Etobicoke: Difference between revisions
m Added reference |
|||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
In 1911, the community of [[Mimico]] was incorporated on land taken from Etobicoke township.<ref>{{cite web|url = http://www.torontofamilyhistory.org/chronology.html|title = Toronto Chronology}}</ref> [[New Toronto]] was incorporated on January 1, 1913.<ref name = "BH" /> Early on there was talk of merging Mimico and New Toronto. A 1916 referendum on amalgamating the two communities was approved by the residents of Mimico, but rejected by residents of New Toronto.<ref name = "NTH" /> In 1917, Mimico became a town and in 1920, New Toronto became the Town of New Toronto. [[Long Branch, Ontario|Long Branch]] was incorporated in 1930 as a village.{{Citation needed|date=May 2009}} |
In 1911, the community of [[Mimico]] was incorporated on land taken from Etobicoke township.<ref>{{cite web|url = http://www.torontofamilyhistory.org/chronology.html|title = Toronto Chronology}}</ref> [[New Toronto]] was incorporated on January 1, 1913.<ref name = "BH" /> Early on there was talk of merging Mimico and New Toronto. A 1916 referendum on amalgamating the two communities was approved by the residents of Mimico, but rejected by residents of New Toronto.<ref name = "NTH" /> In 1917, Mimico became a town and in 1920, New Toronto became the Town of New Toronto. [[Long Branch, Ontario|Long Branch]] was incorporated in 1930 as a village.{{Citation needed|date=May 2009}} |
||
In 1954, Etobicoke Township became a part of the newly-formed regional government, the Municipality of [[Metropolitan Toronto]] ("Metro"). In 1967, the township of Etobicoke was merged with three small lakeside municipalities — the Village of [[Long Branch, Ontario|Long Branch]], the Town of [[New Toronto, Ontario|New Toronto]], and the Town of Mimico — to form the Borough of Etobicoke. The borough was reincorporated as a city in 1984.<ref name="archives"/> In 1998, six local municipalities (including Etobicoke) and the Metropolitan Toronto government [[megacity#Canada|merged]] to form the amalgamated city of Toronto.{{ |
In 1954, Etobicoke Township became a part of the newly-formed regional government, the Municipality of [[Metropolitan Toronto]] ("Metro"). In 1967, the township of Etobicoke was merged with three small lakeside municipalities — the Village of [[Long Branch, Ontario|Long Branch]], the Town of [[New Toronto, Ontario|New Toronto]], and the Town of Mimico — to form the Borough of Etobicoke. The borough was reincorporated as a city in 1984.<ref name="archives"/> In 1998, six local municipalities (including Etobicoke) and the Metropolitan Toronto government [[megacity#Canada|merged]] to form the amalgamated city of Toronto.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.toronto.ca/toronto_history/amalgamation/amal_speech.htm|title=The Toronto Amalgamation: Looking Back, Moving Ahead|author=Roda McInnis|accessdate=2012-04-12}}</ref> |
||
==Demographics== |
==Demographics== |
||
Revision as of 17:41, 12 April 2012
Etobicoke | |
|---|---|
 Etobicoke skyline in 2009 | |
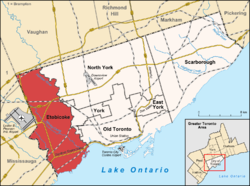 Location of Etobicoke (red) compared to the rest of Toronto. | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Municipality | |
| Incorporated | 1 January 1850 (township) 1 January 1967 (borough) June 1983 (city) |
| Changed Region | 1954 |
| Amalgamated | 1 January 1998 into Toronto |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Rob Ford (Toronto Mayor) |
| • Governing Body | Toronto City Council |
| • MPs | Kirsty Duncan (L) Ted Opitz (C) Bernard Trottier (C) |
| • MPPs | Shafiq Qaadri (L) Donna Cansfield (L) Laurel Broten (L) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 123.93 km2 (47.85 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 347,948 |
| • Density | 2,728.3/km2 (7,066/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Postal code span | M8V-M9C, M9P-M9R, M9V-M9W |
| Area code(s) | 416, 647 |
Etobicoke /ɛˈtoʊb[invalid input: 'ɨ']koʊ/ (with a silent 'k') is a dissolved municipality located within the current city of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Comprising the western section of the current city, it had an official population of 347,948 residents as of the Canada 2011 Census. While it only contains 13% of Toronto's population, it occupies about 20% of its total land area. It is bordered on the south by Lake Ontario, on the east by the Humber River, on the west by Etobicoke Creek, the city of Mississauga and Toronto Pearson International Airport (though a small portion of the airport extends into Etobicoke) and on the north by Steeles Avenue West.
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2009) |
Different groups of First Nations peoples used the land that is now Etobicoke at different times. As the Algonquins gradually moved west from the Atlantic to Lake Erie, it is almost certain that they would have occupied this land at some point. By the time they were mostly settled on the shores of Georgian Bay, The Huron-Wendat were the primary residents of the north shore of Lake Ontario and, somewhere in the 17th century, they were pushed out by the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) people. After continued harassment from the south, a coalition of the Ojibway, Odawa and Potawatomi Algonquin nations, known as the Three Fires, gradually pushed the Haudenosaunee off this land and the Mississaugas settled there by 1695, fishing and growing crops more locally in the summer and hunting further afield in the winter.[1]
The name "Etobicoke" was derived from the Mississauga word wah-do-be-kang (wadoopikaang),[2] meaning "place where the alders grow", which was used to describe the area between Etobicoke Creek and the Humber River. The first provincial land surveyor, Augustus Jones, also spelled it as "ato-be-coake". Etobicoke was finally adopted as the official name in 1795 on the direction of Lieutenant Governor John Graves Simcoe.[3]
Etobicoke was intended by the British to be included in the Toronto Purchase of 1787.[3] However, whether the western boundary of the purchase was the Humber River or the Etobicoke River (now, Etobicoke Creek) was disputed. The Mississauga Indians allowed British surveyor Alexander Aitkin to survey the disputed land, and eventually the dispute was settled, with the Mississauga recognising the purchase as extending to Etobicoke Creek, and the British paying an additional 10 shillings for the purchase.[citation needed]
Settlers began to move in from Britain. Early settlers included many of the Queen's Rangers, who were given land in the area by Simcoe to help protect the new capital of Upper Canada. In 1793-95, the Honourable Samuel Smith, a colonel in the Queen's Rangers, received land grants of 1,530 acres (6.2 km2), extending from today's Kipling Avenue to Etobicoke Creek, and north to Bloor Street.[4] The first land patent was issued to Sergeant Patrick Mealey on March 18, 1797 for a plot on the west side of Royal York Road on Lake Ontario.[5] This was part of the First Military Tract, or "Militia Lands", which extended from today's Royal York Road to Kipling Avenue, south from Bloor Street. More land was granted the members of the Queen's Rangers in the First Military tract, but most Rangers did not occupy their land and many sold their acreage to others after a short time.
The census of 1805 counted 84 people in the township of Etobicoke. In 1806 William Cooper built a grist mill and saw mill on the west bank of the Humber river, just south of Dundas Street. The 1809 census counted 137 residents.[3] The Dundas Street bridge opened in 1816, making the township more accessible.[citation needed]
On May 18, 1846 the Albion Road Company was incorporated. Its purpose was to build and maintain a road to the north-west corner of Etobicoke, where a new community was planned. At the same time, John Grubb, who had already founded Thistletown, hired land surveyor John Stoughton Dennis to plan a community at the intersection of Islington Avenue and Albion Road, to be named Saint Andrew's. Plan 6 for this community was registered on October 15, 1847. The French master of Upper Canada College, Jean du Petit Pont de la Haye, contracted land surveyor James McCallum Jr to create a plan for the community planned by the Albion Road Company, and Plan 28 was registered for Claireville on October 12, 1849.[5]

The township of Etobicoke was incorporated on January 1, 1850.[6] The first meeting of the town council was held on January 21. Present at the meeting were reeve William Gamble, vice-reeve W. B. Wadsworth and aldermen Moses Appleby, Thomas Fisher and John Geddes.[7] The council convened monthly meetings at a variety of places. In 1850, the population of the township was 2904.[citation needed] By 1881, the population of Etobicoke township was 2976.[7]
In 1911, the community of Mimico was incorporated on land taken from Etobicoke township.[8] New Toronto was incorporated on January 1, 1913.[3] Early on there was talk of merging Mimico and New Toronto. A 1916 referendum on amalgamating the two communities was approved by the residents of Mimico, but rejected by residents of New Toronto.[4] In 1917, Mimico became a town and in 1920, New Toronto became the Town of New Toronto. Long Branch was incorporated in 1930 as a village.[citation needed]
In 1954, Etobicoke Township became a part of the newly-formed regional government, the Municipality of Metropolitan Toronto ("Metro"). In 1967, the township of Etobicoke was merged with three small lakeside municipalities — the Village of Long Branch, the Town of New Toronto, and the Town of Mimico — to form the Borough of Etobicoke. The borough was reincorporated as a city in 1984.[6] In 1998, six local municipalities (including Etobicoke) and the Metropolitan Toronto government merged to form the amalgamated city of Toronto.[9]
Demographics
In 2011, Etobicoke was 55.5% White, 20.4% South Asian, 9.5% Black, 2.5% Latin American, 2.6% Chinese, 2.5% Filipino, 1.4% Korean, 1.1% West Asian, 1.0% Arab, 1.0% Southeast Asian, and 2.5% Other. 48.1% of the population are immigrants.[10]
English is the most spoken language in Etobicoke, followed by Italian, Punjabi, Russian, Gujarati, Somali, Persian and Hindi/Urdu.[citation needed]
Arts and culture


Etobicoke has the lowest population density of the former cities and boroughs that currently make up the city of Toronto. This is mainly due to its expanses of industrial lands. Several major freeways are routed through the area, making the area ideal for automobile-based transportation. Public transit does not serve the area well, with few rapid transit connections; however, there are many bus routes that service the area frequently.
Many exceptions to Toronto's gridded street matrix are found in Etobicoke. A number of overpasses and awkward intersections, such as Bloor/Kipling/Dundas West (Six-Points), have been created in an effort to reconcile the grid with these planning anomalies.
Etobicoke has numerous public parks, notable among them is James Gardens on the banks of the Humber River. The park includes seasonal flowers, walkways, a rock garden, streams, and waterfalls. It is a very popular site for taking wedding photographs. The Humber Bay park is located in Etobicoke.
The central/southern areas of Etobicoke are better served by public transit and closer to the city centre. These areas, such as Markland Wood, The Kingsway, New Toronto, Mimico and Long Branch, consist of large green spaces, numerous parks, golf courses (including St. George's Golf and Country Club, ranked 3rd best in Canada),[11] numerous restaurants and cafes, and fine boutiques. Residential development consists primarily of single-family dwellings, although several large multi-storey hi rise condominium developments have been built in south Etobicoke near the Humber River over the past few years. Kingsway South neighbourhood has attracted many affluent individuals and families (as of 2001, over 50% of households have an income in excess of C$100,000/year),[12] and remains one of Toronto's more prominent neighbourhoods.
The central areas of Etobicoke, although farther from the subway line, are still well-served by public transit buses. These neighbourhoods are generally middle class.
Unfortunately, some areas in Etobicoke have become neglected, "inner-ring" suburbs, such as Rexdale. These central and northern areas of Etobicoke contain numerous high-density apartment complexes set in the middle of sizable, open fields and parks.
Etobicoke is home to Humber College, University of Guelph-Humber, Woodbine Race Track and Slots, Woodbine Centre and Sherway Gardens Shopping Centre.
Education
Public schools in Etobicoke are overseen by the Toronto District School Board. High schools include Central Etobicoke High School, Etobicoke Collegiate Institute, founded in 1928, Kipling Collegiate Institute, Lakeshore Collegiate Institute (originally New Toronto Secondary School, founded in 1950), Martingrove Collegiate Institute, North Albion Collegiate Institute, Richview Collegiate Institute, founded in 1958, Silverthorn Collegiate Institute, Thistletown Collegiate Institute, West Humber Collegiate Institute, founded in 1966, Etobicoke School of the Arts, founded in 1981 in the former Royal York Collegiate Institute, Scarlett Heights Entrepreneurial Academy (formerly, Collegiate Institute), and the School of Experiential Education, an alternative school founded in 1971.
In addition to the public school system, Etobicoke is home to several Catholic schools, overseen by the Toronto Catholic District School Board. These include Michael Power/St. Joseph, Bishop Allen Academy, Don Bosco Catholic Secondary School (formerly Keiller Mackay Collegiate Institute), Father John Redmond, Father Henry Carr, Holy Child, Our Lady of Sorrows Elementary School, Nativity of Our Lord Elementary School, Father Serra Catholic School, and Monsignor Percy Johnson Catholic Secondary School.
Grade schools include: Second Street Junior-Middle School (1950), Seventh Street Junior School (c1925), and Twentieth Street Junior School (all in New Toronto); James S. Bell Junior-Middle School in Long Branch; John English Junior-Middle School, which is now located in the former Mimico High School (the original John English School is now a community centre), David Hornell Junior School on Victoria Street in Mimico, for grades JK-5 (1961) and the Karen Kain School of the Arts formerly Crestwood Public School.
Other schools include: Humberwood Downs J.M.A., West Humber Junior, Smithfield, Elmbank, Humbercrest, Eatonville Junior School and Missisauga private school; West Glen Junior School, located on Cowley Avenue, educates in grades JK-5 (1953; Norseman Junior Middle School, which opened its doors to students from Kindergarten to Grade 6 in January 1953. From 1968 to 1981, it became the middle school for the area with Grades 6, 7, and 8. Since 1981, the school has served students from Junior Kindergarten to Grade 8. The second storey serves middle school, Grades 6 to 8.
Economy
Skyservice, an airline, was headquartered in Etobicoke, until its recent demise.[13][14] Canada 3000 had its headquarters in the City of Etobicoke before it became a part of Toronto;[15] the headquarters remained there until the closing of the airline. The construction industry in Etobicoke has been booming with many new condo towers being developed along the waterfront near humber bay and along Bloor street. This has helped increase Etobicoke's populaton after a short period of decline. [16]
Sport
Etobicoke has a wide range of indoor and outdoor sporting leagues including baseball, soccer, football, hockey, and ringette. Some of the prominent clubs include the Etobicoke Kangaroos Australian rules football club the Serbian White Eagles FC club, the Stars Diving Club and Toronto Croatia. Southern Etobicoke is also home to the new Lakeshore Lions Arena. Etobicoke is the hometown of Major League Baseball Star Joey Votto
Neighbourhoods
Etobicoke is generally divided into three large areas that roughly correspond to the three political ridings. Each consisting of neighbourhoods, mostly developments of 19th century 'postal villages' (rural neighbourhoods), that were built at important points along the early roads and railways; especially the three former 'Lakeshore Municipalities' that separated from Etobicoke in the early 20th century and Etobicoke's central Islington community:
- "The Lakeshore" (Etobicoke—Lakeshore); along the north shore of Lake Ontario and the 'Lake Shore Road' (now Lake Shore Boulevard West), comprises three communities that were the first in Etobicoke to urbanize and became separate municipalities during the first half of the 20th century: the Town of Mimico, the Town of New Toronto, Village of Long Branch, and related communities that were never separate from the Township of Etobicoke; namely, Alderwood (originally a suburb of New Toronto), and Humber Bay (a historic gateway community connecting to Toronto) which was originally sprawl from the east side of the Humber River that was subsequently split by the construction of Ontario's first motor vehicle 'freeway' in 1938, which cuts across the top of southern Etobicoke; (the Queen Elizabeth Way). The original remnant residential (northern) section of Humber Bay today is located north of The Queensway, east of Mimico Creek to the Humber River. The commercial, southern section of Humber Bay today retains only Christie's Biscuits bakery, as high-rise condo towers and clustered row housing have forced out virtually all other commercial/industrial employment uses. The former McGuiness Whiskey factory was converted into a high-rise loft condo in the late 1990s which became the centrepiece of the Mystic Pointe development. Etobicoke's first railway opened though the area in the 1855, just north of the Lake Ontario shoreline, leading to the first period of growth as it replaced Dundas Street in Central Etobicoke as the main means of transportation and the industrial centre along its right-of-way.
- Central Etobicoke (Etobicoke Centre); the oldest communities in Etobicoke developed along the first street, Dundas Street, in the south of this area, which crosses the width of Etobicoke on the escarpment formed by the ancient shoreline of Lake Iroquois. This area centres around the Islington community, the former administrative centre of Etobicoke and later Etobicoke's 'downtown' which is near the central 'Six Points' intersection at its western boundary. The rural Richview community developed directly to the north of Islington in the 19th century on Eglinton Ave. (formerly Richview Rd.) as did the gateway Humber Heights communities (connecting to Toronto): Westmount and Humbervale, to the east on Eglinton. Development of the, until then largely undeveloped eastern part of central Etobicoke (originally a forest reserved for the use of government mills as "The King's Mill Reserve"; 'Kingsmill'), the 'Humber Valley', was largely the work of Robert Home Smith starting about 1900 which included the communities of the Kingsway and Edenbridge. As Etobicoke developed in the post war years, low density residential areas filled in most of the rural areas between the old communities including Princess-Rosethorn and Eringate-Centennial-West Deane as well as the older Eatonville community to the west of Islington. Central Etobicoke includes Etobicoke's most exclusive neighbourhoods, with fine housing stock and many large treed properties. Along the East and West Mall parallel to Highway 427 exists a mix of hi-rise rentals, townhouses and post war bungalows.
Markland Wood is the farthest western community within Etobicoke/Toronto along Bloor Street west, a mixed area for housing with some hi-rise rentals.
- Rexdale (Etobicoke North); named after a 1950s development of the area, the name Rexdale is now more frequently used to refer to all the northern 19th century Etobicoke communities (Clairville, Highfield, Smithfield, Thistletown) which grew along two formerly private roads (now Albion Rd. and Rexdale Blvd.) constructed diagonally across farms in Northern Etobicoke as a shortcut for travellers to Peel County (especially modern Brampton). First developed as an urban area by Rex Heslop in the post war years around the new Rexdale (the Elms) community, northern Etobicoke now has many apartment buildings as well as a large 'skyway' industrial park to the west which developed after Malton Airport (in nearby Mississauga) became Toronto's main 'Pearson International' Airport, and faces many of the problems associated with such areas.
Institutions

- Etobicoke Civic Centre Former City Hall.
- Etobicoke's former township offices (was also Etobicoke's first Methodist church and is beside Etobicoke's first cemetery)
- Montgomery's Inn
- Mimico GO Station Former Mimico Railway Station was the first station in Etobicoke.
- Humber Bay Park Artificial Park created with lakefill beginning in the 1970s).
- Churches/Temples
- St. Philip's Anglican Church (1828)
- St. Philip's Lutheran Church (1958)
- Islington Methodist Church (First Methodist Church in Etobicoke, later the Council Offices)
- Christ Church Anglican, Mimico (Burnt down) First Church in Etobicoke.
- Our Lady of Sorrows Roman Catholic Church
- St. Leo's Roman Catholic Church, Mimico First Catholic Parish in Etobicoke.
- St. Michaels Ukrainian Catholic Church (1954)
- St. Demitrius Ukrainian Orthodox Church (1958)
- Swaminarayan Mandir New ornate Hindu Temple in Etobicoke.
- Iglesia ni Cristo
- Schools
- University of Guelph-Humber
- Humber College
- Lakeshore Collegiate Institute Originally New Toronto Secondary School (1950), the first technical Secondary School in Etobicoke
- North Albion Collegiate Secondary School
- Father Henry Carr Catholic High School
- Thistletown Collegiate Secondary School
- St. Dorothy Catholic School
- Elmbank Middle School
- Mimico High School, the first High School in Etobicoke (1924)
- Transfiguration of Our Lord Catholic School
- St.Maurice Catholic School
- Etobicoke Collegiate Institute
- Martingrove Collegiate Institute
- Kipling Collegiate Institute
- Etobicoke School of the Arts Originally Royal York Collegiate Institute, now the oldest, free-standing arts-focused high school in Canada.
- Michael Power/St. Joseph First Catholic Secondary School in Etobicoke.
- Highfield Separate School
- John English Junior Middle School First Primary School in Etobicoke (at its original site). Today's location is the former Mimico High School
- Silverthorn Collegiate Institute
- Bishop Allen Academy
- St.Benadics Catholic School
- Kingsview Public School
- St.John The Avalgelist Catholic School
- Bishop Allen Secondary school
- Scarlett Heights Entrepreneurial Academy
- Father John Redmond Catholic Secondary School
See also
Sister cities
Notes
- ^ Mississaugas of the New Credit First Nation and Praxis Research Associates. Date unknown. The History of the Mississaugas of the New Credit First Nation. Hagersville, ON: Author.
- ^ Nichols, John D; Nyholm, Earl (1995). A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 978-0-8166-2427-0. OCLC 31242698.
- ^ a b c d "A Brief History of Etobicoke". Retrieved 2012-03-15.
{{cite web}}:|first=missing|last=(help); Missing pipe in:|first=(help) - ^ a b "Early History". New Toronto Historical Society.
- ^ a b Bob Given. "Beginnings!". Etobicoke Historical Society.
- ^ a b "Etobicoke Records". City of Toronto.
- ^ a b Robert A Given. "Our Municipal Government". Etobicoke Historical Society.
- ^ "Toronto Chronology".
- ^ Roda McInnis. "The Toronto Amalgamation: Looking Back, Moving Ahead". Retrieved 2012-04-12.
- ^ "2001 Community Profiles. Statistics Canada". 2.statcan.ca. 2002-03-12. Retrieved 2012-02-02.
- ^ St. George's Golf and Country Club in Etobicoke, Ontario, Canada[dead link]
- ^ Kingsway South (15): Social Profile #3 – Neighbourhoods Households & Income. 2001. City of Toronto. [1]
- ^ "Skyservice Corporate Brochure." Skyservice. Retrieved on August 28, 2009.
- ^ "Contact Skyservice Ailrines." Skyservice. Retrieved on March 31, 2010.
- ^ World Business Directory: 1997. Company Listings : Afghanistan - Germany, Volume 1. Gale Research, 1996. 474. Retrieved from Google Books on February 13, 2011. "3000 Airlines Ltd. 27 Fasken Dr. Etobicoke, ON, Canada M9W 1K6" ISBN 0810361892, 9780810361898.
- ^ "Canada 3000 Airlines Worldwide Offices". Canada 3000. January 18, 2001. Archived from the original on January 18, 2001. Retrieved May 20, 2009. "CANADA 3000 Airlines Limited Head Office 27 Fasken Drive Toronto, Ontario M9W 1K6"
References
- Inside Toronto – The Weekender; March 27, 2005
