Helicobacter pylori
| Helicobacter pylori | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |
Helicobacter pylori, previously Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found usually in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Australian scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in a person with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions not previously believed to have a microbial cause. It is also linked to the development of duodenal ulcers and stomach cancer. However, over 80% of individuals infected with the bacterium are asymptomatic, and it may play an important role in the natural stomach ecology.[3]
More than 50% of the world's population harbor H. pylori in their upper gastrointestinal tract.[4] Infection is more prevalent in developing countries, and incidence is decreasing in Western countries. H. pylori's helical shape (from which the genus name is derived) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach.[5][6]
Signs and symptoms
Up to 85% of people infected with H. pylori never experience symptoms or complications.[7] Acute infection may appear as an acute gastritis with abdominal pain (stomach ache) or nausea.[8] Where this develops into chronic gastritis, the symptoms, if present, are often those of non-ulcer dyspepsia: stomach pains, nausea, bloating, belching, and sometimes vomiting or black stool.[9][10]
Individuals infected with H. pylori have a 10 to 20% lifetime risk of developing peptic ulcers and a 1 to 2% risk of acquiring stomach cancer.[11][12] Inflammation of the pyloric antrum is more likely to lead to duodenal ulcers, while inflammation of the corpus (body of the stomach) is more likely to lead to gastric ulcers and gastric carcinoma.[13] However, H. pylori possibly plays a role only in the first stage that leads to common chronic inflammation, but not in further stages leading to carcinogenesis.[6] A meta-analysis conducted in 2009 concluded the eradication of H. pylori reduces gastric cancer risk in previously infected individuals, suggesting the continued presence of H. pylori constitutes a relative risk factor of 65% for gastric cancers; in terms of absolute risk, the increase was from 1.1% to 1.7%.[14]
H. pylori has been associated with colorectal polyps and colorectal cancer.[15] It may also be associated with eye disease.[16]
Microbiology
| Helicobacter pylori | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | H. pylori
|
| Binomial name | |
| Helicobacter pylori (Marshall et al. 1985) Goodwin et al., 1989
| |

H. pylori is a helix-shaped (classified as a curved rod, not spirochaete) Gram-negative bacterium about 3 μm long with a diameter of about 0.5 μm. It is microaerophilic; that is, it requires oxygen, but at lower concentration than is found in the atmosphere. It contains a hydrogenase which can be used to obtain energy by oxidizing molecular hydrogen (H2) produced by intestinal bacteria.[17] It produces oxidase, catalase, and urease. It is capable of forming biofilms[18] and can convert from spiral to a possibly viable but nonculturable coccoid form,[19] both likely to favor its survival and be factors in the epidemiology of the bacterium.
H. pylori possesses five major outer membrane protein families.[12] The largest family includes known and putative adhesins. The other four families are porins, iron transporters, flagellum-associated proteins, and proteins of unknown function. Like other typical Gram-negative bacteria, the outer membrane of H. pylori consists of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The O antigen of LPS may be fucosylated and mimic Lewis blood group antigens found on the gastric epithelium.[12] The outer membrane also contains cholesterol glucosides, which are found in few other bacteria.[12] H. pylori has four to six lophotrichous flagella; all gastric and enterohepatic Helicobacter species are highly motile owing to flagella.[20] The characteristic sheathed flagellar filaments of Helicobacter are composed of two copolymerized flagellins, FlaA and FlaB.[21]
Microscopy
H. pylori can be demonstrated in tissue by Gram stain, Giemsa stain, haematoxylin–eosin stain, Warthin–Starry silver stain, acridine orange stain, and phase-contrast microscopy.
Genome
H. pylori consists of a large diversity of strains, and the genomes of three have been completely sequenced.[22][23][24][25][26] The genome of the strain "26695" consists of about 1.7 million base pairs, with some 1,576 genes. The two sequenced strains show large genetic differences, with up to 6% of the nucleotides differing.[24]
Transcriptome
In 2010, Sharma et al. presented a comprehensive analysis of transcription at single-nucleotide resolution by differential RNA-seq which confirmed the known acid induction of major virulence loci such as the urease (ure) operon or the cag pathogenicity island (see below).[27] More importantly, this study identified a total of 1,907 transcriptional start sites, 337 primary operons, and 126 additional suboperons, and 66 monocistrons. Until 2010, only about 55 transcriptional start sites (TSSs) were known in this species. Notably, 27% of the primary TSSs are also antisense TSSs, indicating that—similar to E. coli—antisense transcription occurs across the entire H. pylori genome. At least one antisense TSS is associated with about 46% of all open reading frames, including many housekeeping genes.[27] Most (about 50%) of the 5' UTRs are 20–40 nucleotides (nt) in length and support the AAGGag motif located about 6 nt (median distance) upstream of start codons as the consensus Shine–Dalgarno sequence in H. pylori.[27]
Genes involved in virulence and pathogenesis
Study of the H. pylori genome is centered on attempts to understand pathogenesis, the ability of this organism to cause disease. About 29% of the loci have a colonization defect when mutated. Two of sequenced strains have an around 40-kb-long Cag pathogenicity island (a common gene sequence believed responsible for pathogenesis) that contains over 40 genes. This pathogenicity island is usually absent from H. pylori strains isolated from humans who are carriers of H. pylori but remain asymptomatic.[28]
The cagA gene codes for one of the major H. pylori virulence proteins. Bacterial strains with the cagA gene are associated with an ability to cause ulcers.[29] The cagA gene codes for a relatively long (1186-amino acid) protein. The cag pathogenicity island (PAI) has about 30 genes, part of which code for a complex type IV secretion system. The low GC-content of the cag PAI relative to the rest of the Helicobacter genome suggests the island was acquired by horizontal transfer from another bacterial species.[22]
Pathophysiology
Adaptation to the stomach's acidic environment
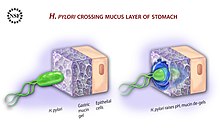
To avoid the acidic environment of the interior of the stomach (lumen), H. pylori uses its flagella to burrow into the mucus lining of the stomach to reach the epithelial cells underneath, where it is less acidic.[30] H. pylori is able to sense the pH gradient in the mucus and move towards the less acidic region (chemotaxis). This also keeps the bacteria from being swept away into the lumen with the bacteria's mucus environment, which is constantly moving from its site of creation at the epithelium to its dissolution at the lumen interface.[31]
H. pylori is found in the mucus, on the inner surface of the epithelium, and occasionally inside the epithelial cells themselves.[32] It adheres to the epithelial cells by producing adhesins, which bind to lipids and carbohydrates in the epithelial cell membrane. One such adhesion, BabA, binds to the Lewis b antigen displayed on the surface of stomach epithelial cells.[33] Another such adhesion, SabA, binds to increased levels of sialyl-Lewis x antigen expressed on gastric mucosa.[34]
In addition to using chemotaxis to avoid areas of low pH, H. pylori also neutralizes the acid in its environment by producing large amounts of urease, which breaks down the urea present in the stomach to carbon dioxide and ammonia. The ammonia, which is basic, then neutralizes stomach acid.
Inflammation, gastritis, and ulcer
H. pylori harms the stomach and duodenal linings by several mechanisms. The ammonia produced to regulate pH is toxic to epithelial cells, as are biochemicals produced by H. pylori such as proteases, vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA) [this damages epithelial cells, disrupts tight junctions and causes apoptosis, and certain phospholipases.[35] Cytotoxin associated gene CagA can also cause inflammation and is potentially a carcinogen.[36]
Colonization of the stomach by H. pylori can result in chronic gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining, at the site of infection. Helicobacter cysteine-rich proteins (Hcp), particularly HcpA (hp0211), are known to trigger an immune response, causing inflammation.[37] Chronic gastritis is likely to underlie H. pylori-related diseases.[38]
Ulcers in the stomach and duodenum result when the consequences of inflammation allow stomach acid and the digestive enzyme pepsin to overwhelm the mechanisms that protect the stomach and duodenal mucous membranes. The location of colonization of H. pylori, which affects the location of the ulcer, depends on the acidity of the stomach.[39] In people producing large amounts of acid, H. pylori colonizes near the pyloric antrum (exit to the duodenum) to avoid the acid-secreting parietal cells at the fundus (near the entrance to the stomach).[12] In people producing normal or reduced amounts of acid, H. pylori can also colonize the rest of the stomach.
The inflammatory response caused by bacteria colonizing near the pyloric antrum induces G cells in the antrum to secrete the hormone gastrin, which travels through the bloodstream to parietal cells in the fundus.[40] Gastrin stimulates the parietal cells to secrete more acid into the stomach lumen, and over time increases the number of parietal cells, as well.[41] The increased acid load damages the duodenum, which may eventually result in ulcers forming in the duodenum.
When H. pylori colonizes other areas of the stomach, the inflammatory response can result in atrophy of the stomach lining and eventually ulcers in the stomach. This also may increase the risk of stomach cancer.[42]
The cag pathogenicity island
The pathogenicity of H. pylori may be increased by genes of the cag pathogenicity island; about 50–70% of H. pylori strains in Western countries carry it.[43] Western people infected with strains carrying the cag PAI have a stronger inflammatory response in the stomach and are at a greater risk of developing peptic ulcers or stomach cancer than those infected with strains lacking the island.[12] Following attachment of H. pylori to stomach epithelial cells, the type IV secretion system expressed by the cag PAI "injects" the inflammation-inducing agent, peptidoglycan, from their own cell walls into the epithelial cells. The injected peptidoglycan is recognized by the cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor (immune sensor) Nod1, which then stimulates expression of cytokines that promote inflammation.[44]
The type-IV secretion apparatus also injects the cag PAI-encoded protein CagA into the stomach's epithelial cells, where it disrupts the cytoskeleton, adherence to adjacent cells, intracellular signaling, cell polarity, and other cellular activities.[45] Once inside the cell, the CagA protein is phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by a host cell membrane-associated tyrosine kinase (TK). CagA then allosterically activates protein tyrosine phosphatase/protooncogene Shp2.[46] Pathogenic strains of H. pylori have been shown to activate the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a membrane protein with a TK domain. Activation of the EGFR by H. pylori is associated with altered signal transduction and gene expression in host epithelial cells that may contribute to pathogenesis. A C-terminal region of the CagA protein (amino acids 873–1002) has also been suggested to be able to regulate host cell gene transcription, independent of protein tyrosine phosphorylation.[28][29] A great deal of diversity exists between strains of H. pylori, and the strain with which one is infected is predictive of the outcome.
Cancer
Two related mechanisms by which H. pylori could promote cancer are under investigation. One mechanism involves the enhanced production of free radicals near H. pylori and an increased rate of host cell mutation. The other proposed mechanism has been called a "perigenetic pathway",[47] and involves enhancement of the transformed host cell phenotype by means of alterations in cell proteins, such as adhesion proteins. H. pylori has been proposed to induce inflammation and locally high levels of TNF-α and/or interleukin 6 (IL-6). According to the proposed perigenetic mechanism, inflammation-associated signaling molecules, such as TNF-α, can alter gastric epithelial cell adhesion and lead to the dispersion and migration of mutated epithelial cells without the need for additional mutations in tumor suppressor genes, such as genes that code for cell adhesion proteins.[48]
The strain of H. pylori to which a person is exposed may influence the risk of developing gastric cancer. Strains of H. pylori that produce high levels of two proteins, vacuolating toxin A (VacA) and the cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA), appear to cause greater tissue damage than those that produce lower levels or that lack those genes completely. These proteins are directly toxic to cells lining the stomach and signal strongly to the immune system that an invasion is underway. As a result of the bacterial presence, neutrophils and macrophages set up residence in the tissue to fight the bacteria assault. [49]
Survival of H. pylori
The pathogenesis of H. pylori depends on its ability to survive in the harsh gastric environment characterized by acidity, peristalsis, and attack by phagocytes accompanied by release of reactive oxygen species.[50] In particular, H. pylori elicits an oxidative stress response during host colonization. This oxidative stress response induces potentially lethal and mutagenic oxidative DNA adducts in the H. pylori genome.[51]
Vulnerability to oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage occurs commonly in many studied bacterial pathogens, including Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Hemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. mutans, and H. pylori.[52] For each of these pathogens, surviving the DNA damage induced by oxidative stress appears to be supported by transformation-mediated recombinational repair. Thus, transformation and recombinational repair appear to contribute to successful infection.
Transformation (the transfer of DNA from one bacterial cell to another through the intervening medium) appears to be part of an adaptation for DNA repair. H. pylori is naturally competent for transformation. While many organisms are competent only under certain environmental conditions, such as starvation, H. pylori is competent throughout logarithmic growth.[53] All organisms encode genetic programs for response to stressful conditions including those that cause DNA damage.[53] In H. pylori, homologous recombination is required for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The AddAB helicase-nuclease complex resects DSBs and loads RecA onto single-strand DNA (ssDNA), which then mediates strand exchange, leading to homologous recombination and repair. The requirement of RecA plus AddAB for efficient gastric colonization suggests, in the stomach, H. pylori is either exposed to double-strand DNA damage that must be repaired or requires some other recombination-mediated event. In particular, natural transformation is increased by DNA damage in H. pylori, and a connection exists between the DNA damage response and DNA uptake in H. pylori,[53] suggesting natural competence contributes to persistence of H. pylori in its human host and explains the retention of competence in most clinical isolates.
RuvC protein is essential to the process of recombinational repair, since it resolves intermediates in this process termed Holliday junctions. H. pylori mutants that are defective in RuvC have increased sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents and to oxidative stress, exhibit reduced survival within macrophages, and are unable to establish successful infection in a mouse model.[54] Similarly, RecN protein plays an important role in DSB repair in H. pylori.[55] An H. pylori recN mutant displays an attenuated ability to colonize mouse stomachs, highlighting the importance of recombinational DNA repair in survival of H. pylori within its host.[55]
Diagnosis

Colonization with H. pylori is not a disease in and of itself, but a condition associated with a number of disorders of the upper gastrointestinal tract.[12] Testing for H. pylori is recommended if peptic ulcer disease or low-grade gastric MALT lymphoma is present, after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer, first-degree relatives h gastric cancer, and in certain cases of dyspepsia,[56] not routinely.[12] Several ways of testing exist. One can test noninvasively for H. pylori infection with a blood antibody test, stool antigen test, or with the carbon urea breath test (in which the patient drinks 14C—or 13C-labelled urea, which the bacterium metabolizes, producing labelled carbon dioxide that can be detected in the breath).[56] Also, a urine ELISA test with a 96% sensitivity and 79% specificity is available. None of the test methods is completely failsafe. Even biopsy is dependent on the location of the biopsy. Blood antibody tests, for example, range from 76% to 84% sensitivity. Some drugs can affect H. pylori urease activity and give false negatives with the urea-based tests. The most accurate method for detecting H. pylori infection is with a histological examination from two sites after endoscopic biopsy, combined with either a rapid urease test or microbial culture.[57]
Prevention
H. pylori is a major cause of certain diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Rising antibiotic resistance increases the need to search for new therapeutic strategies; this might include prevention in form of vaccination.[58] Much work has been done on developing viable vaccines aimed at providing an alternative strategy to control H. pylori infection and related diseases, including stomach cancer.[59] Researchers are studying different adjuvants, antigens, and routes of immunization to ascertain the most appropriate system of immune protection; however, most of the research only recently moved from animal to human trials.[60] An economic evaluation of the use of a potential H. pylori vaccine in babies found its introduction could, at least in the Netherlands, prove cost-effective for the prevention of peptic ulcer and stomach cancer.[61] A similar approach has also been studied for the United States.[62]
The presence of bacteria in the stomach may be beneficial, reducing the prevalence of asthma,[63] rhinitis,[63] dermatitis,[63] inflammatory bowel disease,[63] gastroesophageal reflux disease,[64] and esophageal cancer[64] by influencing systemic immune responses.[63][65]
Recent evidence suggests that nonpathogenic strains of H. pylori may be beneficial, e.g., by normalizing stomach acid secretion,[66] and may play a role in regulating appetite, since its presence in the stomach results in a persistent but reversible reduction in the level of ghrelin.[66]
Treatment
Once H. pylori is detected in a person with a peptic ulcer, the normal procedure is to eradicate it and allow the ulcer to heal. The standard first-line therapy is a one-week "triple therapy" consisting of proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole and the antibiotics clarithromycin and amoxicillin.[67] Variations of the triple therapy have been developed over the years, such as using a different proton pump inhibitor, as with pantoprazole or rabeprazole, or replacing amoxicillin with metronidazole for people who are allergic to penicillin.[68] Such a therapy has revolutionized the treatment of peptic ulcers and has made a cure to the disease possible. Previously, the only option was symptom control using antacids, H2-antagonists or proton pump inhibitors alone.[69][70]
An increasing number of infected individuals are found to harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This results in initial treatment failure and requires additional rounds of antibiotic therapy or alternative strategies, such as a quadruple therapy, which adds a bismuth colloid, such as bismuth subsalicylate.[56][71][72] For the treatment of clarithromycin-resistant strains of H. pylori, the use of levofloxacin as part of the therapy has been suggested.[73][74]
Ingesting lactic acid bacteria exerts a suppressive effect on H. pylori infection in both animals and humans, and supplementing with Lactobacillus- and Bifidobacterium-containing yogurt improved the rates of eradication of H. pylori in humans.[75] Symbiotic butyrate-producing bacteria which are normally present in the intestine are sometimes used as probiotics to help suppress H. pylori infections as an adjunct to antibiotic therapy.[76] Butyrate itself is an antimicrobial which destroys the cell envelope of H. pylori by inducing regulatory T cell expression (specifically, FOXP3) and synthesis of an antimicrobial peptide called LL-37, which arises through its action as a histone deacetylase inhibitor.[77][78][79]
The substance sulforaphane, which occurs in broccoli and cauliflower, has been proposed as a treatment.[80][81][82] Periodontal therapy or scaling and root planing has also been suggested as an additional treatment.[83]
Prognosis
H. pylori colonizes the stomach and induces chronic gastritis, a long-lasting inflammation of the stomach. The bacterium persists in the stomach for decades in most people. Most individuals infected by H. pylori will never experience clinical symptoms despite having chronic gastritis. About 10–20% of those colonized by H. pylori will ultimately develop gastric and duodenal ulcers.[12] H. pylori infection is also associated with a 1–2% lifetime risk of stomach cancer and a less than 1% risk of gastric MALT lymphoma.[12]
In the absence of treatment, H. pylori infection—once established in its gastric niche—is widely believed to persist for life.[6] In the elderly, however, infection likely can disappear as the stomach's mucosa becomes increasingly atrophic and inhospitable to colonization. The proportion of acute infections that persist is not known, but several studies that followed the natural history in populations have reported apparent spontaneous elimination.[84][85]
Mounting evidence suggests H. pylori has an important role in protection from some diseases.[86] The incidence of acid reflux disease, Barrett's esophagus, and esophageal cancer have been rising dramatically at the same time as H. pylori's presence decreases.[87] In 1996, Martin J. Blaser advanced the hypothesis that H. pylori has a beneficial effect: by regulating the acidity of the stomach contents.[40][87] The hypothesis is not universally accepted as several randomized controlled trials failed to demonstrate worsening of acid reflux disease symptoms following eradication of H. pylori.[88][89] Nevertheless, Blaser has reasserted his view that H. pylori is a member of the normal flora of the stomach.[90] He postulates that the changes in gastric physiology caused by the loss of H. pylori account for the recent increase in incidence of several diseases, including type 2 diabetes, obesity, and asthma.[90][91] His group has recently shown that H. pylori colonization is associated with a lower incidence of childhood asthma.[92]
Epidemiology
At least half the world's population is infected by the bacterium, making it the most widespread infection in the world.[93] Actual infection rates vary from nation to nation; the developing world has much higher infection rates than the West (Western Europe, North America, Australasia), where rates are estimated to be around 25%.[93]
The age at which this bacterium is acquired seems to influence the possible pathologic outcome of the infection; people infected with it at an early age are likely to develop more intense inflammation that may be followed by atrophic gastritis with a higher subsequent risk of gastric ulcer, gastric cancer, or both. Acquisition at an older age brings different gastric changes more likely to lead to duodenal ulcer.[6] Infections are usually acquired in early childhood in all countries.[12] However, the infection rate of children in developing nations is higher than in industrialized nations, probably due to poor sanitary conditions, perhaps combined with lower antibiotics usage for unrelated pathologies. In developed nations, it is currently uncommon to find infected children, but the percentage of infected people increases with age, with about 50% infected for those over the age of 60 compared with around 10% between 18 and 30 years.[93] The higher prevalence among the elderly reflects higher infection rates in the past when the individuals were children rather than more recent infection at a later age of the individual.[12] In the United States, prevalence appears to be higher in African-American and Hispanic populations, most likely due to socioeconomic factors.[94][95] The lower rate of infection in the West is largely attributed to higher hygiene standards and widespread use of antibiotics. Despite high rates of infection in certain areas of the world, the overall frequency of H. pylori infection is declining.[96] However, antibiotic resistance is appearing in H. pylori; many metronidazole- and clarithromycin-resistant strains are found in most parts of the world.[97]
H. pylori is contagious, although the exact route of transmission is not known.[98][99] Person-to-person transmission by either the oral–oral or fecal–oral route is most likely. Consistent with these transmission routes, the bacteria have been isolated from feces, saliva, and dental plaque of some infected people. Findings suggest H. pylori is more easily transmitted by gastric mucus than saliva.[6] Transmission occurs mainly within families in developed nations, yet can also be acquired from the community in developing countries.[100] H. pylori may also be transmitted orally by means of fecal matter through the ingestion of waste-tainted water, so a hygienic environment could help decrease the risk of H. pylori infection.[6]
Evolution
H. pylori migrated out of Africa along with its human host circa 60,000 years ago.[101] Its subsequent evolution created seven prototypes—Europe (isolated from Europe, the Middle East, India, and Iran), NE Africa (from northeast Africa), Africa1 (from countries in Western Africa and South Africa), Africa2 (from South Africa), Asia2 (from Northern India and among isolates from Bangladesh, Thailand, and Malaysia), Sahul (from Australian Aboriginals and Papua New Guineans) and East Asia with the subpopulations E Asia (from East Asians), Maori (from Taiwanese Aboriginals, Melanesians and Polynesians) and Amerind (Native Americans). The precursors of these prototypes have been named ancestral Europe1, ancestral Europe2, ancestral East Asia, ancestral Africa1, ancestral Africa2, and ancestral Sahul. These ancestral prototypes appear to have originated in Africa and Central and East Asia. European and African strains were introduced into the Americas along with its colonisation—both thousands of years ago and more recently in the slave trade.
Recent research states that genetic diversity in H. pylori, like that of its host, decreases with geographic distance from East Africa. Using the genetic diversity data, researchers have created simulations that indicate the bacteria seem to have spread from East Africa around 58,000 years ago. Their results indicate modern humans were already infected by H. pylori before their migrations out of Africa, and it has remained associated with human hosts since that time.[102]
History
H. pylori was first discovered in the stomachs of patients with gastritis and ulcers in 1982 by Drs. Barry Marshall and Robin Warren of Perth, Australia. At the time, the conventional thinking was that no bacterium could live in the acid environment of the human stomach. In recognition of their discovery, Marshall and Warren were awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.[103]
Before the research of Marshall and Warren, German scientists found spiral-shaped bacteria in the lining of the human stomach in 1875, but they were unable to culture them, and the results were eventually forgotten.[87] The Italian researcher Giulio Bizzozero described similarly shaped bacteria living in the acidic environment of the stomach of dogs in 1893.[104] Professor Walery Jaworski of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków investigated sediments of gastric washings obtained by lavage from humans in 1899. Among some rod-like bacteria, he also found bacteria with a characteristic spiral shape, which he called Vibrio rugula. He was the first to suggest a possible role of this organism in the pathogenesis of gastric diseases. His work was included in the Handbook of Gastric Diseases, but it had little impact, as it was written in Polish.[105] Several small studies conducted in the early 20th century demonstrated the presence of curved rods in the stomachs of many people with peptic ulcers and stomach cancers.[106] Interest in the bacteria waned, however, when an American study published in 1954 failed to observe the bacteria in 1180 stomach biopsies.[107]
Interest in understanding the role of bacteria in stomach diseases was rekindled in the 1970s, with the visualization of bacteria in the stomachs of people with gastric ulcers.[108] The bacteria had also been observed in 1979, by Robin Warren, who researched it further with Barry Marshall from 1981. After unsuccessful attempts at culturing the bacteria from the stomach, they finally succeeded in visualizing colonies in 1982, when they unintentionally left their Petri dishes incubating for five days over the Easter weekend. In their original paper, Warren and Marshall contended that most stomach ulcers and gastritis were caused by bacterial infection and not by stress or spicy food, as had been assumed before.[109]
Some skepticism was expressed initially, but within a few years multiple research groups had verified the association of H. pylori with gastritis and, to a lesser extent, ulcers.[110] To demonstrate H. pylori caused gastritis and was not merely a bystander, Marshall drank a beaker of H. pylori culture. He became ill with nausea and vomiting several days later. An endoscopy 10 days after inoculation revealed signs of gastritis and the presence of H. pylori. These results suggested H. pylori was the causative agent. Marshall and Warren went on to demonstrate antibiotics are effective in the treatment of many cases of gastritis. In 1987, the Sydney gastroenterologist Thomas Borody invented the first triple therapy for the treatment of duodenal ulcers.[111] In 1994, the National Institutes of Health stated most recurrent duodenal and gastric ulcers were caused by H. pylori, and recommended antibiotics be included in the treatment regimen.[112]
The bacterium was initially named Campylobacter pyloridis, then renamed C. pylori (pylori being the genitive of pylorus, the circular opening leading from the stomach into the duodenum, from the Ancient Greek word πυλωρός, which means gatekeeper.[113]). When 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing and other research showed in 1989 that the bacterium did not belong in the genus Campylobacter, it was placed in its own genus, Helicobacter from the ancient Greek hělix/έλιξ "spiral" or "coil".[113]
In October 1987, a group of experts met in Copenhagen to found the European Helicobacter Study Group (EHSG), an international multidisciplinary research group and the only institution focused on H. pylori.[114] The Group is involved with the Annual International Workshop on Helicobacter and Related Bacteria,[115] the Maastricht Consensus Reports (European Consensus on the management of H. pylori),[116][117][118][119] and other educational and research projects, including two international long-term projects:
- European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg) – a database systematically registering the routine clinical practice of European gastroenterologists[120]
- Optimal H. pylori management in primary care (OptiCare) – a long-term educational project aiming to disseminate the evidence based recommendations of the Maastricht IV Consensus to primary care physicians in Europe, funded by an educational grant from United European Gastroenterology[121]
See also
References
- ^ "Helicobacter". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster., "pylori". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster..
- ^ "pylori". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ^ Blaser MJ (2006). "Who are we? Indigenous microbes and the ecology of human diseases" (PDF). EMBO Reports. 7 (10): 956–60. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400812. PMC 1618379. PMID 17016449.
- ^ Amieva, Manuel; Peek, Richard M. (2016). "Pathobiology of Helicobacter pylori–Induced Gastric Cancer". Gastroenterology. 150 (1): 64–78. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.004. ISSN 0016-5085. PMID 26385073.
- ^ Yamaoka, Yoshio (2008). Helicobacter pylori: Molecular Genetics and Cellular Biology. Caister Academic Pr. ISBN 1-904455-31-X.
- ^ a b c d e f Brown LM (2000). "Helicobacter pylori: epidemiology and routes of transmission" (PDF). Epidemiol Rev. 22 (2): 283–97. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a018040. PMID 11218379.
- ^ Bytzer P, Dahlerup JF, Eriksen JR, Jarbøl DE, Rosenstock S, Wildt S (April 2011). "Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection". Dan Med Bull. 58 (4): C4271. PMID 21466771. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ Butcher, Graham P. (2003). Gastroenterology: An Illustrated Colour Text. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 25. ISBN 0-443-06215-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Butcher 2003, pp. 24–5
- ^ Ryan, Kenneth (2010). Sherris Medical Microbiology. McGraw-Hill. pp. 573, 576. ISBN 978-0-07-160402-4.
- ^ Chang, A. H.; Parsonnet, J. (2010). "Role of Bacteria in Oncogenesis". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 23 (4): 837–857. doi:10.1128/CMR.00012-10. ISSN 0893-8512. PMC 2952975. PMID 20930075.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Kusters JG, van Vliet AH, Kuipers EJ (July 2006). "Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection". Clin Microbiol Rev. 19 (3): 449–90. doi:10.1128/CMR.00054-05. PMC 1539101. PMID 16847081.
- ^ Suerbaum S, Michetti P (October 2002). "Helicobacter pylori infection". N. Engl. J. Med. 347 (15): 1175–86. doi:10.1056/NEJMra020542. PMID 12374879.
- ^ Fuccio L, Zagari RM, Eusebi LH, Laterza L, Cennamo V, Ceroni L, Grilli D, Bazzoli F (2009). "Meta-analysis: can Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment reduce the risk for gastric cancer?". Ann Intern Med. 151 (2): 121–8. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-2-200907210-00009. PMID 19620164.
- ^ Wu Q, Yang ZP, Xu P, Gao LC, Fan DM (2013). "Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of colorectal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Colorectal Dis. 15 (7): e352–64. doi:10.1111/codi.12284. PMID 23672575.
- ^ Saccà, SC; Vagge, A; Pulliero, A; Izzotti, A (December 2014). "Helicobacter pylori infection and eye diseases: a systematic review". Medicine. 93 (28): e216. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000000216. PMID 25526440.
- ^ Olson JW, Maier RJ (November 2002). "Molecular hydrogen as an energy source for Helicobacter pylori". Science. 298 (5599): 1788–90. doi:10.1126/science.1077123. PMID 12459589.
- ^ Stark RM, Gerwig GJ, Pitman RS, Potts LF, Williams NA, Greenman J, Weinzweig IP, Hirst TR, Millar MR (February 1999). "Biofilm formation by Helicobacter pylori". Lett Appl Microbiol. 28 (2): 121–6. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00481.x. PMID 10063642.
- ^ Chan WY, Hui PK, Leung KM, Chow J, Kwok F, Ng CS (October 1994). "Coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori in the human stomach". Am J Clin Pathol. 102 (4): 503–7. PMID 7524304.
- ^ Josenhans C, Eaton KA, Thevenot T, Suerbaum S (August 2000). "Switching of Flagellar Motility in Helicobacter pylori by Reversible Length Variation of a Short Homopolymeric Sequence Repeat in fliP, a Gene Encoding a Basal Body Protein". Infect Immun. 68 (8): 4598–603. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.8.4598-4603.2000. PMC 98385. PMID 10899861.
- ^ Rust M, Schweinitzer T, Josenhans C (2008). "Helicobacter Flagella, Motility and Chemotaxis". In Yamaoka Y (ed.). Helicobacter pylori: Molecular Genetics and Cellular Biology. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 1-904455-31-X.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Tomb JF, White O, Kerlavage AR, Clayton RA, Sutton GG, Fleischmann RD, Ketchum KA, Klenk HP, Gill S, Dougherty BA, Nelson K, Quackenbush J, Zhou L, Kirkness EF, Peterson S, Loftus B, Richardson D, Dodson R, Khalak HG, Glodek A, McKenney K, Fitzegerald LM, Lee N, Adams MD, Hickey EK, Berg DE, Gocayne JD, Utterback TR, Peterson JD, Kelley JM, Cotton MD, Weidman JM, Fujii C, Bowman C, Watthey L, Wallin E, Hayes WS, Borodovsky M, Karp PD, Smith HO, Fraser CM, Venter JC (August 1997). "The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori". Nature. 388 (6642): 539–47. doi:10.1038/41483. PMID 9252185.
- ^ "Genome information for the H. pylori 26695 and J99 strains". Institut Pasteur. 2002. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^ a b "Helicobacter pylori 26695, complete genome". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^ "Helicobacter pylori J99, complete genome". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^ Oh JD, Kling-Bäckhed H, Giannakis M, Xu J, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, Cordum HS, Wang C, Elliott G, Edwards J, Mardis ER, Engstrand LG, Gordon JI (June 2006). "The complete genome sequence of a chronic atrophic gastritis Helicobacter pylori strain: Evolution during disease progression". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103 (26): 9999–10004. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603784103. PMC 1480403. PMID 16788065.
- ^ a b c Sharma, C. M.; Hoffmann, S.; Darfeuille, F.; Reignier, J. R. M.; Findeiss, S.; Sittka, A.; Chabas, S.; Reiche, K.; Hackermüller, J. R.; Reinhardt, R.; Stadler, P. F.; Vogel, J. R. (2010). "The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori". Nature. 464 (7286): 250–255. doi:10.1038/nature08756. PMID 20164839.
- ^ a b Baldwin DN, Shepherd B, Kraemer P, Hall MK, Sycuro LK, Pinto-Santini DM, Salama NR (February 2007). "Identification of Helicobacter pylori Genes That Contribute to Stomach Colonization". Infect Immun. 75 (2): 1005–16. doi:10.1128/IAI.01176-06. PMC 1828534. PMID 17101654.
- ^ a b Broutet N, Marais A, Lamouliatte H, de Mascarel A, Samoyeau R, Salamon R, Mégraud F (April 2001). "cagA Status and Eradication Treatment Outcome of Anti-Helicobacter pylori Triple Therapies in Patients with Nonulcer Dyspepsia" (PDF). J Clin Microbiol. 39 (4): 1319–22. doi:10.1128/JCM.39.4.1319-1322.2001. PMC 87932. PMID 11283049.
- ^ Amieva MR, El-Omar EM (January 2008). "Host-bacterial interactions in Helicobacter pylori infection". Gastroenterology. 134 (1): 306–23. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.009. PMID 18166359.
- ^ Schreiber S, Konradt M, Groll C, Scheid P, Hanauer G, Werling HO, Josenhans C, Suerbaum S (April 2004). "The spatial orientation of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucus". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (14): 5024–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308386101. PMC 387367. PMID 15044704.
- ^ Petersen AM, Krogfelt KA (May 2003). "Helicobacter pylori: an invading microorganism? A review". FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 36 (3): 117–26. doi:10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00020-8. PMID 12738380.
- ^ Ilver D, Arnqvist A, Ogren J, Frick IM, Kersulyte D, Incecik ET, Berg DE, Covacci A, Engstrand L, Borén T (January 1998). "Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding fucosylated histo-blood group antigens revealed by retagging". Science. 279 (5349): 373–7. doi:10.1126/science.279.5349.373. PMID 9430586.
- ^ Mahdavi J, Sondén B, Hurtig M, Olfat FO, Forsberg L, Roche N, Angstrom J, Larsson T, Teneberg S, Karlsson KA, Altraja S, Wadström T, Kersulyte D, Berg DE, Dubois A, Petersson C, Magnusson KE, Norberg T, Lindh F, Lundskog BB, Arnqvist A, Hammarström L, Borén T (July 2002). "Helicobacter pylori SabA Adhesin in Persistent Infection and Chronic Inflammation". Science. 297 (5581): 573–8. doi:10.1126/science.1069076. PMC 2570540. PMID 12142529.
- ^ Smoot DT (December 1997). "How does Helicobacter pylori cause mucosal damage? Direct mechanisms". Gastroenterology. 113 (6 Suppl): S31–4, discussion S50. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(97)80008-X. PMID 9394757.
- ^ Hatakeyama M, Higashi H (2005). "Helicobacter pylori CagA: A new paradigm for bacterial carcinogenesis". Cancer Science. 96 (12): 835–43. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00130.x. PMID 16367902.
- ^ Dumrese C, Slomianka L, Ziegler U, Choi SS, Kalia A, Fulurija A, Lu W, Berg DE, Benghezal M, Marshall B, Mittl PR (May 2009). "The secreted Helicobacter cysteine-rich protein A causes adherence of human monocytes and differentiation into a macrophage-like phenotype". FEBS Letters. 583 (10): 1637–43. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.04.027. PMC 2764743. PMID 19393649.
- ^ Shiotani A, Graham DY (November 2002). "Pathogenesis and therapy of gastric and duodenal ulcer disease". Med. Clin. North Am. 86 (6): 1447–66, viii. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(02)00083-4. PMID 12510460.
- ^ Dixon MF (February 2000). "Patterns of inflammation linked to ulcer disease". Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 14 (1): 27–40. doi:10.1053/bega.1999.0057. PMID 10749087.
- ^ a b Blaser MJ, Atherton JC (February 2004). "Helicobacter pylori persistence: biology and disease". J. Clin. Invest. 113 (3): 321–33. doi:10.1172/JCI20925. PMC 324548. PMID 14755326.
- ^ Schubert ML, Peura DA (June 2008). "Control of gastric acid secretion in health and disease". Gastroenterology. 134 (7): 1842–60. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.021. PMID 18474247.
- ^ Suerbaum S, Michetti P (October 2002). "Helicobacter pylori infection". N. Engl. J. Med. 347 (15): 1175–86. doi:10.1056/NEJMra020542. PMID 12374879.
- ^ Peek RM, Crabtree JE (January 2006). "Helicobacter infection and gastric neoplasia". J. Pathol. 208 (2): 233–48. doi:10.1002/path.1868. PMID 16362989.
- ^ Viala J, Chaput C, Boneca IG, Cardona A, Girardin SE, Moran AP, Athman R, Mémet S, Huerre MR, Coyle AJ, DiStefano PS, Sansonetti PJ, Labigne A, Bertin J, Philpott DJ, Ferrero RL (November 2004). "Nod1 responds to peptidoglycan delivered by the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island". Nat. Immunol. 5 (11): 1166–74. doi:10.1038/ni1131. PMID 15489856.
- ^ Backert S, Selbach M (August 2008). "Role of type IV secretion in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis". Cell. Microbiol. 10 (8): 1573–81. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01156.x. PMID 18410539.
- ^ Hatakeyama M (September 2004). "Oncogenic mechanisms of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein". Nat Rev Cancer. 4 (9). United States: 688–94. doi:10.1038/nrc1433. PMID 15343275.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laysource=,|laysummary=, and|laydate=(help) - ^ Tsuji S, Kawai N, Tsujii M, Kawano S, Hori M (July 2003). "Review article: inflammation-related promotion of gastrointestinal carcinogenesis--a perigenetic pathway". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 18 (Suppl 1): 82–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.18.s1.22.x. PMID 12925144.
- ^ Suganuma M, Yamaguchi K, Ono Y, Matsumoto H, Hayashi T, Ogawa T, Imai K, Kuzuhara T, Nishizono A, Fujiki H (July 2008). "TNF-α-inducing protein, a carcinogenic factor secreted from H. pylori, enters gastric cancer cells". Int. J. Cancer. 123 (1): 117–22. doi:10.1002/ijc.23484. PMID 18412243.
- ^ Kim, W.; Moss, S.F. (December 2008). "The role of H. pylori in the development of stomach cancer". Oncology Review. 1 (Suppl 1): 165–168. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ Olczak AA, Olson JW, Maier RJ (June 2002). "Oxidative-stress resistance mutants of Helicobacter pylori". J. Bacteriol. 184 (12): 3186–93. doi:10.1128/JB.184.12.3186-3193.2002. PMC 135082. PMID 12029034.
- ^ O'Rourke EJ, Chevalier C, Pinto AV, Thiberge JM, Ielpi L, Labigne A, Radicella JP (March 2003). "Pathogen DNA as target for host-generated oxidative stress: role for repair of bacterial DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori colonization". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (5): 2789–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.0337641100. PMC 151419. PMID 12601164.
- ^ Michod RE, Bernstein H, Nedelcu AM (May 2008). "Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens". Infect. Genet. Evol. 8 (3): 267–85. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002. PMID 18295550.
- ^ a b c Dorer MS, Fero J, Salama NR (2010). Blanke SR (ed.). "DNA damage triggers genetic exchange in Helicobacter pylori". PLoS Pathog. 6 (7): e1001026. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001026. PMC 2912397. PMID 20686662.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Loughlin MF, Barnard FM, Jenkins D, Sharples GJ, Jenks PJ (April 2003). "Helicobacter pylori mutants defective in RuvC Holliday junction resolvase display reduced macrophage survival and spontaneous clearance from the murine gastric mucosa". Infect. Immun. 71 (4): 2022–31. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.4.2022-2031.2003. PMC 152077. PMID 12654822.
- ^ a b Wang G, Maier RJ (January 2008). "Critical role of RecN in recombinational DNA repair and survival of Helicobacter pylori". Infect. Immun. 76 (1): 153–60. doi:10.1128/IAI.00791-07. PMC 2223656. PMID 17954726.
- ^ a b c Stenström B, Mendis A, Marshall B (August 2008). "Helicobacter pylori—The latest in diagnosis and treatment". Aust Fam Physician. 37 (8): 608–12. PMID 18704207.
- ^ Logan RP, Walker MM (October 2001). "Epidemiology and diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection". BMJ. 323 (7318): 920–2. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7318.920. PMC 1121445. PMID 11668141.
- ^ Selgrad M, Malfertheiner P (October 2008). "New strategies for Helicobacter pylori eradication". Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8 (5): 593–7. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2008.04.010. PMID 18555746.
- ^ Blanchard, T G; Nedrud, J G (2010). "9. Helicobacter pylori Vaccines". In Sutton, Philip; Mitchell, Hazel (eds.). Helicobacter Pylori in the 21st Century. Mitchell, Hazel. CABI. pp. 167–189. ISBN 978-1-84593-594-8. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ Kabir S (April 2007). "The current status of Helicobacter pylori vaccines: a review". Helicobacter. 12 (2): 89–102. doi:10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00478.x. PMID 17309745.
- ^ de Vries R, Klok RM, Brouwers JR, Postma MJ (February 2009). "Cost-effectiveness of a potential future Helicobacter pylori vaccine in the Netherlands: the impact of varying the discount rate for health". Vaccine. 27 (6): 846–52. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.11.081. PMID 19084566.
- ^ Rupnow MF, Chang AH, Shachter RD, Owens DK, Parsonnet J (October 2009). "Cost-effectiveness of a potential prophylactic Helicobacter pylori vaccine in the United States". J. Infect. Dis. 200 (8): 1311–7. doi:10.1086/605845. PMID 19751153.
- ^ a b c d e Salama N. R.; et al. (2013). "Life in the human stomach: persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 11: 385–399. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3016.
- ^ a b Blaser M (2011). "Antibiotic overuse: Stop the killing of beneficial bacteria". Nature. 476 (7361): 393–4. doi:10.1038/476393a. PMID 21866137.
- ^ Willyard, C. Gut reaction. Nature 479, S5–S7 (2011)
- ^ a b Ackerman, Jennifer; Blaser, Martin (1 June 2012). "How Bacteria in Our Bodies Protect Our Health". Scientific American (June 1, 2012): 42. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain CA, Atherton J, Axon AT, Bazzoli F, Gensini GF, Gisbert JP, Graham DY, Rokkas T, El-Omar EM, Kuipers EJ (May 2012). "Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report". Gut. 61 (5): 646–64. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302084. PMID 22491499.
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain C, Bazzoli F, El-Omar E, Graham D, Hunt R, Rokkas T, Vakil N, Kuipers EJ (June 2007). "Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report". Gut. 56 (6): 772–81. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.101634. PMC 1954853. PMID 17170018.
- ^ Rauws EA, Tytgat GN (May 1990). "Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori". Lancet. 335 (8700): 1233–5. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(90)91301-P. PMID 1971318.
- ^ Graham DY, Lew GM, Evans DG, Evans DJ, Klein PD (August 1991). "Effect of triple therapy (antibiotics plus bismuth) on duodenal ulcer healing. A randomized controlled trial". Ann. Intern. Med. 115 (4): 266–9. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-115-4-266. PMID 1854110.
- ^ Fischbach L, Evans EL (August 2007). "Meta-analysis: the effect of antibiotic resistance status on the efficacy of triple and quadruple first-line therapies for Helicobacter pylori". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 26 (3): 343–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03386.x. PMID 17635369.
- ^ Graham DY, Shiotani A (June 2008). "Newer concepts regarding resistance in the treatment Helicobacter pylori infections". Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5 (6): 321–31. doi:10.1038/ncpgasthep1138. PMC 2841357. PMID 18446147.
- ^ Perna F, Zullo A, Ricci C, Hassan C, Morini S, Vaira D (November 2007). "Levofloxacin-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori re-treatment: role of bacterial resistance". Dig Liver Dis. 39 (11): 1001–5. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2007.06.016. PMID 17889627.
- ^ Hsu PI, Wu DC, Chen A, Peng NJ, Tseng HH, Tsay FW, Lo GH, Lu CY, Yu FJ, Lai KH (June 2008). "Quadruple rescue therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection after two treatment failures". Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 38 (6): 404–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2008.01951.x. PMID 18435764.
- ^ Wang KY, Li SN, Liu CS, Perng DS, Su YC, Wu DC, Jan CM, Lai CH, Wang TN, Wang WM (September 2004). "Effects of ingesting Lactobacillus- and Bifidobacterium-containing yogurt in subjects with colonized Helicobacter pylori" (PDF). The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 80 (3): 737–41. PMID 15321816.
- ^ Franceschi F, Cazzato A, Nista EC, Scarpellini E, Roccarina D, Gigante G, Gasbarrini G, Gasbarrini A (2007). "Role of probiotics in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection". Helicobacter. 12 Suppl 2: 59–63. doi:10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00565.x. PMID 17991178.
- ^ Wang G (2014). "Human antimicrobial peptides and proteins". Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 7 (5): 545–94. doi:10.3390/ph7050545. PMC 4035769. PMID 24828484.
The establishment of a link between light therapy, vitamin D and human cathelicidin LL-37 expression provides a completely different way for infection treatment. Instead of treating patients with traditional antibiotics, doctors may be able to use light or vitamin D [291,292]. Indeed using narrow-band UV B light, the level of vitamin D was increased in psoriasis patients (psoriasis is a common autoimmune disease on skin) [293]. In addition, other small molecules such as butyrate can induce LL-37 expression [294]. Components from Traditional Chinese Medicine may regulate the AMP expression as well [295]. These factors may induce the expression of a single peptide or multiple AMPs [296]. It is also possible that certain factors can work together to induce AMP expression. While cyclic AMP and butyrate synergistically stimulate the expression of chicken β-defensin 9 [297], 4-phenylbutyrate (PBA) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (or lactose) can induce AMP gene expression synergistically [294,298]. It appears that stimulation of LL-37 expression by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors is cell dependent. Trichostatin and sodium butyrate increased the peptide expression in human NCI-H292 airway epithelial cells but not in the primary cultures of normal nasal epithelial cells [299]. However, the induction of the human LL-37 expression may not be a general approach for bacterial clearance. During Salmonella enterica infection of human monocyte-derived macrophages, LL-37 is neither induced nor required for bacterial clearance [300].
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
Table 3: Select human antimicrobial peptides and their proposed targets
Table 4: Some known factors that induce antimicrobial peptide expression - ^ Yonezawa H, Osaki T, Hanawa T, Kurata S, Zaman C, Woo TD, Takahashi M, Matsubara S, Kawakami H, Ochiai K, Kamiya S (2012). "Destructive effects of butyrate on the cell envelope of Helicobacter pylori". J. Med. Microbiol. 61 (Pt 4): 582–9. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.039040-0. PMID 22194341.
- ^ McGee DJ, George AE, Trainor EA, Horton KE, Hildebrandt E, Testerman TL (2011). "Cholesterol enhances Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics and LL-37". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55 (6): 2897–904. doi:10.1128/AAC.00016-11. PMC 3101455. PMID 21464244.
- ^ Moon JK, Kim JR, Ahn YJ, Shibamoto T (2010). "Analysis and anti-Helicobacter activity of sulforaphane and related compounds present in broccoli ( Brassica oleracea L.) sprouts". J. Agric. Food Chem. 58 (11): 6672–7. doi:10.1021/jf1003573. PMID 20459098.
- ^ Fahey JW, Haristoy X, Dolan PM, Kensler TW, Scholtus I, Stephenson KK, Talalay P, Lozniewski A (2002). "Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents benzo[a]pyrene-induced stomach tumors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (11): 7610–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.112203099. PMC 124299. PMID 12032331.
- ^ Haristoy X, Angioi-Duprez K, Duprez A, Lozniewski A (2003). "Efficacy of sulforaphane in eradicating Helicobacter pylori in human gastric xenografts implanted in nude mice". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47 (12): 3982–4. doi:10.1128/aac.47.12.3982-3984.2003. PMC 296232. PMID 14638516.
- ^ Ren, Q; Yan, X; Zhou, Y; Li, WX (7 February 2016). "Periodontal therapy as adjunctive treatment for gastric Helicobacter pylori infection". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2: CD009477. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009477.pub2. PMID 26852297.
- ^ Goodman KJ, O'rourke K, Day RS, Wang C, Nurgalieva Z, Phillips CV, Aragaki C, Campos A, de la Rosa JM (December 2005). "Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori infection in a US-Mexico cohort during the first two years of life". Int J Epidemiol. 34 (6): 1348–55. doi:10.1093/ije/dyi152. PMID 16076858.
- ^ Goodman KJ, Cockburn M (March 2001). "The role of epidemiology in understanding the health effects of Helicobacter pylori". Epidemiology. 12 (2): 266–71. doi:10.1097/00001648-200103000-00023. PMID 11246592.
- ^ Testerman TL, Morris J (2014). "Beyond the stomach: an updated view of Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment". World Journal of Gastroenterology (Review). 20 (36): 12781–808. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12781. PMC 4177463. PMID 25278678.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c Blaser MJ (February 2005). "An endangered species in the stomach". Sci. Am. 292 (2): 38–45. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0205-38. PMID 15715390.
- ^ Graham DY, Yamaoka Y, Malaty HM (November 2007). "Contemplating the Future without Helicobacter pylori and the Dire Consequences Hypothesis". Helicobacter. 12 (Suppl 2): 64–8. doi:10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00566.x. PMC 3128250. PMID 17991179.
- ^ Delaney B, McColl K (August 2005). "Review article: Helicobacter pylori and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 22 (Suppl 1): 32–40. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02607.x. PMID 16042657.
- ^ a b Blaser MJ (October 2006). "Who are we? Indigenous microbes and the ecology of human diseases". EMBO Reports. 7 (10): 956–60. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400812. PMC 1618379. PMID 17016449.
- ^ Blaser MJ, Chen Y, Reibman J (May 2008). "Does Helicobacter pylori protect against asthma and allergy?". Gut. 57 (5): 561–7. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.133462. PMID 18194986.
- ^ Chen Y, Blaser MJ (August 2008). "Helicobacter pylori colonization is inversely associated with childhood asthma". J. Infect. Dis. 198 (4): 553–60. doi:10.1086/590158. PMID 18598192.
- ^ a b c Pounder RE, Ng D (1995). "The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in different countries". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 9 (Suppl 2): 33–9. PMID 8547526.
- ^ Smoak BL, Kelley PW, Taylor DN (March 1994). "Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori infections in a cohort of US Army recruits". Am. J. Epidemiol. 139 (5): 513–9. PMID 8154475.
- ^ Everhart JE, Kruszon-Moran D, Perez-Perez GI, Tralka TS, McQuillan G (April 2000). "Seroprevalence and ethnic differences in Helicobacter pylori infection among adults in the United States". J. Infect. Dis. 181 (4): 1359–63. doi:10.1086/315384. PMID 10762567.
- ^ Malaty HM (2007). "Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 21 (2): 205–14. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2006.10.005. PMID 17382273.
- ^ Mégraud F (September 2004). "H pylori antibiotic resistance: prevalence, importance, and advances in testing". Gut. 53 (9): 1374–84. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.022111. PMC 1774187. PMID 15306603.
- ^ Mégraud F (1995). "Transmission of Helicobacter pylori: faecal–oral versus oral–oral route". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 9 (Suppl 2): 85–91. PMID 8547533.
- ^ Cave DR (May 1996). "Transmission and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori". Am. J. Med. 100 (5A): 12S–17S, discussion 17S–18S. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(96)80224-5. PMID 8644777.
- ^ Delport W, van der Merwe SW (2007). "The transmission of Helicobacter pylori: the effects of analysis method and study population on inference". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 21 (2): 215–36. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2006.10.001. PMID 17382274.
- ^ Correa P, Piazuelo MB (January 2012). "Evolutionary History of the Helicobacter pylori Genome: Implications for Gastric Carcinogenesis". Gut Liver. 6 (1): 21–8. doi:10.5009/gnl.2012.6.1.21. PMC 3286735. PMID 22375167.
- ^ Linz B, Balloux F, Moodley Y, Manica A, Liu H, Roumagnac P, Falush D, Stamer C, Prugnolle F, van der Merwe SW, Yamaoka Y, Graham DY, Perez-Trallero E, Wadstrom T, Suerbaum S, Achtman M (February 2007). "An African origin for the intimate association between humans and Helicobacter pylori". Nature. 445 (7130): 915–8. doi:10.1038/nature05562. PMC 1847463. PMID 17287725.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2005". Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Bizzozero G (1893). "Ueber die schlauchförmigen Drüsen des Magendarmkanals und die Beziehungen ihres Epitheles zu dem Oberflächenepithel der Schleimhaut". Archiv für mikroskopische Anatomie. 42: 82–152. doi:10.1007/BF02975307.
- ^ Konturek JW (December 2003). "Discovery by Jaworski of Helicobacter pylori and its pathogenetic role in peptic ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer" (PDF). J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 54 (Suppl 3): 23–41. PMID 15075463. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2004. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ^ Egan BJ, O'Morain CA (2007). "A historical perspective of Helicobacter gastroduodenitis and its complications". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 21 (2): 335–46. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2006.12.002. PMID 17382281.
- ^ Palmer ED (August 1954). "Investigation of the gastric mucosa spirochetes of the human". Gastroenterology. 27 (2): 218–20. PMID 13183283.
- ^ Steer HW (August 1975). "Ultrastructure of cell migration through the gastric epithelium and its relationship to bacteria" (PDF). J. Clin. Pathol. 28 (8): 639–46. doi:10.1136/jcp.28.8.639. PMC 475793. PMID 1184762.
- ^ Marshall BJ, Warren JR (June 1984). "Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration". Lancet. 1 (8390): 1311–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(84)91816-6. PMID 6145023.
- ^ Atwood IV KC (2004). "Bacteria, Ulcers, and Ostracism? H. pylori and the making of a myth". Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Borody TJ, Cole P, Noonan S, Morgan A, Lenne J, Hyland L, Brandl S, Borody EG, George LL (October 1989). "Recurrence of duodenal ulcer and Campylobacter pylori infection after eradication". Med. J. Aust. 151 (8): 431–5. PMID 2687668.
- ^ "Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease". NIH Consensus Statement Online. 7–9 January 1994. pp. 1–23. Retrieved 21 December 2004.
- ^ a b Liddell HG, Scott R (1966). A Lexicon: Abridged from Liddell and Scott's Greek-English Lexicon. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-910207-4.
- ^ Buckley MJ, O'Morain CA (1998). "Helicobacter biology—discovery". Br Med Bull. 54 (1): 7–16.
- ^ Mégraud F (November 2007). "European Helicobacter Study Group. Evolution of Helicobacter pylori research as observed through the workshops of the European Helicobacter Study Group". Helicobacter. 12 (Suppl 2): 1–5. doi:10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00581.x.
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain CA, Atherton J, Axon AT, Bazzoli F, Gensini GF, Gisbert JP, Graham DY, Rokkas T, El-Omar EM, Kuipers EJ (May 2012). "European Helicobacter Study Group. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report". Gut. 61 (5): 646–64. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302084. PMID 22491499.
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain C, Bazzoli F, El-Omar E, Graham D, Hunt R, Rokkas T, Vakil N, Kuipers EJ (June 2007). "Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report". Gut. 56 (6): 772–81. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.101634. PMC 1954853. PMID 17170018.
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Hungin AP, Jones R, Axon A, Graham DY, Tytgat G (February 2002). "European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group (EHPSG). Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report". Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 16 (2): 167–80. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2002.01169.x. PMID 11860399..
- ^ Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Bell D, Bianchi Porro G, Deltenre M, Forman D, Gasbarrini G, Jaup B, Misiewicz JJ, Pajares J, Quina M, Rauws E (January 1997). "Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht Consensus Report. The European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group (EHPSG)". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9 (1): 1–2.
- ^ McNicholl AG, Gasbarrini A, Tepes B, et al. (September 2014). "Pan-European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg): Interim Analysis of 5,792 Patients". Helicobacter. 2014: 69.
- ^ "Management of Helicobacter pylori infection" and "Annual Report 2012", United European Gastroenterology
