Bissa language
| Bissa | |
|---|---|
| Bisa, Busansi | |
| Bɩsa | |
| Region | Burkina Faso, Ghana, Togo |
| Ethnicity | Bissa people |
Native speakers | (590,000 cited 1999–2003)[1] |
Niger–Congo?
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bib |
| Glottolog | biss1248 |
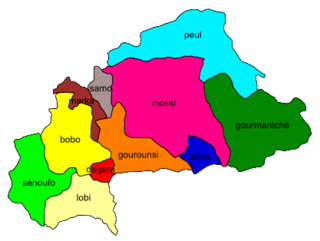 Majority areas of northern dialects of Bissa, in dark blue, on a map of Burkina Faso. | |
| Bissa | |
|---|---|
| Person | Bɩsan |
| People | Bɩsanno |
| Language | Bɩsa |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 1.7 million | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| approx 6.8 million | |
| 1.1 million | |
| 3,356 | |
| Languages | |
| Bissa, French | |
| Religion | |
| Islam African Traditional Religion | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| other Mandé peoples | |
Bissa (or Bisa (singular), Bisan, Bissanno (plural)), is a Mande ethnic group of south-central Burkina Faso, northeastern Ghana and the northernmost tip of Togo. Their language, Bissa,[2] is a Mande language that is related to, but not the same as, a cluster of languages in the old Borgu Kingdom area of Northeast Benin and Northwest Nigeria, including Busa, Boko, and Kyenga. An alternate name for the Bissa is Busansi which is used by the Mossi people and Kusasi people or Busanga.
Names
[edit]The name is usually spelled Bissa. It can also be spelled Bisa, and the name in the Mossi language is Busansi (Singular) or Busanga (Plural); This should not be confused with the Bisa language of Zambia or the Busa language of Nigeria and Benin.
Geographic distribution
[edit]In Burkina Faso, Bissa is spoken in Boulgou, Koulpélogo, and Kouritenga Provinces of the Centre-Est Region, in Bazaga and Zoundwéogo Provinces of the Centre–Sud Region (Garango, Gomboussougou, Zabré, and Tenkodogo Cities), and in the Boudry Department of Ganzargou Province of the Plateau-Central Region.
In Ghana, Bissa is spoken in Bawku Municipal District of the Upper East Region.
In Togo, Bissa is spoken in Tône Prefecture of the Savanes Region. There are also some Bissa speakers in Ivory Coast.
Classification
[edit]Bissa language is the most populous of the Mande languages of Ghana and Togo. It is part of the Eastern Mande group, which also includes several other languages spoken across the Volta River and the Borgu Kingdom, including Boko, Busa, Samo, and Bokobaru.
Dialects
[edit]Bissa has three dialect:
- Barka or Baraka (also known as Eastern Bissa)
- Lebir or Zeba (also known as Western Bissa)
- Lere (also known as Northern Bissa)
The most widely spoken dialects of Bissa are Barka and Lebir.
To the East the Bissa people speak Barka/Baraka. To The West people speak Lebir/Zeba. To the North the Lere dialect is used. To the South, there is no specifics dialect.
Phonology
[edit]Vowels
[edit]| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i, ĩ | u | |
| Near-close | ɪ, ɪ̃ | ʊ, ʊ̃ | |
| Close-mid | e | o | |
| Open-mid | ɛ, ɛ̃ | ɐ, ɐ̃ | ɔ, ɔ̃ |
| Open | a, ã |
Consonants
[edit]| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | |
| voiced | b | d | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | ||
| voiced | v | z | |||
| Approximant | l | j | w | ||
| Trill | r | ||||
Writing system
[edit]High tone is marked with an acute accent and low tone is marked with a grave accent. The following is the alphabet of the Lere and Lebir dialects of Bissa:
| A | B | C | D | E | Ǝ | Ɛ | F | G | H | I | Ɩ | J | K | L | M | N | Ny | Ŋ | O | Ɔ | P | R | S | T | U | Ʋ | V | W | Y | Z |
| a | b | c | d | e | ǝ | ɛ | f | g | h | i | ɩ | j | k | l | m | n | ny | ŋ | o | ɔ | p | r | s | t | u | ʋ | v | w | y | z |
The following is the alphabet of the Barka dialect of Bissa:
| A | B | D | E | Ɛ | Ǝ | F | G | H | I | Ɩ | K | L | M | N | Ɲ | Ŋ | O | Ɔ | P | R | S | T | U | Ʋ | W | Y | Z |
| a | b | d | e | ɛ | ə | f | g | h | i | ɩ | k | l | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | o | ɔ | p | r | s | t | u | ʋ | w | y | z |
Comparison of dialects
[edit]| Phrase | Lere | Barka | Lebir |
|---|---|---|---|
| Good morning | Domireh ki | Idomleki | |
| come | bur | iahh | Eyaham |
| water | pi | hi | |
| food | forbile | hobile |
Lere phrases
[edit]- Good morning: Domireh ki (Response: Domireh zain)
- Good afternoon: Sundareh ki (Response: Sundareh zain)
- Good evening/night: Yirbaa ki (Response: Yirbaa zain)
- Thank you: Barka
- Good: Minga
- Come: Bur
- Go: Ta
- You're welcome: An barka boi
- I love you: Moi wam
The Busa and Boko peoples of Benin and Nigeria
[edit]The Busa and Boko peoples, two subgroups of the Bissa people, live in Northwestern Nigeria and Northern Benin near Borgu in the Nigerian States of Niger, Kebbi and Kwara (mostly Bokobaru subgroup) and in the Beninese Departments of Alibori and Borgou.
They speak Busa (also known as Bisã) and Boko (also known as Boo). This peoples are referred to as Bussawa in Hausa.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]Sources
[edit]- "Dictionnaire Bissa-Barka". SIL International. 25 April 2016., the SIL entry direct towards "Dictionnaire Bissa-Barka". Sous-Commission de la langue Bisa.
