Dravidian peoples: Difference between revisions
Vanjagenije (talk | contribs) →List of Dravidian people based on population: this column is useless. |
The sources here do not mention relationship to australian aborigines at all. Changed "is" to "are" (plural)... |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==Origins== |
==Origins== |
||
[[File:Dancing girl.jpg|thumb|The [[Dancing Girl (sculpture)|Dancing Girl]], a prehistoric [[bronze sculpture]] made in approximately 2500 BCE in the [[Indus Valley Civilisation]] city of [[Mohenjo-daro]].]] |
[[File:Dancing girl.jpg|thumb|The [[Dancing Girl (sculpture)|Dancing Girl]], a prehistoric [[bronze sculpture]] made in approximately 2500 BCE in the [[Indus Valley Civilisation]] city of [[Mohenjo-daro]].]] |
||
The origins of the Dravidians are a "very complex subject of research and debate." <ref name="Davies2008_p.400"/> They may have been indigenous to the [[Indian subcontinent]],<ref>{{cite book|title=Ancient India: A History of the Indian Sub-Continent from C. 7000 BC to AD 1200|page=13|author = Burjor Avari|publisher=Routledge}}</ref><ref name="Masica_p39">{{cite book|title=The Indo-Aryan Languages|page=39|publisher=Cambridge University|author=Colin P. Masica}}</ref><ref name="Kopstein_p345">{{cite book|year=2005|title=Comparative Politics: Interests, Identities, and Institutions in a Changing Global Order|page=345|author=Jeffrey Kopstein, Mark Lichbach|publisher=Cambridge University}}</ref> but origins in, or influence from, West-Asia have also been proposed.{{sfnp|Cavalli-Sforza|1994|pp=221-222}}<ref name="kumar2004"/>{{sfn|Kivisild|1999|p=1333}}{{sfn|Parpola|2015|p=17}}{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}} According to Narasimhan et al. (2018), Dravidians have a mixture of origins: Archaic Ancestral South Asians, descended from the first migrants out of Africa who are related to |
The origins of the Dravidians are a "very complex subject of research and debate." <ref name="Davies2008_p.400"/> They may have been indigenous to the [[Indian subcontinent]],<ref>{{cite book|title=Ancient India: A History of the Indian Sub-Continent from C. 7000 BC to AD 1200|page=13|author = Burjor Avari|publisher=Routledge}}</ref><ref name="Masica_p39">{{cite book|title=The Indo-Aryan Languages|page=39|publisher=Cambridge University|author=Colin P. Masica}}</ref><ref name="Kopstein_p345">{{cite book|year=2005|title=Comparative Politics: Interests, Identities, and Institutions in a Changing Global Order|page=345|author=Jeffrey Kopstein, Mark Lichbach|publisher=Cambridge University}}</ref> but origins in, or influence from, West-Asia have also been proposed.{{sfnp|Cavalli-Sforza|1994|pp=221-222}}<ref name="kumar2004"/>{{sfn|Kivisild|1999|p=1333}}{{sfn|Parpola|2015|p=17}}{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}} According to Narasimhan et al. (2018), Dravidians have a mixture of origins: Archaic Ancestral South Asians, descended from the first migrants out of Africa who are not related to any group outside of the Indian subcontinent. Another group are neolithic farmers from Iran. These farmers brought agriculture to the Indian Subcontinent, but are distinct from the later Indo-Aryan migrations.{{sfn|Narasimhan|2018}} |
||
Although in modern times speakers of various [[Dravidian language]]s have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout the Indian subcontinent before the [[Indo-Aryan peoples|Indo-Aryan]] migration into the subcontinent.<ref name="britannicaOnline">{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/topic/Dravidian-languages |title=Dravidian languages |date=8 July 2015 |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica|Encyclopædia Britannica Online]]}}</ref> According to Carole Davies, "many academic researchers have attempted to connect the Dravidians with the remnants of the great [[Indus Valley Civilisation]], located in Northwestern India,"<ref name="Davies2008_p.400">{{cite book|year=2008|title=Encyclopedia of the African Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture [3 volumes]: Origins, Experiences, and Culture|page=400|author=Carole Elizabeth Boyce Davies|publisher=ABC-CLIO|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nkVxNVvex-sC&pg=PA400&dq=dravidian|isbn=9781851097050}}</ref> most noteworthy [[Asko Parpola]],{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}} who did extensive research on the IVC-scripts.{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}}{{sfn|Parpola|2015}} The [[Brahui people|Brahui]] population of [[Balochistan (Pakistan)|Balochistan]] in [[Pakistan]] has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a [[relict]] population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages.<ref>{{Harvnb|Mallory|1989|p=44}}: "There are still remnant northern Dravidian languages including Brahui ... The most obvious explanation of this situation is that the Dravidian languages once occupied nearly all of the Indian subcontinent and it is the intrusion of Indo-Aryans that engulfed them in northern India leaving but a few isolated enclaves. This is further supported by the fact that Dravidian loan words begin to appear in Sanskrit literature from its very beginning."</ref> The Dravidian influence is also noted to have been found in ancient civilisations of India. The ancient Dravidians are considered to be the direct ancestors of the Tamils, Malayalis, Telugus, Kannadigas that make up around 20% of India's population.<ref>{{cite book|title=Dravidian India|page=21|author=T.R. Sesha Iyengar}}</ref> |
Although in modern times speakers of various [[Dravidian language]]s have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout the Indian subcontinent before the [[Indo-Aryan peoples|Indo-Aryan]] migration into the subcontinent.<ref name="britannicaOnline">{{cite web |url=http://www.britannica.com/topic/Dravidian-languages |title=Dravidian languages |date=8 July 2015 |website=[[Encyclopædia Britannica|Encyclopædia Britannica Online]]}}</ref> According to Carole Davies, "many academic researchers have attempted to connect the Dravidians with the remnants of the great [[Indus Valley Civilisation]], located in Northwestern India,"<ref name="Davies2008_p.400">{{cite book|year=2008|title=Encyclopedia of the African Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture [3 volumes]: Origins, Experiences, and Culture|page=400|author=Carole Elizabeth Boyce Davies|publisher=ABC-CLIO|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nkVxNVvex-sC&pg=PA400&dq=dravidian|isbn=9781851097050}}</ref> most noteworthy [[Asko Parpola]],{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}} who did extensive research on the IVC-scripts.{{sfn|Samuel|2008|p=54 note 15}}{{sfn|Parpola|2015}} The [[Brahui people|Brahui]] population of [[Balochistan (Pakistan)|Balochistan]] in [[Pakistan]] has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a [[relict]] population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages.<ref>{{Harvnb|Mallory|1989|p=44}}: "There are still remnant northern Dravidian languages including Brahui ... The most obvious explanation of this situation is that the Dravidian languages once occupied nearly all of the Indian subcontinent and it is the intrusion of Indo-Aryans that engulfed them in northern India leaving but a few isolated enclaves. This is further supported by the fact that Dravidian loan words begin to appear in Sanskrit literature from its very beginning."</ref> The Dravidian influence is also noted to have been found in ancient civilisations of India. The ancient Dravidians are considered to be the direct ancestors of the Tamils, Malayalis, Telugus, Kannadigas that make up around 20% of India's population.<ref>{{cite book|title=Dravidian India|page=21|author=T.R. Sesha Iyengar}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 17:03, 9 December 2018
| Dravidian | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | South Asia and South East Asia, mainly South India and Sri Lanka | ||
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families | ||
| Proto-language | Proto-Dravidian | ||
| Subdivisions |
| ||
| Language codes | |||
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | dra | ||
| Linguasphere | 49= (phylozone) | ||
| Glottolog | drav1251 | ||
 Distribution of subgroups of Dravidian languages:
| |||
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| approx. 245 million | |
| Languages | |
| Dravidian languages | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Hinduism, and others: Jainism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Islam, Christianity, Judaism |
| Part of a series on |
| Dravidian culture and history |
|---|
 |
Dravidians are speakers of any of the Dravidian languages. There are around 245 million native speakers of Dravidian languages.[1] They form the majority of the population of South India. Dravidian-speaking people are natively found in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan,[2] the Maldives, and Sri Lanka.[3]
The third century BCE onwards saw the development of large Dravidian empires like Chera, Chola, Pandyan, Rashtrakuta, Satavahana, Vijayanagara, Pallava, Chalukya, Hoysala and smaller kingdoms like Ay, Alupa, Western Ganga, Eastern Ganga, Kadamba, Kalabhra, Andhra Ikshvaku, Vishnukundina, Western Chalukya, Eastern Chalukya, Sena, Kakatiya, Reddy, Mysore, Jaffna, Travancore, Venad, Cochin, Cannanore, Calicut and the Nayakas.
Medieval Tamil guilds and trading organisations like the "Ayyavole and Manigramam" played an important role in the Southeast Asia trade.[4] Traders and religious leaders travelled to Southeast Asia and played an important role in the cultural Indianisation of the region. Locally developed scripts such as Grantha and Pallava script induced the development of many native scripts such as Khmer, Javanese Kawi script, Baybayin, and Thai.
Dravidian visual art is dominated by stylised Temple architecture in major centres, and the production of images of stone and bronze sculptures. The sculptures dating from the Chola period has become notable as a symbol of Hinduism.
Etymology
The Sanskrit word drāviḍa is used to denote the geographical region of South India.[5] It was coined by Adi Shankara (788 CE-820 CE) when he was questioned as to where he had come from by locals in Mandhata, to which he proclaimed himself to be a "Drāviḍa Śiśu," with shishu meaning 'child' or 'child of' and dravida being a sandhi word combining the elements dravya, meaning water, and vida, meaning meeting place. Therefore, drāviḍa could be interpreted as meaning "the place where the three waters meet" with those "three waters" being the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea, and the Bay of Bengal.[6][7] Southern Brahmins are known as Pancha Dravida while northern Brahmins are known as Pancha Gauda, denoting geographical region.
In Prakrit, words such as "Damela", "Dameda", "Dhamila" and "Damila," which later evolved from "Tamila," could have been used to denote an ethnic identity.[8] Epigraphic evidence of an ethnic group termed as such is found in ancient India where a number of inscriptions have come to light datable from the 6th to the 5th century BCE mentioning Damela or Dameda persons. The Hathigumpha inscription of the Kalinga ruler Kharavela refers to a T(ra)mira samghata (Confederacy of Tamil rulers) dated to 150 BCE. It also mentions that the league of Tamil kingdoms had been in existence for 113 years by that time.[9] In Amaravati in present-day Andhra Pradesh there is an inscription referring to a Dhamila-vaniya (Tamil trader) datable to the 3rd century CE.[9] Another inscription of about the same time in Nagarjunakonda seems to refer to a Damila. A third inscription in Kanheri Caves refers to a Dhamila-gharini (Tamil house-holder). In the Buddhist Jataka story known as Akiti Jataka there is a mention to Damila-rattha (Tamil dynasty).
Thamizhar is etymologically related to Tamil, the language spoken by Tamil people. Southworth suggests that the name comes from tam-miz > tam-iz 'self-speak', or 'one's own speech'.[10] Zvelebil suggests an etymology of tam-iz, with tam meaning "self" or "one's self", and "-iz" having the connotation of "unfolding sound". Alternatively, he suggests a derivation of tamiz < tam-iz < *tav-iz < *tak-iz, meaning in origin "the proper process (of speaking)."[11] The term Thamizhar was likely derived from the name of the ancient people Dravida > Dramila > Damila > Tamila > Tamilar.[12]
While the English word Dravidian was first employed by Robert Caldwell in his book of comparative Dravidian grammar based on the usage of the Sanskrit word drāviḍa in the work Tantravārttika by Kumārila Bhaṭṭa,[5] the word drāviḍa in Sanskrit has been historically used to denote geographical regions of Southern India as whole. Some theories concern the direction of derivation between tamiẓ and drāviḍa; such linguists as Zvelebil assert that the direction is from tamiẓ to drāviḍa.[13] The modern word Dravidian is devoid of any ethnic significance, and is only used to classify a linguistic family of the referred group.[8]
Origins

The origins of the Dravidians are a "very complex subject of research and debate." [14] They may have been indigenous to the Indian subcontinent,[15][16][17] but origins in, or influence from, West-Asia have also been proposed.[18][19][20][21][22] According to Narasimhan et al. (2018), Dravidians have a mixture of origins: Archaic Ancestral South Asians, descended from the first migrants out of Africa who are not related to any group outside of the Indian subcontinent. Another group are neolithic farmers from Iran. These farmers brought agriculture to the Indian Subcontinent, but are distinct from the later Indo-Aryan migrations.[23]
Although in modern times speakers of various Dravidian languages have mainly occupied the southern portion of India, Dravidian speakers must have been widespread throughout the Indian subcontinent before the Indo-Aryan migration into the subcontinent.[24] According to Carole Davies, "many academic researchers have attempted to connect the Dravidians with the remnants of the great Indus Valley Civilisation, located in Northwestern India,"[14] most noteworthy Asko Parpola,[22] who did extensive research on the IVC-scripts.[22][25] The Brahui population of Balochistan in Pakistan has been taken by some as the linguistic equivalent of a relict population, perhaps indicating that Dravidian languages were formerly much more widespread and were supplanted by the incoming Indo-Aryan languages.[26] The Dravidian influence is also noted to have been found in ancient civilisations of India. The ancient Dravidians are considered to be the direct ancestors of the Tamils, Malayalis, Telugus, Kannadigas that make up around 20% of India's population.[27]
Ancestral components
Reich et al. (2009) discerned two major ancestral components in India,[28][29][30] namely the Ancestral North Indians (ANI) who are "genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans," and the Ancestral South Indians (ASI) which are clearly distinct from ANI[28] and "not closely related to groups outside the subcontinent."[31] Basu et al. (2016), discerned two additional components, Ancestral Tibeto-Burmese (ATB) and Ancestral Austro-Asiatic (AAA), noting that the ASI and the AAA were early settlers of India who differentiated after their arrival in India.[32][note 1] The ANI and ASI mixed in India between 4,200 and 1,900 years ago (2200 BCE-100 CE), whereafter a shift to endogamy took place,[30] possibly by the enforcement of "social values and norms" by the "Hindu Gupta rulers."[34] Northern Indians and higher castes are more related to West Eurasians, while southern Indians and lower castes are less related to West Eurasians.[35]
Moorjani et al. (2013) describe three scenarios regarding the bringing together of the two groups:
- migrations before the development of agriculture (8,000–9,000 years before present (BP);
- migration of western Asian people together with the spread of agriculture, maybe up to 4,600 years BP;
- migrations of western Eurasians from 3,000 to 4,000 years BP.[36]
Proposed agricultural origins
According to Gallego Romero et al. (2011), their research on lactose tolerance in India suggests that "the west Eurasian genetic contribution identified by Reich et al. (2009) principally reflects gene flow from Iran and the Middle East."[37] Gallego Romero notes that Indians who are lactose-tolerant show a genetic pattern regarding this tolerance which is "characteristic of the common European mutation."[38] According to Romero, this suggests that "the most common lactose tolerance mutation made a two-way migration out of the Middle East less than 10,000 years ago. While the mutation spread across Europe, another explorer must have brought the mutation eastward to India – likely traveling along the coast of the Persian Gulf where other pockets of the same mutation have been found."[38]
Asko Parpola, who regards the Harappans to have been Dravidian, notes that Mehrgarh (7000 BCE to c. 2500 BCE), to the west of the Indus River valley,[39] is a precursor of the Indus Valley Civilisation, whose inhabitants migrated into the Indus Valley and became the Indus Valley Civilisation.[21] It is one of the earliest sites with evidence of farming and herding in South Asia.[40][41] According to Lukacs and Hemphill, while there is a strong continuity between the neolithic and chalcolithic (Copper Age) cultures of Mehrgarh, dental evidence shows that the chalcolithic population did not descend from the neolithic population of Mehrgarh,[42] which "suggests moderate levels of gene flow."[42] They further noted that "the direct lineal descendants of the Neolithic inhabitants of Mehrgarh are to be found to the south and the east of Mehrgarh, in northwestern India and the western edge of the Deccan plateau," with neolithic Mehrgarh showing greater affinity with chalocolithic Inamgaon, south of Mehrgarh, than with chalcolithic Mehrgarh.[42]
Narasimhan et al. (2018) conclude that ANI and ASI were formed in the 2nd millennium BCE.[43] They were preceded by a mixture of AASI (ancient ancestral south Indians, that is, hunter-gatherers), and Iranian agri-culturalists who arrived in India at ca. 4700-3000 BCE, and "must have reached the Indus Valley by the 4th millennium BCE."[43] According to Narasimhan et al., this population, which probably was native to the Indus Valley Civilisation, "contributed in large proportions to both the ANI and ASI," which took shape during the 2nd millennium BCE. ANI formed out of a mixture of "Indus_Periphery-related groups" and migrants from the steppe, while ASI was formed out of "Indus_Periphery-related groups" who moved south and mixed with hunter-gatherers.[43]
History
Indus Valley Civilization

Dravidian identification
The Indus Valley civilization (2,600-1,900 BCE) located in Northwestern Indian subcontinent is sometimes identified as having been Dravidian.[44] Cultural and linguistic similarities have been cited by researchers Henry Heras, Kamil Zvelebil, Asko Parpola and Iravatham Mahadevan as being strong evidence for a proto-Dravidian origin of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation.[45][46] The discovery in Tamil Nadu of a late Neolithic (early 2nd millennium BCE, i.e. post-dating Harappan decline) stone celt allegedly marked with Indus signs has been considered by some to be significant for the Dravidian identification.[47][48]
Yuri Knorozov surmised that the symbols represent a logosyllabic script and suggested, based on computer analysis, an underlying agglutinative Dravidian language as the most likely candidate for the underlying language.[49] Knorozov's suggestion was preceded by the work of Henry Heras, who suggested several readings of signs based on a proto-Dravidian assumption.[50]
Linguist Asko Parpola writes that the Indus script and Harappan language are "most likely to have belonged to the Dravidian family".[51] Parpola led a Finnish team in investigating the inscriptions using computer analysis. Based on a proto-Dravidian assumption, they proposed readings of many signs, some agreeing with the suggested readings of Heras and Knorozov (such as equating the "fish" sign with the Dravidian word for fish, "min") but disagreeing on several other readings. A comprehensive description of Parpola's work until 1994 is given in his book Deciphering the Indus Script.[52]
Decline and migration
Paleoclimatologists believe the fall of the Indus Valley Civilisation and eastward migration during the late Harappan period was due to climate change in the region, with a 200-year long drought being the major factor.[53][54][55] The Indus Valley Civilisation seemed to slowly lose their urban cohesion, and their cities were gradually abandoned during the late Harappan period, followed by eastward migrations before the Indo-Aryan migration into the Indian subcontinent.[54]
Dravidian and Indo-Aryan interactions
The Dravidian language influenced the Indo-Aryan languages. Dravidian languages show extensive lexical (vocabulary) borrowing, but only a few traits of structural (either phonological or grammatical) borrowing from Indo-Aryan, whereas Indo-Aryan shows more structural than lexical borrowings from the Dravidian languages.[24] Many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian. The linguistic evidence for Dravidian impact grows increasingly strong as we move from the Samhitas down through the later Vedic works and into the classical post-Vedic literature.[56] This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[57][note 2] or synthesis[59] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans.[60][58][61][62]
According to Mallory there are an estimated thirty to forty Dravidian loanwords in Rig Veda.[63] Some of those for which Dravidian etymologies are certain include ಕುಲಾಯ kulāya "nest", ಕುಲ್ಫ kulpha "ankle", ದಂಡ daṇḍa "stick", ಕುಲ kūla "slope", ಬಿಲ bila "hollow", ಖಲ khala "threshing floor".[64]: 81 [64] While J. Bloch and M. Witzel believe that the Indo-Aryans moved into an already Dravidian speaking area after the oldest parts of the Rig Veda were already composed.[65]
According to Thomason and Kaufman, there is strong evidence that Dravidian influenced Indic through "shift", that is, native Dravidian speakers learning and adopting Indic languages.[66] According to Erdosy, the most plausible explanation for the presence of Dravidian structural features in Old Indo-Aryan is that the majority of early Old Indo-Aryan speakers had a Dravidian mother tongue which they gradually abandoned.Erdosy (1995:18) Even though the innovative traits in Indic could be explained by multiple internal explanations, early Dravidian influence is the only explanation that can account for all of the innovations at once. Early Dravidian influence accounts for several of the innovative traits in Indic better than any internal explanation that has been proposed.[67] According to Zvelebil, "several scholars have demonstrated that pre-Indo-Aryan and pre-Dravidian bilingualism in India provided conditions for the far-reaching influence of Dravidian on the Indo-Aryan tongues in the spheres of phonology, syntax and vocabulary."[68]
With the rise of the Kuru Kingdom a process of Sanskritization started which influenced all of India, with the populations of the north of the Indian subcontinent predominantly speaking the Indo-Aryan languages.[69]
Dravidian culture
Language
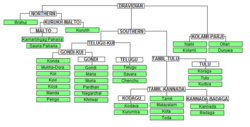
The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are Tamil (தமிழ்), Telugu (తెలుగు), Kannada (ಕನ್ನಡ), Malayalam (മലയാളം), Brahui (براہوئی), Tulu (ತುಳು), Gondi and Coorg. There are three subgroups within the Dravidian language family: North Dravidian, Central Dravidian, and South Dravidian, matching for the most part the corresponding regions in the Indian subcontinent.
Dravidian grammatical impact on the structure and syntax of Indo-Aryan languages is considered far greater than the Indo-Aryan grammatical impact on Dravidian. Some linguists explain this anomaly by arguing that Middle Indo-Aryan and New Indo-Aryan were built on a Dravidian substratum.[70] There are also hundreds of Dravidian loanwords in Indo-Aryan languages, and vice versa.
According to David McAlpin and his Elamo-Dravidian hypothesis, the Dravidian languages were brought to India by immigration into India from Elam, located in present-day southwestern Iran.[19][71] In the 1990s, Renfrew and Cavalli-Sforza have also argued that Proto-Dravidian was brought to India by farmers from the Iranian part of the Fertile Crescent,[18][72][73][note 3] but more recently Heggerty and Renfrew noted that "McAlpin's analysis of the language data, and thus his claims, remain far from orthodoxy", adding that Fuller finds no relation of Dravidian language with other languages, and thus assumes it to be native to India.[74] Renfrew and Bahn conclude that several scenarios are compatible with the data, and that "the linguistic jury is still very much out."[74]
As a proto-language, the Proto-Dravidian language is not itself attested in the historical record. Its modern conception is based solely on reconstruction. It is suggested that the language was spoken in the 4th millennium BCE, and started disintegrating into various branches around 3rd millennium BCE.[75] According to Krishnamurti, Proto-Dravidian may have been spoken in the Indus civilization, suggesting a "tentative date of Proto-Dravidian around the early part of the third millennium."[76] Krishnamurti further states that South Dravidian I (including pre-Tamil) and South Dravidian II (including Pre-Telugu) split around the eleventh century BCE, with the other major branches splitting off at around the same time.[77]
Religious belief
Ancient Dravidian religion constituted of a non-Vedic form of Hinduism in that they were either historically or are at present Āgamic. The Agamas are non-Vedic in origin [78] and have been dated either as post-Vedic texts [79] or as pre-Vedic compositions.[80] The Agamas are a collection of Tamil and Sanskrit scriptures chiefly constituting the methods of temple construction and creation of murti, worship means of deities, philosophical doctrines, meditative practices, attainment of sixfold desires and four kinds of yoga.[81] The worship of tutelary deities, sacred flora and fauna in Hinduism is also recognized as a survival of the pre-Vedic Dravidian religion.[82] Dravidian linguistic influence on early Vedic religion is evident; many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian. The linguistic evidence for Dravidian impact grows increasingly strong as we move from the Samhitas down through the later Vedic works and into the classical post-Vedic literature.[56] This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[57][note 2] or synthesis[59] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans that went on to influence and shape Hinduism, Sramana, Jainism, Buddhism, Charvaka, and Ājīvika.[60][58][61][62]

Ancient Tamil grammatical works Tolkappiyam, the ten anthologies Pattuppāṭṭu, and the eight anthologies Eṭṭuttokai shed light on early ancient Dravidian religion. Seyyon was glorified as the red god seated on the blue peacock, who is ever young and resplendent, as the favored god of the Tamils.[83] Sivan was also seen as the supreme God.[83] Early iconography of Seyyon[84] and Sivan[85][86][87] and their association with native flora and fauna goes back to the Indus Valley Civilisation.[88][89] The Sangam landscape was classified into five categories, thinais, based on the mood, the season and the land. Tolkappiyam mentions that each of these thinai had an associated deity such as Seyyon in Kurinji-the hills, Thirumaal in Mullai-the forests, and Kotravai in Marutham-the plains, and Wanji-ko in the Neithal-the coasts and the seas. Other gods mentioned were Mayyon and Vaali who are all major deities in Hinduism today. This represents an early religious and cultural fusion[57][note 2] or synthesis[59] between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans, which became more evident over time with sacred iconography, traditions, philosophy, flora and fauna that went on to influence and shape Indian civilisation.[60][58][61][62]

Throughout Tamilakam, a king was considered to be divine by nature and possessed religious significance.[90] The king was 'the representative of God on earth’ and lived in a "koyil", which means the "residence of a god". The Modern Tamil word for temple is koil (Tamil: கோயில்). Ritual worship was also given to kings.[91][92] Modern words for god like "kō" (Tamil: கோ "king"), "iṟai" (இறை "emperor") and "āṇḍavar" (ஆண்டவன் "conqueror") now primarily refer to gods. These elements were incorporated later into Hinduism like the legendary marriage of Shiva to Queen Mīnātchi who ruled Madurai or Wanji-ko, a god who later merged into Indra.[93] Tolkappiyar refers to the Three Crowned Kings as the "Three Glorified by Heaven", (Tamil: வாண்புகழ் மூவர், Vāṉpukaḻ Mūvar).[94] In the Dravidian-speaking South, the concept of divine kingship led to the assumption of major roles by state and temple.[95]
The cult of the mother goddess is treated as an indication of a society which venerated femininity. This mother goddess was conceived as a virgin, one who has given birth to all and one, and were typically associated with Shaktism.[96] The temples of the Sangam days, mainly of Madurai, seem to have had priestesses to the deity, which also appear predominantly a goddess.[97] In the Sangam literature, there is an elaborate description of the rites performed by the Kurava priestess in the shrine Palamutircholai.[98]
Among the early Dravidians the practice of erecting memorial stones "Natukal and Viragal’' had appeared, and it continued for quite a long time after the Sangam age, down to about the 16th century.[99] It was customary for people who sought victory in war to worship these hero stones to bless them with victory.[100]
Architecture and visual art


Throughout Tamilakam, a king was considered to be divine by nature and possessed religious significance.[90] The king was 'the representative of God on earth’ and lived in a "koyil", which means the "residence of a god". The Modern Tamil word for temple is koil (Tamil: கோயில்). Titual worship was also given to kings.[91][92] Modern words for god like "kō" (Tamil: கோ "king"), "iṟai" (இறை "emperor") and "āṇḍavar" (ஆண்டவன் "conqueror") now primarily refer to gods.[93] Tolkappiyar refers to the Three Crowned Kings as the "Three Glorified by Heaven", (Tamil: வாண்புகழ் மூவர், Vāṉpukaḻ Mūvar).[94] In the Dravidian-speaking South, the concept of divine kingship led to the assumption of major roles by state and temple.[95]
Mayamata and Manasara shilpa texts estimated to be in circulation by the 5th to 7th century AD, are guidebooks on the Dravidian style of Vastu Shastra design, construction, sculpture and joinery technique.[101][102] Isanasivagurudeva paddhati is another text from the 9th century describing the art of building in India in south and central India.[101][103] In north India, Brihat-samhita by Varāhamihira is the widely cited ancient Sanskrit manual from the 6th century describing the design and construction of Nagara style of Hindu temples.[104][105][106] Traditional Dravidian architecture and symbolism are also based on Agamas. The Agamas are non-Vedic in origin[78] and have been dated either as post-Vedic texts [79] or as pre-Vedic compositions.[80] The Agamas are a collection of Tamil and Sanskrit scriptures chiefly constituting the methods of temple construction and creation of murti, worship means of deities, philosophical doctrines, meditative practices, attainment of sixfold desires and four kinds of yoga.[81]
Chola style temples consist almost invariably of the three following parts, arranged in differing manners, but differing in themselves only according to the age in which they were executed:[107]
- The porches or Mantapas, which always cover and precede the door leading to the cell.
- Gate-pyramids, Gopuras, which are the principal features in the quadrangular enclosures that surround the more notable temples. Gopuras are very common in Dravidian temples.
- Pillared halls (Chaultris or Chawadis) are used for many purposes and are the invariable accompaniments of these temples.
Besides these, a south Indian temple usually has a tank called the Kalyani or Pushkarni – to be used for sacred purposes or the convenience of the priests – dwellings for all the grades of the priesthood are attached to it, and other buildings for state or convenience.[107]
Theatre, dance and music

Literary evidence of traditional form of theatre, dance and music dates back to the 3rd century BCE.[108] Ancient literary works, such as the Cilappatikaram, describe a system of music.[108] The theatrical culture flourished during the early Sangam age. Theatre-dance traditions have a long and varied history whose origins can be traced back almost two millennia to dance-theatre forms like Kotukotti and Pandarangam, which are mentioned in an ancient anthology of poems entitled the Kalingathu Parani.[109] Dance forms such as Bharatanatyam are based older temple dance forms known as Catir Kacceri as practised by courtesans and a class of women known as Devadasis.[110]
Carnatic music originated in the Dravidian region. With the growing influence of Persian and Sufi music on Indian music, a clear distinction in style appeared from the 12th century onwards. Many literary works were composed in Carnatic style and it soon spread wide in the Dravidian regions. The most notable Carnatic musician is Purandara Dasa who lived in the court of Krishnadevaraya of the Vijayanagara empire. He formulated the basic structure of Carnatic music and is regarded as the Pitamaha (lit, "father" or the "grandfather") of Carnatic Music. Kanakadasa is another notable Carnatic musician who was Purandaradasa's contemporary.
Each of the major Dravidian languages has its own film industry like Kollywood (Tamil), Tollywood (Telugu), Sandalwood (Kannada), Mollywood (Malayalam). Kollywood and Tollywood produce most films in India.[111]
|
|
Costume
Dravidian speakers in southern India wear varied traditional costumes depending on their region, largely influenced by local customs and traditions.
Martial arts and sports
In Mahabaratha was mentioned, that Bhishma claimed that Southerns are skilled with sword-fighting in general and Sahadeva was chosen for the conquest of the southern kingdoms, because of his swordsman skills.[112] In South India various types of martial arts are practiced like Kalaripayattu and Silambam. It is speculated that Bodhidarma was a sixth century Pallava prince, who became a Buddhist monk, although the credibility of the same is debatable.[113]
In ancient times there were fights ankam, public duels to the death, to solve disputes between his opposing rules.[114] Among some communities, young girls received preliminary training up until the onset of menses.[114] In vadakkan pattukal ballads, at least a few women warriors continued to practice and achieved a high degree of expertise.[114]
Sports like Kambala, Jallikattu, Kabaddi, Vallam Kali, Lambs and Tigers, Maramadi are parts of Dravidian culture.
Traditional weapons
Weapons used in Kalaripayattu.
- Valari (throwing stick)
- Maduvu (deer horns)
- Surul Vaal (curling blade)
- Vaal (sword) + Ketayam (shield)
- Itti or Vel (spear)
- Savuku (whip)
- Various types of stick
- Kattari (fist blade)
- Veecharuval (battle Machete)
- Silambam (long bamboo staff)
- Kuttu Katai (spiked knuckleduster)
- Katti (dagger/knife)
- Vil (bow)
- Tantayutam (mace)
- Soolam (trident)
- Theekutchi (flaming baton)
- Yeratthai Mulangkol (dual stick)
- Yeretthai Vaal (dual sword)
Ethnic groups
The largest-Dravidian ethnic groups are the Telugus from Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, the Tamils from Tamil Nadu, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Singapore, the Kannadigas from Karnataka, the Malayalis from Kerala, and the Tulu people from Karnataka. Certain communities of Marathis from Maharashtra are considered as Scytho-Dravidians.[115][116]
List of Dravidian people based on population
| Name | Subgroup | Population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telugus | Central Dravidian | 85.1 million[117] | Telugus are native to Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Puducherry. |
| Tamils | South Dravidian | 78 million[118] | Tamils are native to Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Northern-eastern Sri Lanka, but are also found parts of Kerala, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, although they have a large diaspora and are also widespread throughout in many countries like South Africa, Singapore, United States of America and Malaysia.[119] |
| Kannadigas | South Dravidian | 43.7 million[120] | Kannadigas are native to Karnataka in India but considerable population is also found in Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Kerala. |
| Malayalis | South Dravidian | 32.2 million[120] | Malayalis are native to Kerala and Lakshadweep, but are also found in Puducherry and parts of Tamil Nadu. They are also found in large numbers in Middle East countries as migrant workers. |
| Brahuis | North Dravidian | 2.5 million | Brahuis are mostly found in Balochistan region of Pakistan, with smaller numbers in Southwestern Afghanistan. |
| Tuluvas | South Dravidian | 2 million (approx.) | Tuluvas are found in coastal Karnataka in India. A state named Tulu Nadu was proposed to represent them in India. |
| Gondis | Central Dravidian | 13 million (approx.) | Gondi belong to the central Dravidian subgroup. They are spread over the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar and Odisha. A state named Gondwana was proposed to represent them in India. |
| Kurukh | North Dravidian | 3.6 million (approx.)[121] | Kurukh are spread over the states of Chhatishgarh, Jharkhand and Odisha. |
See also
- Dravidian languages
- Dravidian University (dedicated to research and learning of Dravidian languages)
Notes
- ^ Basu et al. (2016): "The absence of significant resemblance with any of the neighboring populations is indicative of the ASI and the AAA being early settlers in India, possibly arriving on the “southern exit” wave out of Africa. Differentiation between the ASI and the AAA possibly took place after their arrival in India."[33]
- ^ a b c Lockard: "The encounters that resulted from Aryan migration brought together several very different peoples and cultures, reconfiguring Indian society. Over many centuries a fusion of Aryan and Dravidian occurred, a complex process that historians have labeled the Indo-Aryan synthesis."[57] Lockard: "Hinduism can be seen historically as a synthesis of Aryan beliefs with Harappan and other Dravidian traditions that developed over many centuries."[58]
- ^ Derenko: "The spread of these new technologies has been associated with the dispersal of Dravidian and Indo-European languages in southern Asia. It is hypothesized that the proto-Elamo-Dravidian language, most likely originated in the Elam province in southwestern Iran, spread eastwards with the movement of farmers to the Indus Valley and the Indian sub-continent."[73]
Derenko refers to:
* Renfrew (1987), Archaeology and Language: The Puzzle of Indo-European Origins
* Renfrew (1996), Language families and the spread of farming. In: Harris DR, editor, The origins and spread of Agriculture and Pastoralism in Eurasia, pp. 70–92
* Cavalli-Sforza, Menozzi, Piazza (1994), The History and Geography of Human Genes.
References
- ^ West, Barbara A. (19 May 2010). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania. Infobase Publishing. pp. 193–194. ISBN 978-1-4381-1913-7. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- ^ Louis, Rosenblatt; Steever, Sanford B. (15 April 2015). The Dravidian Languages. Routledge. p. 388. ISBN 978-1-136-91164-4. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- ^ Swan, Michael; Smith, Bernard (26 April 2001). Learner English: A Teacher's Guide to Interference and Other Problems. Cambridge University Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-521-77939-5. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- ^ The Emporium of the World: Maritime Quanzhou, 1000-1400 by Angela Schottenhammer p.293
- ^ a b Zvelebil 1990, p. xx harvnb error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFZvelebil1990 (help)
- ^ Dr. Subramanian Swamy’s Factual Rebuttal of the Bogus Aryan-Dravidian Theory - Dr. Subramanian Swamy’s Researched Discourse Pertaining To Hindu Topics
- ^ Comprehensive Etymological Resource - Sanskritic Terms Explained
- ^ a b RC Majumdar (1977). "Dravidians". Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 18. ISBN 978-81-208-0436-4.
- ^ a b Indrapala, K The Evolution of an ethnic identity: The Tamils of Sri Lanka, pp.155-156
- ^ Southworth, Franklin C. (1998), "On the Origin of the word tamiz", International Journal of Dravidial Linguistics, 27 (1): 129–132
- ^ Zvelebil, Kamil V. (1992), Companion Studies to the history of Tamil literature, Leiden: E.J. Brill at pp. x–xvi.
- ^ Gustav Salomon Oppert, On the Original Inhabitants of Bharatavarsa Or India: The Dravidians, p 41
- ^ Zvelebil 1990, p. xxi harvnb error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFZvelebil1990 (help)
- ^ a b Carole Elizabeth Boyce Davies (2008). Encyclopedia of the African Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture [3 volumes]: Origins, Experiences, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. p. 400. ISBN 9781851097050.
- ^ Burjor Avari. Ancient India: A History of the Indian Sub-Continent from C. 7000 BC to AD 1200. Routledge. p. 13.
- ^ Colin P. Masica. The Indo-Aryan Languages. Cambridge University. p. 39.
- ^ Jeffrey Kopstein, Mark Lichbach (2005). Comparative Politics: Interests, Identities, and Institutions in a Changing Global Order. Cambridge University. p. 345.
- ^ a b Cavalli-Sforza (1994), pp. 221–222.
- ^ a b Dhavendra Kumar (2004), Genetic Disorders of the Indian Subcontinent, Springer, ISBN 978-1-4020-1215-0, retrieved 25 November 2008,
... The analysis of two Y chromosome variants, Hgr9 and Hgr3 provides interesting data (Quintan-Murci et al., 2001). Microsatellite variation of Hgr9 among Iranians, Pakistanis and Indians indicate an expansion of populations to around 9000 YBP in Iran and then to 6,000 YBP in India. This migration originated in what was historically termed Elam in south-west Iran to the Indus valley, and may have been associated with the spread of Dravidian languages from south-west Iran (Quintan-Murci et al., 2001). ...
- ^ Kivisild 1999, p. 1333.
- ^ a b Parpola 2015, p. 17.
- ^ a b c Samuel 2008, p. 54 note 15.
- ^ Narasimhan 2018.
- ^ a b "Dravidian languages". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 8 July 2015.
- ^ Parpola 2015.
- ^ Mallory 1989, p. 44: "There are still remnant northern Dravidian languages including Brahui ... The most obvious explanation of this situation is that the Dravidian languages once occupied nearly all of the Indian subcontinent and it is the intrusion of Indo-Aryans that engulfed them in northern India leaving but a few isolated enclaves. This is further supported by the fact that Dravidian loan words begin to appear in Sanskrit literature from its very beginning."
- ^ T.R. Sesha Iyengar. Dravidian India. p. 21.
- ^ a b Reich et al. (2009).
- ^ Metspalu et al. (2011).
- ^ a b Moorjani et al. (2013).
- ^ Moorjani 2013.
- ^ Basu 2016.
- ^ Basu 2016, p. 1598.
- ^ Basu et al. (2016), p. 1598.
- ^ Metspalu 2011.
- ^ Moorjani et al. (2013), pp. 422–423.
- ^ Gallego Romero (2011), p. 9.
- ^ a b Rob Mitchum (2011), Lactose Tolerance in the Indian Dairyland, ScienceLife
- ^ "Stone age man used dentist drill". 6 April 2006.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage. 2004. ". Archaeological Site of Mehrgarh
- ^ Hirst, K. Kris. 2005. "Mehrgarh". Guide to Archaeology
- ^ a b c Coningham & Young 2015, p. 114.
- ^ a b c Narasimhan et al. 2018, p. 15.
- ^ Mahadevan, Iravatham (6 May 2006). "Stone celts in Harappa". Harappa. Archived from the original on 4 September 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rahman, Tariq. "Peoples and languages in pre-Islamic Indus valley". Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 20 November 2008.
most scholars have taken the 'Dravidian hypothesis' seriously
- ^ Cole, Jennifer (2006). "The Sindhi language" (PDF). In Brown, K. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics, 2nd Edition. Vol. 11. Elsevier. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2007.
Harappan language...prevailing theory indicates Dravidian origins
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Subramanium 2006; see also A Note on the Muruku Sign of the Indus Script in light of the Mayiladuthurai Stone Axe Discovery Archived 4 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine by I. Mahadevan (2006)
- ^ Subramanian, T.S. (1 May 2006). "Significance of Mayiladuthurai find". The Hindu.
- ^ Knorozov 1965, p. 117
- ^ Heras 1953, p. 138
- ^ Edwin Bryant (2003). The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford. p. 183. ISBN 9780195169478.
- ^ Parpola 1994
- ^ Keys, David (2 March 2014). "How climate change ended worlds first great civilisations". The Independent. London.
- ^ a b Marris, Emma (3 March 2014). "200-Year Drought Doomed Indus Valley Civilization". Nature – via Scientific American.
- ^ Sinha, Kounteya (28 February 2014). "Climate change caused Indus Valley civilization collapse". Times of India.
- ^ a b Krishnamurti 2003, p. 6
- ^ a b c d Lockard 2007, p. 50.
- ^ a b c d Lockard 2007, p. 52.
- ^ a b c Hiltebeitel 2007, p. 12.
- ^ a b c Tiwari 2002, p. v.
- ^ a b c Zimmer 1951, pp. 218–219.
- ^ a b c Larson 1995, p. 81.
- ^ Mallory, J. P.; Adams, D. Q. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. p. 308.
- ^ a b Zvelebil, Kamil (1990). Dravidian Linguistics: An Introduction. Pondicherry Institute of Linguistics and Culture.
- ^ Bryant, Edwin (2001). "Linguistic Substrata in Sanskrit Texts". The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 76–107. ISBN 978-0-19-513777-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Thomason & Kaufman 1988.
- ^ Thomason & Kaufman 1988, pp. 141–144.
- ^ Dravidian languages – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ^ Witzel 1995.
- ^ Krishnamurti 2003, pp. 40–1
- ^ David McAlpin, "Toward Proto-Elamo-Dravidian", Language vol. 50 no. 1 (1974); David McAlpin: "Elamite and Dravidian, Further Evidence of Relationships", Current Anthropology vol. 16 no. 1 (1975); David McAlpin: "Linguistic prehistory: the Dravidian situation", in Madhav M. Deshpande and Peter Edwin Hook: Aryan and Non-Aryan in India, Center for South and Southeast Asian Studies, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (1979); David McAlpin, "Proto-Elamo-Dravidian: The Evidence and its Implications", Transactions of the American Philosophical Society vol. 71 pt. 3, (1981)
- ^ Namita Mukherjee; Almut Nebel; Ariella Oppenheim; Partha P. Majumder (December 2001), "High-resolution analysis of Y-chromosomal polymorphisms reveals signatures of population movements from central Asia and West Asia into India" (PDF), Journal of Genetics, 80 (3): 125–35, doi:10.1007/BF02717908, PMID 11988631, retrieved 25 November 2008,
... More recently, about 15,000–10,000 years before present (ybp), when agriculture developed in the Fertile Crescent region that extends from Israel through northern Syria to western Iran, there was another eastward wave of human migration (Cavalli-Sforza et al., 1994; Renfrew 1987), a part of which also appears to have entered India. This wave has been postulated to have brought the Dravidian languages into India (Renfrew 1987). Subsequently, the Indo-European (Aryan) language family was introduced into India about 4,000 ybp ...
- ^ a b Derenko (2013).
- ^ a b Heggarty, Paul; Renfrew, Collin (2014), "South and Island Southeast Asia; Languages", in Renfrew, Colin; Bahn, Paul (eds.), The Cambridge World Prehistory, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9781107647756
- ^ History and Archaeology, Volume 1, Issues 1-2 p.234, Department of Ancient History, Culture, and Archaeology, University of Allahabad
- ^ Krishnamurti 2003, p. 501.
- ^ Krishnamurti 2003, p. 501-502.
- ^ a b Mudumby Narasimhachary (Ed) (1976). Āgamaprāmāṇya of Yāmunācārya, Issue 160 of Gaekwad's Oriental Series. Oriental Institute, Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda.
- ^ a b Tripath, S. M. (2001). Psycho-Religious Studies Of Man, Mind And Nature. Global Vision Publishing House. pp. 54–. ISBN 978-81-87746-04-1.
- ^ a b Nagalingam, Pathmarajah (2009). The Religion of the Agamas. Siddhanta Publications. [1]
- ^ a b Grimes, John A. (1996). A Concise Dictionary of Indian Philosophy: Sanskrit Terms Defined in English (New and Revised Edition). State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-3068-2.
- ^ The Modern review: Volume 28; Volume 28. Prabasi Press Private, Ltd. 1920.
- ^ a b Kanchan Sinha, Kartikeya in Indian art and literature, Delhi: Sundeep Prakashan (1979).
- ^ Mahadevan, Iravatham (2006). A Note on the Muruku Sign of the Indus Script in light of the Mayiladuthurai Stone Axe Discovery. harappa.com. Archived from the original on 4 September 2006.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ranbir Vohra (2000). The Making of India: A Historical Survey. M.E. Sharpe. p. 15.
- ^ Grigorii Maksimovich Bongard-Levin (1985). Ancient Indian Civilization. Arnold-Heinemann. p. 45.
- ^ Steven Rosen, Graham M. Schweig (2006). Essential Hinduism. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 45.
- ^ Basham, p. 27
- ^ Frederick J. Simoons (1998). Plants of life, plants of death. p. 363.
- ^ a b Harman, William P. (1992). The sacred marriage of a Hindu goddess. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 6.
- ^ a b Anand, Mulk Raj (1980). Splendours of Tamil Nadu. Marg Publications.
- ^ a b Chopra, Pran Nath (1979). History of South India. S. Chand.
- ^ a b Bate, Bernard (2009). Tamil oratory and the Dravidian aesthetic: democratic practice in south India. Columbia University Press.
- ^ a b A. Kiruṭṭin̲an̲ (2000). Tamil culture: religion, culture, and literature. Bharatiya Kala Prakashan. p. 17.
- ^ a b Embree, Ainslie Thomas (1988). Encyclopedia of Asian history: Volume 1. Scribner. ISBN 9780684188980.
- ^ Thiruchandran, Selvy (1997). Ideology, caste, class, and gender. Vikas Pub. House.
- ^ Manickam, Valliappa Subramaniam (1968). A glimpse of Tamilology. Academy of Tamil Scholars of Tamil Nadu. p. 75.
- ^ Lal, Mohan (2006). The Encyclopaedia Of Indian Literature (Volume Five (Sasay To Zorgot), Volume 5. Sahitya Akademi. p. 4396. ISBN 978-8126012213.
- ^ Shashi, S. S. (1996). Encyclopaedia Indica: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh: Volume 100. Anmol Publications.
- ^ Subramanium, N. (1980). Śaṅgam polity: the administration and social life of the Śaṅgam Tamils. Ennes Publications.
- ^ a b Stella Kramrisch (1976), The Hindu Temple Volume 1 & 2, ISBN 81-208-0223-3
- ^ Tillotson, G. H. R. (1997). Svastika Mansion: A Silpa-Sastra in the 1930s. South Asian Studies, 13(1), pp 87-97
- ^ Ganapati Sastri (1920), Īśānaśivagurudeva paddhati, Trivandrum Sanskrit Series, OCLC 71801033
- ^ Meister, Michael W. (1983). "Geometry and Measure in Indian Temple Plans: Rectangular Temples". Artibus Asiae. 44 (4): 266–296. doi:10.2307/3249613. JSTOR 3249613.
- ^ Heather Elgood (2000), Hinduism and the religious arts, ISBN 978-0304707393, Bloomsbury Academic, pp 121-125
- ^ H Kern (1865), The Brhat Sanhita of Varaha-mihara, The Asiatic Society of Bengal, Calcutta
- ^ a b Fergusson, James (1997) [1910]. History of Indian and Eastern Architecture (3rd ed.). New Delhi: Low Price Publications. p. 309.
- ^ a b Nijenhuis, Emmie te (1974), Indian Music: History and Structure, Leiden: Brill, ISBN 978-90-04-03978-0 at pp. 4–5
- ^ Dennis Kennedy "The Oxford Encyclopedia of Theatre and Performance, Publisher:Oxford University Press
- ^ Leslie, Julia. Roles and rituals for Hindu women, pp.149–152
- ^ "Tamil leads as India tops film production". timesofindia.indiatimes/. 22 December 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2017.
- ^ "Mahabharata Text".
- ^ The Dancing Girl: A History of Early India, Balaji Sadasivan, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies 2011, pp 90
- ^ a b c Zarrilli, Phillip B. (1998). When the Body Becomes All Eyes: Paradigms, Discourses and Practices of Power in Kalaripayattu, a South Indian Martial Art. Oxford University Press. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-19-563940-7.
- ^ Barnett, Lionel D. (1999). Antiquities of India: An Account of the History and Culture of Ancient Hindustan. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. p. 31. ISBN 978-81-7156-442-2.
- ^ Wright, Arnold (1914). Southern India: Its History, People, Commerce, and Industrial Resources. Asian Educational Services. p. 71. ISBN 978-81-206-1344-7.
- ^ "Census 2011: Languages by state". Censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ "World Tamil Population". Tamilo.com. August 2008.
- ^ Sivasupramaniam, V. "History of the Tamil Diaspora". Murugan.org.
- ^ a b "Census 2011: Languages by state". Censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ "A-11 Individual Scheduled Tribe Primary Census Abstract Data and its Appendix". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
Sources
- Basham, A. L. (1967). The Wonder That was India (3rd ed.). London: Sidgwick & Jackson. OCLC 459272.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Basu, Analabha; Sarkar-Roya, Neeta; Majumder, Partha P. (9 February 2016), "Genomic reconstruction of the history of extant populations of India reveals five distinct ancestral components and a complex structure", PNAS, 113 (6): 1594–9, Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.1594B, doi:10.1073/pnas.1513197113, PMC 4760789, PMID 26811443
- Cavalli-Sforza, Luigi Luca; Menozzi, Paolo; Piazza, Alberto (1994), The History and Geography of Human Genes, Princeton University Press
- Coningham, Robin; Young, Ruth (2015), The Archaeology of South Asia: From the Indus to Asoka, c.6500 BCE–200 CE, Cambridge University Press
- Derenko, Miroslava (2013), "Complete Mitochondrial DNA Diversity in Iranians", PLoS ONE, 8 (11): e80673, Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880673D, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080673, PMC 3828245, PMID 24244704
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Gallego Romero, Irene; et al. (2011), "Herders of Indian and European Cattle Share their Predominant Allele for Lactase Persistence", Mol. Biol. Evol., 29 (1): 249–60, doi:10.1093/molbev/msr190, PMID 21836184
- Heras, Henry (1953). Studies in Proto-Indo-Mediterranean Culture. Bombay: Indian Historical Research Institute. OCLC 2799353.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kivisild; et al. (1999), "Deep common ancestry of Indian and western-Eurasian mitochondrial DNA lineages" (PDF), Curr. Biol., 9 (22): 1331–1334, doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(00)80057-3, PMID 10574762
- Knorozov, Yuri V. (1965). "Характеристика протоиндийского языка" [Characteristics of Proto-Indian language]. Predvaritel'noe soobshchenie ob issledovanii protoindiyskikh textov Предварительное сообщение об исследовании протоиндийских текстов [A Preliminary Report on the Study of Proto Texts] (in Russian). Moscow: Institute of Ethnography of the USSR.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Invalid|script-title=: missing prefix (help) - Krishnamurti, Bhadriraju (2003). The Dravidian Languages. Cambridge Language Surveys. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77111-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mallory, J. P. (1989). In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology and Myth. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-05052-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Metspalu, Mait; Romero, Irene Gallego; Yunusbayev, Bayazit; Chaubey, Gyaneshwer; Mallick, Chandana Basu; Hudjashov, Georgi; Nelis, Mari; Mägi, Reedik; Metspalu, Ene; Remm, Maido; Pitchappan, Ramasamy; Singh, Lalji; Thangaraj, Kumarasamy; Villems, Richard; Kivisild, Toomas (2011), "Shared and Unique Components of Human Population Structure and Genome-Wide Signals of Positive Selection in South Asia", The American Journal of Human Genetics, 89 (6): 731–744, doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.010, ISSN 0002-9297, PMC 3234374, PMID 22152676
- Moorjani, P.; Thangaraj, K.; Patterson, N.; Lipson, M.; Loh, P. R.; Govindaraj, P.; Singh, L. (2013), "Genetic evidence for recent population mixture in India", The American Journal of Human Genetics, 93 (3): 422–438, doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.07.006, PMC 3769933, PMID 23932107
- Narasimhan, Vagheesh M.; Anthony, David; Mallory, James; Reich, David (2018), "The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia", BioRxic Preprint, doi:10.1101/292581
- Palanichamy, Malliya Gounder (2015), "West Eurasian mtDNA lineages in India: an insight into the spread of the Dravidian language and the origins of the caste system", Human Genetics, 134 (6): 637–47, doi:10.1007/s00439-015-1547-4, PMID 25832481
- Parpola, Asko (1994). Deciphering the Indus script. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43079-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Parpola, Asko (2015), The Roots of Hinduism. The Early Arians and the Indus Civilization, Oxford University Press
- Reich, David; Thangaraj, Kumarasamy; Patterson, Nick; Price, Alkes L.; Singh, Lalji (2009), "Reconstructing Indian population history", Nature, 461 (7263): 489–494, Bibcode:2009Natur.461..489R, doi:10.1038/nature08365, ISSN 0028-0836, PMC 2842210, PMID 19779445
- Samuel, Geoffrey (2008), The Origins of Yoga and Tantra: Indic Religions to the Thirteenth Century, Cambridge University Press
- Witzel, Michael (1995), "Early Sanskritization: Origin and Development of the Kuru state" (PDF), Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies, 1 (4): 1–26, archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2007
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Zvelebil, Kamil (1990). Dravidian Linguistics: An Introduction. Pondicherry: Pondicherry Institute of Linguistics and Culture. ISBN 978-81-85452-01-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Erdosy, George (1995). The Indo-Aryans of Ancient South Asia: Language, Material Culture and Ethnicity. Berlin: de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-014447-5.
- Indian Genome Variation Consortium (2008). "Genetic landscape of the people of India: A canvas for disease gene exploration". Journal of Genetics. 87 (1): 3–20. doi:10.1007/s12041-008-0002-x. PMID 18560169.
- Thomason, Sarah Grey; Kaufman, Terrence (1988). Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-05789-0.
