South Slavic languages: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kwamikagami (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
** [[Old Church Slavonic]] - extinct (ISO 639-1 code: '''cu'''; ISO 639-2 code: '''chu'''; SIL code: '''chu''') |
** [[Old Church Slavonic]] - extinct (ISO 639-1 code: '''cu'''; ISO 639-2 code: '''chu'''; SIL code: '''chu''') |
||
*Western Section |
*Western Section |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
** [[Slovene language|Slovene]] (ISO 639-1 code: '''sl'''; ISO 639-2 code: '''slv'''; SIL code: '''slv''') |
** [[Slovene language|Slovene]] (ISO 639-1 code: '''sl'''; ISO 639-2 code: '''slv'''; SIL code: '''slv''') |
||
**[[Serbo-Croatian]] (ISO 639-1 code: '''sh'''; ISO 639-2/3 code: '''hsb'''; SIL code: '''scr'''). |
**[[Serbo-Croatian]] (ISO 639-1 code: '''sh'''; ISO 639-2/3 code: '''hsb'''; SIL code: '''scr'''). <br>There are four national [[standard language]]s based on the [[Shtokavian dialect]] of Serbo-Croatian: |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Cultural orientation === |
=== Cultural orientation === |
||
Southeast of the Slavic languages belong to the Orthodox cultural "cultural circle", these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Greek language and culture. Official letter in the Cyrillic script. These languages were influenced by oriental culture, which left its mark in a number of Turkish words |
Southeast of the Slavic languages belong to the Orthodox cultural "cultural circle", these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Greek language and culture. Official letter in the Cyrillic script. These languages were influenced by oriental culture, which left its mark in a number of Turkish words. |
||
* |
*[[Orthodox Church|Orthodox]] cultural languages |
||
** Bulgarian |
|||
** Bulgarian. Besides Orthodox, Bulgarian had strong Christian non-Orthodox culture, that influenced the development of Bulgarian: Pavlikans, later mostly converted to Catholics<ref name="Forum">{{hr icon}} Ante Marinović: Filolozi i književnici o hrvatskom jeziku, Forum 36 (1997.), knj. 69, 9/10, p. 1296-1297</ref> |
|||
** Macedonian |
** Macedonian |
||
** Serbian |
** Serbian and Montenegrin |
||
Mixed east-west with a strong influence of oriental-Islamic culture influenced the Bosnian language. |
Mixed east-west with a strong influence of oriental-Islamic culture influenced the Bosnian language. |
||
Southwest Slavic languages belong to the cultural circle of Catholic culture, these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Latin language and Western culture. Official letter in the Latin script. |
|||
Halfway from these groups is Montenegrin language, now belonging to Orthodox cultural circle. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* Montenegrin. Early Montenegro, before being conquested by Serbian Empire, belonged to Catholic culture. Influences of Mediterranean circle from the southwest (Romanic loanwords), oriental culture (Turkish loanwords). Unlike Serbian, Montenegrin has significantly higher use of infinitive form. |
|||
Southwest Slavic languages belong to the cultural circle of Catholic culture, these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Latin language and Western culture. Official letter is the Latin script. Catholic Church gave special privilege to Croats from early Middle Ages: to use Croatian language in liturgy. Croatian developed its own redaction of Church Slavonic. Catholic Church promoted, supported and maintained (due to influence of local Croat priests) the use of Croatian Cyrillic and Glagolitic script among Croats until 19th century. Slovenian was influenced by Central European culture (German loanwords and some other features). Croatian was influenced by Central European (German, Hungarian, Czech loanwords) on north, Mediterranean culture on littoral (Romanic loanwords) and Oriental culture on east (Turkish loanwords). Therefore Croatian and Slovenian tend to translate foreign words, since it's the tradition of Central European languages. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
** Croatian |
** Croatian |
||
** Slovenian |
** Slovenian |
||
| Line 81: | Line 78: | ||
**** Timok-Lužica subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia and Bulgaria |
**** Timok-Lužica subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia and Bulgaria |
||
**** Belogradčik subdialect (Ekavian) in Bulgaria |
**** Belogradčik subdialect (Ekavian) in Bulgaria |
||
| ⚫ | |||
** Western |
** Western |
||
*** '''[[Štokavian dialect]] 7''' |
*** '''[[Štokavian dialect]] 7''' |
||
| ⚫ | |||
**** New Shtokavian accentuation |
|||
**** Kosovo-Resava subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia and Kosovo |
|||
***** Dalmatian-Bosnian subdialect ([[Ikavian]]) in Croatia [[Zagora]] (South Croatia), Croats in Western Herzegovina, NW Bosnia, [[Tomislavgrad]] (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Bunjevci Croats in Serbia [[Subotica]], [[Molise Croatian dialect]] (Croats in Italy, Štokavian-Čakavian), Štoji group of Croats in Burgenland (Austria) |
|||
***** |
***** Smederevo-Vršac variant subdialect (Kosovo-Resava) (Ekavian) in Serbia |
||
| ⚫ | |||
**** Herzegovina subdialect in Bosnia and Herzegovina [[Goražde]],(Serbia) [[Užice]],(Montenegro) and (Croatia)[[Dubrovnik]]. |
|||
***** Šumadija-Vojvodina subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia (some dialectologists treat these two as separate subdialects) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<!-- more info on these, please |
|||
**** |
**** Ikavian subdialect in Croatia [[Sinj]], and Croats in [[Tomislavgrad]] (Bosnia and Herzegovina), in Croats of (Serbia) [[Subotica]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
--> |
|||
***** [[Gradišče dialect]] (Croats in south Austria, and Hungary) |
|||
**** Old Shtokavian accentuation |
|||
***** [[Molise Croatian dialect]] (Croats in Italy) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
***** [[Bunjevac dialect]] (Croats in Serbia [[Subotica]]) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*** '''[[Čakavian]] Croatian dialect 6''' |
*** '''[[Čakavian]] Croatian dialect 6''' |
||
**** [[Burgenland Croatian]] (in Austria, and Hungary) |
***** [[Burgenland Croatian]] (in Austria, and Hungary) |
||
**** Buzet subdialect in Croatia |
**** Buzet subdialect in Croatia |
||
**** Western čakavian subdialect in Croatia |
**** Western čakavian subdialect in Croatia |
||
| Line 207: | Line 202: | ||
This dialect is spoken primarily in the federal state of [[Burgenland]] in Austria, but also in nearby areas in Vienna, [[Slovakia]], and Hungary by descendants of Croats who migrated there in the 16th century. This dialect or possibly family of dialects is quite different from standard Croatian. It has been heavily influenced by German and also Hungarian. In addition, it has some properties from all three of the major dialectical groups in Croatia, as the migrants did not all come from the same areas of Croatia. The "micro-literary" standard is based on a Čakavian dialect, and, like all Čakavian dialects, is characterized by very conservative grammatical structures: it preserves, prominently, case endings lost in the Štokavian base of standard Croatian. |
This dialect is spoken primarily in the federal state of [[Burgenland]] in Austria, but also in nearby areas in Vienna, [[Slovakia]], and Hungary by descendants of Croats who migrated there in the 16th century. This dialect or possibly family of dialects is quite different from standard Croatian. It has been heavily influenced by German and also Hungarian. In addition, it has some properties from all three of the major dialectical groups in Croatia, as the migrants did not all come from the same areas of Croatia. The "micro-literary" standard is based on a Čakavian dialect, and, like all Čakavian dialects, is characterized by very conservative grammatical structures: it preserves, prominently, case endings lost in the Štokavian base of standard Croatian. |
||
At most 100,000 people speak Burgenland Croatian and almost all are bilingual in German. Its future is uncertain, but there is some movement to preserve it. It has official status in six districts of Burgenland, and is used in some schools in Burgenland and |
At most 100,000 people speak Burgenland Croatian and almost all are bilingual in German. Its future is uncertain, but there is some movement to preserve it. It has official status in six districts of Burgenland, and is used in some schools in Burgenland and neighboring western parts of Hungary. |
||
== Central-western South Slavic dialects == |
== Central-western South Slavic dialects == |
||
| Line 214: | Line 209: | ||
{{Main|Kajkavian dialect}} |
{{Main|Kajkavian dialect}} |
||
Kaykavian is mostly spoken in northern and northwest Croatia including 1/3 of country near the Hungarian and Slovenian borders: chiefly in and around towns [[Zagreb]], ''Varaždin, Čakovec, Koprivnica, Petrinja, Delnice'', etc. It renders ''yat'' mostly as ''e'' (rarely as diphthongal ''ie''); note that this pronouncing cannot be equated to that of the Ekavian dialects, as many kaykavian dialects distinguish a closed ''e'' nearly ''ae'' (from ''yat'') and an open ''e'' (from original ''e'' |
Kaykavian is mostly spoken in northern and northwest Croatia including 1/3 of country near the Hungarian and Slovenian borders: chiefly in and around towns [[Zagreb]], ''Varaždin, Čakovec, Koprivnica, Petrinja, Delnice'', etc. It renders ''yat'' mostly as ''e'' (rarely as diphthongal ''ie''); note that this pronouncing cannot be equated to that of the Ekavian dialects, as many kaykavian dialects distinguish a closed ''e'' nearly ''ae'' (from ''yat'') and an open ''e'' (from original ''e''). |
||
It almost lacks several palatals ''(ć, lj, nj, dž)'' found in Shtokavian dialect, and has some loanwords from the nearby [[Slovene dialects]], as well as from [[German language|German]] chiefly in towns. |
It almost lacks several palatals ''(ć, lj, nj, dž)'' found in Shtokavian dialect, and has some loanwords from the nearby [[Slovene dialects]], as well as from [[German language|German]] chiefly in towns. |
||
| Line 256: | Line 251: | ||
** nouns: ''volk'' (wolf) → ''volkova'' (two wolves) → ''volkovi'' (some wolves) |
** nouns: ''volk'' (wolf) → ''volkova'' (two wolves) → ''volkovi'' (some wolves) |
||
** verbs: ''hodim'' (I walk) → ''hodiva'' (the two of us walk) → ''hodimo'' (we walk) |
** verbs: ''hodim'' (I walk) → ''hodiva'' (the two of us walk) → ''hodimo'' (we walk) |
||
** pronouns: |
|||
=== Division within Eastern dialects === |
=== Division within Eastern dialects === |
||
Revision as of 02:16, 24 April 2010
This article needs attention from an expert in Linguistics. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. (November 2008) |
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. |
| South Slavic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Eastern Europe |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-5 | zls |
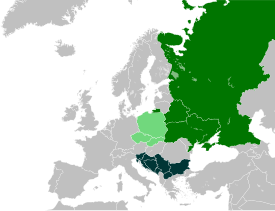 | |
| South Slavic languages and dialects |
|---|
South Slavic languages comprise one of the three geographical groups of Slavic languages (besides West and East Slavic). There are around 30 million speakers of these languages, mainly in the Balkans. The South Slavic languages are further subdivided into Eastern and Western subgroups.
German, Hungarian and Romanian generally form a belt which geographically separates speakers of South Slavic languages from their counterpart West and East Slavic language speakers.
The first South Slavic language to be written was Old Church Slavonic in the 9th century, which was based on the local dialect in the Thessalonica region. It is retained as a liturgical language in some South Slavic Orthodox churches.
Classification
The South Slavic languages constitute a diasystem and a dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect within this continuum [1].
- Eastern Section
- Macedonian - (ISO 639-1 code: mk; ISO 639-2(B) code: mac; ISO 639-2(T) code: mkd; SIL code: mkd)
- Bulgarian - (ISO 639-1 code: bg; ISO 639-2 code: bul; SIL code: bul)
- Old Church Slavonic - extinct (ISO 639-1 code: cu; ISO 639-2 code: chu; SIL code: chu)
- Western Section
- Slovene (ISO 639-1 code: sl; ISO 639-2 code: slv; SIL code: slv)
- Serbo-Croatian (ISO 639-1 code: sh; ISO 639-2/3 code: hsb; SIL code: scr).
There are four national standard languages based on the Shtokavian dialect of Serbo-Croatian:- Serbian (ISO 639-1 code: sr; ISO 639-2/3 code: srp; SIL code: srp)
- Croatian (ISO 639-1 code: hr; ISO 639-2/3 code: hrv; SIL code: hrv)
- Bosnian (ISO 639-1 code: bs; ISO 639-2/3 code: bos; SIL code: bos)
- Montenegrin (not regulated but official in Montenegro)
Cultural orientation
Southeast of the Slavic languages belong to the Orthodox cultural "cultural circle", these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Greek language and culture. Official letter in the Cyrillic script. These languages were influenced by oriental culture, which left its mark in a number of Turkish words.
- Orthodox cultural languages
- Bulgarian
- Macedonian
- Serbian and Montenegrin
Mixed east-west with a strong influence of oriental-Islamic culture influenced the Bosnian language.
Southwest Slavic languages belong to the cultural circle of Catholic culture, these languages were exposed to the strong influence of the Latin language and Western culture. Official letter in the Latin script.
- Catholic cultural languages
- Croatian
- Slovenian
Classification of the South Slavic languages
 Slavic languages belong to Balto-Slavic group, which itself belongs to the Indo-European language family. The South Slavic family itself exists strictly as a geographical grouping, not forming a genetic node in Slavic language family - there was never a period in which all South Slavic dialects exhibited exclusive set of extensive phonological, morphological and lexical changes peculiar to them and them only.[citation needed] The was never a period of cultural or political unity in which "Proto-South-Slavic" could have existed, in which Common South Slavic innovations could have occurred. Several South-Slavic-only lexical and morphological patterns that have been proposed have all been proven to be Common Slavic archaisms, or are shared with some Slovakian or Ukrainian dialects.[citation needed]
Slavic languages belong to Balto-Slavic group, which itself belongs to the Indo-European language family. The South Slavic family itself exists strictly as a geographical grouping, not forming a genetic node in Slavic language family - there was never a period in which all South Slavic dialects exhibited exclusive set of extensive phonological, morphological and lexical changes peculiar to them and them only.[citation needed] The was never a period of cultural or political unity in which "Proto-South-Slavic" could have existed, in which Common South Slavic innovations could have occurred. Several South-Slavic-only lexical and morphological patterns that have been proposed have all been proven to be Common Slavic archaisms, or are shared with some Slovakian or Ukrainian dialects.[citation needed]
Within South Slavic, however, there could have been Proto-West-South-Slavic (ancestral to dialects of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Serbia, Montenegro and Slavic dialects of Kosovo) and Proto-East-South-Slavic (ancestral to Bulgaro-Macedonian dialects). Older literature also frequently makes a notion of "Serbo-Croatian" or "Central-South-Slavic" dialect continuum or diasystem which would in theory compromise Čakavian, Kajakvian, Štokavian and sometimes Torlakian dialects. Čakavian, Kajkavian and Torlakian dialects have over the centuries exhibited extensive lexical and, to a lesser degree, morphological influences (such as transitional ščakavian mixture) from dominant Štokavian, which has lead many into false assumption of some common ancestral dialect, or of exclusive set of isoglosses which would connect them all, but very important thing to note is that there was never a language ancestral to idioms spoken nowadays by Bosniaks, Croats, Monenegrins and Serbs. "Serbo-Croatian dialect system" or its much less common but politically more correct alternative "Central South Slavic diasystem" exists only as an arbitrary geographical grouping, nowadays largely obsoleted as a term due to the break-up of Yugoslavia and the advent of newly-established republics.
All South Slavic dialects form a dialectal continuum stretching from today's southern Austria to southeast Bulgaria. On the level of dialectology or linguistic typology, several major dialects can be distinguished, but their borders are blurred due to strong contact and frequent migrations in the past. On the other hand, cultural establishment and national liberation from occupying Ottoman and Austro-Hungarian Empires, followed by formation of nation-states in 19th and 20th century, caused development and codification of standard national languages. These processes have (almost) ended just at the end of 20th century, with the breakup of Yugoslavia (with only the Montenegrin national and linguistic issue left to be resolved). Most of those languages selected one dialect as the basis of a literary language and, as a result, some dialects got deprecated and marginalized, while others flourished. Further, the national and ethnic borders do not coincide with dialectal boundaries in most cases.
Thus, two distinct classifications of South Slavic languages can be drawn; one from a geographic point of view, and the other from a sociolinguistic point of view. The two classifications seldom map 1:1. For example, Croats speak three main and two exclaval dialects in four countries, while their standard language is based on Ijekavian Neo-Štokavian.
Note: Due to different political statuses of languages/dialects and different historical contexts, the classifications are necessarily arbitrary to some extent.
Dialectal classification
- South Slavic languages
- Eastern
- Bulgarian language
- Bulgarian dialect (Torlakian)
- Macedonian language
- Macedonian dialect (Torlakian)
- Torlakian dialect in Macedonia, (Bulgaria and Serbia)
- Bulgarian language
- Transitional
- Western
- Štokavian dialect 7
- Šumadija-Vojvodina subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia
- Kosovo-Resava subdialect (Ekavian) in Serbia and Kosovo
- Smederevo-Vršac variant subdialect (Kosovo-Resava) (Ekavian) in Serbia
- Zeta-Sandžak subdialect Montenegro Podgorica and (Serbia)
- Herzegovina subdialect in Bosnia and Herzegovina Goražde,(Serbia) Užice,(Montenegro) and (Croatia)Dubrovnik.
- Ijekavian subdialect (east Bosnian) in Croatia Hrvatska Kostajnica and Croats in (Bosnia and Herzegovina) Kiseljak, Bosnijak Tuzla.
- Ikavian subdialect in Croatia Sinj, and Croats in Tomislavgrad (Bosnia and Herzegovina), in Croats of (Serbia) Subotica
- Slavonia dialect Croatia Slavonski Brod.
- Gradišče dialect (Croats in south Austria, and Hungary)
- Molise Croatian dialect (Croats in Italy)
- Caraşova dialect (Croats in Romania)
- Bunjevac dialect (Croats in Serbia Subotica)
- Čakavian Croatian dialect 6
- Burgenland Croatian (in Austria, and Hungary)
- Buzet subdialect in Croatia
- Western čakavian subdialect in Croatia
- Southwestern Istrian subdialect in Croatia
- North Čakavian subdialect in Croatia
- South Čakavian subdialect in Croatia
- Lastovo subdialect in Croatia
- Kajkavian Croatian dialect 6
- Zagorje-Međimurje subdialect in Croatia
- Križevci-Podravina subdialect in Croatia
- Turopolje-Posavina subdialect in Croatia
- Prigorski subdialect in Croatia
- Donja Sutla subdialect in Croatia
- Goranski subdialect in Croatia
- Slovene language
- Slovene dialects alike croatian kajkavian dialects.
- Štokavian dialect 7
- Eastern

Eastern group of South Slavic languages
Bulgarian dialects
- Eastern Bulgarian dialects
- Western Bulgarian dialects; includes Torlakian dialect
Macedonian dialects
- Southeast macedonian dialects
- North macedonian; Torlakian dialect
- see also:Dialects of Macedonian language
Transitional South Slavic languages
Bulgarian Serbian, and Macedonian Torlakian dialect
There also exists another dialect, called torlački or Torlak, which is spoken in southern and eastern Serbia, northern Republic of Macedonia and western Bulgaria, and often considered transitional between Central and Eastern group of South Slavic languages.
It is even thought to fit into the so-called Balkan sprachbund, an area of linguistic convergence among languages due to long-term contact rather than being genetically related.
Central or Eastern Western group of South Slavic languages
History
Each of these primary and secondary dialectical units breaks down into subdialects and accentological isoglosses by region. In the past (and now in mountains and islands), it was not uncommon for individual villages to have some of their own words and phrases. However, throughout the twentieth century the various dialects have been strongly influenced by the Štokavian standards through mass media and public education, and much of the "local color" has been lost chiefly in towns.
With the breakup of Yugoslavia, rise of national awareness has also caused many to modify their speech according to newly established standard language guidelines. The various wars have also caused mass migrations, and changed the ethnic and thus dialectal picture of some areas, especially in Bosnia and Herzegovina, but also in central Croatia and in Serbia (especially in Vojvodina). In some areas it is unclear whether location or ethnicity is now the dominant factor in the dialect of the speaker.
Because of these forces, the speech patterns of some communities and regions are in a state of flux, and it is difficult to determine which dialects will die out entirely. Further research over the next few decades will be necessary to determine the changes made in the dialectical distribution of the language.
Dialect to language name mapping
The table below shows the relationship between the dialects of so-called South Slavic continum and Central South Slavic diasystem and the names their native speakers might call them.
| Dialect | Sub-Dialect | Bulgarian | Macedonian | Serbian | Montenegrin | Bosnian | Croatian | Slovene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torlakian | x | x | x | |||||
| Štokavian | Kosovo-Resava | x | ||||||
| Šumadija-Vojvodina | x | |||||||
| Zeta-South Sandžak | x | x | x | |||||
| Eastern Herzgovinian | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Eastern Bosnian | x | x | ||||||
| Western Ikavian | x | x | ||||||
| Slavonian | x | |||||||
| Čakavian | x | |||||||
| Kajkavian | x | x |
Štokavian dialects and standard languages
- Serbian language, east new štokavian dialect (east neoštokavian dialects and southeast serbian torlakian dialects).
- Bosnian language, central new štokavian dialects (east bosnian dialect and east herzegovina dialect).
- Croatian language, western new štokavian dialects (western ijekavian and ikavian dialects, slavonian dialects and kaykavian in cakavian dialects.
Molise Croatian
The Molise Croatian (or Molise Slavic) dialect is spoken in three villages of the Italian region of Molise, by the descendants of South Slavs who migrated there from the eastern Adriatic coast in the 15th century. Because these people have migrated away from the rest of their kinsmen so long ago, their diaspora language is rather distinct from the standard language, and rather influenced by Italian. However, their speech retains some archaic features that were lost in all the other Štokavian dialects after the 15th century, and thus makes it a valuable tool in accentological research.
Relation dialects system and official central South Slavic languages
Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian languages, both as sets of dialects and as codified standard languages:
- Serbian language is a system of two dialects: Štokavian and Torlakian.
- Bosnian language is dialects: Štokavian East Bosnian dialects.
- Montenegrin language is dialects: Štokavian Montenegrin dialects (Zetski).
- Croatian language is a system of three dialects: Čakavian, Štokavian and Kajkavian.
Croatian Čakavian dialects and Burgenland Croatian standard language
Čakavian dialects
Chakavian (Čakavian) is spoken in the western, central, and southern parts of Croatia, mainly in Istria, Kvarner Gulf, Dalmatia, and also in Croatian inlands (Gacka, Pokupje etc.). The Čakavian renders Proto-Slavic yat mostly as i or also as e (rarely as (i)je), or even mixed Ekavian-Ikavian. Many dialects of Čakavian preserved significant number of Dalmatian words, but also have a lot of loan words from Venetian, Italian, Greek and other Mediterranean languages.
Example: Ča je, je, tako je vavik bilo, ča će bit, će bit, a nekako će već bit!
Burgenland Croatian standard language
This dialect is spoken primarily in the federal state of Burgenland in Austria, but also in nearby areas in Vienna, Slovakia, and Hungary by descendants of Croats who migrated there in the 16th century. This dialect or possibly family of dialects is quite different from standard Croatian. It has been heavily influenced by German and also Hungarian. In addition, it has some properties from all three of the major dialectical groups in Croatia, as the migrants did not all come from the same areas of Croatia. The "micro-literary" standard is based on a Čakavian dialect, and, like all Čakavian dialects, is characterized by very conservative grammatical structures: it preserves, prominently, case endings lost in the Štokavian base of standard Croatian.
At most 100,000 people speak Burgenland Croatian and almost all are bilingual in German. Its future is uncertain, but there is some movement to preserve it. It has official status in six districts of Burgenland, and is used in some schools in Burgenland and neighboring western parts of Hungary.
Central-western South Slavic dialects
Croatian kaykavian dialects
Kaykavian is mostly spoken in northern and northwest Croatia including 1/3 of country near the Hungarian and Slovenian borders: chiefly in and around towns Zagreb, Varaždin, Čakovec, Koprivnica, Petrinja, Delnice, etc. It renders yat mostly as e (rarely as diphthongal ie); note that this pronouncing cannot be equated to that of the Ekavian dialects, as many kaykavian dialects distinguish a closed e nearly ae (from yat) and an open e (from original e).
It almost lacks several palatals (ć, lj, nj, dž) found in Shtokavian dialect, and has some loanwords from the nearby Slovene dialects, as well as from German chiefly in towns.
Example: Kak je, tak je; tak je navek bilo, kak bu tak bu, a bu vre nekak kak bu!
Western group of South Slavic language
Slovene language
- Slovenian dialects having partition croatian kaykavian dialects.
- Prekmurje dialects, minority slovenian dialect of Hungaria.
Grammar
Eastern-Western division
In the broadest terms, the Eastern dialects of South Slavic (ie. Bulgarian, Macedonian and southeast Serbian dialects) most differ from the Western dialects in the following ways :
- The Eastern dialects have almost completely lost their noun declensions, and have become entirely analytic.[3]
- The Eastern dialects have developed definite article suffixes in similar fashion to the other languages in the Balkan Sprachbund.[4]
- The Eastern dialects have completely lost the infinitive. Thus, the first person singular is considered the main part of a verb. Sentences that in other languages would require an infinitive are constructed through a clause – eg. Bulgarian - искам да ходя (iskam da hodya) - "I want to go" (lit. "I want that I go").
Aside from these three main areas, there are several smaller, but still significant differences:
- The Western dialects have three genders in both the singular and plural (and Slovenian even has dual, see below), while the Eastern dialects only have them in the singular, eg. Serbian - on (he), ona (she), ono (it), oni (they, masc), one (they, fem), ona (they, neut); in Bulgarian, te (they) covers the whole plural.
- Inheriting a generalization of another demonstrative as a base form for 3rd person pronoun that already occurred in Late Proto-Slavic, standard literary Bulgarian, just like Old Church Slavonic, does not use Slavic "on-/ov-" as base forms, such as on, ona, ono, oni (he, she, it, they), and ovaj, ovde (this, here), but uses instead "to-/t-"based pronouns, such as toy, tya, to, te, and tozi, tuk (it only retains onzi - "that" and its derivatives); Western Bulgarian dialects and Macedonian do have some "ov-/on-" pronouns, and sometimes use them interchangeably.
- All dialects of the Central South Slavic area contain the concept of "any" - eg. Serbian neko "someone"; niko "no one"; iko "anyone". All others lack the last, and make do with some- or no- constructions instead. [5]
Division within Western dialects
- While Serbian, Bosnian and Croatian Shtokavian dialects have basically the same grammar, its usage is very diverse. While all three languages are relatively highly inflected, the further east one goes, the more likely it is that analytic forms are used - if not spoken, at least in the written language. A very basic example is :
- Croatian - hoću ići - "I want - to go" ; "Glede kakvoće zraka točna je procjena sigurnosti pučanstva grada Jeruzalema" - "With regard to air quality assessment is correct safety population of Jerusalem ".
- Serbian - hoću da idem - "I want - that - I go" ; "U pogledu kvalitete vazduha tačna je procena bezbednosti stanovništva grada Jerusalima" - "With regard to air quality assessment is correct safety population of Jerusalem ".
- Slovenian has retained Proto-Slavic dual number (which means that it has nine personal pronouns in the third person) for both nouns and verbs, eg. –
- nouns: volk (wolf) → volkova (two wolves) → volkovi (some wolves)
- verbs: hodim (I walk) → hodiva (the two of us walk) → hodimo (we walk)
Division within Eastern dialects
- In Macedonian, the perfect tense is largely based on the verb "to have", as in other Balkan languages like Greek and Albanian (like in English), as opposed to the verb "to be", which is used as the auxiliary in all other Slavic languages (see also here) - eg.
- Macedonian - imam videno - I have seen (imam - "to have")
- Bulgarian - vidyal sum - I have seen (sum - "to be")
Writing systems
The languages to the West of Serbian use the Roman alphabet, while those to the East and South use Cyrillic. Serbian itself constitutionally uses the Cyrillic script, though commonly, it is the Roman alphabet which is in greater use. For example, most newspapers are written in Cyrillic, while most magazines - in Roman script; books written by Serbian authors are written in Cyrillic, while books translated from foreign authors are usually in Roman script; on television, any writing as part of a television programme is usually in Cyrillic, while adverts are usually in Western script.
The division is traditionally partly based on religion – Serbia, Montenegro, Bulgaria and Macedonia, which use Cyrillic, are Orthodox countries, while Croatia and Slovenia, which use Roman script, are Catholic;[6] the Bosnian language, used by the Muslim Bosniaks, also uses the Roman script.
The Glagolitic alphabet was also used in the Middle Ages, most notably in Bulgaria and Croatia, but gradually disappeared.
Notes
- ^ Roland Sussex (2006). The Slavic languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 43–44. ISBN 9780521223157.
- ^ Torlakian can be treated as the part of both the Eastern South Slavic group and the Western. Speakers generally identify as ethnic Serbs, Bulgarians and Macedonians depending on their country of origin. Most Torlakian dialects are spoken in Serbia, and thus considered Serbian.
- ^ Note that some remnants of cases do still exist in Bulgarian – see here.
- ^ In Macedonian, these are especially well-developed, also taking on a role similar to demonstrative pronouns:
Serbian : sto - "chair" → stolovi - "the chair" → stolovi "this chair here"(incorrect information)- Bulgarian : stol - "chair" → stolat - "the chair"
- Macedonian : stol - "chair" → stolot - "the chair" → stolov - "this chair here" → stolon - "that chair there". As well as these, Macedonian also has a separate set of demonstratives: ovoj stol - "this chair"; onoj stol - "that chair".
- ^ In Bulgarian, more complex constructions such as "koyto i da bilo" ("whoever it may be" ≈ "anyone") can be used if the distinction is absolutely necessary.
- ^ This distinction is true for the whole Slavic world: the Orthodox Russia, Ukraine and Belarus also use Cyrillic, as does Rusyn (Eastern Orthodox/Eastern Catholic), while the Catholic Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia use Roman script, as does Sorbian. Romania and Moldova, which are not Slavic but are Orthodox, also used Cyrillic until 1860 and 1989, respectively, and it is still used in Transdnistria.
See also
- Differences in official languages in Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia
- Yat
- South Slavic languages [1]
References
- Ranko Matasović (2008). Poredbenopovijesna gramatika hrvatskoga jezika (in Croatian). Zagreb: Matica hrvatska. ISBN 978-953-150-840-7.
External links
- Burgenland Croat Center (in English, German and Croatian)
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{lang-en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. sub Template:It Victor Friedman (University of Chicago) lecture: Balkan linguistics, Balkan languages, Balkan ethnicities, from Autochthony to Multilingualism
