; Madigan, M. T.; Hollibaugh, J. T.; Fisher, J. C.; Stolz, J. F.; Culbertson, C. W.; Miller, L. G. (2008). "Arsenic(III) fuels anoxygenic photosynthesis in hot spring biofilms from Mono Lake, California". Science. 321 (5891): 967–970. Bibcode:2008Sci...321..967K. doi:10.1126/science.1160799. PMID 18703741.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - ^ Baccarelli, A.; Bollati, V. (2009). "Epigenetics and environmental chemicals". Current opinion in Pediatrics. 21 (2): 243–251. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e32832925cc. PMC 3035853. PMID 19663042.
- ^ Nicholis, I.; Curis, E.; Deschamps, P.; Bénazeth, S. (2009). "Arsenite medicinal use, metabolism, pharmacokinetics and monitoring in human hair". Biochimie. 91 (10): 12601267. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2009.06.003. PMID 19527769.
{{cite journal}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite jstor}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by jstor:1514012, please use {{cite journal}} with
|jstor=1514012instead. - ^ Wolfe-Simon, Felisa; Switzer Blum, Jodi S.; Kulp, Thomas R.; Gordon, G. W.; Hoeft, S. E.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Stolz, J. F.; Webb, S. M.; Weber, P. K. (2010). "A Bacterium That Can Grow by Using Arsenic Instead of Phosphorus". Science. 332 (6034): 1163–6. Bibcode:2011Sci...332.1163W. doi:10.1126/science.1197258. PMID 21127214.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|unused_data=ignored (help) - ^ "New Life Finding Linking Poison Arsenic Thrills The World- Implications On Extraterrestrial Life". SciGuru.com. Retrieved 3 December 2010.
- ^ "Arsenic-eating microbe may redefine chemistry of life". Nature News. 2 December 2010. Retrieved 2010-12-02.
{{cite news}}:|first=missing|last=(help) - ^ Bortman, Henry (2010-12-02). "Arsenic-Eating Bacteria Opens New Possibilities for Alien Life". Space.Com web site. Space.com. Retrieved 2010-12-02.
{{cite news}}: External link in|work= - ^ Sakurai, Teruaki Sakurai (2003). "Biomethylation of Arsenic is Essentially Detoxicating Event". Journal of Health Science. 49 (3): 171–178. doi:10.1248/jhs.49.171. Retrieved 2011-01-10.
- ^ Bentley, Ronald; Chasteen, TG (2002). "Microbial Methylation of Metalloids: Arsenic, Antimony, and Bismuth". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 66 (2): 250–271. doi:10.1128/MMBR.66.2.250-271.2002. PMC 120786. PMID 12040126.
- ^ Cullen, William R; Reimer, Kenneth J. (1989). "Arsenic speciation in the environment". Chemical Reviews. 89 (4): 713–764. doi:10.1021/cr00094a002.
- ^ Meharg, Andrew (2005). Venomous Earth – How Arsenic Caused The World's Worst Mass Poisoning. Macmillan Science. ISBN 9781403944993.
- ^ Lamm, S. H.; Engel, A.; Penn, C. A.; Chen, R.; Feinleib, M. (2006). "Arsenic cancer risk confounder in southwest Taiwan data set". Environ. Health Perspect. 114 (7): 1077–82. doi:10.1289/ehp.8704. PMC 1513326. PMID 16835062.
- ^ Kohnhorst, Andrew; Laird, Allan; Prayad, Pokethitiyoke; Suthida, Anyapo (2002). "Groundwater arsenic in central Thailand" (PDF). 28th WEDC Conference Calcutta. Retrieved 2009-01-29. [dead link]
- ^ "Arsenic in Drinking Water: 3. Occurrence in U.S. Waters" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-05-15.
- ^ Knobeloch, L. M.; Zierold, K. M.; Anderson, H. A. (2006). "Association of arsenic-contaminated drinking-water with prevalence of skin cancer in Wisconsin's Fox River Valley". J. Health Popul Nutr. 24 (2): 206–13. PMID 17195561.
- ^ "In Small Doses:Arsenic". The Dartmouth Toxic Metals Superfund Research Program. Dartmouth College.
- ^ Courtney, D; Ely, Kenneth H.; Enelow, Richard I.; Hamilton, Joshua W. (2009). "Low Dose Arsenic Compromises the Immune Response to Influenza A Infection in vivo". Environmental Health Perspectives. 117 (9): 1441–7. doi:10.1289/ehp.0900911. PMC 2737023. PMID 19750111.
{{cite journal}}: More than one of|magazine=and|journal=specified (help) - ^ Ferreccio, C.; Sancha, A. M. (2006). "Arsenic exposure and its impact on health in Chile". J Health Popul Nutr. 24 (2): 164–75. PMID 17195557.
- ^ Chu, H. A.; Crawford-Brown, D. J. (2006). "Inorganic arsenic in drinking water and bladder cancer: a meta-analysis for dose-response assessment". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 3 (4): 316–22. doi:10.3390/ijerph2006030039. PMID 17159272.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Arsenic in drinking water seen as threat - USATODAY.com". USA Today. 2007-08-30. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- ^ Gulledge, John H.; O'Connor, John T. (1973). "Removal of Arsenic (V) from Water by Adsorption on Aluminum and Ferric Hydroxides". J. American Water Works Assn. 65 (8): 548–552.
- ^ O'Connor, J. T.; O'Connor, T. L. "Arsenic in Drinking Water: 4. Removal Methods" (PDF).
- ^ "In situ arsenic treatment". Retrieved 2010-05-13.
- ^ Radloff, K. A.; Zheng, Y.; Michael, H. A.; Stute, M.; Bostick, B. C.; Mihajlov, I.; Bounds, M.; Huq, M. R.; Choudhury, I. (2011). "Arsenic migration to deep groundwater in Bangladesh influenced by adsorption and water demand". Nature Geoscience. doi:10.1038/ngeo1283.
{{cite journal}}: no-break space character in|title=at position 87 (help) - ^ Yavuz, Cafer T; Mayo, J. T.; Yu, W. W.; Prakash, A.; Falkner, J. C.; Yean, S.; Cong, L.; Shipley, H. J.; Kan, A. (2005). "Low-Field Magnetic Separation of Monodisperse Fe3O4 Nanocrystals". Science. 314 (5801): 964–967. doi:10.1126/science.1131475. PMID 17095696.
- ^ Reese, Jr, Robert G. "Commodity Summaries 2002: Arsenic" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-11-08.
- ^ "Chromated Copper Arsenate (CCA)". US Environmental Protection Agency.
- ^ "TRI Releases Map". Toxmap.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
- ^ TOXNET – Databases on toxicology, hazardous chemicals, environmental health, and toxic releases. Toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved on 2011-10-24.
- ^ Klaassen, Curtis; Watkins, John (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. McGraw-Hill. p. 512. ISBN 978-0071389143.
- ^ Croal, Laura R.; Gralnick, Jeffrey A.; Malasarn, Davin; Newman, Dianne K. (2004). "The Genetics of Geochemisty". Annual Review of Genetics. 38: 175–206. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.091138. PMID 15568975.
- ^ The Psychiatric, Psychogenic ans Somatopsychic Disorders Handbook. New Hyde Park, NY: Medical Examination Publishing Co. 1978. pp. 81–82.
- ^ The Tox Guide for Arsenic (2007). The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
- ^ "OSHA Arsenic". United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
External links
- CTD's Arsenic page and CTD's Arsenicals page from the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database
- A Small Dose of Toxicology
- Arsenic in groundwater Book on arsenic in groundwater by IAH's Netherlands Chapter and the Netherlands Hydrological Society
- Contaminant Focus: Arsenic by the EPA.
- Environmental Health Criteria for Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds, 2001 by the WHO.
- Evaluation of the carcinogenicity of arsenic and arsenic compounds by the IARC.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Arsenic Page
- National Pollutant Inventory – Arsenic
- origen.net – CCA wood and arsenic: toxicological effects of arsenic