Western Bloc
Appearance
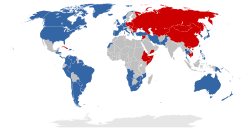
First World: Countries aligned with the Western Bloc (i.e., NATO and allies), led by the United States
Second World: Countries aligned with the Eastern Bloc (i.e., Warsaw Pact, China, and allies), led by the Soviet Union
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2014) |

The Western Bloc during the Cold War refers to the countries allied with the United States and NATO against the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact. The latter were referred to as the Eastern Bloc. The governments and press of the Western Bloc were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "Western world", whereas the Eastern Bloc was often called the "Communist world" or Second world".
Western Bloc associations
 Belgium
Belgium Canada
Canada Denmark
Denmark France
France Germany (from 1990)
Germany (from 1990)
 West Germany (from 1955)
West Germany (from 1955)
 Greece (from 1952)
Greece (from 1952) Iceland
Iceland Italy
Italy Luxembourg
Luxembourg Netherlands
Netherlands Norway
Norway Portugal
Portugal Spain (from 1982)
Spain (from 1982) Turkey (from 1952)
Turkey (from 1952) United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
 Australia
Australia France (until 1965)
France (until 1965) New Zealand
New Zealand Pakistan (until 1972)
Pakistan (until 1972) Philippines
Philippines Thailand
Thailand South Vietnam (until 1975)
South Vietnam (until 1975) United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
See also
- Allies
- Axis powers
- Eastern Bloc
- Free world
- First World
- Second World
- Third World
- Operation Condor
- Western betrayal
- Western world
References
Sources
- Matloff, Maurice. Makers of Modern Strategy. Ed. Peter Paret. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1971. 702.
- Kissinger, Henry. Diplomacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. 447,454.
