Acesulfame potassium: Difference between revisions
→Properties: context lacking, relevance unclear |
→Effectiveness for weight reduction: Replacing individual observational study with systematic reviews that include randomized controlled trials. Also adding a caveat to the potential bias of industry sponsorship. |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
== Effectiveness for weight reduction == |
== Effectiveness for weight reduction == |
||
Acesulfame potassium provides a sweet taste without affecting glycaemic responses and without the high content of caloric sugars. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of different types of evidence lead to different conclusions. Observational [[cohort study|cohort studies]] show a correlation with no or some increase in body weight or [[body mass index]] (BMI),<ref name="Miller2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Miller PE, Perez V | title = Low-calorie sweeteners and body weight and composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies | journal = The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | date = September 2014 | pmid = 24944060 | doi = 10.3945/ajcn.113.082826 }}</ref><ref name=Az2017>{{cite journal | vauthors = Azad MB, Abou-Setta AM, Chauhan BF, Rabbani R, Lys J, Copstein L, Mann A, Jeyaraman MM, Reid AE, Fiander M, MacKay DS, McGavock J, Wicklow B, Zarychanski R | title = Nonnutritive sweeteners and cardiometabolic health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies | journal = CMAJ | volume = 189 | issue = 28 | pages = E929–E939 | date = July 2017 | pmid = 28716847 | pmc = 5515645 | doi = 10.1503/cmaj.161390 }}</ref><ref name="Rogers2015">{{cite journal | vauthors = Rogers PJ, Hogenkamp PS, de Graaf C, Higgs S, Lluch A, Ness AR, Penfold C, Perry R, Putz P, Yeomans MR, Mela DJ | title = Low-calorie sweeteners and body weight and composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies | journal = International Journal of Obesity | issue = 40 | pages = 381–94 | date = September 2015 | doi = 10.1038/ijo.2015.177 }}</ref> though without providing conclusions about cause and effect for whether people could be consuming sweeteners because they have poor health, or whether they have poor health because they consume sweeteners.<ref name="SciBasedLowEnergy>{{cite web |title=Low Energy Sweeteners and Weight Control | publisher=[[Science-Based Medicine]] |accessdate=29 June 2019 |url=https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/low-energy-sweeteners-and-weight-control/}}</ref> [[Randomized controlled trial]]s instead show no or some causal decrease in body weight or BMI.<ref name="Miller2014"/><ref name=Az2017/><ref name="Rogers2015"/><ref name=San2017>{{cite journal | vauthors = Santos NC, de Araujo LM, De Luca Canto G, Guerra EN, Coelho MS, Borin MF | title = Metabolic effects of aspartame in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials | journal = Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition | volume = 58 | issue = 12 | pages = 2068–2081 | date = April 2017 | pmid = 28394643 | doi = 10.1080/10408398.2017.1304358 }}</ref> |
|||
Acesulfame potassium provides a sweet taste without affecting glycaemic responses and without the high content of caloric sugars. Some studies, however, discovered that the consumption of non-nutritive sweeteners has led to weight gain because people over-ingest calories, thus increasing the risk of [[type 2 diabetes]].<ref>Dewinter, Louise; Casteels, Kristina; Corthouts, Karen; Van de Kerckhove, Kristel; Van der Vaerent, Katrien; Vanmeerbeeck, Kelly; Matthys, Christophe. Dietary intake of non-nutritive sweeteners in type 1 diabetes mellitus children Food additives contaminants. Part A.Chemistry, analysis, control, exposure risk assessment, 2015, 33, 1, 1-8, Taylor Francis, ENGLAND</ref> |
|||
Systematic reviews of published studies about the effects of artificially sweetened beverages on weight found that industry-sponsored artificial sweetener studies were significantly more likely to have favorable results than non-industry sponsored studies, and that all published studies that were funded by competitor industries reported unfavorable conclusions.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Mandrioli|first=Daniele|last2=Kearns|first2=Cristin E.|last3=Bero|first3=Lisa A.|date=2016-09-08|title=Relationship between Research Outcomes and Risk of Bias, Study Sponsorship, and Author Financial Conflicts of Interest in Reviews of the Effects of Artificially Sweetened Beverages on Weight Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Reviews|journal=PLOS ONE|language=en|volume=11|issue=9|pages=e0162198|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0162198|pmid=27606602|pmc=5015869|issn=1932-6203|bibcode=2016PLoSO..1162198M}}</ref><ref name=Az2017/> It is however noted that the expensive high-quality longer-term randomized controlled trials were industry-sponsored, making it impossible to isolate high-quality evidence and industry sponsorship.<ref name=Az2017/> |
|||
==Discovery== |
==Discovery== |
||
Revision as of 11:42, 30 June 2019
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
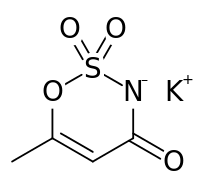
Potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate
| |
| Other names
Acesulfame K; Ace K
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.269 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E950 (glazing agents, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4KNO4S | |
| Molar mass | 201.242 |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.81 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
| 270 g/L at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acesulfame potassium (/ˌeɪsiːˈsʌlfeɪm/ AY-see-SUL-faym[1]), also known as acesulfame K (K is the symbol for potassium) or Ace K, is a calorie-free sugar substitute (artificial sweetener) often marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E number (additive code) E950.[2] It was discovered accidentally in 1967 by German chemist Karl Clauss at Hoechst AG (now Nutrinova).[3] In chemical structure, acesulfame potassium is the potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide. It is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C
4H
4KNO
4S and a molecular weight of 201.24 g/mol.[4]
Properties
Acesulfame K is 200 times sweeter than sucrose (common sugar), as sweet as aspartame, about two-thirds as sweet as saccharin, and one-third as sweet as sucralose. Like saccharin, it has a slightly bitter aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. Kraft Foods patented the use of sodium ferulate to mask acesulfame's aftertaste.[5] Acesulfame K is often blended with other sweeteners (usually sucralose or aspartame). These blends are reputed to give a more sucrose-like taste whereby each sweetener masks the other's aftertaste, or exhibits a synergistic effect by which the blend is sweeter than its components.[6] Acesulfame potassium has a smaller particle size than sucrose, allowing for its mixtures with other sweeteners to be more uniform.[7]
Unlike aspartame, acesulfame K is stable under heat, even under moderately acidic or basic conditions, allowing it to be used as a food additive in baking, or in products that require a long shelf life. Although acesulfame potassium has a stable shelf life, it can eventually degrade to acetoacetamide, which is toxic in high doses.[8] In carbonated drinks, it is almost always used in conjunction with another sweetener, such as aspartame or sucralose. It is also used as a sweetener in protein shakes and pharmaceutical products,[9] especially chewable and liquid medications, where it can make the active ingredients more palatable. The acceptable daily intake of acesulfame potassium is listed as 15 mg/kg/day.[10]
Acesulfame potassium is widely used in the human diet and excreted by the kidneys. It thus has been used by researchers as a marker to estimate to what degree swimming pools are contaminated by urine.[11]
Other names for acesulfame K are potassium acesulfamate, potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxothiazin-4(3H)-one-2,3-dioxide, and potassium 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one-3-ate-2,2-dioxide.
Effectiveness for weight reduction
Acesulfame potassium provides a sweet taste without affecting glycaemic responses and without the high content of caloric sugars. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of different types of evidence lead to different conclusions. Observational cohort studies show a correlation with no or some increase in body weight or body mass index (BMI),[12][13][14] though without providing conclusions about cause and effect for whether people could be consuming sweeteners because they have poor health, or whether they have poor health because they consume sweeteners.[15] Randomized controlled trials instead show no or some causal decrease in body weight or BMI.[12][13][14][16]
Systematic reviews of published studies about the effects of artificially sweetened beverages on weight found that industry-sponsored artificial sweetener studies were significantly more likely to have favorable results than non-industry sponsored studies, and that all published studies that were funded by competitor industries reported unfavorable conclusions.[17][13] It is however noted that the expensive high-quality longer-term randomized controlled trials were industry-sponsored, making it impossible to isolate high-quality evidence and industry sponsorship.[13]
Discovery
Acesulfame potassium was developed after the accidental discovery of a similar compound (5,6-dimethyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide) in 1967 by Karl Clauss and Harald Jensen at Hoechst AG.[18][19] After accidentally dipping his fingers into the chemicals with which he was working, Clauss licked them to pick up a piece of paper.[20] Clauss is the inventor listed on a United States patent issued in 1975 to the assignee Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft for one process of manufacturing acesulfame potassium.[21] Subsequent research showed a number of compounds with the same basic ring structure had varying levels of sweetness. 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide had particularly favourable taste characteristics and was relatively easy to synthesize, so it was singled out for further research, and received its generic name (acesulfame-K) from the World Health Organization in 1978.[18] Acesulfame potassium first received approval for table top use in the United States in 1988.[10]
Safety
As with other artificial sweeteners, concern exists over the safety of acesulfame potassium. However, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved its general use. Critics say acesulfame potassium has not been studied adequately and may be carcinogenic,[22] although these claims have been dismissed by the European Food Safety Authority[23] and FDA.[24]
Environment Canada tested the water from the Grand River at 23 sites between its headwaters and where it flows into Lake Erie. The results suggest that acesulfame appears in far higher concentrations than saccharin or sucralose at the various test sites.[25]
Compendial status
References
- ^ "acesulfame–K". Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- ^ "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". UK: Food Standards Agency. 2012-03-14.
- ^ Clauss, K.; Jensen, H. (1973). "Oxathiazinone Dioxides - A New Group of Sweetening Agents". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 12 (11): 869–876. doi:10.1002/anie.197308691.
- ^ Ager, D. J.; Pantaleone, D. P.; Henderson, S. A.; Katritzky, A. R.; Prakash, I.; Walters, D. E. (1998). "Commercial, Synthetic Nonnutritive Sweeteners" (PDF). Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 37 (13–14): 1802–1817. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980803)37:13/14<1802::AID-ANIE1802>3.0.CO;2-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ United States Patent 5,336,513 (expired in 2006)
- ^ Deis RC (November 2006). "Customizing Sweetness Profiles" (PDF). Food Product Design. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- ^ Mullarney, M.; Hancock, B.; Carlson, G.; Ladipo, D.; Langdon, B. The powder flow and compact mechanical properties of sucrose and three high-intensity sweeteners used in chewable tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 257, 227–236.
- ^ Findikli, Z.; Zeynep, F.; Sifa, T. Determination of the effects of some artificial sweeteners on human peripheral lymphocytes using the comet assay. Journal of toxicology and environmental health sciences 2014, 6, 147–153.
- ^ "Home - WHO - Prequalification of Medicines Programme". Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ^ a b Whitehouse, C.; Boullata, J.; McCauley, L. The potential toxicity of artificial sweeteners. AAOHN J. 2008, 56, 251-9 quiz 260.
- ^ Erika Engelhaupt (March 1, 2017). "Just How Much Pee Is In That Pool?". NPR. Retrieved March 2, 2017.
- ^ a b Miller PE, Perez V (September 2014). "Low-calorie sweeteners and body weight and composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.082826. PMID 24944060.
- ^ a b c d Azad MB, Abou-Setta AM, Chauhan BF, Rabbani R, Lys J, Copstein L, Mann A, Jeyaraman MM, Reid AE, Fiander M, MacKay DS, McGavock J, Wicklow B, Zarychanski R (July 2017). "Nonnutritive sweeteners and cardiometabolic health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies". CMAJ. 189 (28): E929–E939. doi:10.1503/cmaj.161390. PMC 5515645. PMID 28716847.
- ^ a b Rogers PJ, Hogenkamp PS, de Graaf C, Higgs S, Lluch A, Ness AR, Penfold C, Perry R, Putz P, Yeomans MR, Mela DJ (September 2015). "Low-calorie sweeteners and body weight and composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies". International Journal of Obesity (40): 381–94. doi:10.1038/ijo.2015.177.
- ^ "Low Energy Sweeteners and Weight Control". Science-Based Medicine. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ^ Santos NC, de Araujo LM, De Luca Canto G, Guerra EN, Coelho MS, Borin MF (April 2017). "Metabolic effects of aspartame in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 58 (12): 2068–2081. doi:10.1080/10408398.2017.1304358. PMID 28394643.
- ^ Mandrioli, Daniele; Kearns, Cristin E.; Bero, Lisa A. (2016-09-08). "Relationship between Research Outcomes and Risk of Bias, Study Sponsorship, and Author Financial Conflicts of Interest in Reviews of the Effects of Artificially Sweetened Beverages on Weight Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Reviews". PLOS ONE. 11 (9): e0162198. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1162198M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0162198. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5015869. PMID 27606602.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b O'Brien-Nabors, L. (2001). Alternative Sweeteners. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-8247-0437-7.
- ^ Williams, R. J.; Goldberg, I. (1991). Biotechnology and Food Ingredients. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. ISBN 978-0-442-00272-5.
- ^ Newton, D. E. (2007). Food Chemistry (New Chemistry). New York: Infobase Publishing. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-8160-5277-6.
- ^ Clauss, K. Process for the manufacture of 6-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4-one-2,2-dioxide. US Patent 3917589, 1975.
- ^ Karstadt, M. L. (2006). "Testing Needed for Acesulfame Potassium, an Artificial Sweetener". Environmental Health Perspectives. 114 (9): A516, author reply A516–7. doi:10.1289/ehp.114-a516a. PMC 1570055. PMID 16966071.
- ^ Scientific Committee on Food (2000). "Opinion - Re-evaluation of acesulfame K with reference to the previous SCF opinion of 1991" (PDF). SCF/CS/ADD/EDUL/194 final. EU Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Kroger, M.; Meister, K.; Kava, R. (2006). "Low-Calorie Sweeteners and Other Sugar Substitutes: A Review of the Safety Issues". Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 5 (2): 35–47. doi:10.1111/j.1541-4337.2006.tb00081.x.
- ^ "Major Canadian river contains artificial sweeteners". Waterloo News. University of Waterloo. December 13, 2013.
- ^ British Pharmacopoeia Commission Secretariat (2009). "Index, BP 2009" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-04-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
External links
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives evaluation monograph of Acesulfame Potassium
- FDA approval of Acesulfame Potassium
- FDA approval of Acesulfame Potassium as a General Purpose Sweetener in Food
- Elmhurst College, Illinois Virtual ChemBook Acesulfame K
- Discovery News Sweeteners Linger in Groundwater

