User:IDidThisForSchool/sandbox
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron (brain cell) to another 'target' neuron.[1] Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane in the axon terminal, on the presynaptic side of a synapse. Neurotransmitters are released into and diffuse across the synaptic cleft, where they bind to specific receptors in the membrane on the postsynaptic side of the synapse.[2] Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from plentiful and simple precursors, such as amino acids, which are readily available from the diet and which require only a small number of biosynthetic steps to convert. Neurotransmitters play a major role in shaping everyday life and functions. Scientists do not yet know exactly how many neurotransmitters exist, but more than 100 chemical messengers have been identified.[3]
Most neurotransmitters are about the size of a single amino acid, but some neurotransmitters may be the size of larger proteins or peptides. A released neurotransmitter is typically available in the synaptic cleft for a short time before it is metabolized by enzymes, pulled back into the presynaptic neuron through reuptake, or bound to a postsynaptic receptor. Nevertheless, short-term exposure of the receptor to neurotransmitter is typically sufficient for causing a postsynaptic response by way of synaptic transmission.
In response to a threshold action potential or graded electrical potential, a neurotransmitter is released at the presynaptic terminal. Low level "baseline" release also occurs without electrical stimulation. The released neurotransmitter may then move across the synapse to be detected by and bind with receptors in the postsynaptic neuron. Binding of neurotransmitters may influence the postsynaptic neuron in either an inhibitory or excitatory way. This neuron may be connected to many more neurons, and if the total of excitatory influences is greater than that of inhibitory influences, it will also "fire". That is to say, it will create a new action potential at its axon hillock to release neurotransmitters and pass on the information to yet another neighboring neuron.[4]
Discovery
[edit]Until the early 20th century, scientists assumed that the majority of synaptic communications within the brain were electrical. However, careful histological examinations by Ramón y Cajal (1852–1934), led to the discovery of what is presently known as the synaptic cleft, a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons. The presence of synaptic clefts suggested communications via chemical messengers traversing the synaptic cleft. Furthermore, in 1921, German pharmacologist Otto Loewi (1873–1961) confirmed that neurons can communicate by releasing chemicals. Loewi led a series of experiments involving the vagus nerves of frogs and was able to manually slow the heart rate of frogs by controlling the amount of saline solution present around the vagus nerve. Upon completion of this experiment, Loewi asserted that sympathetic regulations of cardiac function can be mediated through changes in chemical concentrations. Otto Loewi is now accredited with discovering acetylcholine (ACh)—the first known neurotransmitter.[5] Some neurons, nevertheless, communicate via electrical synapses through the use of gap junctions, which allow specific ions to pass directly from one cell to another.[6]
Neurons form elaborate networks through which nerve impulses (action potentials) travel. Each neuron has 15,000 connections with neighboring neurons. Neurons do not make physical contact with one another (except in the case of an electrical synapse through a gap junction); instead, neurons interact at synapses- a junction within two nerve cells, consisting of a miniature gap which impulses pass by a neurotransmitter. A neuron transports information through nerve impulse. When a nerve impulse arrives at the synapse, it releases neurotransmitters which influence another cell, either in an inhibitory or excitatory way. The next neuron may be connected to many more neurons, and if the total of excitatory influences is greater than that of inhibitory influences, it will also "fire". That is to say, it will create a new action potential at its axon hillock, releasing neurotransmitters and passing on the information to yet another neighboring neuron.
Identification
[edit]There are four main criteria for identifying neurotransmitters:
- The chemical must be synthesized in the neuron or otherwise be present in it.
- When the neuron is active, the chemical must be released and produce a response in some target.
- The same response must be obtained when the chemical is experimentally placed on the target.
- A mechanism must exist for removing the chemical from its site of activation after its work is done.
However, given advances in pharmacology, genetics, and chemical neuroanatomy, the term "neurotransmitter" can be applied to chemicals that:
- carry messages between neurons via influence on the postsynaptic membrane.
- have little or no effect on membrane voltage, but have a common carrying function such as changing the structure of the synapse.
- also communicate by sending reverse-direction messages that have an impact on the release or reuptake of transmitters.
Various techniques and experiments such as staining, stimulating, and collecting can be used to identify neurotransmitters throughout the central nervous system.[7]
Types
[edit]There are numerous ways to classify neurotransmitters. However, for classification purposes, the main neurotransmitters are: amino acids, amines (monoamines and other biogenic amines), peptides, and certain soluble gases.
Major neurotransmitters:
- Amino acids: glutamate,[4] aspartate, D-serine, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine
- Amines: dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (noradrenaline; NE, NA), epinephrine (adrenaline), histamine, serotonin (SER, 5-HT)
- Trace amines: phenethylamine, N-methylphenethylamine, tyramine, 3-iodothyronamine, octopamine, tryptamine, etc.
- Peptides: somatostatin, substance P, cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript, opioid peptides[8]
- Soluble gasess: nitric oxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO)
- Others: acetylcholine (ACh), adenosine, anandamide, etc.
In addition, over fifty neuroactive peptides have been discovered and more recent peptides are found regularly. Many of these are "co-released" along with a small-molecule transmitter. Nevertheless, in some cases a peptide is the primary transmitter at a synapse. β-endorphin is a relatively well known example of a peptide neurotransmitter because it engages in highly specific interactions with opioid receptors in the central nervous system.
Single ions, such as synaptically released zinc, are also considered neurotransmitters by some,[9] as are some gaseous molecules such as nitric oxide (NO), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and carbon monoxide (CO).[10] Because they are not packaged into vesicles, they are not classical neurotransmitters by the strictest definition; they have all been presented experimentally to be released by presynaptic terminals in an activity-dependent way.
The most prevalent transmitter is glutamate, which is excitatory at well over 90% of the synapses in the human brain.[4] Next is Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid, or GABA, which is inhibitory at more than 90% of the synapses that do not use glutamate. Although other transmitters are used in fewer synapses, they may be very important functionally: the great majority of psychoactive drugs exert their effects by altering the actions of some neurotransmitter systems, often acting through transmitters other than glutamate or GABA. Addictive drugs such as cocaine and amphetamine exert their effects primarily on the dopamine system. The addictive opiate drugs exert their effects primarily as functional analogs of opioid peptides, which, in turn, regulate dopamine levels.
Excitatory and inhibitory
[edit]A neurotransmitter can influence the function of a neuron through a remarkable number of mechanisms. In its direct actions in influencing a neuron’s electrical excitability, however, a neurotransmitter acts in only one of two ways. It influences transmembrane ion flow either to increase or to decrease the probability that the cell with which it comes in contact will produce an action potential. Thus, despite the wide variety of synapses, they all convey messages of only these two types, excitatory or inhibitory, and they are labeled as such. Type I synapses are excitatory in their actions, whereas type II synapses are inhibitory. Each type has a different appearance and is located on different parts of the neurons under its influence.Each neuron receives thousands of excitatory and inhibitory signals every second.
Type I (excitatory) synapses are typically located on the shafts or the spines of dendrites, whereas type II (inhibitory) synapses are typically located on a cell body. In addition, Type I synapses have round synaptic vesicles, whereas the vesicles of type II synapses are flattened. The material on the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is denser in a Type I synapse than it is in a type II, and the type I synaptic cleft is wider. Finally, the active zone on a Type I synapse is larger than that on a Type II synapse.
The different locations of type I and type II synapses divide a neuron into two zones: an excitatory dendritic tree and an inhibitory cell body. You can think of excitatory and inhibitory messages as interacting from these two different perspectives.
From an inhibitory perspective, you can picture excitation coming in over the dendrites and spreading to the axon hillock to trigger an action potential. If the message is to be stopped, it is best stopped by applying inhibition on the cell body, close to the axon hillock where the action potential originates. Another way to conceptualize excitatory–inhibitory interaction is to picture excitation overcoming inhibition. If the cell body is normally in an inhibited state, the only way to generate an action potential at the axon hillock is to reduce the cell body’s inhibition. In this “open the gates” strategy, the excitatory message is like a racehorse ready to run down the track, but first the inhibitory starting gate must be removed.[11]
Actions
[edit]As explained above, the only direct action of a neurotransmitter is to activate a receptor. Therefore, the effects of a neurotransmitter system depend on the connections of the neurons that use the transmitter, and the chemical properties of the receptors that the transmitter binds to.
Here are a few examples of important neurotransmitter actions:
- Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. Excessive glutamate release can overstimulate the brain and lead to excitotoxicity causing cell death resulting in seizures or strokes.[12] Excitotoxicity has been implicated in certain chronic diseases including ischemic stroke, epilepsy, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington disease, and Parkinson's disease.[13]
- GABA is used at the great majority of fast inhibitory synapses in virtually every part of the brain. Many sedative/tranquilizing drugs act by enhancing the effects of GABA.[14] Correspondingly, glycine is the inhibitory transmitter in the spinal cord.
- Acetylcholine is distinguished as the transmitter at the neuromuscular junction connecting motor nerves to muscles. The paralytic arrow-poison curare acts by blocking transmission at these synapses. Acetylcholine also operates in many regions of the brain, but using different types of receptors, including nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.[15]
- Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain; this includes regulation of motor behavior, pleasures related to motivation and also emotional arousal. It plays a critical role in the reward system; people with Parkinson's disease have been linked to low levels of dopamine and people with schizophrenia have been linked to high levels of dopamine.[16]
- Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Most is produced by and found in the intestine (approximately 90%), and the remainder in central nervous system neurons. It functions to regulate appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature, mood, behaviour, muscle contraction, and function of the cardiovascular system and endocrine system. It is speculated to have a role in depression, as some depressed patients are seen to have lower concentrations of metabolites of serotonin in their cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue.[17]
- Norepinephrine which focuses on the central nervous system, based on patients sleep patterns, focus and alertness. It is synthesized from tyrosine.
- Epinephrine which is also synthesized from tyrosine takes part in controlling the adrenal glands. It plays a role in sleep, with ones ability to stay become alert, and the fight-or-flight response.
- Histamine works with the central nervous system (CNS), specifically the hypothalamus (tuberomamillary nucleus) and CNS mast cells.
Neurons expressing certain types of neurotransmitters sometimes form distinct systems, where activation of the system affects large volumes of the brain, called volume transmission. Major neurotransmitter systems include the noradrenaline (norepinephrine) system, the dopamine system, the serotonin system and the cholinergic system.
A brief comparison of the major neurotransmitter systems follows:
| System | Origin [18] | Regulated effects and processes[18] |
|---|---|---|
| Noradrenaline system [19][20] |
Noradernergic pathways:
|
|
| Dopamine system [21] |
Dopaminergic pathways:
|
|
| Histamine system [22] |
Histaminergic pathways:
|
|
| Serotonin system [19][23][24] |
Serotonergic pathways:
Caudal nuclei (CN):
Rostral nuclei (RN):
|
|
| GABA system [25] |
GABAergic pathways:
|
|
| Acetylcholine system [19][26] |
Cholinergic pathways:
Brainstem cholinergic nuclei (BCN):
Forebrain cholinergic nuclei (FCN):
|
|
Drug effects
[edit]Drugs can influence behavior by altering neurotransmitter activity. For instance, drugs can decrease the rate of synthesis of neurotransmitters by affecting the synthetic enzyme(s) for that neurotransmitter. When neurotransmitter synthesis' are blocked, the amount of neurotransmitters available for release becomes substantially lower, resulting in a decrease in neurotransmitter activity. Some drugs block or stimulate the release of specific neurotransmitters. Alternatively, drugs can prevent neurotransmitter storage in synaptic vesicles by causing the synaptic vesicle membranes to leak. Drugs that prevent a neurotransmitter from binding to its receptor are called receptor antagonists. For example, drugs used to treat patients with schizophrenia such as haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and clozapine are antagonists at receptors in the brain for dopamine. Other drugs act by binding to a receptor and mimicking the normal neurotransmitter. Such drugs are called receptor agonists. An example of a receptor agonist is Valium, a benzodiazepine that mimics effects of the endogenous neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) to decrease anxiety. Other drugs interfere with the deactivation of a neurotransmitter after it has been released, thereby prolonging the action of a neurotransmitter. This can be accomplished by blocking reuptake or inhibiting degradative enzymes. Lastly, drugs can also prevent an action potential from occurring, blocking neuronal activity throughout the central and peripheral nervous system. Drugs such as tetrodotoxin that block neural activity are typically lethal.

Drugs targeting the neurotransmitter of major systems affect the whole system which can explain the complexity of action of some drugs. Cocaine, for example, blocks the reuptake of dopamine back into the presynaptic neuron, leaving the neurotransmitter molecules in the synaptic gap for an extended period of time. Since the dopamine remains in the synapse longer, the neurotransmitter continues to bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, eliciting a pleasurable emotional response. Physical addiction to cocaine may result from prolonged exposure to excess dopamine in the synapses, which leads to the downregulation of some postsynaptic receptors. After the effects of the drug wear off, an individual can become depressed due to decreased probability of the neurotransmitter binding to a receptor. Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), which blocks re-uptake of serotonin by the presynaptic cell which increases the amount of serotonin present at the synapse and furthermore allows it to remain there longer, providing potential for the effect of naturally released serotonin.[27] AMPT prevents the conversion of tyrosine to L-DOPA, the precursor to dopamine; reserpine prevents dopamine storage within vesicles; and deprenyl inhibits monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B and thus increases dopamine levels.
Diseases may affect specific neurotransmitter systems. For example, Parkinson's disease is at least in part related to failure of dopaminergic cells in deep-brain nuclei, for example the substantia nigra. Levodopa is a precursor of dopamine, and is the most widely used drug to treat Parkinson's disease.
List of neurotransmitters, peptides, and gasotransmitters
[edit]Precursors
[edit]While intake of neurotransmitter precursors does increase neurotransmitter synthesis, evidence is mixed as to whether neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic receptor firing is increased. Even with increased neurotransmitter release, it is unclear whether this will result in a long-term increase in neurotransmitter signal strength, since the nervous system can adapt to changes such as increased neurotransmitter synthesis and may therefore maintain constant firing.[32] Some neurotransmitters may have a role in depression, and there is some evidence to suggest that intake of precursors of these neurotransmitters may be useful in the treatment of mild and moderate depression.[32][33]
Catecholamine and trace amine precursors
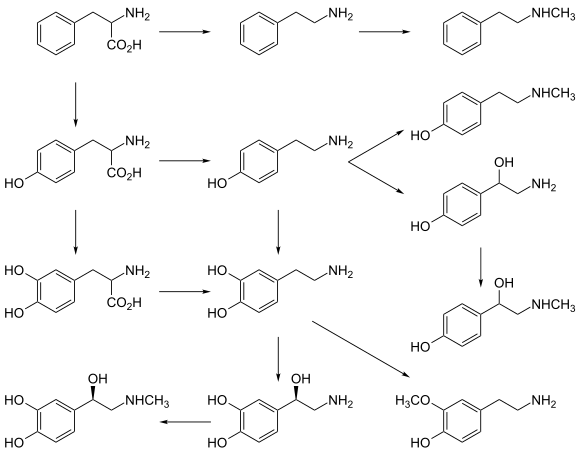
[edit]L-DOPA, a precursor of dopamine that crosses the blood–brain barrier, is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. For depressed patients where low activity of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine is implicated, there is only little evidence for benefit of neurotransmitter precursor administration. L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine are both precursors for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. These conversions require vitamin B6, vitamin C, and S-adenosylmethionine. A few studies suggest potential antidepressant effects of L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine, but there is much room for further research in this area.[32]
Serotonin precursors
[edit]Administration of L-tryptophan, a precursor for serotonin, is seen to double the production of serotonin in the brain. It is significantly more effective than a placebo in the treatment of mild and moderate depression.[32] This conversion requires vitamin C.[17] 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), also a precursor for serotonin, is also more effective than a placebo.[32]
Elimination Of neurotransmitters
[edit]A neurotransmitter must be broken down once it reaches the post-synaptic cell to prevent further excitatory or inhibitory signal transduction. This allows new signals to be produced from the adjacent nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are terminated in three different ways:
- Diffusion – the neurotransmitter detaches from receptor, drifting out of the synaptic cleft, here it becomes absorbed by glial cells.
- Enzyme degradation – special chemicals called enzymes break it down.
- Reuptake – re-absorption of a neurotransmitter into the neuron. Transporters, or membrane transport proteins, pump neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft back into axon terminals (the presynaptic neuron) where they are stored.[34]
For example choline is taken up and recycled by the pre-synaptic neuron to synthesize more ACh. Other neurotransmitters such as dopamine are able to diffuse away from their targeted synaptic junctions and are eliminated from the body via the kidneys, or destroyed in the liver. Each neurotransmitter has very specific degradation pathways at regulatory points, which may be targeted by the body's regulatory system or by recreational drugs.
Agonists
[edit]An agonist is a chemical capable of binding to a receptor, such as a neurotransmitter receptor, and initiating the same reaction typically produced by the binding of the endogenous substance.[35] An agonist of a neurotransmitter will thus initiate the same receptor response as the transmitter.[36]
Nicotine, found in tobacco, is an agonist for acetylcholine at nicotinic receptors.[37] Opiate agonists include morphine, heroin, hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine, and methadone. These drugs activate mu opioid receptors that typically respond to endogenous transmitters such as enkephalins. When these receptors are activated, individuals experience euphoria, pain relief, and drowsiness.[37]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Neurotransmitter" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Elias, L. J, & Saucier, D. M. (2005). Neuropsychology: Clinical and Experimental Foundations. Boston: Pearson
- ^ Cherry, Kendra. "What is a Nuerotransmitter?". Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ a b c Robert Sapolsky (2005). "Biology and Human Behavior: The Neurological Origins of Individuality, 2nd edition". The Teaching Company.
see pages 13 & 14 of Guide Book
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. McGraw Hill. 2009 ISBN 0-07-727620-5
- ^ "Junctions Between Cells". Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- ^ Whishaw, Bryan Kolb, Ian Q. (2014). An introduction to brain and behavior (4th ed.). New York, NY: Worth Publishers. pp. 150–151. ISBN 978-1429242288.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Snyder SH, Innis RB (1979). "Peptide neurotransmitters". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 48: 755–82. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003543. PMID 38738.
- ^ Kodirov,Sodikdjon A., Shuichi Takizawa, Jamie Joseph, Eric R. Kandel, Gleb P. Shumyatsky, and Vadim Y. Bolshakov. Synaptically released zinc gates long-term potentiation in fear conditioning pathways. PNAS, 10 October 2006. 103(41): 15218-23. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607131103
- ^ Nitric oxide and other gaseous neurotransmitters
- ^ Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. Q. (2014). An introduction to brain and behavior. Worth Publishers.
- ^ Glutamate: Seizures and strokes- PLoS Biol. 2006 November; 4(11): e371. Published online 2006 October 17. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040371 by author Liza Gross- Courtesy Public Library of Science (2006); PubMed (PMC) of NCBI, Retrieved 2013-16-13
- ^ Yang JL, Sykora P, Wilson DM, Mattson MP, Bohr VA (August 2011). "The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate stimulates DNA repair to increase neuronal resiliency". Mech. Ageing Dev. 132 (8–9): 405–11. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.005. PMC 3367503. PMID 21729715.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Orexin receptor antagonists a new class of sleeping pill, National Sleep Foundation.
- ^ "Acetylcholine Receptors". Ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ Schacter, Gilbert and Weger. Psychology.United States of America.2009.Print.
- ^ a b University of Bristol. "Introduction to Serotonin". Retrieved 15 October 2009.
- ^ a b Rang, H. P. (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 474 for noradrenaline system, page 476 for dopamine system, page 480 for serotonin system and page 483 for cholinergic system. ISBN 0-443-07145-4.
- ^ a b c Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 155. ISBN 9780071481274.
Different subregions of the VTA receive glutamatergic inputs from the prefrontal cortex, orexinergic inputs from the lateral hypothalamus, cholinergic and also glutamatergic and GABAergic inputs from the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and pedunculopontine nucleus, noradrenergic inputs from the locus ceruleus, serotonergic inputs from the raphe nuclei, and GABAergic inputs from the nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 156–157. ISBN 9780071481274.
The locus ceruleus (LC), which is located on the floor of the fourth ventricle in the rostral pons, contains more than 50% of all noradrenergic neurons in the brain; it innervates both the forebrain (eg, it provides virtually all the NE to the cerebral cortex) and regions of the brainstem and spinal cord. ... The other noradrenergic neurons in the brain occur in loose collections of cells in the brainstem, including the lateral tegmental regions. These neurons project largely within the brainstem and spinal cord. NE, along with 5HT, ACh, histamine, and orexin, is a critical regulator of the sleep-wake cycle and of levels of arousal. ... LC firing may also increase anxiety ...Stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors in the amygdala results in enhanced memory for stimuli encoded under strong negative emotion ... Epinephrine occurs in only a small number of central neurons, all located in the medulla. Epinephrine is involved in visceral functions, such as control of respiration.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 147–148, 154–157. ISBN 9780071481274.
Neurons from the SNc densely innervate the dorsal striatum where they play a critical role in the learning and execution of motor programs. Neurons from the VTA innervate the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens), olfactory bulb, amygdala, hippocampus, orbital and medial prefrontal cortex, and cingulate cortex. VTA DA neurons play a critical role in motivation, reward-related behavior, attention, and multiple forms of memory. ... Thus, acting in diverse terminal fields, dopamine confers motivational salience ("wanting") on the reward itself or associated cues (nucleus accumbens shell region), updates the value placed on different goals in light of this new experience (orbital prefrontal cortex), helps consolidate multiple forms of memory (amygdala and hippocampus), and encodes new motor programs that will facilitate obtaining this reward in the future (nucleus accumbens core region and dorsal striatum). ... DA has multiple actions in the prefrontal cortex. It promotes the "cognitive control" of behavior: the selection and successful monitoring of behavior to facilitate attainment of chosen goals. Aspects of cognitive control in which DA plays a role include working memory, the ability to hold information "on line" in order to guide actions, suppression of prepotent behaviors that compete with goal-directed actions, and control of attention and thus the ability to overcome distractions. ... Noradrenergic projections from the LC thus interact with dopaminergic projections from the VTA to regulate cognitive control. ...
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 175–176. ISBN 9780071481274.
Within the brain, histamine is synthesized exclusively by neurons with their cell bodies in the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) that lies within the posterior hypothalamus. There are approximately 64000 histaminergic neurons per side in humans. These cells project throughout the brain and spinal cord. Areas that receive especially dense projections include the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, neostriatum, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ... While the best characterized function of the histamine system in the brain is regulation of sleep and arousal, histamine is also involved in learning and memory ...It also appears that histamine is involved in the regulation of feeding and energy balance.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 158–160. ISBN 9780071481274.
[The] dorsal raphe preferentially innervates the cerebral cortex, thalamus, striatal regions (caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens), and dopaminergic nuclei of the midbrain (eg, the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area), while the median raphe innervates the hippocampus, septum, and other structures of the limbic forebrain. ... it is clear that 5HT influences sleep, arousal, attention, processing of sensory information in the cerebral cortex, and important aspects of emotion (likely including aggression) and mood regulation. ...The rostral nuclei, which include the nucleus linearis, dorsal raphe, medial raphe, and raphe pontis, innervate most of the brain, including the cerebellum. The caudal nuclei, which comprise the raphe magnus, raphe pallidus, and raphe obscuris, have more limited projections that terminate in the cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal cord.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nestler, Eric J. "BRAIN REWARD PATHWAYS". Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Nestler Lab. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
The dorsal raphe is the primary site of serotonergic neurons in the brain, which, like noradrenergic neurons, pervasively modulate brain function to regulate the state of activation and mood of the organism.
- ^ Barrot M, Sesack SR, Georges F, Pistis M, Hong S, Jhou TC; Sesack; Georges; Pistis; Hong; Jhou (October 2012). "Braking dopamine systems: a new GABA master structure for mesolimbic and nigrostriatal functions". J. Neurosci. 32 (41): 14094–101. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3370-12.2012. PMC 3513755. PMID 23055478.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 167–175. ISBN 9780071481274.
The basal forebrain cholinergic nuclei are comprised of the medial septal nucleus (Ch1), the vertical nucleus of the diagonal band (Ch2), the horizontal limb of the diagonal band (Ch3), and the nucleus basalis of Meynert (Ch4). Brainstem cholinergic nuclei include the pedunculopontine nucleus (Ch5), the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (Ch6), the medial habenula (Ch7), and the parabigeminal nucleus (Ch8).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Yadav VK, Ryu JH, Suda N, Tanaka KF, Gingrich JA, Schütz G, Glorieux FH, Chiang CY, Zajac JD, Insogna KL, Mann JJ, Hen R, Ducy P, Karsenty G (November 2008). "Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum". Cell. 135 (5): 825–37. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.059. PMC 2614332. PMID 19041748.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lin Y, Hall RA, Kuhar MJ; Hall; Kuhar (October 2011). "CART peptide stimulation of G protein-mediated signaling in differentiated PC12 cells: identification of PACAP 6-38 as a CART receptor antagonist". Neuropeptides. 45 (5): 351–358. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2011.07.006. PMC 3170513. PMID 21855138.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Broadley KJ (March 2010). "The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 125 (3): 363–375. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.11.005. PMID 19948186.
- ^ Lindemann L, Hoener MC (May 2005). "A renaissance in trace amines inspired by a novel GPCR family". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 26 (5): 274–281. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2005.03.007. PMID 15860375.
- ^ Wang X, Li J, Dong G, Yue J (February 2014). "The endogenous substrates of brain CYP2D". European Journal of Pharmacology. 724: 211–218. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.025. PMID 24374199.
- ^ a b c d e Meyers, Stephen (2000). "Use of Neurotransmitter Precursors for Treatment of Depression" (PDF). Alternative Medicine Review. 5 (1): 64–71. PMID 10696120.
- ^ Van Praag, HM (1981). "Management of depression with serotonin precursors". Biol Psychiatry. 16 (3): 291–310. PMID 6164407.
- ^ "General, Organic ans Biological Chemistry Structures of Life" by Karen C. Timberlake p.661
- ^ "Agonist - Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary". Merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Drug Receptor Interactions". Virtual Chembook, Elmhurst College.
- ^ a b "Neurotransmitters and Drugs Chart". Ocw.mit.edu. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
External links
[edit]- Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery: The Neurotransmitter Collection
- Brain Neurotransmitters
- Endogenous Neuroactive Extracellular Signal Transducers
- Neurotransmitter at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- neuroscience for kids website
- brain explorer website
- wikibooks cellular neurobiology