Potassium bisulfate
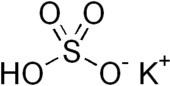
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium hydrogen sulfate
| |
| Other names
Potassium acid sulfate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.722 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E515(ii) (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 2509 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KHSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 136.169 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.245 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 197 °C (387 °F; 470 K) |
| Boiling point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) (decomposes) |
| 36.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 49 g/100 mL (20 °C) 121.6 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone, ethanol. |
| −49.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-1163.3 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2340 mg*kg−1 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Sodium bisulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium bisulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KHSO4 and is the potassium acid salt of sulfuric acid.
Natural Occurrence
Mercallite, the mineralogical form of potassium bisulfate, occurs very rarely. Misenite is another, more complex, form of potassium bisulfate.
Preparation
Potassium bisulfate is prepared by neutralizing sulfuric acid with an equal molar amount of a potassium containing base, for example potassium hydroxide:[1]
- H2SO4 + KOH → KHSO4 + H2O
Potassium bisulfate is also formed by the union of sulfuric acid with potassium sulfate:[2]
- H2SO4 + K2SO4 → 2 KHSO4
Potassium bisulfate is also the main by-product in the production of nitric acid from potassium nitrate and sulfuric acid:[3]
- KNO3 + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HNO3
Chemical Properties
Thermal decomposition of potassium bisulfate forms potassium pyrosulfate and water:[2]
- 2 KHSO4 → K2S2O7 + H2O
Temperatures above 600 °C further decompose potassium bisulfate to potassium sulfate and sulfur trioxide:[4]
- 2 KHSO4 → K2SO4 + SO3 + H2O
Aqueous solutions of potassium bisulfate behave as two separate, uncombined compounds, K2SO4 and H2SO4. Adding ethanol to the solution precipitates out potassium sulfate.[citation needed]
Uses
Potassium bisulfate is commonly used to prepare potassium bitartrate for winemaking.[citation needed] Potassium bisulfate is also used as a disintegrating agent in analytical chemistry or as a precursor to prepare potassium persulfate, a powerful oxidizing agent.[5]
See also
References
- ^ McPherson, William (1913). A Course in General Chemistry. New York: Ginn and Company. p. 156. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^ a b Washington Wiley, Harvey (1895). Principles and Practice of Agricultural Analysis: Fertilizers. Easton, PA.: Chemical Publishing Co. p. 218. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^ Pradyot, Patnaik (2003). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 636. ISBN 0070494398.
- ^ Iredelle Dillard Hinds, John (1908). Inorganic Chemistry: With the Elements of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry. New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 547. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^ Brauer, Georg (1963). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry Vol. 1, 2nd Ed. Newyork: Academic Press. p. 392. ISBN 978-0121266011.
