Rhodium(IV) oxide
Appearance
(Redirected from Rhodium dioxide)
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.021 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| RhO2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.904 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystalline solid |
| Density | 7.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,050 °C (1,920 °F; 1,320 K) (decomposes) |
| Solubility | insoluble in aqua regia |
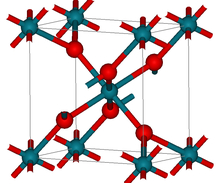
| Structure | |
| tetragonal (rutile) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rhodium(IV) oxide (or rhodium dioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula RhO2.
Chemical properties
[edit]RhO2 is highly insoluble even in hot aqua regia.[1]
Structure
[edit]RhO2 has the tetragonal rutile structure.[2]
Physical properties
[edit]RhO2 has metallic resistivity with values <10−4 Ohm·cm. It transforms in air to Rh2O3 at 850 °C and then to metal and oxygen at 1050 °C.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ O. Muller and R. Roy (1968). "Formation and stability of the platinum and rhodium oxides at high oxygen pressures and the structures of Pt3O4, β-PtO2 and RhO2". Journal of the Less Common Metals. 16 (2): 129–146. doi:10.1016/0022-5088(68)90070-2.
- ^ a b R. D. Shannon (1968). "Synthesis and properties of two new members of the rutile family RhO2 and PtO2". Solid State Communications. 6 (3): 139–143. Bibcode:1968SSCom...6..139S. doi:10.1016/0038-1098(68)90019-7.
