Affordable Care Act
 | |
| Long title | The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act |
|---|---|
| Acronyms (colloquial) | PPACA, ACA |
| Nicknames | Affordable Care Act, Health Insurance Reform, Healthcare Reform, Obamacare |
| Enacted by | the 111th United States Congress |
| Effective | March 23, 2010 Most major provisions phased in by January 2014; remaining provisions phased in by 2020 |
| Citations | |
| Public law | 111–148 |
| Statutes at Large | 124 Stat. 119 through 124 Stat. 1025 (906 pages) |
| Legislative history | |
| |
| Major amendments | |
| Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 Comprehensive 1099 Taxpayer Protection and Repayment of Exchange Subsidy Overpayments Act of 2011 | |
| United States Supreme Court cases | |
| National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius Burwell v. Hobby Lobby King v. Burwell | |
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), commonly called the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or Obamacare, is a United States federal statute enacted by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act amendment, it represents the most significant regulatory overhaul of the U.S. healthcare system since the passage of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965. Under the act, hospitals and primary physicians would transform their practices financially, technologically, and clinically to drive better health outcomes, lower costs, and improve their methods of distribution and accessibility.
The Affordable Care Act was intended to increase health insurance quality and affordability, lower the uninsured rate by expanding insurance coverage and reduce the costs of healthcare. It introduced mechanisms including mandates, subsidies and insurance exchanges.[1][2] The law requires insurers to accept all applicants, cover a specific list of conditions and charge the same rates regardless of pre-existing conditions or sex.[3] In 2011, the Congressional Budget Office projected that the ACA would lower future deficits[4] and Medicare spending.[5]
The law and its implementation faced challenges in Congress and federal courts, and from some state governments, conservative advocacy groups, labor unions, and small business organizations. The United States Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of the ACA's individual mandate as an exercise of Congress's taxing power,[6] found that states cannot be forced to participate in the ACA's Medicaid expansion,[7][8][9] and found that the law's subsidies to help individuals pay for health insurance are available in all states, not just in those that have set up state exchanges.
The law has caused a significant reduction in the number and percentage of people without health insurance. The CDC reported that the percentage of people without health insurance fell from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.9% during the January-June 2016 period.[10] The Congressional Budget Office reported in March 2016 that there were approximately 23 million people with insurance due to the law, with 12 million people covered by the exchanges (10 million of whom received subsidies to help pay for insurance) and 11 million made eligible for Medicaid.[11] By 2017, nearly 70% of those on the exchanges could purchase insurance for less than $75/month after subsidies, which rose to offset significant pre-subsidy price increases in the exchange markets.[12] According to the Kaiser Foundation, healthcare premium cost increases in the employer market continued to moderate. For example, healthcare premiums for those covered by employers rose by 69% from 2000-2005, but only 27% from 2010 to 2015,[13] with only a 3% increase from 2015 to 2016.[14]
As implementation began, first opponents and then most others adopted the term "Obamacare" to refer to the ACA.[15]
Provisions

The ACA includes provisions to take effect between 2010 and 2020, although most took effect on January 1, 2014. The number and complexity of changes was unprecedented[citation needed] in the US health care system. Not all provisions took full effect. Some were made discretionary, some were deferred and others were discarded before implementation.
Individual insurance
Guaranteed issue prohibits insurers from denying coverage to individuals due to pre-existing conditions. States were required to ensure the availability of insurance for individual children who did not have coverage via their families.
States were required to expand Medicaid eligibility to include individuals and families with incomes up to 133% of the federal poverty level, including adults without disabilities or dependent children.[16] The law provides a 5% "income disregard", making the effective income eligibility limit for Medicaid 138% of the poverty level.[17]
The State Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) enrollment process was simplified.[16]
Dependents were permitted to remain on their parents' insurance plan until their 26th birthday, including dependents that no longer live with their parents, are not a dependent on a parent's tax return, are no longer a student, or are married.[18][19]
Among the groups who remained uninsured were:
- Illegal immigrants, estimated at around 8 million—or roughly a third of the 23 million projection—are ineligible for insurance subsidies and Medicaid.[20][21] They remain eligible for emergency services.
- Eligible citizens not enrolled in Medicaid.[22]
- Citizens who pay the annual penalty instead of purchasing insurance, mostly younger and single.[22]
- Citizens whose insurance coverage would cost more than 8% of household income and are exempt from the penalty.[22]
- Citizens who live in states that opt out of the Medicaid expansion and who qualify for neither existing Medicaid coverage nor subsidized coverage through the states' new insurance exchanges.[23]
Subsidies
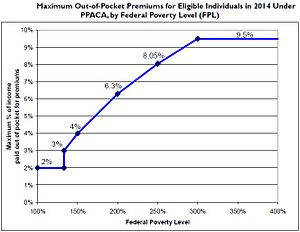
Households with incomes between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level were eligible to receive federal subsidies for policies purchased via an exchange.[24][25] Subsidies are provided as an advanceable, refundable tax credit[26][27] Small businesses are eligible for subsidies.[28] Under the law, workers whose employers offer "affordable coverage" will not be eligible for subsidies via the exchanges. To be eligible the cost of employer-based health insurance must exceed 9.5% of the worker's household income.
| Income % of federal poverty level | Premium Cap as a Share of Income | Incomea | Max Annual Out-of-Pocket Premium | Premium Savingsb | Additional Cost-Sharing Subsidy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 133% | 3% of income | $31,900 | $992 | $10,345 | $5,040 |
| 150% | 4% of income | $33,075 | $1,323 | $9,918 | $5,040 |
| 200% | 6.3% of income | $44,100 | $2,778 | $8,366 | $4,000 |
| 250% | 8.05% of income | $55,125 | $4,438 | $6,597 | $1,930 |
| 300% | 9.5% of income | $66,150 | $6,284 | $4,628 | $1,480 |
| 350% | 9.5% of income | $77,175 | $7,332 | $3,512 | $1,480 |
| 400% | 9.5% of income | $88,200 | $8,379 | $2,395 | $1,480 |
|
a.^ Note: In 2014, the FPL was $11,800 for a single person and $24,000 for family of four.[34][35] See Subsidy Calculator for specific dollar amount.[36] b.^ DHHS and CBO estimate the average annual premium cost in 2014 would have been $11,328 for a family of 4 without the reform.[31] | |||||
Premiums were the same for everyone of a given age, regardless of preexisting conditions. Premiums were allowed to vary by enrollee age, but those for the oldest enrollees (age 45-64 average expenses $5,542) could only be three times as large as those for adults (18-24 $1,836).[37]
Mandates
Individual
The individual mandate[38] is the requirement to buy insurance or pay a penalty for everyone not covered by an employer sponsored health plan, Medicaid, Medicare or other public insurance programs (such as Tricare). Also exempt were those facing a financial hardship or who were members in a recognized religious sect exempted by the Internal Revenue Service.[39]
The mandate and the limits on open enrollment[40][41] were designed to avoid the insurance death spiral in which healthy people delay insuring themselves until they get sick. In such a situation, insurers would have to raise their premiums to cover the relatively sicker and thus more expensive policies,[38][42][43] which could create a vicious cycle in which more and more people drop their coverage.[44]
The mandate was to allow a stable equilibrium relying on relatively high premiums for the insured and little coverage (and thus more illness and medical bankruptcy) for the uninsured.[42][45][46] Studies by the CBO, Gruber and Rand Health concluded that a mandate was required.[47][48][49] The mandate increased the size and diversity of the insured population, including more young and healthy participants to broaden the risk pool, spreading costs.[50] Experience in New Jersey and Massachusetts offered divergent outcomes.[45][48][51]
Business
Businesses that employ 50 or more people but do not offer health insurance to their full-time employees pay a tax penalty if the government has subsidized a full-time employee's healthcare through tax deductions or other means. This is commonly known as the employer mandate.[52][53] This provision was included to encourage employers to continue providing insurance once the exchanges began operating.[54] Approximately 44% of the population was covered directly or indirectly through an employer.[55][56]
Insurance standards
Essential health benefits
The Institute of Medicine defined the law's "essential health benefits" as "ambulatory patient services; emergency services; hospitalization; maternity and newborn care; mental health and substance use disorder services, including behavioral health treatment; prescription drugs; rehabilitative and habilitative services and devices; laboratory services; preventive and wellness services and chronic disease management; and pediatric services, including oral and vision care"[57][58][59][60][61][62][63] and others[64] rated Level A or B by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.[65] In determining what would qualify as an essential benefit, the law required that standard benefits should offer at least that of a "typical employer plan".[62] States may require additional services.[66]
Contraceptives
One provision in the law mandates that health insurance cover "additional preventive care and screenings" for women.[67] The guidelines mandate "[a]ll Food and Drug Administration approved contraceptive methods, sterilization procedures, and patient education and counseling for all women with reproductive capacity".[68] This mandate applies to all employers and educational institutions except for religious organizations.[69][70] These regulations were included on the recommendations of the Institute of Medicine.[71][72]
Risk management
ACA provided three ways to control risk for insurers in the individual and business markets: temporary reinsurance (insurance for insurers against unexpectedly high claims), temporary risk corridors and permanent risk adjustment. Risk adjustment was a permanent program. The other two closed after 2016. These limit insurer losses.[citation needed]
Risk adjustment attempts to spread risk among insurers to prevent purchasers with good knowledge of their medical needs from using insurance to cover their costs (adverse selection). Plans with low actuarial risk compensate plans with high actuarial risk.
Other provisions
Annual and lifetime coverage caps on essential benefits were banned.[73][74]
Prohibits insurers from dropping policyholders when they get sick.[75]
All health policies sold in the United States must cap an individual's (or family's) medical expenses out of pocket annually (excluding premiums).[76]
A partial community rating requires insurers to offer the same premium to all applicants of the same age and location without regard to gender or most pre-existing conditions (excluding tobacco use).[77][78][79] Premiums for older applicants can be no more than three times those for the youngest.[80]
Preventive care, vaccinations and medical screenings cannot be subject to co-payments, co-insurance or deductibles.[81][82][83] Specific examples of covered services include: mammograms and colonoscopies, wellness visits, gestational diabetes screening, HPV testing, STI counseling, HIV screening and counseling, contraceptive methods, breastfeeding support/supplies and domestic violence screening and counseling.[84]
The law established four tiers of coverage: bronze, silver, gold and platinum. All categories offer the essential health benefits. The categories vary in their division of premiums and out-of-pocket costs: bronze plans have the lowest monthly premiums and highest out-of-pocket costs, while platinum plans are the reverse.[62][85] The percentages of health care costs that plans are expected to cover through premiums (as opposed to out-of-pocket costs) are, on average: 60% (bronze), 70% (silver), 80% (gold), and 90% (platinum).[86]
Insurers are required to implement an appeals process for coverage determination and claims on all new plans.[75]
Insurers must spend at least 80–85% of premium dollars on health costs; rebates must be issued to policyholders if this is violated.[87][88]
Exchanges
Established the creation of health insurance exchanges in all fifty states. The exchanges are regulated, largely online marketplaces, administered by either federal or state government, where individuals and small business can purchase private insurance plans.[89][90][91]
Setting up an exchange gives a state partial discretion on standards and prices of insurance.[92][93] For example, states approve plans for sale, and influence (through limits on and negotiations with private insurers) the prices on offer. They can impose higher or state-specific coverage requirements—including whether plans offered in the state can cover abortion.[94] States without an exchange do not have that discretion. The responsibility for operating their exchanges moves to the federal government.[92]
State waivers
From 2017 onwards, states can apply for a "waiver for state innovation" that allows them to conduct experiments that meet certain criteria.[95] To obtain a waiver, a state must pass legislation setting up an alternative health system that provides insurance at least as comprehensive and as affordable as ACA, covers at least as many residents and does not increase the federal deficit.[96] Such states can exempt states from some of ACA's central requirements, including the individual and employer mandates and the provision of an insurance exchange.[97] The state would receive compensation equal to the aggregate amount of any federal subsidies and tax credits for which its residents and employers would have been eligible under ACA plan, if they cannot be paid out due to the structure of the state plan.[95]
In May 2011, Vermont enacted Green Mountain Care, a state-based single-payer system for which they intended to pursue a waiver to implement.[98][99][100] In December 2014, Vermont decided not to continue due to high expected costs.[101]
Accountable Care Organizations
The Act allowed the creation of Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), which are groups of doctors, hospitals and other providers that commit to give coordinated, high quality care to Medicare patients. ACOs were allowed to continue using a fee for service billing approach. They receive bonus payments from the government for minimizing costs while achieving quality benchmarks that emphasize prevention and mitigating chronic disease. If they fail to do so, they are subject to penalties.[102]
Unlike Health Maintenance Organizations, ACO patients are not required to obtain all care from the ACO. Also, unlike HMOs, ACOs must achieve quality of care goals.[102]
Others
- The Medicare payment system switched from fee-for-service to bundled payments.[103][104] A single payment was to be paid to a hospital and a physician group for a defined episode of care (such as a hip replacement) rather than individual payments to individual service providers. In addition, the Medicare Part D coverage gap (commonly called the "donut hole") was to shrink incrementally, closing completely by January 1, 2020.[105]
- The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRPP) was established as an addition to the Social Security Act, in an effort to reduce hospital readmissions. This program penalizes hospitals with higher than expected readmission rates by decreasing their Medicare reimbursement rate.
- Medicare Part D participants received a 50% discount on brand name drugs purchased after exhausting their initial coverage and before reaching the catastrophic-coverage threshold.[106]
- Health care cost/quality initiatives including incentives to reduce hospital infections, to adopt electronic medical records and adopt bundled payments to coordinate care and prioritize quality over quantity.[107]
- The Community Living Assistance Services and Supports Act (or CLASS Act) established a voluntary and public long-term care insurance option for employees,[108][109][110]
- Consumer Operated and Oriented Plans (CO-OP), member-governed non-profit insurers, could start providing health care coverage, based on a 5-year federal loan.[111]
Legislative history
Background
An individual mandate coupled with subsidies for private insurance as a means for universal healthcare was considered the best way to win the support of the Senate because it had been included in prior bipartisan reform proposals. The concept goes back to at least 1989, when the conservative Heritage Foundation proposed an individual mandate as an alternative to single-payer health care.[112] It was championed for a time by conservative economists and Republican senators as a market-based approach to healthcare reform on the basis of individual responsibility and avoidance of free rider problems. Specifically, because the 1986 Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA) requires any hospital participating in Medicare (nearly all do) to provide emergency care to anyone who needs it, the government often indirectly bore the cost of those without the ability to pay.[113][114][115]
President Bill Clinton proposed a healthcare reform bill in 1993 that included a mandate for employers to provide health insurance to all employees through a regulated marketplace of health maintenance organizations. Republican Senators proposed an alternative that would have required individuals, but not employers, to buy insurance.[114] Ultimately the Clinton plan failed amid an unprecedented barrage of negative advertising funded by politically conservative groups and the health insurance industry and due to concerns that it was overly complex.[116] Clinton negotiated a compromise with the 105th Congress to instead enact the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) in 1997.[117]

The 1993 Republican alternative, introduced by Senator John Chafee as the Health Equity and Access Reform Today Act, contained a "universal coverage" requirement with a penalty for noncompliance—an individual mandate—as well as subsidies to be used in state-based 'purchasing groups'.[118] Advocates for the 1993 bill included prominent Republicans such as Senators Orrin Hatch, Chuck Grassley, Bob Bennett and Kit Bond.[119][120] Of 1993's 43 Republican Senators, 20 supported the HEART Act.[112][121] Another Republican proposal, introduced in 1994 by Senator Don Nickles (R-OK), the Consumer Choice Health Security Act, contained an individual mandate with a penalty provision;[122] however, Nickles subsequently removed the mandate from the bill, stating he had decided "that government should not compel people to buy health insurance".[123] At the time of these proposals, Republicans did not raise constitutional issues with the mandate; Mark Pauly, who helped develop a proposal that included an individual mandate for George H. W. Bush, remarked, "I don't remember that being raised at all. The way it was viewed by the Congressional Budget Office in 1994 was, effectively, as a tax."[112]

In 2006, an insurance expansion bill was enacted at the state level in Massachusetts. The bill contained both an individual mandate and an insurance exchange. Republican Governor Mitt Romney vetoed the mandate, but after Democrats overrode his veto, he signed it into law.[125] Romney's implementation of the 'Health Connector' exchange and individual mandate in Massachusetts was at first lauded by Republicans. During Romney's 2008 presidential campaign, Senator Jim DeMint praised Romney's ability to "take some good conservative ideas, like private health insurance, and apply them to the need to have everyone insured". Romney said of the individual mandate: "I'm proud of what we've done. If Massachusetts succeeds in implementing it, then that will be the model for the nation."[126]
In 2007, a year after the Massachusetts reform, Republican Senator Bob Bennett and Democratic Senator Ron Wyden introduced the Healthy Americans Act, which featured an individual mandate and state-based, regulated insurance markets called "State Health Help Agencies".[115][126] The bill initially attracted bipartisan support, but died in committee. Many of the sponsors and co-sponsors remained in Congress during the 2008 healthcare debate.[127]
By 2008 many Democrats were considering this approach as the basis for healthcare reform. Experts said that the legislation that eventually emerged from Congress in 2009 and 2010 bore similarities to the 2007 bill[118] and that it was deliberately patterned after Romney's state healthcare plan.[128]
Healthcare debate, 2008–10
Healthcare reform was a major topic during the 2008 Democratic presidential primaries. As the race narrowed, attention focused on the plans presented by the two leading candidates, Hillary Clinton and the eventual nominee, Barack Obama. Each candidate proposed a plan to cover the approximately 45 million Americans estimated to not have health insurance at some point each year. Clinton's proposal would have required all Americans to obtain coverage (in effect, an individual mandate), while Obama's proposal provided a subsidy but rejected the use of an individual mandate.[129][130] During the general election, Obama said that fixing healthcare would be one of his top four priorities as president.[131]

After his inauguration, Obama announced to a joint session of Congress in February 2009 his intent to work with Congress to construct a plan for healthcare reform.[132][133] By July, a series of bills were approved by committees within the House of Representatives.[134] On the Senate side, from June to September, the Senate Finance Committee held a series of 31 meetings to develop a healthcare reform bill. This group — in particular, Democrats Max Baucus, Jeff Bingaman and Kent Conrad, along with Republicans Mike Enzi, Chuck Grassley and Olympia Snowe — met for more than 60 hours, and the principles that they discussed, in conjunction with the other committees, became the foundation of the Senate healthcare reform bill.[135][136][137]
Congressional Democrats and health policy experts like MIT economics professor Jonathan Gruber[138] and David Cutler argued that guaranteed issue would require both community rating and an individual mandate to ensure that adverse selection and/or "free riding" would not result in an insurance "death spiral".[139] This approach was taken because the president and congressional leaders had concluded that more progressive plans, such as the (single-payer) Medicare for All act, could not obtain filibuster-proof support in the Senate. By deliberately drawing on bipartisan ideas — the same basic outline was supported by former Senate majority leaders Howard Baker, Bob Dole, Tom Daschle and George J. Mitchell—the bill's drafters hoped to garner the votes necessary for passage.[140][141]
However, following the adoption of an individual mandate, Republicans came to oppose the mandate and threatened to filibuster any bills that contained it.[112] Senate minority leader Mitch McConnell, who led the Republican congressional strategy in responding to the bill, calculated that Republicans should not support the bill, and worked to prevent defections:[142]
It was absolutely critical that everybody be together because if the proponents of the bill were able to say it was bipartisan, it tended to convey to the public that this is O.K., they must have figured it out.[143]
Republican Senators, including those who had supported previous bills with a similar mandate, began to describe the mandate as "unconstitutional". Journalist Ezra Klein wrote in The New Yorker that "a policy that once enjoyed broad support within the Republican Party suddenly faced unified opposition."[115] Reporter Michael Cooper of The New York Times wrote that: "the provision ... requiring all Americans to buy health insurance has its roots in conservative thinking."[114][121]

The reform negotiations also attracted attention from lobbyists,[144] including deals between certain lobby groups and the advocates of the law to win the support of groups that had opposed past reforms, as in 1993.[145][146] The Sunlight Foundation documented many of the reported ties between "the healthcare lobbyist complex" and politicians in both parties.[147]
During the August 2009 summer congressional recess, many members went back to their districts and held town hall meetings on the proposals. The nascent Tea Party movement organized protests and many conservative groups and individuals attended the meetings to oppose the proposed reforms.[133] Many threats were made against members of Congress over the course of the debate.[148][149]
When Congress returned from recess, in September 2009 President Obama delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress supporting the ongoing Congressional negotiations.[150] He acknowledged the polarization of the debate, and quoted a letter from the late Senator Edward "Ted" Kennedy urging on reform: "what we face is above all a moral issue; that at stake are not just the details of policy, but fundamental principles of social justice and the character of our country."[151] On November 7, the House of Representatives passed the Affordable Health Care for America Act on a 220–215 vote and forwarded it to the Senate for passage.[133]
Senate

The Senate began work on its own proposals while the House was still working. The United States Constitution requires all revenue-related bills to originate in the House.[152] To formally comply with this requirement, the Senate used H.R. 3590, a bill regarding housing tax changes for service members.[153] It had been passed by the House as a revenue-related modification to the Internal Revenue Code. The bill became the Senate's vehicle for its healthcare reform proposal, discarding the bill's original content.[154] The bill ultimately incorporated elements of proposals that were reported favorably by the Senate Health and Finance committees. With the Republican Senate minority vowing to filibuster, 60 votes would be necessary to pass the Senate.[155] At the start of the 111th Congress, Democrats had only 58 votes; the Senate seat in Minnesota ultimately won by Al Franken was still undergoing a recount, while Arlen Specter was still a Republican (he became a Democrat in April, 2009).
Negotiations were undertaken attempting to satisfy moderate Democrats and to bring Republican senators aboard; particular attention was given to Republicans Bennett, Enzi, Grassley and Snowe. On July 7 Franken was sworn into office, providing a potential 60th vote. On August 25 Ted Kennedy—a longtime healthcare reform advocate—died. Paul Kirk was appointed as Senator Kennedy's temporary replacement on September 24.
After the Finance Committee vote on October 15, negotiations turned to moderate Democrats. Majority leader Harry Reid focused on satisfying centrists. The holdouts came down to Joe Lieberman of Connecticut, an independent who caucused with Democrats, and conservative Nebraska Democrat Ben Nelson. Lieberman's demand that the bill not include a public option[139][156] was met,[157] although supporters won various concessions, including allowing state-based public options such as Vermont's Green Mountain Care.[157][158]
The White House and Reid addressed Nelson's concerns[159] during a 13-hour negotiation with two concessions: a compromise on abortion, modifying the language of the bill "to give states the right to prohibit coverage of abortion within their own insurance exchanges", which would require consumers to pay for the procedure out of pocket if the state so decided; and an amendment to offer a higher rate of Medicaid reimbursement for Nebraska.[133][160] The latter half of the compromise was derisively termed the "Cornhusker Kickback"[161] and was repealed in the subsequent reconciliation amendment bill.
On December 23, the Senate voted 60–39 to end debate on the bill: a cloture vote to end the filibuster. The bill then passed, also 60–39, on December 24, 2009, with all Democrats and two independents voting for it, and all Republicans against (except Jim Bunning, who did not vote).[162] The bill was endorsed by the AMA and AARP.[163]
On January 19, 2010, Massachusetts Republican Scott Brown was elected to the Senate in a special election to replace Kennedy, having campaigned on giving the Republican minority the 41st vote needed to sustain Republican filibusters.[133][164][165] His victory had become significant because of its effects on the legislative process. The first was psychological: the symbolic importance of losing Kennedy's traditionally Democratic Massachusetts seat made many Congressional Democrats concerned about the political cost of passing a bill.[166][167]
House


Brown's election meant Democrats could no longer break a filibuster in the Senate. In response, White House Chief of Staff Rahm Emanuel argued that Democrats should scale back to a less ambitious bill; House Speaker Nancy Pelosi pushed back, dismissing Emanuel's scaled-down approach as "Kiddie Care".[168][169]
Obama remained insistent on comprehensive reform. The news that Anthem Blue Cross in California intended to raise premium rates for its patients by as much as 39% gave him new evidence of the need for reform.[168][169] On February 22, he laid out a "Senate-leaning" proposal to consolidate the bills.[170] He held a meeting with both parties' leaders on February 25. The Democrats decided that the House would pass the Senate's bill, to avoid another Senate vote.
House Democrats had expected to be able to negotiate changes in a House-Senate conference before passing a final bill. Since any bill that emerged from conference that differed from the Senate bill would have to pass the Senate over another Republican filibuster, most House Democrats agreed to pass the Senate bill on condition that it be amended by a subsequent bill.[167] They drafted the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, which could be passed by the reconciliation process.[168][171][172]
As per the Congressional Budget Act of 1974, reconciliation cannot be subject to a filibuster. But reconciliation is limited to budget changes, which is why the procedure was not used to pass ACA in the first place; the bill had inherently non-budgetary regulations.[173][174] Although the already-passed Senate bill could not have been passed by reconciliation, most of House Democrats' demands were budgetary: "these changes—higher subsidy levels, different kinds of taxes to pay for them, nixing the Nebraska Medicaid deal—mainly involve taxes and spending. In other words, they're exactly the kinds of policies that are well-suited for reconciliation."[171]
The remaining obstacle was a pivotal group of pro-life Democrats led by Bart Stupak who were initially reluctant to support the bill. The group found the possibility of federal funding for abortion significant enough to warrant opposition. The Senate bill had not included language that satisfied their concerns, but they could not address abortion in the reconciliation bill as it would be non-budgetary. Instead, Obama issued Executive Order 13535, reaffirming the principles in the Hyde Amendment.[175] This won the support of Stupak and members of his group and assured the bill's passage.[172][176] The House passed the Senate bill with a 219–212 vote on March 21, 2010, with 34 Democrats and all 178 Republicans voting against it.[177] The next day, Republicans introduced legislation to repeal the bill.[178] Obama signed ACA into law on March 23, 2010.[179] Since passage, Republicans have voted to repeal all or parts of the Affordable Care Act over sixty times; no such attempt by Republicans has been successful.[180] The amendment bill, The Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, cleared the House on March 21; the Senate passed it by reconciliation on March 25, and Obama signed it on March 30.
Impact
Overview
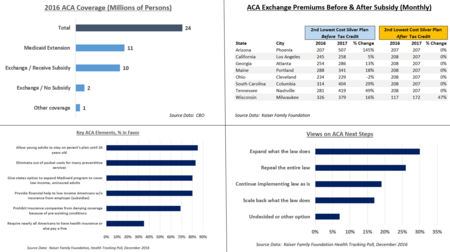
The law has caused a significant reduction in the number and percentage of people without health insurance. The CDC reported that the percentage of people without health insurance fell from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.9% during the January-June 2016 period.[10] The Congressional Budget Office reported in March 2016 that there were approximately 12 million people covered by the exchanges (10 million of whom received subsidies to help pay for insurance) and 11 million made eligible for Medicaid by the law, a total of 23 million people.[11] By 2017, nearly 70% of those on the exchanges could purchase insurance for less than $75/month after subsidies, which rose to offset significant pre-subsidy price increases in the exchange markets.[12] According to the Kaiser Foundation, healthcare premium cost increases in the employer market continued to moderate. For example, healthcare premiums for those covered by employers rose by 69% from 2000-2005, but only 27% from 2010 to 2015,[13] with only a 3% increase from 2015 to 2016.[14]
Uninsured population
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) originally estimated that the legislation would reduce the number of uninsured by 32 million, leaving 23 million uninsured in 2019.[20][181][182] With the elderly covered by Medicare, the CBO estimate projected that the law would raise the proportion of insured non-elderly from 83% to 94%.[20]
In March 2016, the CBO reported that there were approximately 27 million people without insurance in 2016, a figure they expected would range from 26-28 million through 2026. CBO also estimated the percentage of insured among all U.S. residents would remain at 90% through that period, 92-93% excluding unauthorized immigrants.[11] The CDC reported that the percentage of people without health insurance fell from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.9% during the January-June 2016 period.[10]
From Q4-2013 to Q1-2016, a Gallup survey found that the uninsured rate among adults declined from 17.1% to 11.0%, a decline of 6.1 percentage points.[183] In a 2016 review, Obama presented data showing that the uninsured rate had declined by 43%, from 16.0% in 2010 to 9.1% in 2015, mostly in 2014.[184] According to the American Community Survey, the uninsured rate dropped in every congressional district in the U.S. between 2013 and 2015.[185]
Exchanges
The ACA-established exchanges built websites and call centers that present private plans for comparison and purchase and allow buyers to apply for subsidies.[186]

Exchange-marketed plans are either approved by individual states or federally approved and available in multiple states.[187][188]
As of August 2016, 15 states operated their own exchanges. Other states either used the federal exchange, or operated in partnership with or supported by the federal government.[189]
Health outcomes
According to a 2014 study, Obamacare likely prevented an estimated 50,000 preventable patient deaths from 2010 to 2013.[190]
Insurance standards
Contraceptive coverage
In an unsuccessful attempt to accommodate groups opposed to contraception on doctrinal grounds,[191] the administration adjusted contraceptive regulations to "allow religious organizations to opt out of the requirement to include birth control coverage in their employee insurance plans. In those instances, the insurers themselves will offer contraception coverage to enrollees directly, at no additional cost".[192] Subsequent litigation exempted closely held corporations, such as Hobby Lobby, from the contraception rule[193] and led to an injunction exempting religious nonprofits from filling out a form that would ostensibly transfer the cost of employee contraceptives to insurers.[194]
Medicaid expansion

As of 2016, 32 states had expanded their Medicaid programs.[196] In a report to Congress, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) estimated that the cost of expansion was $6,366 per person for 2015, about 49 percent above previous estimates. An estimated 9 million to 10 million people had gained Medicaid coverage, mostly low-income adults.[197]
A 2016 study led by Harvard University health economics professor Benjamin Sommers found that residents of Kentucky and Arkansas, which both accepted the Medicaid expansion, were more likely to receive health care services and less likely to incur emergency room costs or have trouble paying their medical bills than before the expansion. Residents of Texas, which did not accept the Medicaid expansion, did not see a similar improvement during the same period.[198]
Kentucky opted for increased managed care, while Arkansas subsidized private insurance. The new Arkansas and Kentucky governors have proposed reducing or modifying their programs. Between 2013 and 2015, the uninsured rate dropped from 42% to 14% in Arkansas and from 40% to 9% in Kentucky, compared with 39% to 32% in Texas. Specific improvements included additional primary and preventive care, fewer emergency departments visits, reported higher quality care, improved health, improved drug affordability, reduced out-of-pocket spending and increased outpatient visits, increased diabetes screening, glucose testing among diabetes patients and regular care for chronic conditions.[199]
A 2016 DHHS study found that states that expanded Medicaid had lower premiums on exchange policies, because they had fewer low income enrollees, whose health on is worse than that of those with higher income.[200]
Family budgets

In 2010 the CBO forecast that by 2016 that premiums per person would increase by 10% to 13% but that over half of these individuals would receive subsidies that would decrease the premium paid to "well below" premiums charged under current law.[202][203] Subsidies were projected to be worth an average of $5,548 per receiving household.[204]
CBO forecast that small group (13% of the market) premiums would be impacted 1% to -3%, and -8% to -11% for those receiving subsidies; for large groups (70%), premiums would be impacted 0% to -3%, with those under high premium plans subject to excise taxes paying 9% to 12% less. Factors included increased benefits, particularly for the individual market, more healthy policyholders due to the mandate, administrative efficiencies related to the health exchanges and high-premium insurance plans reducing some benefits in response to the tax.[203]
A 2016 informal survey of Blue Cross/Blue Shield insurers estimated that 40% of individual enrollees (including 15% of those who purchase plans on exchanges) do not receive subsidies and are therefore subject to the full impact of annual premium increases.[205][206] A 2016 survey found that since 2011, deductibles had grown at 10 times the rate of inflation and nearly six times as fast as wages. Half of employer-insured workers had individual deductibles of at least $1,000 compared to 10 percent in 2006. Premiums and deductibles grew by 63%, while incomes grew by 11% over the period.[207]
Healthcare cost inflation


The law is designed to pay subsidies in the form of tax credits to the individuals or families purchasing the insurance, based on income levels. Higher income consumers receive lower subsidies. While pre-subsidy prices rose considerably from 2016 to 2017, so did the subsidies, to reduce the after-subsidy cost to the consumer. For example, a study published in 2016 found that the average requested 2017 premium increase among 40-year-old non-smokers was about 9 percent, according to an analysis of 17 cities, although Blue Cross Blue Shield proposed increases of 40 percent in Alabama and 60 percent in Texas.[208] However, some or all of these costs are offset by subsidies, paid as tax credits. For example, the Kaiser Foundation reported that for the second-lowest cost "Silver plan" (a plan often selected and used as the benchmark for determining financial assistance), a 40-year old non-smoker making $30,000 per year would pay effectively the same amount in 2017 as they did in 2016 (about $208/month) after the subsidy/tax credit, despite large increases in the pre-subsidy price. This was consistent nationally. In other words, the subsidies increased along with the pre-subsidy price, fully offsetting the price increases.[209]
According to the Kaiser Foundation, healthcare premium cost increases in the employer market continued to moderate after the implementation of the law. For example, healthcare premiums for those covered by employers rose by 69% from 2000-2005, but only 27% from 2010 to 2015,[13] with only a 3% increase from 2015 to 2016.[14]
| Year | Rate of increase (%) |
|---|---|
| 2007 | 11.9 |
| 2008 | 9.9 |
| 2009 | 9.2 |
| 2010 | 9.0 |
| 2011 | 9.0 |
| 2012 | 8.5 |
| 2013 | 7.5 |
| 2014 | 6.5 |
| 2015 | 6.8 |
| 2016 | 6.5 (estimated) |
| 2017 | 6.5 (estimated) |
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reported that U.S. spending on drugs increased by 12.2% in 2013. A 2015 study found that retail prices for 115 widely used specialty drugs increased 10.6% from 2012 to 2013.[citation needed]
Several studies found that the financial crisis and accompanying recession could not account for the entirety of the slowdown and that structural changes likely share at least partial credit.[211][212][213][214]
A 2013 study estimated that changes to the health system had been responsible for about a quarter of the recent reduction in inflation.[215] Paul Krawzak claimed that even if cost controls succeed in reducing the amount spent on healthcare, such efforts on their own may be insufficient to outweigh the long-term burden placed by demographic changes, particularly the growth of the population on Medicare.[216]
In a 2016 review of the ACA published in JAMA, Barack Obama himself wrote that from 2010 through 2014 mean annual growth in real per-enrollee Medicare spending was negative, down from a mean of 4.7% per year from 2000 through 2005 and 2.4% per year from 2006 to 2010; similarly, mean real per-enrollee growth in private insurance spending was 1.1% per year over the period, compared with a mean of 6.5% from 2000 through 2005 and 3.4% from 2005 to 2010.[217]
Federal deficit
CBO estimates of revenue and impact on deficit

The 2011 comprehensive CBO estimate projected a net deficit reduction of more than $200 billion during the 2012–2021 period:[219][220] it calculated the law would result in $604 billion in total outlays offset by $813 billion in total receipts, resulting in a $210 billion net deficit reduction.[219] The CBO separately predicted that while most of the spending provisions do not begin until 2014,[221][222] revenue would exceed spending in those subsequent years.[223] The CBO claimed that the bill would "substantially reduce the growth of Medicare's payment rates for most services; impose an excise tax on insurance plans with relatively high premiums; and make various other changes to the federal tax code, Medicare, Medicaid, and other programs"[202]—ultimately extending the solvency of the Medicare trust fund by 8 years.[224]
This estimate was made prior to the Supreme Court's ruling that enabled states to opt out of the Medicaid expansion, thereby forgoing the related federal funding. The CBO and JCT subsequently updated the budget projection, estimating the impact of the ruling would reduce the cost estimate of the insurance coverage provisions by $84 billion.[182][225][226]
The CBO in June 2015 forecasted that repeal of ACA would increase the deficit between $137 billion and $353 billion over the 2016–2025 period, depending on the impact of macroeconomic feedback effects. CBO also forecasted that repeal of ACA would likely raise economic output, mainly by boosting the supply of labor as low-income persons would have more incentive to work without ACA healthcare coverage.[227]
Major new sources of increased tax receipts include:[82] higher Medicare taxes; annual fees on insurance providers; fees on the healthcare industry such as manufacturers and importers of brand-name pharmaceutical drugs and certain medical devices; limits on tax deductions of medical expenses and flexible spending accounts; a 40% excise tax on plans with annual insurance premiums in excess of $10,200 for an individual or $27,500 for a family; revenue from mandate penalty payments; a 10% federal sales tax on indoor tanning services. Predicted spending reductions included a reduction in Medicare reimbursements to insurers and drug companies for private Medicare Advantage policies that the Government Accountability Office and Medicare Payment Advisory Commission found to be excessively costly relative to government Medicare;[228][229] and reductions in Medicare reimbursements to hospitals that failed standards of efficiency and care.[228]
Although the CBO generally does not provide cost estimates beyond the 10-year budget projection period because of the degree of uncertainty involved in the projection, it decided to do so in this case at the request of lawmakers, and estimated a second decade deficit reduction of $1.2 trillion.[202][230] CBO predicted deficit reduction around a broad range of one-half percent of GDP over the 2020s while cautioning that "a wide range of changes could occur".[231]
The CBO cost estimates were criticized because they excluded the effects of potential legislation that would increase Medicare payments by more than $200 billion from 2010 to 2019.[232][233][234] However, the so-called "doc fix" is a separate issue that would have existed whether or not ACA became law - omitting its cost from ACA was no different from omitting the cost of other tax cuts.[235][236][237]
Opinions on CBO projections
Uwe Reinhardt, a Princeton health economist, wrote. "The rigid, artificial rules under which the Congressional Budget Office must score proposed legislation unfortunately cannot produce the best unbiased forecasts of the likely fiscal impact of any legislation", but went on to say "But even if the budget office errs significantly in its conclusion that the bill would actually help reduce the future federal deficit, I doubt that the financing of this bill will be anywhere near as fiscally irresponsible as was the financing of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003."[238] Douglas Holtz-Eakin, CBO director during the George W. Bush administration, who later served as the chief economic policy adviser to U.S. Senator John McCain's 2008 presidential campaign, alleged that the bill would increase the deficit by $562 billion because, he argued, it front-loaded revenue and back-loaded benefits.[239]
Scheiber and Cohn rejected critical assessments of the law's deficit impact, arguing that predictions were biased towards underestimating deficit reduction. They noted that for example, it is easier to account for the cost of definite levels of subsidies to specified numbers of people than account for savings from preventive healthcare, and that the CBO had a track record of overestimating costs and underestimating savings of health legislation;[240][241] stating, "innovations in the delivery of medical care, like greater use of electronic medical records[242] and financial incentives for more coordination of care among doctors, would produce substantial savings while also slowing the relentless climb of medical expenses... But the CBO would not consider such savings in its calculations, because the innovations hadn't really been tried on such large scale or in concert with one another—and that meant there wasn't much hard data to prove the savings would materialize."[240]
In 2010 David Walker, former U.S. Comptroller General then working for The Peter G. Peterson Foundation, stated that the CBO estimates are not likely to be accurate, because they were based on the assumption that the law would not change.[243] The Center on Budget and Policy Priorities objected that Congress had a good record of implementing Medicare savings. According to their study, Congress followed through on the implementation of the vast majority of provisions enacted in the past 20 years to produce Medicare savings, although not the payment reductions addressed by the annual "doc fix".[244][245]
Employer mandate and part-time work
The employer mandate applies to employers with more than 50 employees that do not offer health insurance to their full-time workers.[246]
Critics claimed that the mandate created a perverse incentive for business to keep their full-time headcount below 50 and to hire part-time workers instead.[247][248] Between March 2010 and 2014 the number of part-time jobs declined by 230,000, while the number of full-time jobs increased by 2 million.[249][250] In the public sector full-time jobs turned into part-time jobs much more than in the private sector.[249][251] A 2016 study found only limited evidence that ACA had increased part-time employment.[252]
Several businesses and the state of Virginia added a 29-hour-a-week cap for their part-time employees,[253][unreliable source?][254][unreliable source?] to reflect the 30-hour-or-more definition for full-time worker.[246] As of yet, however, only a small percent of companies have shifted their workforce towards more part-time hours (4% in a survey from the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis).[248] Trends in working hours[255] and the effects of the Great Recession correlate with part-time working hour patterns.[256][257] The impact of this provision may have been offset by other factors, including that health insurance helps attract and retain employees, increases productivity and reduces absenteeism; and the lower training and administration costs of a smaller full-time workforce over a larger part-time work force.[248][255][258] Relatively few firms employ over 50 employees[248] and more than 90% of them offered insurance.[259] Workers without employer insurance could purchase insurance on the exchanges.[260]
Most policy analysts (on both right and left) were critical of the employer mandate provision.[247][259] They argued that the perverse incentives regarding part-time hours, even if they did not change existing plans, were real and harmful;[261][262] that the raised marginal cost of the 50th worker for businesses could limit companies' growth;[263] that the costs of reporting and administration were not worth the costs of maintaining employer plans;[261][262] and noted that the employer mandate was not essential to maintain adequate risk pools.[264][265] The effects of the provision generated vocal opposition from business interests and some unions not granted exemptions.[262][266]
A 2013/4 survey by the National Association for Business Economics found that about 75 percent of those surveyed said ACA hadn’t influenced their planning or expectations for 2014, and 85 percent said the law wouldn’t prompt a change in their hiring practices. Some 21 percent of 64 businesses surveyed said that the act would have a harmful effect and 5 percent said it would be beneficial.[267]
Hospitals
From the start of 2010 to November 2014, 43 hospitals in rural areas closed, according to the North Carolina Rural Health Research Program. Critics claimed that the new law caused these hospitals to close. Many of these rural hospitals were built using funds from the 1946 Hill–Burton Act, to increase access to medical care in rural areas. Some of these hospitals reopened as other medical facilities, but only a small number operated emergency rooms (ER) or urgent care centers.[268]
Between January 2010 and 2015, a quarter of emergency room doctors said they had seen a major surge in patients, while nearly half had seen a smaller increase. Seven in ten ER doctors claimed that they lacked the resources to deal with large increases in the number of patients. The biggest factor in the increased number of ER patients was insufficient primary care providers to handle the larger number of insured patients.[269]
Insurers claimed that because they have access to and collect patient data that allow evaluations of interventions, they are essential to ACO success. Large insurers formed their own ACOs. Many hospitals merged and purchased physician practices. The increased market share gave them more leverage in negotiations with insurers over costs and reduced patient care options.[102]
Public opinion
Prior to the law's passage, polling indicated the public's views became increasingly negative in reaction to specific plans discussed during the legislative debate over 2009 and 2010. Polling statistics showed a general negative opinion of the law; with those in favor at approximately 40% and those against at 51%, as of October 2013.[270][271] About 29% of whites approve of the law, compared with 61% of Hispanics and 91% of African Americans.[272] Opinions were divided by age of the person at the law's inception, with a solid majority of seniors opposing the bill and a solid majority of those younger than forty years old in favor.[273]

Specific elements were popular across the political spectrum, while others, such as the mandate to purchase insurance, were widely disliked. In a 2012 poll 44% supported the law, with 56% against. By party affiliation, 75% of Democrats, 27% of Independents and 14% of Republicans favored the law overall. 82% favored banning insurance companies from denying coverage to people with pre-existing conditions, 61% favored allowing children to stay on their parents' insurance until age 26, 72% supported requiring companies with more than 50 employees to provide insurance for their employees, and 39% supported the individual mandate to own insurance or pay a penalty. By party affiliation, 19% of Republicans, 27% of Independents, and 59% of Democrats favored the mandate.[274] Other polls showed additional provisions receiving majority support, including the creation of insurance exchanges, pooling small businesses and the uninsured with other consumers so that more people can take advantage of large group pricing benefits and providing subsidies to individuals and families to make health insurance more affordable.[275][276]
In a 2010 poll, 62% of respondents said they thought ACA would "increase the amount of money they personally spend on health care", 56% said the bill "gives the government too much involvement in health care", and 19% said they thought they and their families would be better off with the legislation.[277] Other polls found that people were concerned that the law would cost more than projected and would not do enough to control costs.[278]
Some opponents believed that the reform did not go far enough: a 2012 poll indicated that 71% of Republican opponents rejected it overall, while 29% believed it did not go far enough; independent opponents were divided 67% to 33%; and among the much smaller group of Democratic opponents, 49% rejected it overall and 51% wanted more.[274] In June 2013, a majority of the public (52–34%) indicated a desire for "Congress to implement or tinker with the law rather than repeal it".[279] After the Supreme Court upheld the individual mandate, a 2012 poll held that "most Americans (56%) want to see critics of President Obama's health care law drop efforts to block it and move on to other national issues".[280]A 2014 poll reported that 48.9% of respondents had an unfavorable view of ACA vs. 38.3% who had a favorable view (of more than 5,500 individuals).[281]
A 2014 poll reported that 26% of Americans support ACA.[282] Another held that 8% of respondents say that the Affordable Care Act "is working well the way it is".[283] In late 2014, a poll reported Repeal: 30%, Leave as is: 13%, Improve: 52%, i.e., 65% wanted to leave ACA alone or improve upon it.[284]
In 2015, a poll reported that 47% of Americans approved the health care law. This was the first time that a major poll indicated that more respondents approved ACA than disapproved of it.[285] The recurring Kaiser Health Tracking Poll from December 2016 reported that: a) 30% wanted to expand what the law does; b) 26% wanted to repeal the entire law; c) 19% wanted to move forward with implementing the law as it is; and d) 17% wanted to scale back what the law does, with the remainder undecided.[286]
Political
"Obamacare"
The term "Obamacare" was originally coined by opponents as a pejorative. The term emerged in March 2007 when healthcare lobbyist Jeanne Schulte Scott used it in a health industry journal, writing "We will soon see a 'Giuliani-care' and 'Obama-care' to go along with 'McCain-care', 'Edwards-care', and a totally revamped and remodeled 'Hillary-care' from the 1990s".[15][287] According to research by Elspeth Reeve, the expression was used in early 2007, generally by writers describing the candidate's proposal for expanding coverage for the uninsured.[288] It first appeared in a political campaign by Mitt Romney in May 2007 in Des Moines, Iowa. Romney said, "In my state, I worked on healthcare for some time. We had half a million people without insurance, and I said, 'How can we get those people insured without raising taxes and without having government take over healthcare?' And let me tell you, if we don't do it, the Democrats will. If the Democrats do it, it will be socialized medicine; it'll be government-managed care. It'll be what's known as Hillarycare or Barack Obamacare, or whatever you want to call it."[15]
By mid-2012, Obamacare had become the colloquial term used by both supporters and opponents. In contrast, the use of "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" or "Affordable Care Act" became limited to more formal and official use.[288] Use of the term in a positive sense was suggested by Democrat John Conyers.[289] Obama endorsed the nickname, saying, "I have no problem with people saying Obama cares. I do care."[290]
In March 2012, the Obama reelection campaign embraced the term "Obamacare", urging Obama's supporters to post Twitter messages that begin, "I like #Obamacare because...".[291]
In October 2013 the Associated Press and NPR began cutting back on use of the term.[292] Stuart Seidel, NPR's managing editor, said that the term "seems to be straddling somewhere between being a politically-charged term and an accepted part of the vernacular".[293]
Common misconceptions
"Death panels"
On August 7, 2009, Sarah Palin pioneered the term "death panels" to describe groups that would decide whether sick patients were "worthy" of medical care.[294] The allegation was named PolitiFact's "Lie of the Year",[294][295] one of FactCheck.org's "whoppers"[296][297] and the most outrageous term by the American Dialect Society.[298] AARP described such rumors as "rife with gross—and even cruel—distortions".[299] In 2010, the Pew Research Center reported that 85% of Americans were familiar with the claim, and 30% believed it was true, backed by three contemporaneous polls.[300] A poll in August 2012 found that 39% of Americans believed the claim.[301]
"Death panel" referred to two claims about early drafts. One was that under the law, seniors could be denied care due to their age[302] and the other that the government would advise seniors to end their lives instead of receiving care. The ostensible basis of these claims was the provision for an Independent Payment Advisory Board (IPAB).[303] IPAB was given the authority to recommend cost-saving changes to Medicare by facilitating the adoption of cost-effective treatments and cost-recovering measures when the statutory levels set for Medicare were exceeded within any given 3-year period. In fact, the Board was prohibited from recommending changes that would reduce payments to certain providers before 2020, and was prohibited from recommending changes in premiums, benefits, eligibility and taxes, or other changes that would result in rationing.[304][305]
The other related issue concerned advance-care planning consultation: a section of the House reform proposal would have reimbursed physicians for providing patient-requested consultations for Medicare recipients on end-of-life health planning (which is covered by many private plans), enabling patients to specify, on request, the kind of care they wished to receive.[306] The provision was not included in ACA.[307]
Members of Congress
ACA requires members of Congress and their staffs to obtain health insurance either through an exchange or some other program approved by the law (such as Medicare), instead of using the insurance offered to federal employees (the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program).[308][309][310][311][312]
Illegal immigrants
ACA does not provide benefits to illegal immigrants.[313] It explicitly denies insurance subsidies to "unauthorized (illegal) aliens".[20][21][314]
Opposition
Opposition and efforts to repeal the legislation have drawn support from sources that include labor unions,[315][316] conservative advocacy groups,[317][318] Republicans, small business organizations and the Tea Party movement.[319] These groups claimed that the law would disrupt existing health plans, increase costs from new insurance standards, and increase the deficit.[320] Some opposed the idea of universal healthcare, viewing insurance as similar to other unsubsidized goods.[321][322] President-elect Donald Trump has promised to repeal it.[323]
As of 2013[update] unions that expressed concerns about ACA included the AFL-CIO,[324] which called ACA "highly disruptive" to union health care plans, claiming it would drive up costs of union-sponsored plans; the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, United Food and Commercial Workers International Union, and UNITE-HERE, whose leaders sent a letter to Reid and Pelosi arguing, " ACA will shatter not only our hard-earned health benefits, but destroy the foundation of the 40-hour work week that is the backbone of the American middle class."[316] In January 2014, Terry O'Sullivan, president of the Laborers' International Union of North America (LIUNA) and D. Taylor, president of Unite Here sent a letter to Reid and Pelosi stating, " ACA, as implemented, undermines fair marketplace competition in the health care industry".[315]
Legal challenges
National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius
Opponents challenged ACA's constitutionality in multiple lawsuits on multiple grounds.[325][326][failed verification] In National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, the Supreme Court ruled on a 5–4 vote that the individual mandate was constitutional when viewed as a tax, although not under the Commerce Clause.
The Court further determined that states could not be forced to participate in the Medicaid expansion. ACA withheld all Medicaid funding from states declining to participate in the expansion. The Court ruled that this withdrawal of funding was unconstitutionally coercive and that individual states had the right to opt out without losing preexisting Medicaid funding.[327]
Contraception mandate
In March 2012 the Roman Catholic Church, while supportive of ACA's objectives, voiced concern through the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops that aspects of the mandate covering contraception and sterilization and HHS's narrow definition of a religious organization violated the First Amendment right to free exercise of religion and conscience. Various lawsuits addressed these concerns.[328][329]
On June 25, 2015, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled 6–3 that federal subsidies for health insurance premiums could be used in the 34 states that did not set up their own insurance exchanges.[330]
House v. Burwell
In United States House of Representatives v. Burwell the House sued the administration alleging that the money for premium subsidy payments to insurers had not been appropriated, as required for any federal government spending. The Obamacare subsidy that helps customers pay premiums was not part of the suit. Without the cost-sharing subsidies, the government estimated that premiums would increase by 20 percent to 30 percent for silver plans.[331]
Medicaid expansion
Following the Supreme Court ruling, several states rejected expanded Medicaid coverage. Over half of the national uninsured population lived in those states.[332] As of January 2016[update], 31 states and the District of Columbia had expanded Medicaid; a few states remained undecided.[195][333][334]
States that rejected the Medicaid expansion could maintain their Medicaid eligibility thresholds, which in many states were significantly below 133% of the poverty line.[335] Many states did not make Medicaid available to childless adults at any income level.[336] Because subsidies on exchange insurance plans were not available to those below the poverty line, such individuals had no new options.[337][338] For example, in Kansas, where only able-bodied adults with children and with an income below 32% of the poverty line were eligible for Medicaid, those with incomes from 32% to 100% of the poverty level ($6,250 to $19,530 for a family of three) were ineligible for both Medicaid and federal subsidies to buy insurance. Absent children, able-bodied adults were not eligible for Medicaid in Kansas.[332] Studies of the impact of state decisions to reject the Medicaid expansion calculated that up to 6.4 million people could fall into this status.[339] The federal government initially paid for 100% of the expansion (through 2016). The subsidy tapered to 90% by 2020 and continued to shrink thereafter.[340] Several states argued that they could not afford their 10% contribution.[340][341] Studies suggested that rejecting the expansion would cost more than expanding Medicaid due to increased spending on uncompensated emergency care that otherwise would have been partially paid for by Medicaid coverage,[342][343] as well as eliminating federal funding.[344]: 4 Medicaid expansion was claimed to be associated with increased tax revenue, job growth and reductions in the uninsured population.[345] A 2015 study found that states not expanding Medicaid left 7.74 million uninsured, leading to "between 7,076 and 16,945 more deaths".[346]
Non-cooperation
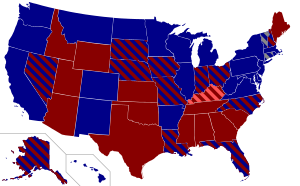
Officials in Texas, Florida, Alabama, Wyoming, Arizona, Oklahoma and Missouri opposed those elements of ACA over which they had discretion.[347][348] For example, Missouri declined to expand Medicaid or establish a health insurance marketplace engaging in active non-cooperation, enacting a statute forbidding any state or local official to render any aid not specifically required by federal law.[349] Other (Republican) politicians discouraged efforts to advertise the benefits of the law. Some (conservative) political groups launched ad campaigns to discourage enrollment.[350][351]
Health care quality
In 2014 97 ACOs qualified for bonus payments of more than $422 million. In 2015 6 million Medicare beneficiaries were in an ACO. More than 744 organizations became ACOs. Some 23.5 million people received service from an ACO.[102]
Hospital systems in many areas purchased many physician practices as part of becoming an ACO.[102]
Large health insurers, including Humana, UnitedHealth and Aetna, formed ACOs for the private market.[102]
Repeal efforts
ACA was the subject of unsuccessful repeal efforts by Republicans in the 111th, 112th, and 113th Congresses: Representatives Steve King (R-IA) and Michele Bachmann (R-MN) introduced bills in the House to repeal ACA the day after it was signed, as did Senator Jim DeMint (R-SC) in the Senate.[352] In 2011, after Republicans gained control of the House of Representatives, one of the first votes held was on a bill titled "Repealing the Job-Killing Health Care Law Act" (H.R. 2), which the House passed 245–189.[353] All Republicans and 3 Democrats voted for repeal.[354] House Democrats proposed an amendment that repeal not take effect until a majority of the Senators and Representatives had opted out of the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program; Republicans voted down the measure.[355] In the Senate, the bill was offered as an amendment to an unrelated bill, but was voted down.[356] President Obama had stated that he would have vetoed the bill even if it had passed both chambers of Congress.[357]
Following the 2012 Supreme Court ruling upholding ACA as constitutional, Republicans held another vote to repeal the law on July 11;[358] the House of Representatives voted with all 244 Republicans and 5 Democrats in favor of repeal, which marked the 33rd, partial or whole, repeal attempt.[359][360] On February 3, 2015, the House of Representatives added its 67th repeal vote to the record (239 to 186). This attempt also failed[361]
2013 federal government shutdown
Strong partisan disagreement in Congress prevented adjustments to the Act's provisions.[362] However, at least one change, a proposed repeal of a tax on medical devices, has received bipartisan support.[363] Some Congressional Republicans argued against improvements to the law on the grounds they would weaken the arguments for repeal.[262][364]
Republicans attempted to defund its implementation,[348][365] and in October 2013, House Republicans refused to fund the federal government unless accompanied with a delay in ACA implementation, after the President unilaterally deferred the employer mandate by one year, which critics claimed he had no power to do. The House passed three versions of a bill funding the government while submitting various versions that would repeal or delay ACA, with the last version delaying enforcement of the individual mandate. The Democrat Senate leadership stated the Senate would only pass a "clean" funding bill without any restrictions on ACA. The government shutdown began on October 1.[366][367][368] Senate Republicans threatened to block appointments to relevant agencies, such as the Independent Payment Advisory Board[369] and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.[370][371]
Economic consequences
As of 2014 company policies were still the norm, since tax laws continued to make benefits cheaper than cash until 2018. Many employees have been losing their "paternalistic" corporate policies and must find their own insurance. Under ACA employers who stopped their company sponsored insurance plan eliminated one of their largest non-wage benefits and shifted more costs to employees. These include insurance premiums rising to 28% in 2013, compared with 26% in 2003, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation, and more workers paying deductibles of $1,000, reaching 38% in 2013, more than twice that of 2008. According to one study, as of 2014, only 25% of firms saw themselves offering insurance in 10 years.[372]
In 2015 the Center for Economic and Policy Research found no evidence that companies were reducing worker hours to avoid ACA requirements[373] for employees working over 30 hours per week.[374]
Cohn, citing CBO's projections, claimed that ACA's primary employment effect was to alleviate job lock: "People who are only working because they desperately need employer-sponsored health insurance will no longer do so."[375] He concluded that the "reform's only significant employment impact was a reduction in the labor force, primarily because people holding onto jobs just to keep insurance could finally retire", because they have health insurance outside of their jobs.[376]
Impact of repeal on federal budget projections
In May 2011, CBO analyzed proposals to repeal the law and estimated that repealing the entire law (both its taxing and spending provisions) would increase the net 2011–2021 federal deficit by $210 billion.[377][378] Revised CBO accounting, following the July 11, 2012, House repeal vote (H.R. 6079), and taking into account the impact of the Supreme Court ruling, was consistent with its previous estimate: that repeal would increase federal budget deficits by $109 billion over the 2013–2022 period.[379]
Implementation history
Once the law was signed, provisions began taking effect, in a process that continued for years. Some provisions never took effect, while others were deferred for various periods.
Existing individual health plans
Plans purchased after the date of enactment, March 23, 2010, or old plans that changed in specified ways would eventually have to be replaced by ACA-compliant plans.[citation needed]
At various times during and after the ACA debate, Obama stated that "if you like your health care plan, you'll be able to keep your health care plan".[380][381] However, in fall 2013 millions of Americans with individual policies received notices that their insurance plans were terminated,[382] and several million more risked seeing their current plans cancelled.[383][384][385]
Obama's previous unambiguous assurance that consumers' could keep their own plans became a focal point for critics, who challenged his truthfulness.[386][387] On November 7, 2013, President Obama stated: "I am sorry that [people losing their plans] are finding themselves in this situation based on assurances they got from me".[388] Various bills were introduced in Congress to allow people to keep their plans.[389]
In the fall of 2013, the Obama Administration announced a transitional relief program that would let states and carriers allow non-compliant individual and small group policies to renew at the end of 2013. In March 2014, HHS allowed renewals as late as October 1, 2016. In February 2016, these plans were allowed to renew up until October 1, 2017, but with a termination date no later than December 31, 2017.[citation needed]
2010
In June small business tax credits took effect. For certain small businesses, the credits reached up to 35% of premiums. At the same time uninsured people with pre-existing conditions could access the federal high-risk pool. Also, participating employment-based plans could obtain reimbursement for a portion of the cost of providing health insurance to early retirees.[390]
In July the Pre-Existing Condition Insurance Plan (PCIP) took effect to offer insurance to those that had been denied coverage by private insurance companies because of a pre-existing condition. Despite estimates of up to 700,000 enrollees, at a cost of approximately $13,000/enrollee, only 56,257 enrolled at a $28,994 cost per enrollee.[390]
2011
As of September 23, 2010, pre-existing conditions could no longer be denied coverage for children's policies. HHS interpreted this rule as a mandate for "guaranteed issue", requiring insurers to issue policies to such children.[citation needed] By 2011, insurers had stopped marketing child-only policies in 17 states, as they sought to escape this requirement.[391]
The average beneficiary in the prior coverage gap would have spent $1,504 in 2011 on prescriptions. Such recipients saved an average $603. The 50 percent discount on brand name drugs provided $581 and the increased Medicare share of generic drug costs provided the balance. Beneficiaries numbered 2 million[392]
2012
In National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius decided on June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court ruled that the individual mandate was constitutional when the associated penalties were construed as a tax. The decision allowed states to opt out of the Medicaid expansion. Several did so,[393] although some later accepted the expansion.[394]
2013
In January 2013 the Internal Revenue Service ruled that the cost of covering only the individual employee would be considered in determining whether the cost of coverage exceeded 9.5% of income. Family plans would not be considered even if the cost was above the 9.5% income threshold. This was estimated to leave 2–4 million Americans unable to afford family coverage under their employers’ plans and ineligible for subsidies.[395][396]
A June 2013 study found that the MLR provision had saved individual insurance consumers $1.2 billion in 2011 and $2.1 billion in 2012, reducing their 2012 costs by 7.5%.[397] The bulk of the savings were in reduced premiums, but some came from MLR rebates.
On July 2, 2013, the Obama Administration announced that it would delay the implementation of the employer mandate until 2015.[259][398][399]
The Community Living Assistance Services and Supports Act (or CLASS Act) was enacted as Title VIII of Obamacare. It would have created a voluntary and public long-term care insurance option for employees.[108][110] In October 2011 the administration announced it was unworkable and would be dropped.[400] The CLASS Act was repealed January 1, 2013.[401]
The launch for both the state and federal exchanges was troubled due to management and technical failings. HealthCare.gov, the website that offers insurance through the exchanges operated by the federal government, crashed on opening and suffered endless problems.[402] Operations stabilized in 2014, although not all planned features were complete.[403][404]
CMS reported in 2013 that, while costs per capita continued to rise, the rate of increase in annual healthcare costs had fallen since 2002. Per capita cost increases averaged 5.4% annually between 2000 and 2013. Costs relative to GDP, which had been rising, had stagnated since 2009.[405] Several studies attempted to explain the reductions. Reasons included:
- Higher unemployment due to the 2008-2010 recession, which limited the ability of consumers to purchase healthcare;
- Out-of-pocket costs rose, reducing demand for healthcare services.[406] The proportion of workers with employer-sponsored health insurance requiring a deductible climbed to about three-quarters in 2012 from about half in 2006.[211]
- ACA changes[211] that aim to shift the healthcare system from paying-for-quantity to paying-for-quality. Some changes occurred due to healthcare providers acting in anticipation of future implementation of reforms.[107][212]
2014
On July 30, 2014, the Government Accountability Office released a non-partisan study that concluded that the administration did not provide "effective planning or oversight practices" in developing the website.[407]
In Burwell v. Hobby Lobby the Supreme Court exempted closely held corporations with religious convictions from the contraception rule.[193] In Wheaton College vs Burwell the Court issued an injunction allowing the evangelical college and other religiously affiliated nonprofit groups to completely ignore the contraceptive mandate.[194]
A study found that average premiums for the second-cheapest silver plan were 10-21% less than average individual market premiums in 2013, while covering many more conditions. Credit for the reduced premiums was attributed to increased competition stimulated by the larger market, greater authority to review premium increases, the MLR and risk corridors.[citation needed]
Many of the initial plans featured narrow networks of doctors and hospitals.[408][failed verification]
A 2016 analysis found that health care spending by the middle class was 8.9% of household spending in 2014.[409]
2015

By the beginning of the year, 11.7 million had signed up (ex-Medicaid).[411] On December 31, 2015, about 8.8 million consumers had stayed in the program. Some 84 percent, or about 7.4 million, were subsidized.[412]
Bronze plans were the second most popular in 2015, making up 22% of marketplace plan selections. Silver plans were the most popular, accounting for 67% of marketplace selections. Gold plans were 7%. Platinum plans accounted for 3%. On average across the four metal tiers, premiums were up 20% for HMOs and 18% for EPOs. Premiums for POS plans were up 15% from 2015 to 2016, while PPO premiums were up just 8%.[citation needed]
A 2015 study found 14% of privately insured consumers received a medical bill in the past two years from an out-of-network provider in the context of an overall in-network treatment event. Such out-of-network care is not subject to the lower negotiated rates of in-network care, increasing out-of-pocket costs. Another 2015 study found that the average out-of-network charges for the majority of 97 medical procedures examined "were 300% or higher compared to the corresponding Medicare fees" for those services.[citation needed]
Some 47% of the 2015 ACA plans sold on the Healthcare.gov exchange lacked standard out-of-network coverage. Enrollees in such plans, typically received no coverage for out-of-network costs (except for emergencies or with prior authorization). A 2016 study on Healthcare.gov health plans found a 24 percent increase in the percentage of ACA plans that lacked standard out-of-network coverage.[citation needed]
The December spending bill delayed the onset of the "Cadillac tax" by two years, until 2020.[413]
The average price of non-generic drugs rose 16.2% in 2015 and 98.2% since 2011.[409]
2016
As of March 2016 11.1 million people had purchased exchange plans,[citation needed] while an estimated 9 million to 10 million people had gained Medicaid coverage, mostly low-income adults.[197] 11.1 million were still covered, a decline of nearly 13 percent.[414] 6.1 million uninsured 19-25 year olds gained coverage.[415]
Employers
A survey of New York businesses found an increase of 8.5 percent in health care costs, less than the prior year's survey had expected. A 10 percent increase was expected for 2017. Factors included increased premiums, higher drug costs, ACA and aging workers. Some firms lowered costs by increasing cost-sharing (for higher employee contributions, deductibles and co-payments). 60% planned to further increase cost-sharing. Coverage and benefits were not expected to change. Approximately one fifth said ACA had pushed them to reduce their workforce. A larger number said they were raising prices.[416]
Insurers
The five major national insurers expected to lose money on ACA policies in 2016.[417] UnitedHealth withdrew from the Georgia and Arkansas exchanges for 2017, citing heavy losses.[189] Humana exited other markets, leaving it operating in 156 counties in 11 states for 2017.[418] 225 counties across the country had access to only a single ACA insurer. A study released in May estimated that 664 counties would have one insurer in 2017.[419][failed verification]
Aetna cancelled planned expansion of its offerings and following an expected $300 million loss in 2016 and then withdrew from 11 of its 15 states.[420] In August 2016 Anthem said that its offerings were losing money, but also that it would expand its participation if a pending merger with Cigna was approved.[421] Aetna and Humana's exit for 2017 left 8 rural Arizona counties with only Blue Cross/Blue Shield.[422]
Blue Cross/Blue Shield Minnesota announced that it would exit individual and family markets in Minnesota in 2017, due to financial losses of $500 million over three years.[423]
Another analysis found that 17 percent of eligibles may have a single insurer option in 2017. North Carolina, Oklahoma, Alaska, Alabama, South Carolina and Wyoming were expected to have a single insurer,[424] while only 2 percent of 2016 eligibles had only one choice.[425]
Aetna, Humana, UnitedHealth Group also exited various individual markets. Many local Blue Cross plans sharply narrowed their networks. In 2016 two thirds of individual plans were narrow-network HMO plans.[408]
One of the causes of insurer losses is the lower income, older and sicker enrollee population. One 2016 analysis reported that while 81% of the population with incomes from 100-150% of the federal poverty level signed up, only 45% of those from 150-200% did so. The percentage continued to decline as income rose: 2% of those above 400% enrolled.[426]
Costs
The law is designed to pay subsidies in the form of tax credits to the individuals or families purchasing the insurance, based on income levels. Higher income consumers receive lower subsidies. While pre-subsidy prices rose considerably from 2016 to 2017, so did the subsidies, to reduce the after-subsidy cost to the consumer. For example, a study published in 2016 found that the average requested 2017 premium increase among 40-year-old non-smokers was about 9 percent, according to an analysis of 17 cities, although Blue Cross Blue Shield proposed increases of 40 percent in Alabama and 60 percent in Texas.[427] However, some or all of these costs are offset by subsidies, paid as tax credits. For example, the Kaiser Foundation reported that for the second-lowest cost "Silver plan" (a plan often selected and used as the benchmark for determining financial assistance), a 40-year old non-smoker making $30,000 per year would pay effectively the same amount in 2017 as they did in 2016 (about $208/month) after the subsidy/tax credit, despite large increases in the pre-subsidy price. This was consistent nationally. In other words, the subsidies increased along with the pre-subsidy price, fully offsetting the price increases.[209]
Cooperatives
The number of ACA nonprofit insurance cooperatives for 2017 fell from 23 originally to 7 for 2017. The remaining 7 posted annual losses in 2015. A General Accountability Report found that co-ops’ 2015 premiums were generally below average. At the end of 2014, money co-ops and other ACA insurers had counted on risk corridor payments that didn't materialize. Maryland's Evergreen Health claims that ACA's risk-adjustment system does not adequately measure risk.[citation needed]
Medicaid
Newly elected Louisiana Governor John Bel Edwards issued an executive order to accept the expansion, becoming the 32nd state to do so. The program was expected to enroll an additional 300,000 Louisianans.[428]
See also
- Acronyms in healthcare
- Community Living Assistance Services and Supports Act ("Class Act")
- Comparison of the health care systems in Canada and the United States
- EBSA form 700
- Health care reform
- Health systems by country
- Individual shared responsibility provision
- King v. Burwell
- Massachusetts health care reform (sometimes called "RomneyCare")
- Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (Reform to the American Health Care system signed into law by President Obama)
- National health insurance
- Single-payer health care
- Universal health care
- Universal health coverage by country
- U.S. health care compared with 8 other countries (tabular form).
References
- ^ Pear, Robert (July 7, 2012). "Health Law Critics Prepare to Battle Over Insurance Exchange Subsidies". The New York Times. Retrieved July 7, 2012.
- ^ Krugman, Paul (January 31, 2010). "Krugman calls Senate health care bill similar to law in Massachusetts". PolitiFact. Retrieved August 29, 2012.
- ^ "ObamaCare Survives the Supreme Court: 5 Takeaways". The Week. June 28, 2012. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ Elmendorf, Douglas W. (March 30, 2011). "CBO's Analysis of the Major Health Care Legislation Enacted in March 2010" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. Retrieved July 15, 2012.
- ^ Elmendorf, Douglas W. (June 21, 2011). "CBO's 2011 Long-Term Budget Outlook" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. p. 44.
Through those changes and numerous others, the 2010 legislation significantly decreased Medicare outlays relative to what they would have been under prior law.
- ^ ABA Health eSource (July 12, 2012). "Supreme Court Upholds PPACA". Retrieved November 20, 2013.
- ^ Pg 55–58, slip opinion, National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, U.S. Supreme Court (June 28, 2012)
- ^ Barrett, Paul M. (June 28, 2012). "Supreme Court Supports Obamacare, Bolsters Obama". BloombergBusinessweek. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ National Post Wire Services (June 28, 2012). "Obamacare upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court". National Post. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ a b c "National Health Interview Survey, January to June 2016" (PDF). CDC.gov. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance Coverage for People Under Age 65:2016 to 2026". CBO. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ a b "Rates Up 22 Percent For Obamacare Plans, But Subsidies Rise, Too". Retrieved November 19, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Employer Health Benefits 2015". Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved November 19, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Average Annual Workplace Family Health Premiums Rise Modest 3%". Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ a b c Wallace, Gregory (June 25, 2012). "'Obamacare': The word that defined the health care debate". CNN. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- ^ a b "Where are States Today? Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Levels for Children and Non-Disabled Adults". Kaiser Family Foundation. March 28, 2013.
- ^ "Medicaid Expansion". Is Medicaid eligibility expanding to 133 or 138 percent FPL, and what is MAGI?: American Public Health Association (APHA). Retrieved July 24, 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ H.R. 3590 Enrolled, section 1001 (adding section 2714 to the Public Health Service Act): "A group health plan and a health insurance issuer offering group or individual health insurance coverage that provides dependent coverage of children shall continue to make such coverage available for an adult child (who is not married) until the child turns 26 years of age."
- ^ "Young Adults and the Affordable Care Act" (PDF).
- ^ a b c d "Cost Estimate for Pending Health Care Legislation" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. March 20, 2010. Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ a b Chaikind, Hinda; Copeland, Curtis W.; Redhead, C. Stephen; Staman, Jennifer (March 2, 2011). "PPACA: A Brief Overview of the Law, Implementation, and Legal Challenges" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. R41664. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c Trumbull, Mark (March 23, 2010). "Obama signs health care bill: Who won't be covered?". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ Fox, Emily Jane (July 24, 2012). "6 million will lose out on Medicaid expansion". CNNMoney. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
- ^ "Explaining Health Care Reform: Questions About Health Insurance Subsidies". Kaiser Family Foundation. July 1, 2012. Retrieved July 1, 2012.
- ^ Luhby, Tami (April 23, 2013). "Millions eligible for Obamacare subsidies, but most don't know it". CNNMoney. Retrieved June 22, 2013.
- ^ "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act/Title I/Subtitle E/Part I/Subpart A".
- ^ Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: Title I: Subtitle E: Part I: Subpart A: Premium Calculation
- ^ "Small Business Health Care Tax Credit for Small Employers". Internal Revenue Service. December 13, 2011. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ "Treasury Lays the Foundation to Deliver Tax Credits" (PDF).
- ^ "Health Insurance Premium Credits in the PPACA" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. April 28, 2010.
- ^ a b "Explaining Health Care Reform". Kaiser Family Foundation.
- ^ "Explaining Health Care Reform" (PDF). Kaiser Family Foundation.
- ^ "Health Insurance Premium Credits Under PPACA" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. 2014.
- ^ "An Analysis of Health Insurance Premiums Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act".
- ^ "Policies to Improve Affordability and Accountability". The White House.
- ^ "Kaiser Family Foundation:Health Reform Subsidy Calculator – Premium Assistance for Coverage in Exchanges/Gateways".
- ^ Amadeo, Kimberly. "How Much Will Obamacare Cost Me". The Balance. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ a b "Minimum Coverage Provision ("individual mandate")". American Public Health Association (APHA).
- ^ Galewitz, Phil (March 26, 2010). "Consumers Guide To Health Reform". Kaiser Health News.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 5, 2013). "Burn Your Obamacare Card, Burn Yourself". The New Republic.
- ^ McClanahan, Carolyn (August 4, 2013). "Reader's Questions About Obamacare – Misinformation Abounds". Forbes. Retrieved August 15, 2013.
- ^ a b Pippenger, Nathan (March 28, 2012). "Health Care Reform Without The Mandate?". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 9, 2010). "Common Sense". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (April 2, 2012). "What If the Mandate Goes?". The New Republic. - ^ Cohn, Jonathan (July 15, 2013). "Obamacare's Individual Mandate Can't Wait". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (April 2, 2012). "What If the Mandate Goes?". The New Republic. - ^ a b Cohn, Jonathan (March 21, 2012). "Reform With No Mandate? Ask New Jersey About That". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (June 8, 2012). "Just in Case: How Reform Might Survive Without the Mandate". The New Republic.
- ^ Banthin, Jessica (March 20, 2012). "Effects of Eliminating the Individual Mandate to Obtain Health Insurance". CBO.
- ^ a b Jonathan Gruber (economist) (February 2011). "Health Care Reform without the Individual Mandate" (PDF). Center for American Progress.
- ^ Eibner, Christine; Price, Carter (2012). "The Effect of the Affordable Care Act on Enrollment and Premiums, With and Without the Individual Mandate" (PDF). Rand Health.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 9, 2010). "Common Sense". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (April 2, 2012). "What If the Mandate Goes?". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (December 26, 2011). "Was the Mandate a Mistake?". The New Republic. - ^ Cohn, Jonathan (December 26, 2011). "Was the Mandate a Mistake?". The New Republic.
- ^ "Explaining Health Care Reform: What is Employer "Pay-or-Play" Requirement?". Kaiser Family Foundation. May 1, 2009. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ McNamara, Kristen (March 25, 2010). "What Health Overhaul Means for Small Businesses". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (May 21, 2013). "Weaseling Out of Obamacare". The New Republic.
- ^ "Health Coverage & Uninsured". Kaiser Family Foundation. June 20, 2013.
"Health Insurance Coverage of the Total Population". Kaiser Family Foundation. June 20, 2013. - ^ "Pg 14 of 'Kaiser Health Tracking Poll: June 2013'" (PDF). Kaiser Family Foundation. June 2013.
- ^ "The Patients' Bill of Rights: Ending annual and lifetime limits" (PDF) (Press release). FamiliesUSA. September 23, 2010. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2009: Health Insurance Exchanges" (PDF). National Association of Insurance Commissioners. April 20, 2010. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ "HHS and states move to establish Affordable Insurance Exchanges, give Americans the same insurance choices as members of Congress" (Press release). HHS. July 11, 2011. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ "Essential Health Benefits". HealthCare.gov. September 23, 2010. Retrieved February 9, 2016.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (June 12, 2013). "You Call This Insurance?". The New Republic.
- ^ a b c Levitt, Larry; Claxton, Gary; Pollitz, Karen (October 18, 2011). "Questions About Essential Health Benefits". Kaiser Family.
- ^ "Essential Health Benefits". HealthCare.gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
"What does Marketplace health insurance cover?". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. - ^ "Preventive Services Covered Under the Affordable Care Act".
- ^ "Login". Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ^ "Quick Take: Essential Health Benefits: What Have States Decided for Their Benchmark?". Kaiser Family. December 7, 2012.
- ^ PPACA, 2713,(a)(4)
- ^ Women's Preventive Services Guidelines HRSA, US Department of Health and Human Services
- ^ "Women's Preventive Services Coverage and Non-Profit Religious Organizations". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Retrieved September 8, 2013.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah (August 1, 2012). "Five facts about the health law's contraceptive mandate". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 29, 2012.
- ^ Dept. Health and Human Services (February 10, 2012). "Group Health Plans and Health Insurance Issuers Relating to Coverage of Preventive Services Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act – Final Rules" (77 FR 8725). Federal Register. Retrieved February 15, 2012.
Summary: These regulations finalize, without change, interim final regulations authorizing the exemption of group health plans and group health insurance coverage sponsored by certain religious employers from having to cover certain preventive health services under provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.
- ^ Park, Madison (July 19, 2011). "Birth control should be fully covered under health plans, report says". CNN. Retrieved August 27, 2012.
- ^ "Provisions of the Affordable Care Act, By Year". HealthCare.gov. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ "Key Features of the Affordable Care Act By Year". HHS. June 7, 2013. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
- ^ a b Binckes, Jeremy; Wing, Nick (March 22, 2010). "The Top 18 Immediate Effects Of The Health Care Bill". The Huffington Post. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ http://www.bcbsm.com/index/health-insurance-help/faqs/topics/how-health-insurance-works/out-of-pocket-maximums.html
- ^ U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (June 28, 2010). "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act; Requirements for Group Health Plans and Health Insurance Issuers Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act Relating to Preexisting Condition Exclusions, Lifetime and Annual Limits, Rescissions, and Patient Protections; Final Rule and Proposed Rule". Federal Register. 75 (123): 37187–37241. Retrieved July 26, 2010.
- ^ Pool, Gentrie (October 7, 2010). "After PPACA: The Future of the Health Insurance Underwriter". Asjonline.com. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ "Selected Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) implementation dates of interest to RNs as caregivers, RNs as patients, and RNs as employees" (PDF). Nursingworld.org. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ http://www.naifa.org/practice-resources/prp/age-band-rating-(aca)
- ^ Bowman, Lee (March 22, 2010). "Health reform bill will cause several near-term changes". Scripps Howard News Service. Retrieved March 23, 2010.
- ^ a b "Summary of the Affordable Care Act" (PDF). Kaiser Family Foundation. April 23, 2013.
- ^ "Health Insurance Market Reforms: Prevention". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. December 21, 2010. Retrieved September 8, 2013.
- ^ "Next Steps to Comply with Health Care Reform". The National Law Review. October 10, 2012. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
- ^ "How do I choose Marketplace insurance?". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
- ^ "Health Plan Categories". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
- ^ "Medical Loss Ratio". Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services. Retrieved October 2, 2013.
- ^ "Medical Loss Ratio Requirements Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act". Federal Register. December 7, 2011. p. 76573. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "Welcome to the Marketplace". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
"What is the Health Insurance Marketplace?". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. - ^ "Insurance Exchanges". American Public Health Association (APHA).
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 29, 2013). "Obamacare Sticker Shock: Not Very Shocking". The New Republic.
- ^ a b "State Decisions For Creating Health Insurance Exchanges, as of May 28, 2013 - Notes". Kaiser Family Foundation. May 28, 2013.
- ^ "State Health Insurance Exchange Laws: The First Generation". The CommonWealth Fund. July 25, 2012.
- ^ Adams, Rebecca (July 22, 2013). "The Question of Abortion Coverage in Health Exchanges". Roll Call.
- ^ a b "Public Law 111 – 148, section 1332". Government Printing Office. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ "Preparing for Innovation: Proposed Process for States to Adopt Innovative Strategies to Meet the Goals of the Affordable Care Act". U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. November 16, 2011. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Goldstein, Amy; Balz, Dan (March 1, 2011). "Obama offers states more flexibility in health-care law". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Gov. Shumlin issued the following statement on health care rules". Governor.vermont.gov. March 14, 2011. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Estes, Adam Clark (May 26, 2011). "Vermont Becomes First State to Enact Single-Payer Health Care". The Atlantic. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Wing, Nicholas (May 26, 2011). "Vermont Single-Payer Health Care Law Signed By Governor". The Huffington Post.
- ^ "Costs derail Vermont's single-payer health plan - The Boston Globe".
- ^ a b c d e f "Accountable Care Organizations, Explained". Kaiser Health News. September 14, 2015. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- ^ "Access". Medscape. Retrieved January 9, 2012.(registration required)
- ^ "Key Healthcare Reform Initiatives: Medicare Bundled Payment Pilots". Huron Consulting Group. November 19, 2010. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ "More savings in the drug coverage gap coming through 2020". Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
- ^ "What the Affordable Care Act means for prescription coverage". Washington Post. Retrieved August 7, 2016.
- ^ a b Chait, Jonathan (May 29, 2013). "Yuval Levin Dissembles Madly". New York.
- ^ a b Span, Paula (March 29, 2010). "Options Expand for Affordable Long-Term Care". nytimes.com. Retrieved March 29, 2010.
- ^ PriceWaterHouseCoopers. "The CLASS Act." HRS Insight: Human Resource Services. 2010: 1-6. Web.
- ^ a b Carney, Timothy (February 28, 2011) So, yeah, the health-care bill was really an awful piece of legislation that sent the revolving door spinning faster, Washington Examiner
- ^ "Consumer Operated and Oriented Plans (CO-OPs)".
- ^ a b c d Roy, Avik (February 7, 2012). "The Tortuous History of Conservatives and the Individual Mandate". Forbes Magazine.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 9, 2010). "Common Sense". The New Republic.
- ^ a b c Cooper, Michael (February 14, 2012). "Conservatives Sowed Idea of Health Care Mandate, Only to Spurn It Later". The New York Times. Retrieved July 2, 2012.
- ^ a b c Klein, Ezra (June 25, 2012). "Unpopular Mandate". The New Yorker. Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Bob; Clift, Eleanor (September 18, 1994). "The Lost Chance". Newsweek. Retrieved July 2, 2012.
- ^ Fouhy, Beth (October 5, 2007). "Hillary Claims Credit for Child Program". Associated Press for NewsMax. Archived from the original on January 23, 2008.
- ^ a b "Chart: Comparing Health Reform Bills: Democrats and Republicans 2009, Republicans 1993". Kaiser Health News. February 23, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
"Summary Of A 1993 Republican Health Reform Plan". Kaiser Health News. February 23, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2012. - ^ "In 1993, Republicans Proposed A Mandate First". NPR. March 31, 2012.
- ^ "History of the Individual Health Insurance Mandate, 1989-2010 Republican Origins of Democratic Health Care Provision". ProCon.org. February 9, 2012.
- ^ a b "Facebook post says Republicans embraced individual mandate in 1993". PolitiFact. April 19, 2012.
- ^ "AG Suthers couldn't be more wrong in his decision to file lawsuit". Colorado Statesman. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
- ^ "G.O.P. and Health Mandate". The New York Times. February 26, 2012.
- ^ "Romneycare's 98% Success Rate Defies Gripes on Obama Law". Bloomberg. March 26, 2012.
- ^ Ball, Molly (May 31, 2012). "Was Mitt Romney a Good Governor?". The Atlantic. Retrieved October 28, 2013.
- ^ a b Lizza, Ryan (June 6, 2011). "Romney's dilemma". The New Yorker. Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ^ "Bill Summary & Status - S.334". Library of Congress THOMAS. Retrieved September 24, 2013.
- ^ Kuttner, Robert (June 28, 2011). "RomneyCare vs. ObamaCare". The Boston Globe. Retrieved September 23, 2013.
- ^ Cline, Andrew. "How Obama Broke His Promise on Individual Mandates". The Atlantic. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ^ "CNN Democratic presidential debate". CNN. January 21, 2008. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ^ "The First Presidential Debate". The New York Times. September 26, 2008.
- ^ "Remarks of President Barack Obama – Address to Joint Session of Congress". The White House. February 24, 2009. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e "Timeline: Milestones in Obama's quest for healthcare reform". Reuters. March 22, 2010. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ Kruger, Mike (October 29, 2009). "Affordable Health Care for America Act". United States House Committee on Education and Labor. Archived from the original on January 6, 2010. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ "Health Care Reform from Conception to Final Passage". Retrieved November 23, 2010.
- ^ "Senate Finance Committee Hearings for the 111th Congress recorded by C-SPAN". C-SPAN.
- ^ "Senate Finance Committee hearings for 111th Congress". Finance.Senate.Gov. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "Jonathan Gruber (economist)". MIT Department of Economics. Retrieved September 2, 2013."Jonathan Gruber: short biography". MIT Department of Economics. Retrieved September 2, 2013.
- ^ a b Cohn, Jonathan (May 21, 2010). "How They Did It". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (September 4, 2009). "Party Is Such Sweet Sorrow". The New Republic.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (April 22, 2010). "Obama's Moderate Health Care Plan". The New Republic.
Chait, Jonathan (December 19, 2009). "The Republican Health Care Blunder". The New Republic. - ^ Chait, Jonathan (December 19, 2009). "The Republican Health Care Blunder". The New Republic.
- ^ Hulse, Carl; Nagourney, Adam (March 16, 2010). "Senate G.O.P. Leader Finds Weapon in Unity". The New York Times.
- ^ Eaton, Joe; Pell, M. B.; Mehta, Aaron (March 26, 2010). "Lobbying Giants Cash In On Health Overhaul". NPR. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 25, 2009). "Drug Deal". The New Republic.
- ^ Grim, Ryan (August 13, 2009). "Internal Memo Confirms Big Giveaways In White House Deal With Big Pharma". The Huffington Post.
- ^ "Visualizing The Health Care Lobbyist Complex". Sunlight Foundation. July 22, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Horwitz, Sari; Pershing, Ben (April 9, 2010). "Anger over health-care reform spurs rise in threats against Congress members". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 9, 2010.
- ^ Kellman, Laurie; Abrams, Jim (March 26, 2010). "Threats against lawmakers spread after health vote". Associated Press.
- ^ "Remarks by the President to a Joint Session of Congress on Health Care". The White House. September 10, 2009. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ Kennedy, Edward M. (May 12, 2009). "Text of letter to the President from Senator Edward M. Kennedy". White House Press Secretary. Archived from the original on September 10, 2009. Retrieved September 10, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ U.S. Const. art. I, § 7, cl. 1.
- ^ Maze, Rick (October 8, 2009). "House OKs tax breaks for military homeowners". Air Force Times. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ S.Amdt. 2786
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (September 7, 2009). "Why Reform Survived August". The New Republic.
- ^ Hacker, Jacob S. (December 20, 2009). "Why I Still Believe in This Bill". The New Republic.
- ^ a b Cohn, Jonathan (March 12, 2010). "The Public Option, Still Dead". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (December 15, 2009). "What Public Option Supporters Won". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (December 17, 2009). "Ben Nelson, Still a Big Problem (Updated)". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (December 19, 2009). "BREAKING: Nelson Says Yes; That Makes 60". The New Republic.
- ^ "'Cornhusker' Out, More Deals In: Health Care Bill Gives Special Treatment". Fox News. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ "Roll Call vote No. 396 – On Passage of the Bill (H.R. 3590 as Amended)". U.S. Senate. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ "AARP, AMA Announce Support For Health Care Bill: Largest Doctors And Retiree Groups Backing Legislation". The Huffington Post, March 19, 2010.
- ^ Applewhite, J. Scott. "Senator-elect Scott Brown welcomed as Republican hero after upset victory in Massachusetts". McClatchy-Tribune News Service. Associated Press. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
- ^ "Public Statements – Project Vote Smart" (Press release). Votesmart.org. January 13, 2010. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ Silver, Nate (January 21, 2010). "Will the Base Abandon Hope?". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ a b Cohn, Jonathan (January 17, 2010). "How to Pass the Bill--Whatever Happens Tuesday". The New Republic.
- ^ a b c Stolberg, Sheryl; Zeleny, Jeff; Hulse, Carl (March 20, 2010). "Health Vote Caps a Journey Back From the Brink". The New York Times. Retrieved March 23, 2010.
- ^ a b Brown, Carrie; Thrush, Glenn (March 20, 2010). "Pelosi steeled W.H. for health push". Politico. Retrieved March 23, 2010.
- ^ "White House Unveils Revamped Reform Plan, GOP And Industry React". Kaiser Health News. February 22, 2010. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ a b Chait, Jonathan (February 20, 2010). "A Brief Reconciliation Primer". The New Republic.
- ^ a b Silver, Nate (December 26, 2009). "For Pelosi, Many Paths to 218". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Silver, Nate (January 21, 2010). "1. Reconciliation! 2. ??? 3. Profit!". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (September 21, 2009). "Reconciliation: Why Most Dems Don't Want to Go There". The New Republic.
- ^ Executive Order 13535 of March 24, 2010 — Ensuring Enforcement and Implementation of Abortion Restrictions in the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, Vol. 75, No. 59 75 FR 15599, March 29, 2010.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (March 21, 2010). "Stupak Makes A Deal, Reform To Pass". The New Republic.
- ^ "Roll Call vote No. 165: On Motion to Concur in Senate Amendments (Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act)". Office of the Clerk: House of Representatives. March 21, 2010. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ Aro, Margaret; Mooney, Mark (March 22, 2010). "Pelosi Defends Health Care Fight Tactics". ABC News. Retrieved March 23, 2010.
- ^ Stolberg, Sheryl; Pear, Robert (March 23, 2010). "Obama Signs Health Care Overhaul Bill, With a Flourish". The New York Times. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ http://www.msnbc.com/rachel-maddow-show/groundhog-day-republicans-vote-repeal-obamacare
- ^ "Updated Estimates for the Insurance Coverage Provisions of the Affordable Care Act". Congressional Budget Office. March 13, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ a b Pecquet, Julian (March 13, 2012). "CBO: Obama's health law to cost less, cover fewer people than first thought". The Hill. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ Inc., Gallup,. "U.S. Uninsured Rate at 11.0%, Lowest in Eight-Year Trend". Retrieved August 22, 2016.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Obama B (July 11, 2016). "United states health care reform: Progress to date and next steps". JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.9797. ISSN 0098-7484.
- ^ Barry-Jester, Anna Maria; Ben, Casselman (September 22, 2016). "Obamacare Has Increased Insurance Coverage Everywhere". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 30, 2013). "Obamacare's New Paperwork Is Simpler than Private Insurers'". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (April 29, 2013). "Why Obamacare Is Not a 'Train Wreck' (Again)". The New Republic. - ^ Trish Riley; Jane Hyatt Thorpe. "Multi-State Plans Under the Affordable Care Act" (PDF). George Washington University Medical Center, Department of Health Policy.
- ^ Abelson, Reed (June 16, 2013). "Choice of Health Plans to Vary Sharply From State to State". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Nussbaum, Alex (March 4, 2015). "Health Insurance Exchanges". Bloomberg View. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ^ "Obama's claim the Affordable Care Act was a 'major reason' in preventing 50,000 patient deaths". Washington Post. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (February 8, 2012). "Religious Institutions Matter. So Do Their Employees". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (February 10, 2012). "Obama's Deal on Birth Control Coverage". The New Republic.
- ^ a b Burwell v. Hobby Lobby, 573 U.S. (United States Supreme Court 2014).
- ^ a b Adler, Jonathan A. (July 3, 2014). "Supreme Court grants Wheaton College an injunction against contraception mandate accommodation". The New York Times. Retrieved July 9, 2014.
- ^ a b "Status of State Action on the Medicaid Expansion Decision, as of September 1, 2015". Kaiser Family Foundation. June 22, 2015.
- ^ "Status of State Action on the Medicaid Expansion Decision". Kaiser Family Foundation.
- ^ a b "Cost of Obamacare Medicaid Expansion 49% Higher Than Previously Estimated". August 12, 2016. Retrieved August 13, 2016.
- ^ Rutkin, Aviva. "Obamacare has already improved health of low-income Americans". Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- ^ "Medicaid expansion under ACA linked with better health care, improved health for low-income adults | News | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health". www.hsph.harvard.edu. Retrieved August 30, 2016.
- ^ Sanger-katz, Margot (August 25, 2016). "How Expanding Medicaid Can Lower Insurance Premiums for All". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved September 4, 2016.
- ^ "Health Insurance Premium Credits in the PPACA" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved May 17, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Correction Regarding the Longer-Term Effects of the Manager's Amendment to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. December 19, 2009. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ a b "An Analysis of Health Insurance Premiums Under the Patient Protection and Affordable Health Care Act". Cbo.gov. November 30, 2009. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 14, 2013). "The Big Savings Obamacare Critics Miss". The New Republic.
- ^ "Obama Administration Is Downplaying Impact of Large Rate Hikes, Lack of Subsidies Faced by Millions of Individual Enrollees, AIS Newsletter Finds". Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ "Without Subsidies, Many Non-Group Blues Members Aren't Insulated From Rate Hikes | AIS Health". aishealth.com. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Johnson, Carolyn Y. (September 14, 2016). "How companies are quietly changing your health plan to make you pay more". Washington Post. Retrieved September 14, 2016.
- ^ Mali, Meghashyam (August 11, 2016). "Next president faces possible ObamaCare meltdown". Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- ^ a b "2017 Premium Changes and Insurer Participation in the Affordable Care Act's Health Insurance Marketplaces". Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ PricewaterhouseCoopers. "Medical Cost Trend: Behind the Numbers 2017". Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- ^ a b c Lowrey, Annie (May 7, 2013). "Slowdown in Rise of Healthcare Costs May Persist". The New York Times. Retrieved June 10, 2013.
- ^ a b Chait, Jonathan (May 10, 2013). "The Facts Are In and Paul Ryan Is Wrong". New York.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (September 26, 2013). "Someone Tell Ted Cruz the Obamacare War Is Over". New York.
- ^ Wayne, Alex (June 18, 2013). "Health Cost Growth Slows Further Even as Economy Rebounds". Bloomberg L.P.
- ^ "Assessing the Effects of the Economy on the Recent Slowdown in Health Spending". Kaiser Family Foundation. April 22, 2013.
- ^ Krawzak, Paul (June 14, 2013). "In Spending Debate, Baby Boomer Issue Remains a Headache for Legislators". Roll Call.
- ^ Obama, B, JD. United States Health Care Reform - Progress to Date and Next Steps. JAMA. Published online July 11, 2016. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.9797
- ^ "Another Comment on CBO's Estimates for the Insurance Coverage Provisions of the Affordable Care Act". Congressional Budget Office. March 16, 2012. Retrieved October 7, 2013.
- ^ a b "CBO's Analysis of the Major Health Care Legislation Enacted in March 2010". Congressional Budget Office. March 30, 2011. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ "Another Comment on CBO's Estimates for the Insurance Coverage Provisions of the Affordable Care Act". Congressional Budget Office. March 16, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ "H.R. 4872, Reconciliation Act of 2010" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. March 18, 2010. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ Dennis, Steven (March 18, 2010). "CBO: Health Care Overhaul Would Cost $940 Billion". Roll Call. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- ^ Klein, Ezra (March 22, 2010). "What does the health-care bill do in its first year?". The Washington Post.
- ^ Judith Solomon; Paul N. Van de Water (April 18, 2012). "Letter: Improving the Strength and Solvency of Medicare". The Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
- ^ "CBO's Estimates for the Insurance Coverage Provisions of the Affordable Care Act Updated for the Recent Supreme Court Decision". Congressional Budget Office. July 24, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ Sahadi, Jeanne (March 13, 2012). "Health reform coverage cost falls slightly". CNN. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ "Budgetary and Economic Effects of Repealing the Affordable Care Act". Congressional Budget Office. June 18, 2015. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
- ^ a b "Affordable Care Act Update: Implementing Medicare Cost Savings" (PDF). Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. August 2, 2010. Retrieved October 7, 2013.
- ^ "Higher Spending Relative to Medicare Fee-for-Service May Not Ensure Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs for Beneficiaries". Government Accountability Office. February 8, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2013.
- ^ "Where does health care reform stand?". CNN. March 18, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- ^ Farley, Robert (March 18, 2010). "Pelosi: CBO says health reform bill would cut deficits by $1.2 trillion in second decade". PolitiFact.com. Retrieved April 7, 2010.
- ^ "Sen. Tom Coburn: Obamacare PR campaign anchored in spin, not reality". The Washington Examiner. July 8, 2006. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ James Capretta. "Obamacare's Cooked Books and the 'Doc Fix'". National Review.
- ^ Hogberg, David (November 22, 2010). "GOP Might Target ObamaCare As Part Of A Medicare 'Doc Fix'". Investor's Business Daily. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "Responses to Questions About CBO's Preliminary Estimate of the Direct Spending and Revenue Effects of H.R. 4872, the Reconciliation Act of 2010" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (March 24, 2010). "The Doc Fix Myth And The Right's Misinformation Feedback Loop". The New Republic.
- ^ Van de Water, Peter. "Debunking False Claims About Health Reform, Jobs, and the Deficit". Center for Budget and Policy Priorities.
- ^ Uwe Reinhardt (March 24, 2010). "Wrapping Your Head Around the Health Bill". The New York Times. Retrieved October 9, 2010.
- ^ Holtz-Eakin, Douglas (March 21, 2010). "The Real Arithmetic of Health Care Reform". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Cohn, Jonathan (January 21, 2011). "The GOP's Trick Play". The New Republic.
- ^ Scheiber, Noam (September 17, 2009). "Is the CBO Biased Against Health Care Reform?". The New Republic.
- ^ "Electronic Medical Records (Health Information Technology)".
- ^ James, Frank (March 19, 2010). "Health Overhaul Another Promise U.S. Can't Afford: Expert". NPR. Retrieved April 7, 2010.
- ^ "Congress Has Good Record of Implementing Medicare Savings". CBPP. Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ "Can Congress cut Medicare costs?". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ a b Government Printing Office. "Title 26 - Internal Revenue Code" (PDF).
- ^ a b Chait, Jonathan (July 3, 2013). "Obama Employer Mandate Delay Train Wreck! Or Not". New York.
- ^ a b c d Sarah Kliff (May 6, 2013). "Will Obamacare lead to millions more part-time workers? Companies are still deciding". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b Ungar, Rick. "The Real Numbers On 'The Obamacare Effect' Are In-Now Let The Crow Eating Begin". Forbes. Retrieved November 11, 2014.
- ^ "Employment Situation Summary". Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved November 11, 2014.
- ^ Conover, Chris. "Who Can Deny It? Obamacare Is Accelerating U.S. Towards A Part-Time Nation". Forbes. Retrieved November 11, 2014.
- ^ Moriya, A. S.; Selden, T. M.; Simon, K. I. (January 5, 2016). "Little Change Seen In Part-Time Employment As A Result Of The Affordable Care Act". Health Affairs. 35 (1): 119–123. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2015.0949.
- ^ Bill Sizemore (February 8, 2013). "Va. workers' part-time hours capped due to health law". The Virginian-Pilot.
Annie-Rose Strasser (February 11, 2013). "Virginia Cuts State Employees' Hours To Avoid Providing Obamacare Coverage". ThinkProgress. - ^ Ned Resnikoff (January 14, 2013). "Colleges roll back faculty hours in response to Obamacare". MSNBC.
Sy Mukherjee (January 14, 2013). "Four Public Colleges Will Cut Adjunct Faculty Hours To Avoid Providing Health Coverage Under Obamacare". ThinkProgress. - ^ a b "As Health Law Changes Loom, A Shift To Part-Time Workers". NPR. April 29, 2013.
- ^ Jared Bernstein (September 4, 2013). "Stop Blaming Obamacare for Part-Time Workers". Teagan Goddard's Wonkwire.
- ^ Matthew Yglesias (July 15, 2013). "Obamacare's Not To Blame For Increasing Part-time Work". Slate.
- ^ Timothy Jost (July 2, 2013). "Implementing Health Reform: A One-Year Employer Mandate Delay". Health Affairs.
- ^ a b c Cohn, Jonathan (July 2, 2013). "Some Bad News About Obamacare That Isn't Bogus". The New Republic.
- ^ "Am I eligible for coverage in the Marketplace?". HealthCare.Gov, managed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
- ^ a b Robert Greenstein; Judith Solomon (July 3, 2013). "Finance Committee Makes Flawed Employer Requirement in Health Reform Bill Still More Problematic". Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
- ^ a b c d Ezra Klein (July 2, 2013). "Will Obamacare lead to millions more part-time workers? Companies are still deciding". The Washington Post.
- ^ Matthew Yglesias (July 3, 2013). "Delaying Employer Responsibility Fines Is a Good Idea—the Real Problem Comes Later". Slate.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (July 3, 2013). "Obamacare Haters Struggling to Understand What 'Nonessential' Means". New York.
Chait, Jonathan (July 3, 2013). "Obamacare Still Not Collapsing". New York. - ^ Cohn, Jonathan (July 15, 2013). "Obamacare's Individual Mandate Can't Wait". The New Republic.
- ^ "Union Letter: Obamacare Will 'Destroy The Very Health and Wellbeing' of Workers", The Wall Street Journal, July 12, 2013.
- ^ Torres, Carlos (January 27, 2014). "Economists See Little Effect on Hiring From U.S. Health-Care Law". www.businessweek.com. Bloomberg L.P. Retrieved January 27, 2014.
- ^ O'Donnell, Jayne; Ungar, Laura; Hoyer, Meghan (November 12, 2014). "Rural hospitals in critical condition". USA Today. Retrieved January 28, 2015.
Hamada, Omar L. (November 18, 2014). "Obamacare has detrimental effect on rural hospitals". The Tennessean. Retrieved January 28, 2015. - ^ Howell, Tom Jr. (May 4, 2015). "ER visits up under Obamacare despite promises, doctors' poll finds". The Washington Times. Retrieved May 6, 2015.
- ^ "Obama and Democrats' Health Care Plan". RealClearPolitics. October 13, 2013. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ^ Swanson, Emily (July 30, 2009). "Health Care Plan: Favor/Oppose". Pollster.com.
- ^ "As Health Care Law Proceeds, Opposition and Uncertainty Persist" (PDF). Pew Research Center. September 16, 2013.
- ^ Page, Susan (March 24, 2010). "Poll: Health care plan gains favor". USA Today. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ a b Zengerle, Patricia (June 24, 2012). "Reuters-Most Americans Oppose Health Law But Like the Provisions". Reuters. Retrieved June 28, 2012.
- ^ Ezra Klein (June 26, 2012). "Republicans hate 'Obamacare', but like most of what it does". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 28, 2012.
- ^ Greg Sargent (June 25, 2012). "Republicans Support Obama's Health Reforms - As Long As His Name Isn't On Them". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 28, 2012.
- ^ "CNN Opinion Research Poll" (PDF). CNN. March 22, 2010.
- ^ Rasmussen, Scott; Schoen, Doug (March 9, 2010). "Why Obama Can't Move the Health-Care Numbers". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (June 13, 2013). "Obamacare, Public Opinion, and Conservative Self-Delusion". New York Magazine.
- ^ Jackson, David. "Poll: Most oppose blocking Obama health care law". USA Today. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- ^ "RAND Health Reform Opinion Study". RAND Health. May 1, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
- ^ "AP-GfK Poll: Obama's health care fails to gain support". Associated Press. March 28, 2014. Retrieved March 30, 2014.
- ^ "The ObamaCare 8%". The Wall Street Journal. April 30, 2014. Retrieved May 1, 2014.
- ^ Alan Colmes, "Poll: Voters No Longer Want To Repeal Obamacare", Liberaland, December 1, 2014.
- ^ "Poll: Obamacare and the Supreme Court". CBS News. Retrieved June 23, 2015.
- ^ "After the Election, the Public Remains Sharply Divided on Future of the Affordable Care Act". Kaiser Family Foundation. December 3, 2016.
- ^ Amanda Cox; Alicia Desantis; Jeremy White (March 25, 2012). "Fighting to Control the Meaning of 'Obamacare'". The New York Times. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ a b Baker, Peter (August 3, 2012). "Democrats Embrace Once Pejorative 'Obamacare' Tag". The New York Times. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ Nelson, Steven (June 8, 2011). "Democratic Rep. John Conyers wants to reclaim 'ObamaCare', make it a compliment". The Daily Caller. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Madison, Lucy (August 15, 2011). "On bus tour, Obama embraces 'Obamacare', says 'I do care'". CBS News. Retrieved April 28, 2012.
- ^ Strauss, Daniel (March 23, 2012). "Obama camp's pitch to supporters: 'Hell yeah, I'm for Obamacare'". The Hill. Retrieved March 27, 2012.
- ^ Prince, Richard (October 2, 2013). "AP, NPR Curb Use of "Obamacare" Term". Robert C. Maynard Institute for Journalism Education. Retrieved October 5, 2013.
- ^ Gold, Hadas (October 4, 2013). "AP, NPR to cut back on 'Obamacare'". Politico. Retrieved October 19, 2013.
- ^ a b "Sarah Palin falsely claims Barack Obama runs a "death panel"". PolitiFact. August 10, 2009.
- ^ Drobnic Holan, Angie (December 19, 2009). "PolitiFact's Lie of the Year: 'Death panels'". PolitiFact. Retrieved November 19, 2010.
- ^ Henig, Jess; Robertson, Lori (July 29, 2010). "False Euthanasia Claims". FactCheck.org.
- ^ Lori Robertson (December 24, 2009). "Whoppers of 2009—We review the choicest falsehoods from a year that kept us busy". FactCheck.org. Retrieved April 28, 2011.
- ^ "'Tweet' 2009 Word of the Year, 'Google' Word of the Decade, as voted by American Dialect Society" (PDF). American Dialect Society. January 8, 2010. Retrieved October 8, 2010.
- ^ "Euthanasia Counseling". Snopes. August 13, 2009.
- ^ Nyhan, Brendan (2010). "Why the "Death Panel" Myth Wouldn't Die: Misinformation in the Health Care Reform Debate" (PDF). The Forum. 8 (1). Berkeley Electronic Press. doi:10.2202/1540-8884.1354.
- ^ Viebeck, Elise (September 26, 2012). "Poll: Four in 10 believe in Obama healthcare law 'death panels'". The Hill.
- ^ "Seniors Beware". Snopes. August 23, 2012.
- ^ Beutler, Brian (August 13, 2013). "A new kind of birther and death panel insanity explodes". Salon. Retrieved December 3, 2013.
- ^ Ebeler, Jack; Neuman, Tricia; Cubanski, Juliette (April 13, 2011). "The Independent Payment Advisory Board: A New Approach to Controlling Medicare Spending". Kaiser Family Foundation. p. 3. Retrieved November 27, 2013.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 20, 2011). "Here We Go Again, With the Death Panels". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 13, 2009). "Mandatory Death Counseling – exposed!". The New Republic.
- ^ Parsons, Christi; Zajac, Andrew (August 14, 2009). "Senate committee scraps healthcare provision that gave rise to 'death panel' claims; Though the claims are widely discredited, the Senate Finance Committee is withdrawing from its bill the inclusion of advance-care planning consultations, calling them too confusing". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Public Law 111 – 148, section 1312: "... the only health plans that the Federal Government may make available to Members of Congress and congressional staff with respect to their service as a Member of Congress or congressional staff shall be health plans that are (I) created under this Act (or an amendment made by this Act); or (II) offered through an Exchange established under this Act (or an amendment made by this Act)."
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (August 6, 2013). "Congress Exempts Itself From Obamacare! Or Something!". New York.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 13, 2013). "The Latest Obamacare Lie That Just Won't Die". The New Republic.
- ^ Bowers, Becky (August 14, 2013). "Sen. Ted Cruz says Obama 'just granted all of Congress an exception' to Obamacare". PolitiFact. Retrieved August 19, 2013.
- ^ Robertson, Lori (January 20, 2010). "Congress Exempt from Health Bill?". FactCheck.org.
- ^ Viebeck, Elise (February 27, 2013). "Poll: Four in 10 think illegals are covered by Obama healthcare law". The Hill. Retrieved December 7, 2013.
- ^ Farley, Robert (January 21, 2010). "The Democrats' health care bills would provide 'free health care for illegal immigrants'". PolitiFact. Retrieved August 19, 2013.
- ^ a b "Labor leaders' letter to Harry Reid and Nancy Pelosi". The Washington Post. January 27, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ a b "Union Letter: Obamacare Will 'Destroy The Very Health and Wellbeing' of Workers". The Wall Street Journal. July 12, 2013. Retrieved October 7, 2013.
- ^ Stolberg, Sheryl Gay (October 18, 2013). "States Are Focus of Effort to Foil Health Care Law". The New York Times. Retrieved October 19, 2013.
- ^ The Editorial Board (January 25, 2014). "The Koch Party". The New York Times. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- ^ Peters, Jeremy (January 20, 2011). "Conservatives' Aggressive Ad Campaign Seeks to Cast Doubt on Health Law". The New York Times.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (July 23, 2013). "Conservatives Brace for the Possibility Obamacare Won't Totally Suck". The New Republic.
- ^ Michael Cannon (July 6, 2007). "The Anti-Universal Coverage Club Manifesto". Cato Institute.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (June 25, 2012). "Health Care As a Privilege: What the GOP Won't Admit". New York.
- ^ Schoen, John W. (November 9, 2016). "Here's what's coming from the Trump administration". CNBC. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ "Resolution 54: AFL-CIO Convention Resolution on the Affordable Care Act". AFL-CIO. September 11, 2013. Retrieved October 7, 2013.
- ^ Cauchi, Richard (November 15, 2013). "State Legislation and Actions Challenging Certain Health Reforms". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved November 28, 2013.
- ^ "Health Care Lawsuit Case Challenges". Independent Women's Forum. November 26, 2013. Retrieved November 28, 2013.
- ^ "Analysis: U.S. Supreme Court Upholds the Affordable Care Act: Roberts Rules?". The National Law Review. von Briesen & Roper, S.C. June 29, 2012. Retrieved July 2, 2012.
- ^ "March 14, 2012 Statement on Religious Freedom and HHS Mandate". United States Conference of Catholic Bishops. March 14, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2012.
- ^ Goodstein, Laurie (May 21, 2012). "Catholics File Suits on Contraceptive Coverage". The New York Times.
- ^ Taylor, Audrey; Seanz, Arlette; Levine, Mike (June 25, 2015). "Supreme Court Upholds Obamacare Subsidies, President Says ACA 'Is Here to Stay'". ABC News. Retrieved June 25, 2015.
- ^ HABERKORN, JENNIFER (May 12, 2016). "House GOP wins Obamacare lawsuit". Politico. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ a b Robert Pear (May 24, 2013). "States' Policies on Health Care Exclude Some of the Poorest". The New York Times. Retrieved May 25, 2013.
In most cases, [Sandy Praeger, Insurance Commissioner of Kansas], said adults with incomes from 32 percent to 100 percent of the poverty level ($6,250 to $19,530 for a family of three) "will have no assistance".
- ^ Sarah Kliff (May 5, 2013). "Florida rejects Medicaid expansion, leaves 1 million uninsured". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 24, 2013.
- ^ "Beyond the pledges: Where the states stand on Medicaid". The Advisory Board Company. July 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah (July 5, 2012). "What Happens if a State Opts Out of Medicaid, in One Chart". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 15, 2012.
- ^ "Health Reform and MedicaidExpansion". HealthCare Reform Magazine. July 13, 2010. Retrieved January 9, 2012.
- ^ "Analyzing the Impact of State Medicaid Expansion Decisions". Kaiser Family Foundation. July 17, 2013.
- ^ "Enrollment Policy Provisions in the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" (PDF). Families USA. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (July 19, 2013). "We Don't Know Everything About Obamacare. But We Know Who's Trying to Sabotage It". The New Republic.
- ^ a b Tami Luhby (July 1, 2013). "States forgo billions by opting out of Medicaid expansion". CNN.
- ^ "Is Medicaid Expansion Good for the States?". U.S. News & World Report. n.d.
- ^ Evan Soltas (June 4, 2013). "Wonkbook: The terrible deal for states rejecting Medicaid". The Washington Post.
- ^ Price, CC; Eibner, C (June 2013). "For states that opt out of Medicaid expansion: 3.6 million fewer insured and $8.4 billion less in federal payments". Health Affairs (Project Hope). 32 (6): 1030–6. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2012.1019. PMID 23733976.
- ^ Glied, Sherry (December 2013). "How States Stand to Gain or Lose Federal Funds by Opting In or Out of the Medicaid Expansion" (PDF). Commonwealth Fund. Retrieved February 20, 2016.
- ^ "States Expanding Medicaid See Significant Budget Savings and Revenue Gains". Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. March 2016. Retrieved April 22, 2016.
- ^ Dickman, SL; Himmelstein, DU; McCormick, D; Woolhandler, S (2015). "Health and Financial Consequences of 24 States' Decision to Opt Out of Medicaid Expansion". International journal of health services : planning, administration, evaluation. 45 (1): 133–42. PMID 26460452.
- ^ Somashekhar, Sandhya (August 29, 2013). "States find new ways to resist health law". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b Ornstein, Norm (July 24, 2013). "The Unprecedented and Contemptible Attempts to Sabotage Obamacare". National Journal.
- ^ Pear, Robert (August 2, 2013). "Missouri Citizens Face Obstacles to Coverage". The New York Times. Retrieved August 3, 2013.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (July 25, 2013). "The Right's Latest Scheme to Sabotage Obamacare". The New Republic.
- ^ Kliff, Sarah (August 1, 2013). "Inside the Obamacare Resistance". The Washington Post.
- ^ O'Brien, Michael (March 22, 2010). "GOP quick to release 'repeal' bills". The Hill. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "Bill Summary & Status – 112th Congress (2011–2012) – H.R. 2". THOMAS. January 19, 2011.
- ^ "Final Vote Results for passage of Repealing the Job-Killing Health Care Law Act (H.R. 2)". THOMAS. January 19, 2011.
- ^ Beutler, Brian (January 19, 2011). "Dems Press GOPers To Repeal Their Own Benefits Along With Health Care Law". Talking Points Memo. Retrieved January 21, 2011.
- ^ "Motion to Waive All Applicable Budgetary Discipline Re: McConnell Amdt. No. 13". U.S. Senate. February 2, 2011. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "House Passes Health Care Repeal 245–189". C-SPAN. January 19, 2011.
- ^ Boles, Corey (June 28, 2012). "Romney, GOP Pledge to Repeal Health Law". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ^ "House Obamacare Repeal: Thirty-Third Time's the Charm?". ABC News. July 11, 2012.
- ^ Walker, Andrea K. (July 11, 2012). "House of representatives votes to repeal health reform for the 31st time". The Baltimore Sun. Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ Deirdre Walsh (February 3, 2015). "House votes -again-to repeal Obamacare". Reuters. Retrieved February 4, 2015.
- ^ Jonathan Weisman; Robert Pear (May 26, 2013). "Partisan Gridlock Thwarts Effort to Alter Health Law". The New York Times. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
we cannot use any of the normal tools to resolve ambiguities or fix problems
- ^ Lipton, Eric (March 19, 2013). "In Shift, Lobbyists Look for Bipartisan Support to Repeal a Tax". The New York Times.
- ^ Chait, Jonathan (July 3, 2013). "Obamacare Still Not Collapsing". New York.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (December 23, 2010). "What Defunding Health Reform Would Do". The New Republic.
- ^ Lori Montgomery; Paul Kane (October 1, 2013). "Shutdown begins: Stalemate forces first U.S. government closure in 17 years". The Washington Post.
Blake, Aaron (September 19, 2013). "McCain: Efforts to repeal and defund Obamacare 'not rational'". The Washington Post. Retrieved September 24, 2013. - ^ Beutler, Brian (September 19, 2013). "New test could expose GOP's pack of charlatans". Salon. Retrieved September 24, 2013.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (August 7, 2013). "Tea Party to Republicans: Shut Down the Government, or You're a Sellout". The New Republic.
- ^ Goddard, Teagan (May 17, 2013). "Blocking the Medicare Reform Board Won't Stop Reform". WonkWire.RollCall.com.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (May 24, 2010). "Save Donald". The New Republic.
Cohn, Jonathan (July 6, 2010). "Meet The Don". The New Republic. - ^ Cohn, Jonathan (July 19, 2011). "The New Nullification: GOP v. Obama Nominees". The New Republic.
- ^ "Paternalism 2.0". The Economist. August 23, 2014. Retrieved January 19, 2015.
- ^ "The Affordable Care Act and Employers". Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ "Is the Affordable Care Act a Hidden Jobs Killer?". Center for Economic and Policy Research. CEPR. Retrieved August 26, 2015.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (February 11, 2011). "Sorry, The CBO Did Not Say Health Reform Kills 800,000 Jobs". The New Republic.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (June 13, 2012). "Obamacare, Good for the Economy". The New Republic.
- ^ Heavey, Susan (February 18, 2011). "Repealing healthcare law would cost $210 bln: CBO". Reuters. Retrieved August 14, 2016.
- ^ "Analysis Of A Permanent Prohibition On Implementing The Major Health Care Legislation Enacted In March 2010". Congressional Budget Office. May 26, 2011. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ "Letter to the Honorable John Boehner providing an estimate for H.R. 6079, the Repeal of Obamacare Act". Congressional Budget Office. July 24, 2012. Retrieved July 27, 2012.
- ^ "A Town Hall, and a Health Care Model, in Green Bay". The White House Blog. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ Jacobson, Louis. "Barack Obama says that what he'd said was you could keep your plan 'if it hasn't changed since the law passed'". PolitiFact. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ "After the big Obamacare apology: where things stand". CNN. November 8, 2013. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ "Obama apologizes for insurance cancellations due to Obamacare". CNN. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ^ Obama blames 'bad apple' insurers for canceled coverage, Reuters.com, October 30, 2013.
- ^ Sealover, Ed (November 8, 2013). "Health insurers say they're canceling plans because of federal law". Denver Business Journal. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ Weigel, David (November 8, 2013). "The White House's Website Still Says If You Like Your Plan You Can Keep It". Slate. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ "Obamacare: The debacle". The Economist. November 2, 2013. Retrieved November 8, 2013.
- ^ "Obama apologizes to Americans who lost health plans". Fox News. November 8, 2013. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- ^ Schoof, Renee (November 8, 2013). "Congress weighing laws to let people keep health insurance". McClatchyDC. Retrieved November 14, 2013.
- ^ a b "History of the Affordable Care Act (ACA)". October 22, 2014.
- ^ Enzi, Michael B. (August 2, 2011). "Health Care Reforrm Law's Impact on Child-Only Health Insurance Policies" (PDF). United States Senate. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
- ^ Press, RICARDO ALONSO-ZALDIVAR Associated. "Report: Medicare's drug coverage gap shrinks". Retrieved August 7, 2016.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (September 30, 2012). "Supreme Court justices face important rulings in upcoming term September". The New York Times. Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ^ "Status of State Action on the Medicaid Expansion Decision". Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ^ "A Cruel Blow to American Families". The New York Times. February 2, 2013.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (February 5, 2013). "Not-So-Universal Health Care". The New Republic.
- ^ Cox, Cynthia; Claxton, Gary; Levitt, Larry (June 6, 2013). "Beyond Rebates: How Much Are Consumers Saving from the ACA's Medical Loss Ratio Provision?". Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved June 9, 2013.
- ^ Mazur, Mark. "Continuing to Implement the ACA in a Careful, Thoughtful Manner". United States Department of the Treasury. Retrieved July 16, 2013.
- ^ Madara, Matthew R. (February 11, 2014). "ACA Employer Shared Responsibility Delay Included in Final Regs". Tax Notes Today. 2014 TNT 28-1.
- ^ "Obama drops long-term health care program - CNN.com". CNN. October 17, 2011.
- ^ "Watchdogs: CLASS still dead". LifeHealthPro. January 2, 2013.
- ^ Kennedy, Kelly (December 1, 2013). "White House claims success on HealthCare.gov repairs". USA Today. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Cohen, Tom (October 23, 2013). "Rough Obamacare rollout: 4 reasons why". CNN. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ Holland, Steve; Rampton, Roberta (November 6, 2013). "Senate Democrats frustrated with botched rollout of Obamacare". The Christian Science Monitor. Reuters. Retrieved November 19, 2013.
- ^ "Statistics, Trends and Reports". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Retrieved September 23, 2013.
- ^ Cohn, Jonathan (April 12, 2011). "More Skin in the Game – for Seniors?". The New Republic.
- ^ Alonso-Zaldivar, Ricardo (July 31, 2014). "Probe exposes flaws behind HealthCare.gov rollout". AP News. Retrieved July 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Sanger-Katz, Margot (August 19, 2016). "Think Your Obamacare Plan Will Be Like Employer Coverage? Think Again". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 26, 2016.
- ^ a b Sussman, Anna Louie (August 26, 2016). "Burden of Health-Care Costs Moves to the Middle Class". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ^ "National Health interview Survey Early Release Program 2015" (PDF). cdc.gov. CDC. Retrieved November 24, 2016.
- ^ Tracer, Zachary. "Obamacare Sign-Ups Decline to 10.2 Million as Some Don't Pay". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ "December 31, 2015 Effectuated Enrollment Snapshot". cms.gov. March 11, 2016.
- ^ COOK, NANCY (December 16, 2015). "How the White House lost on the Cadillac Tax". Politico. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ "About 1.6M drop-outs from ObamaCare coverage this year | Fox News". Associated Press. June 30, 2016. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ (ASPA), Assistant Secretary for Public Affairs (March 3, 2016). "20 million people have gained health insurance coverage because of the Affordable Care Act, new estimates show". HHS.gov. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ^ "Supplemental Survey Report: Empire State Manufacturing Survey/Business Leaders Survey Firms Assess Effects of Affordable Care Act" (PDF). Federal Reserve Bank of New York. August 2016.
- ^ Mathews, Anna Wilde (August 16, 2016). "Aetna to Drop Some Affordable Care Act Markets". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^ "Humana pulling out of many Obamacare markets". Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- ^ "Following Some Withdrawals, More Counties Could Have One ACA Marketplace Insurer in 2017". Retrieved August 19, 2016.
- ^ Chakraborty, Barnini (August 10, 2016). "ObamaCare problems deepen as insurers scramble to stem losses | Fox News". Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- ^ Tracer, Zachary. "Aetna's Obamacare Reversal Is Latest Blow to U.S. Health Law". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ^ Alltucker, Ken. "Obamacare insurers dwindle as Humana, UnitedHealthcare exit Arizona". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ^ "Minnesota's Largest Health Insurer Will Drop Individual Plans". Retrieved August 26, 2016.
- ^ Goldstein, Amy (October 14, 2016). "In North Carolina, ACA insurer defections leave little choice for many consumers". Washington Post. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- ^ Abelson, Reed; Sanger-katz, Margot (August 19, 2016). "Obamacare Options? In Many Parts of Country, Only One Insurer Will Remain". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ Ip, Greg (August 17, 2016). "The Unstable Economics in Obama's Health Law". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
- ^ Mali, Meghashyam (August 11, 2016). "Next president faces possible ObamaCare meltdown". Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- ^ "Louisiana to Expand Medicaid: Outlook for the States in 2016". Families USA. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
Further reading
- Barr, Donald A. (2011). Introduction to U.S. Health Policy: The Organization, Financing, and Delivery of Health Care in America. JHU Press. ISBN 9781421402185.
- CCH (2010). Law, Explanation and Analysis of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: Including Reconciliation Act Impact. CCH Incorporated. ISBN 9780808022879. 1183pp
- Feldman, Arthur M. (2011). Understanding Health Care Reform: Bridging the Gap Between Myth and Reality. CRC Press. ISBN 9781439879481.
- Jacobs, Lawrence R.; Skocpol, Theda (2010). Health Care Reform and American Politics. Oxford U.P. ISBN 9780199781423.
- McDonough, John E. (August 2, 2011). Inside National Health Reform. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520270190.
- Brill, Steven (January 5, 2015). America's Bitter Pill: Money, Politics, Back-Room Deals, and the Fight to Fix Our Broken Healthcare System. Random House. ISBN 978-0812996951.
Preliminary CBO documents
- Patient Protection And Affordable Care Act, Incorporating The Manager's Amendment, December 19, 2009
- Effects Of The Patient Protection And Affordable Care Act On The Federal Budget And The Balance In The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund (December 23, 2009)
- Estimated Effect Of The Patient Protection And Affordable Care Act (Incorporating The Manager's Amendment) On The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund (December 23, 2009)
- Base Analysis – H.R. 3590, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, November 18, 2009.
(The additional and/or related CBO reporting that follows can be accessed from the above link)- Estimated Distribution Of Individual Mandate Penalties (November 20, 2009)
- Estimated Effects On Medicare Advantage Enrollment And Benefits Not Covered By Medicare (November 21, 2009)
- Estimated Effects On The Status Of The Hospital Insurance Trust Fund (November 21, 2009)
- Estimated Average Premiums Under Current Law (December 5, 2009)
- Additional Information About Employment-Based Coverage (December 7, 2009)
- Budgetary Treatment Of Proposals To Regulate Medical Loss Ratios (December 13, 2009)
CMS Estimates of the impact of P.L. 111-148
- Estimated Financial Effects of the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act", as Amended. April 22, 2010.
- Estimated Effects of the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act", as Amended, on the Year of Exhaustion for the Part A Trust Fund, Part B Premiums, and Part A and Part B Coinsurance Amounts. April 22, 2010.
CMS Estimates of the impact of H.R. 3590
- Estimated Financial Effects of the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2009", as Proposed by the Senate Majority Leader on November 18, 2009. December 10, 2009.
- Estimated Effects of the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act" on the Year of Exhaustion for the Part A Trust Fund, Part B Premiums, and Part A and Part B Coinsurance Amounts. December 10, 2009.
Senate Finance Committee Meetings
- Senate Finance Committee Hearings for the 111th Congress recorded by C-SPAN; also available from Finance.Senate.Gov (accessed April 1, 2012).
External links
This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. (March 2015) |
PPACA text
- Public Law 111–148 after consolidating the amendments made by PPACA Title X and by HCERA.
- Full text, summary, background, provisions and more, via Democratic Policy Committee (Senate.gov)
- Public Law 111–148 U.S. Government Printing Office
Other links
- Video: Obama signs Healthcare Bill
- Supreme Court Ruling on ACA-June 28, 2012
- Remarks by the President on Supreme Court Ruling on the Affordable Care Act-June 28, 2012
- HealthCare.gov – Department of Health and Human Services website on the law
- Affordable Care Act collected news and commentary at The New York Times [dead link]
- Template:WSJtopic
- Basics: Health care reform issues as provided by Emily Smith from CNN June 25, 2012
- Legislative Actions to Repeal, Defund, or Delay the Affordable Care Act Congressional Research Service
- Timeline of the health care law as provided by CNN June 17, 2012
- Kaiser Family Foundation: Health Reform Subsidy Calculator – Premium Assistance for Coverage in Exchanges/Gateways
- Three Days of Argument: Obamacare On Trial Audiobook – Complete coverage of the arguments to the Supreme Court regarding Obamacare
- Obamacare coverage by CBSnews
- Supreme Court ruling caps a century of American debate over how to get medical care for all An Associated Press timeline published in various national newspapers on June 28, 2012, briefly listing key events in a century of debate over what role the government should play in helping people in the United States afford medical care.
- HealthReformGPS.org – Tracking and explanation of the law – as it is implemented – by analysts at the Hirsh Health Law and Policy program of the George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services.
- "Lines Crossed: Separation of Church and State. Has the Obama Administration Trampled on Freedom of Religion and Freedom of Conscience?" Hearing before the Congressional Committee on Oversight and Government Reform February 16, 2012
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
- 111th United States Congress
- 2009 in American politics
- 2009 in American law
- 2010 in American politics
- 2010 in American law
- Controversies in the United States
- Excises
- Healthcare reform legislation in the United States
- Internal Revenue Code
- Internal Revenue Service
- Presidency of Barack Obama
- United States federal health legislation
- United States Supreme Court cases of the Roberts Court
- Life sciences industry
