Fenamic acid: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
حسن علي البط (talk | contribs) m Removed category Aromatic amines; Quick-adding category Anthranilic acids (using HotCat) |
حسن علي البط (talk | contribs) m Removed category Benzoic acids; Quick-adding category Non-standard positional numeral systems (using HotCat) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{NSAIDs}} |
{{NSAIDs}} |
||
[[Category:Benzoic acids]] |
|||
[[Category:Anthranilic acids]] |
[[Category:Anthranilic acids]] |
||
[[Category:Non-standard positional numeral systems]] |
|||
Revision as of 08:15, 26 February 2010
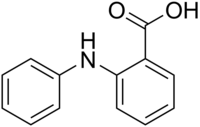
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(phenylamino)benzoic acid
| |
| Other names
N-phenylanthranilic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.879 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 213.23 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fenamic acid is a molecule which serves as a parent structure for several non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
This compound may be synthesized by the reaction of 2-chlorobenzoic acid and aniline, with base and copper oxide catalyst in the Goldberg reaction.[1]
The self-condensation of fenamic acid yields acridone.[1]
References
- ^ a b C. F. H. Allen and G. H. W. McKee (1943). "Acridone". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 2, p. 15.

