Eger
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2011) |
Eger | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | |
| County | Heves |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | László Habis |
| Area | |
| • Total | 92.2 km2 (35.6 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 165 m (541 ft) |
| Population (2013) | |
| • Total | |
| • Rank | 19th |
| • Density | 610.8/km2 (1,582/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 3300 |
| Area code | 36 |
| Website | www |
Eger (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈɛɡɛr] ; Template:Lang-de; Template:Lang-tr; Template:Lang-la; Template:Lang-pl; Template:Lang-sk; Template:Lang-sl; Template:Lang-cz; Template:Lang-srp; Template:Lang-hr) is the county seat of Heves, and the second largest city in Northern Hungary (after Miskolc). Eger is best known for its castle, thermal baths, historic buildings (including the northernmost Turkish minaret), dishes and red wines. It has an estimated population of 56,530 as of 2011, which makes it 19th largest city in Hungary. The city is located on the Eger Stream, on the hills of the Bükk Mountains.
Etymology
The origin of its name is still unknown. One suggestion is that the place was named after the elder ("égerfa" in Hungarian) which grew so abundantly along the banks of the Eger Stream. This explanation seems to be correct because the name of the town reflects its ancient natural environment, and also one of its most typical plants, the elder, large areas of which could be found everywhere on the marshy banks of the Stream although they have since disappeared. The German name of the town: Erlau=Elren-au (elder grove) also speaks in favour of this supposition. And there is another theory which says that Eger's name comes from the Latin word: "ager" (earth). This theory comes from more recent researchers who think that during the 11th and 12th centuries settlers with a Walloon origin ("latins") in Hungarian) moved to this territory. The basin of Eger and the hilly region around it have always been very suitable for human settlements, and there are many archaeological findings from the early ages of history, which support this fact.
The other names of the city are in Latin as Agria, in Serbian and Croatian as Jegar / Јегар or Jegra / Јегра, in Czech Czech and Slovene Slovene language as Jager, in Slovak language as Jáger, in Polish as Jagier, and in Turkish as Eğri.
Coat of Arms

The shield of Eger developed from the shield of Bishop György Fenesy (1686-1689) after an agreement which was made with him in 1694. The bastion with the three gates on it refers to the existence of the fortress. The rampant unicorn between the two bastions on the side of the shield came from the bishop's shield. The sword in the fore-feet of the unicorn symbolises the manorial power of life and death. The snake twisting on the sword stands for the defect of treachery and hatred by faith. The star and the sun symbolise the alternation of days and nights. And finally, the eagle with a gospel in its clutches refers to apostle and evangelist Saint John who is the patron saint of the Archdiocese of Eger.
History
Eger has been inhabited since the Stone Age.
Reign of Saint Stephen

Today's Eger was formed in the 10th century by St. Stephen (997–1038), the first Christian king of Hungary, who founded an episcopal see in Eger. The first cathedral of Eger was built on Castle Hill, within the present site of Eger Castle. Eger grew around this cathedral, and remains an important religious centre in Hungary.
This settlement took up an important place among the Hungarian towns even in the early Middle Ages. The natural fundamentals of the surroundings (meeting of plains and hills) made it possible to establish economic and cultural relations between the different parts of the country.
During the 11th and 12th centuries Walloon settlers came from the areas beyond the Rhine. They settled with the kings' permission, bringing western culture to this region and acclimating the viticulture. The development of the city accelerated with their presence.
Mongol Invasion

This development was blocked for a short time by the Mongol invasion in 1241, when the town was ransacked and burned down during the episcopacy of Kilit the Second.
After the withdrawal of the Mongols, Eger began to flourish all over again. Lambert, the bishop of Eger, received a permit from Béla IV for the building a stone fortress. So the nearly destroyed town revived and reached the peak of its medieval development in the l4th and 15th centuries. During this period the forests which spread to the limits of the town were cleared for the most part, and vines were planted in their place. More and more town-houses were built in the settlement. Roads were constructed among which the ones in the inner town were narrow and twisting but those leading to the northern mining towns were wider. The versions surrounding settlements such as Almagyar and Czigléd were built up along with Eger.
Reign of King Matthias


During the reign of King Matthias (1458-1490) Eger began to develop again. The gothic-styled Bishops Palace of Eger which can be seen at the present time was reconstructed by the order of bishop János Bekensloer. Building operations continued during the bishoprics of Orbán Dóczy and Tamás Bakócz. The beginning of the reconstruction (in late gothic style) of the cathedral fort can also be linked to their names. After the death of King Matthias, during the bishopric of Hyppolit the so-called Hyppolit Gate was built, this has recently been removed.
The Siege of Eger
(see Siege of Eger (1552) and Siege of Eger (1596))


After the Battle of Mohács (1526) a sorrowful period began in the history of Eger. During the dual kingship the town changed hands almost every year and the Turkish army came closer as well. This circumstance provided the reason for reinforcing the fortress. In the autumn of 1552, Captain István Dobó and his handful of soldiers were successful in defending the fortress and northern Hungary from the expanding Turkish Empire. The first writer of note to draw on the story was the Hungarian renaissance poet and musician Sebestyén Tinódi Lantos (c. 1510–1556), whose account may have come partly from eyewitnesses. Géza Gárdonyi wrote his book, "Eclipse of the Crescent Moon" in remembrance of this battle, and his work has been translated into numerous languages.
Despite the fact that István Dobó and his soldiers successfully defended the fortress, it was destroyed during the siege, so it was essential to wholly rebuild it. The reconstruction process of the fortress took place between 1553 and 1596 and Italian artificer officers planned the renovations. The famous Hungarian poet, Bálint Balassi also served here for a few years beginning in April of 1578.
Turkish Rule

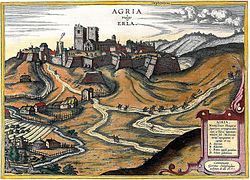
While István Dobó and his soldiers managed to defend the fortress in 1552, in 1596 the captain at that time and the foreign mercenaries under his rule handed it over. This was the beginning of the 91-year-long Turkish rule in Eger. The minaret, which was built at the end of the 17th century, preserves the memory of this period. Among all the buildings of this type, the minaret of Eger is found in the northernmost point of the former Ottoman Empire. During the Turkish occupation Eger became the seat of a vilayet which is a Turkish domain including several sanjaks. Churches were converted into mosques, the castle rebuilt, and other structures erected, including public baths and minarets.
The rule of the Turks in Central Hungary began to collapse after a failed Ottoman attempt to capture Vienna. The Vienna-based Habsburgs, who controlled the rest of Hungary, apart from Transylvania, steadily expelled the Turks from the country. The castle of Eger was starved into surrender by the Christian army led by Charles of Lorraine in 1687, after the castle of Buda had been retaken in 1686. Eger was relieved from Turkish rule in December, 1687. Although the reoccupation was effected by a siege (which starved out the defenders) and not by a bombardment, the town fell into a very poor state. According to the ... records there were only 413 houses in the area within the town walls which were habitable and most of these were occupied by left over Turkish families.
Habsburg Rule




After the expelling of the Turks, the town was considered by the imperial regiment as a demesne of the Crown. Leopold I re-established Eger as a free royal borough in 1688, which meant that it was relieved from the ecclesiastic manorial burdens. This state lasted until 1695, when György Finesse, the returning bishop, had the former legal status of a bishopric town restored by the monarch.
Eger soon began to prosper again. The city was reclaimed by its bishops, which caused many local Protestants to leave. Although the city supported the Hungarian leader Prince Francis II Rákóczi in the 1703–1711 war of independence against the Habsburgs, the Hungarians were eventually defeated by the Imperial army. In 1709 Francis II Rákóczi and Ukranciev, the legate of Czar Peter the First, met here. It must be added that the legate died in Eger and was buried near the Serbian Church of Eger. Soon after that, the city was ravaged by plague. However, immigration into Eger was strong, and the population rose from 6000 to 10,000 between 1725 and 1750. Muslims were assimilated into the Christian population.
In the history of Eger the 18th century was the period of development and prosperity. Many new buildings were built in Baroque and later in Rococo and Neoclassical style, including the cathedral, the Archiepiscopal Palace of Eger, the County Hall of Eger, the Eger Lyceum (now housing the Eszterházy College of Education) and several churches, while others were reclaimed from being mosques.
The building processes attracted many craftsman, merchants and artists with such talented ones among them as Kracker János Lukács, Anton Maulberts, Franz Sigrist, Josef Gerl, Jakab Fellner and Henrik Fasola. The town population grew suddenly. While in 1688 it was only 1200, in 1787 more than 17,000 people lived here. At this time Eger was the 6th largest town of Hungary (based on the number of its inhabitants). Viticulture also reached its brightest period in these days. The wine-growing area was twelve-times larger than it had been earlier.
The 18th century was also important because bishop Barkóczy and Eszterházy decided to found a university in Eger patterned after the ones in Nagyszombat and in Vienna. There were already precedents for this type of education because in 1700 Bishop István Telekessy, who took sides with Ferenc Rákóczy the Second, established a seminary in Eger. Then in 1740 Canon György Foglár founded a Faculty of Law and in 1754 bishop Barkóczy set up a school of philosophy. In 1769 the first medical school of Hungary was opened by the direction of Ferenc Markhot, but it was closed in 1755. Unfortunately the university of Eger could not begin its work because of appoint ... the monarch'. In the building which was marked out for the university we can find the Archdiocese's Library (the most beautiful baroque library in Hungary), and an astronomical museum with original equipment, which was the second museum of this type in Europe. Between 1946 and 1948 there were several more efforts to found a university in Eger all of which also ended in failure.
The 19th century began with disasters: a fire that destroyed half the town in 1800, and a collapse of the south wall of the Castle in 1801, which ruined several houses. Eger became the seat of an archbishopric in 1804, and the church remained in firm control of the city, despite efforts by its citizens to obtain greater freedom. In 1827, much of the city centre was damaged by fire again, and four years later over 200 were killed in an outbreak of cholera.
In 1804 a significant change occurred in the organisation of Eger's bishopric. The monarch made this town a centre of archbisphoric, but the bishoprics of Szatmár and Kassa separated from it.
The Reform Age
The Reform Age (1825-1848) left several lasting marks on the life of Eger, especially on its culture. Pyrker László János, the archbishop of that time, founded a gallery which he donated to the Hungarian National Museum because the town did not guarantee an appropriate place for it. It was Pyrker's present which served as a base for the collection of the Museum of Fine Arts that was opened in 1900. In 1828 Pyrker established the first Hungarian teachers training college in Eger and he was the one who ordered the construction of the basilica which was built in neo-classical style, in accordance with the plans of József Hild. On the basis of its size this basilica is the second among the churches of Hungary. In 1837 János Joó, an art teacher, began to edit Hungary's first technical journal with the title "Héti Lapok".

Revolution and War of Independence
The inhabitants of Eger took an active part in the revolution in 1848. Even though the revolution was suppressed, the age of landowners and serfs had gone forever, and the municipality gained freedom from the rule of the archbishop in 1854.
Age of the Monarchy
The main railway line between Miskolc and Pest bypassed the city, which was only reached later by a branch line from Füzesabony. Unfortunately (unlike other towns) Eger's civil development did not become faster, as distinguished from other towns, after 1849 and the Compromise of 1867. Industrial development was represented only by the mill, the tobacco factory and the sheet-iron works that were founded in the Reform Age.
During the decades after the turn of the century the character of a school-town was dominant in Eger. Because of its schools and other cultural institutions it became known as the Hungarian Athens.
At the beginning of the century, in 1904, the first independent theatre of stone was opened and the canalisation and the provision of public utilities began as well.
20th century

Economic recovery was slow after World War I, although the 1899 publication of Gárdonyi's "Eclipse of the Crescent Moon" made Eger popular as a tourist attraction and archaeological excavation of the castle resumed.
In 1933 Eger was one of those towns that first got the permission for opening a spa.
In World War II, the city suffered under the retreating German Army and the arriving Soviet army, but it managed to escape major bombardment.
In the decades after 1945, industrialization of the town commenced because of the change of regime. As a consequence, Eger's former character of a cultural centre began to fade, which diminished the patina of the settlement.
It was a great good fortune that in 1968 the baroque inner city was preserved. So it was saved from the deterioration (and from the construction of unsuitable, modern buildings).

Eger is famous for its wines, most notably the "Egri Bikavér" (Bull's Blood of Eger). It is also well known for "Egri Víz", a type of brandy which originated in the 18th century, the "bujavászon" (a special Turkish tissue), as well as its thermal baths. Today, Eger is a prosperous city and popular tourist destination with a charming Baroque town centre.
Ecclesiastical history

Eger is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Eger, an ecclesiastical province of Hungary founded as a bishopric in 1009 and made a Metropolitan archdiocese in 1804, by Pope Pius VII. The current archbishop-elect, Archbishop Csaba Ternyak, was previously Secretary for the Congregation For Clergy. He succeeds Archbishop István Seregely, who retired because of age. The constituent dioceses of the province were Košice (Kassa, Kaschau), Rožňava (Rozsnyó, Rosenau, now part of Slovakia), Szatmár and Szepes (Zipo, Zipsen).
Wine

Beside its historic sights and its thermal baths, Eger is famous for its wines. It produces both red and white wines of high quality. The famous and traditional varieties of the region are Egri Leányka, Egerszóláti Olaszrizling, Debrői Hárslevelű (whites), and Egri Bikavér (a red). More recently, Chardonnay and Pinot noir wines have appeared. The region's wines are said to bear a resemblance to those of Burgundy. Although the quality of the wines deteriorated in the second half of the 20th century, especially the cuvees, Eger is slowly recovering its reputation as a wine region.
Tourism
The majority of visitors come for a single day (mostly Slovaks), not staying overnight. Ukrainians and Russians frequent the Eger Castle, along with many Italians. Around the town you may run into many German-speaking travelers (Germans, Austrians, Swiss) as well. However, the city is getting more popular for Turkish tourists, because of the common historical memories. Eger is mainly known for its castle, thermal baths, historic buildings (including the northernmost Turkish minaret) and, above all else, its famous Hungarian red wines. Travel agencies recommends 3 days to enjoy the city fully.
Transportation
Rail
The main railway station is located 1.5 km from the city center. MÁV operates intercity train services to Budapest, and the trip is about 11⁄2 hours. Local trains to Füzesabony and Szilvásvárad also depart from this station.
There are also smaller stations located near the castle and in the Felnémet district that are served by the Eger-Szilvásvárad local trains.
Coach
The bus station is located close to the basilica. Buses depart approx. every 30 minutes to Budapest, and the trip to the capital is about 2 hours. Agria Volán operates an extensive network of suburban and long-distance buses. Other bus companies also offer connections to a variety of destinations. Taking the bus to Felsotarkany gets you close to several hiking and mountain biking trails.
Local Bus
Agria Volan also operates a fleet of local buses, serving most parts of the city, although the majority of buses run in a north-south direction. Line 12 is the busiest line in the city, and it has stops at the railway station, the bus station and in the city centre.
Culture

Districts


(Note: Most of these districts are historical, but they often appear on maps and street signs.)

- Almagyar - This hill in the eastern part of the town is one of the smart areas of Eger, near the castle. The streets are steep, but there are fine views. The southern part contains some of the buildings (campus and dormitories) of Eszterházy College.
- Almár - The northernmost part of the town, it consists mainly of weekend cottages and plots for gardeners.
- Belváros (City centre) - The centre of Eger is often called "the Baroque Pearl of Europe". Here are located Dobó tér, the main square of the historical town, surrounded by Baroque houses and St. Anthony's Church. Other historic buildings nearby include the Cathedral and the Lyceum.
- Berva is now a housing estate about 2 km to the NW of Eger. Founded in 1951, it was a huge industrial park by the name of Finomszerelvénygyár, privatized in 1992.
- Castle of Eger - The oldest and most famous part of Eger.
- Cifra hóstya - North of the centre, this part of town is full of small houses and narrow streets. You can find the Firefighters' Museum there.
- Csákó - a suburban area with larger houses, east of the railway station.
- Érsekkert (Bishop's Garden) - The largest park in Eger, with sport facilities, a small lake, and a fountain.
- Felnémet- This village, north of the town, was annexed to Eger in 1961 but still has a rural character. The parish church (1715–1750s, designed by Gianni Battista Carlone, an Italian who settled in Eger) was started by Bishop Gábor Antal Erdődy as a votive church after an outbreak of bubonic plague in 1710, and completed by his successor. It was dedicated to St. Rosalia, a guardian against plague.
- Felsőváros (Upper Town, formerly Csebokszári (Cheboksary-capital town of Chuvash Republic, Russia) - The largest housing estate of Eger, it is full of four and ten-storied concrete buildings, providing homes for one third of the city's population. There are three high schools there.
- Hajdúhegy - a suburban area similar to Almagyar across the valley with downtown being in between these 2 hills.
- Hatvani hóstya - The district is split by Highway 25. It contains the stadium and the Reformed church.
- Industrial zone - Several multinational companies have moved into this area east of Lajosváros.
- Károlyváros (Charles Town) - One of the largest districts of Eger, Károlyváros is west of downtown. It contains the High School for the Health Professions, and the Agria Park Shopping Mall.
- Lajosváros (Louis Town) - This district in the southern part of the town has several high schools and student hostels. It consists mainly of detached houses. Also called Kanada.
- Maklári hóstya, Tihamér - This district is one of the fastest developing parts of the town. It contains public swimming pools (designed by Imre Makovecz).
- Pásztorvölgy - A suburban area in Felnémet. Also has a high school.
- Rác hóstya - Another suburban area west from Upper Town.
- Szépasszonyvölgy ("Valley of the Beautiful Woman") - An area of Eger famous for its red wines (Bikaver or Bulls Blood) and known for its wine cellars.
- Tetemvár - Another suburban area. The name ("Corpses' Castle") derives from the legend that Turkish war dead were buried here in 1552.
- Vécseyvölgy - A suburban area with a small airfield for sports purposes.
Main sights
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
(Eger has 17 churches, but tourists usually visit only three or four)
- Castle of Eger
- The Cathedral or basilica, built in 1831-37 to Classicist designs by József Hild, is imposing rather than attractive, but contains some remarkable painting and sculpture. Late morning organ recitals are held frequently.
- Minaret, 17th century. The northernmost Turkish minaret in Europe is 40 meters high and one of only three survivors in Hungary. It can be climbed for a good view of the city centre.
- Város a város alatt (literally "City under the city") a system of cellars near the Cathedral.
- Szépasszonyvölgy ("The Valley of the Beautiful Woman". A valley on the southern edge of Eger which has numerous wine cellars, many with their own wine bar catering to tourists. A tram shuttles tourists to/from Dobó tér in the summer months.
- Dobó tér. The Baroque Minorite Church (1758–67), built to the designs of Kilian Ignaz Dientzenhofer of Prague with original ceiling frescoes by Márton Reindl, is the focal point of the city's most imposing square, flanked by the City Hall and the old priory buildings, part of which contain the Palóc Museum, showing the artefacts of a distinctive regional ethnic community. The square and several of the retail streets around it are pedestrianized.
- The Lyceum (Eszterházy College), designed by József Gerl and Jakab Fellner and built in 1765-85, is a splendid example of the restrained Zopf style. There are three remarkable 18th-century frescoed ceilings, of which only the one in the library is open to the public. Painted by the Viennese artist Johann Lukas Kracker in 1778, it depicts the Council of Trent of 1545-63, which launched the Counter-Reformation. Among the figures depicted are the Reformers Luther and Zwingli, whose "heretical" books are being struck by a bolt of lightning. The beautifully furnished library opened in 1793. There is a camera obscura or periscope at the top of the building, projecting images of the city onto a table.
- Turkish Bath
- The Provost Minor's Palace, 1758, is the finest Rococo building in the city. It also has a fine fresco by Kracker ("The Triumph of Virtue over Sin"), other 18th-century murals, and remarkable 18th-century wrought ironwork.
- Agria Park, a shopping mall which opened in March 2008.
- Archbishop's Garden
- The Fazola gate
- The Minorite Church
- The Serbian Orthodox Church (Rác-templom) is in Zopf style (1784–86). The interior was commissioned from the best Viennese artists by the rich local Serbian community of that time. It is dominated by a breath-taking iconostasis.
- The Cistercian church
- The Archbishop's Palace
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1787 | 16,852 | — |
| 1850 | 16,858 | +0.0% |
| 1870 | 19,150 | +13.6% |
| 1891 | 22,427 | +17.1% |
| 1900 | 25,893 | +15.5% |
| 1910 | 28,052 | +8.3% |
| 1920 | 28,753 | +2.5% |
| 1930 | 30,424 | +5.8% |
| 1941 | 32,482 | +6.8% |
| 1949 | 31,844 | −2.0% |
| 1960 | 38,610 | +21.2% |
| 1970 | 47,960 | +24.2% |
| 1980 | 60,897 | +27.0% |
| 1990 | 61,576 | +1.1% |
| 2001 | 58,331 | −5.3% |
| 2011 | 56,569 | −3.0% |
Twin towns — Sister cities
Eger is twinned with:
Notable residents
- Péter Ács, Hungarian chess grandmaster (GM)
References

- ^ "Jerikó lett Eger új testvérvárosa". Index.hu. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- Attribution
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Agria". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Agria". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
External links
- The Complete Guide to Eger Sightseeing, accommodation, activities and wine tourism in the Eger area Template:En icon
- Chasamsofer.com
- Official website Template:En icon Template:Hu icon Template:De icon Template:Fr icon Template:Nl icon
- A modern traveller's account of his visit to Eger
- Eszterházy College Eszterházy College Template:Hu icon Template:En icon
- Egervaros.hu
- Aerial photography: Eger
- Eger and its surroundings on old postcards (collection of the city library)
- Eger - ShtetLink
- Eger at funiq.hu