Mass shooting
There is a lack of consensus on how to define a mass shooting. Most terms define a minimum of three or four victims of gun violence (not including the shooter) in a short period of time, although an Australian study from 2006 required a minimum of five; and added a requirement that the victims actually died as opposed to being shot and injured but not necessarily killed.[2]
In the United States, the Investigative Assistance for Violent Crimes Act of 2012 defines mass killings as three or more killings in a single incident,[3] however the Act does not define mass shootings. Media outlets such as CNN and some crime violence research groups such as the Gun Violence Archive define mass shootings as involving "four or more shot (injured or killed) in a single incident, at the same general time and location, not including the shooter".[4] Mother Jones defines mass shootings as indiscriminate rampages killing three or more people, excluding the perpetrator; this definition doesn't include gang violence or armed robbery.[5][6]
Sometimes shootings involving three or more victims occur in non-public situations such as when one member of a family shoots all the other members in the family home. These killings are known as familicides and are not included in mass shooting statistics.
The motive for mass shootings (that occur in public locations) is usually that they are committed by deeply disgruntled individuals who are seeking revenge for failures in school, career, romance, or life in general[7] or who are seeking fame or attention[8] with at least 16 mass shooters since Columbine citing fame or notoriety as a motive.[9] Fame seekers average more than double the body counts, and many articulated a desire to surpass "past records".[10] If multiple people are shot in a robbery or killed in a group's terrorist attack, that type of violence is usually not included under the definition of mass shootings.[11]
Definitions
There are a variety of definitions of mass shooting:[12][13]
- Under U.S. federal law, the Attorney General – on a request from a state – may assist in investigating "mass killings", rather than mass shootings. The term is defined as the murder of four or more people with no cooling-off period[14][13] but redefined by Congress in 2013 as being murder of three or more people.[15]
- In "Behind the Bloodshed", a report by USA Today, a mass killing is defined as: any incident in which four or more were killed, including familial killings.[16] This definition is also used by the Washington Post.[17]
- A crowdsourced data site cited by CNN, MSNBC, The New York Times, The Washington Post, The Economist, the BBC, etc., Mass Shooting Tracker, defines a mass shooting as any incident in which four or more people are shot, whether injured or killed.[18][19]
- According to the Investigative Assistance for Violent Crimes Act of 2012, signed into law in January 2013, a mass killing is defined as a killing with at least three deaths, excluding the perpetrator.[20][21]
- CBS defines that a mass shooting is an event involving the shooting (not necessarily resulting in death) of five or more people (sometimes four)[22] with no cooling-off period.[18][22][23]
- Mother Jones defines a mass shooting as an indiscriminate rampage in a public place, resulting in three or more victims killed by the attacker, excluding gang violence, armed robbery, and attacks by unidentified perpetrators.[24][25]
- Crime violence research group Gun Violence Archive, whose research is used by major American media outlets, defines mass shooting as having a "minimum of four victims shot, either injured or killed, not including any shooter who may also have been killed or injured in the incident," differentiating between mass shooting and mass murder and not counting shooters as victims.[26]
- Though there are several different definitions of a mass shooting, there are also certain inclusions and exclusions. University of Pennsylvania says no matter how many people are killed, if a shooting occurs by a foreign terrorist that is not included. Another exclusion is if 10 people are shot but only 2 die. Also if 5 people are run over by a car that does not count because no firearm was used. Some inclusions are multiple deaths caused by an armed robbery. Deaths as a result of gang wars are also sometimes included.[27]
The lack of a single definition can lead to alarmism in the news media, with some reports conflating categories of different crimes.[28][29][30]
An act of mass shooting is typically defined as terrorist when it "appears to have been intended" to intimidate or to coerce people;[31] although a mass shooting is not, in itself, an act of terrorism.[11]
By continent and region
Africa
Mass shootings have occurred on the African continent, including the 1927 shooting in South Africa perpetrated by Stephanus Swart, the 2016 Grand Bassam attack in Côte d'Ivoire/Ivory Coast, and the 1994 Kampala wedding massacre in Kampala, Uganda. Whilst incidents of mass violence resulting from terrorism and ethnic conflict have occurred on the continent, "mass shootings" as generally understood are rare in Africa.
Egypt
Various shootings include both the 1997 Luxor massacre and the 2013 Meet al-Attar shooting in Egypt.
Kenya
On 2 April 2015, armed terrorists stormed a public university in the North Eastern part of the country and killed 148 people.
Asia
Several mass shootings have occurred in Asia, including the 1878 Hyderabad shooting and 1983 Pashupatinath Temple shooting in India, the 1938 Tsuyama massacre in Japan, the 1948 Babrra massacre in Pakistan, the 2014 Peshawar school massacre killing 149 people, the 1993 Chongqing shooting and the 1994 Tian Mingjian incident in China, as well as the 2001 Nepalese royal massacre.
India
The Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place on 13 April 1919, when an estimated 379-1500 Indian protesters were killed by the British Army, and an additional 1,200 were injured
Republic of Korea
Mass shootings are extremely rare in Korea. The only mass shooting in South Korea was committed by Woo Bum-kon in 1982, leaving 56 dead. For many years, it was the deadliest mass shooting in modern history, until the 2011 Norway attacks surpassed it.
Japan
Japan has as few as 2 gun-related homicides per year. These numbers include all homicides in the country, not just mass shootings.[32] Japan has had several mass shootings, including the Tsuyama massacre, 2007 Sasebo shooting, and the 2010 Habikino shooting.
Israel
Notable mass shootings in Israel, include the 1972 Lod Airport Massacre, which killed 26 and injured 80, the 2002 Bat Mitzvah massacre in Hadera, Mercaz HaRav Massacre in 2008, the 2014 Jerusalem synagogue attack in Jerusalem and the June 2016 Tel Aviv shooting at the popular Sarona centre complex in Tel Aviv.
There have been two mass shootings by Jews in Israel. Ami Popper was convicted of murdering seven Palestinian men in a mass shooting carried out in 1990. In 1994, terrorist Baruch Goldstein murdered 29 Muslims and injured a further 125 in Hebron during the Cave of the Patriarchs massacre.
Thailand
A mass shooting occurred near and in Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand, colloquially known as Korat, between 8 and 9 February 2020. A soldier of the Royal Thai Police killed 30 people and wounded 58 others before he was eventually shot and killed.
On October 6th, 2022, 38 people, 24 of which were children, were killed in a shooting and stabbing spree by former police officer Panya Kamrab. The main target was a Child Care Centre in Nong Bua Lambhu Province. The perpetrator then killed both his wife and son at his own home.
Europe
There have been many mass shootings in Europe.[33] Recent examples include the 1987 Hungerford massacre, the 1996 Dunblane massacre, the 2010 Cumbria shootings and the 2021 Plymouth shooting in the United Kingdom; the 1990 Puerto Hurraco massacre in Spain; the 2001 Zug massacre in Switzerland; the 2002 Erfurt school massacre, the 2009 Winnenden school shooting, the 2011 Frankfurt Airport shooting, the 2016 Munich shooting, and the 2020 Hanau shootings in Germany; the 2020 Vienna attack in Austria; the 2007 Jokela school shooting and the 2008 Kauhajoki school shooting in Finland; the 2010 Bratislava shooting in Slovakia; the 2011 Alphen aan den Rijn shopping mall shooting in The Netherlands; the 2012 Toulouse and Montauban shootings, the January 2015 Île-de-France attacks, the November 2015 Paris attacks in France; the 2018 Macerata shooting in Italy; the February 2015 Copenhagen shootings the 2022 Copenhagen mall shooting in Denmark; and the 2022 Cetinje shooting in Montenegro. The deadliest mass shooting by a lone individual in modern history occurred in Europe with the 2011 Norway attacks in Norway, in which 77 people died. Of them 67 died of gunshot wounds. 8 other victims were killed by a bomb and 2 indirectly.[33]
Soviet Union/Russia
Notable mass shootings that occurred in the Russian Empire, Soviet Union (Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic) and Russia include the Pogroms in the Russian Empire, 1992 Tatarstan shooting, the 2002 Yaroslavsky shooting, the 2002 Moscow theater hostage crisis, the 2012 Moscow shooting and the 2014 Moscow school shooting, the 2004 Beslan school siege, the 2013 Belgorod shooting, the 2018 Kerch Polytechnic College massacre, the 2021 Kazan school shooting, the 2021 Perm State University shooting, and the 2022 Izhevsk school shooting.
North America
Canada
Notable mass shootings in Canada include the 1989 École Polytechnique massacre (which led to stronger gun control in Canada), the 1992 Concordia University massacre, the 2006 Dawson College shooting in Montreal, the 2012 Danzig Street shooting, the 2014 Edmonton shooting in Edmonton, the 2017 Quebec City mosque shooting in Quebec City, the 2018 Toronto shooting, and the 2020 Nova Scotia attacks. Following the attacks in Nova Scotia, collectively considered to be the deadliest mass shooting in Canadian history, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau banned the use, sale, purchase, and import of AR-15s – the semi-automatic rifle used in the shooting and many other shootings in the US.[34]
Mexico
Notable mass shootings in Mexico include the 2010 Chihuahua shootings in Chihuahua.
United States

The United States has had the most mass shootings of any country.[36][37][38][39][40] In a 2016 study published by criminologist Adam Lankford, it was estimated that 31% of all public mass shooters from 1966 to 2012 attacked in the United States, although the U.S. had less than 5% of the world's population.[41] The study concludes that "The United States and other nations with high firearm ownership rates may be particularly susceptible to future public mass shootings, even if they are relatively peaceful or mentally healthy according to other national indicators."[42]
Criminologist Gary Kleck criticized Lankford's findings, stating the study merely shows a proportional relationship, but fails to prove that gun ownership causes mass shootings. Backlash from economist and gun rights advocate John Lott also raised objections to Lankford's methodology and refusal to share his data. He speculated that Lankford had overlooked a significant number of mass shootings outside the US, which if accounted for would adjust the nation's share closer to 2.88%; slightly below the world average.[43][44] Lankford has since followed up on his research, publishing his data and clarifying that the United States from 1998 to 2012 did in fact have more than six times its global share of public mass shooters who attacked alone, which is almost always the case with mass shooters.[45] Using the data from Lott and Moody's 2019 study of mass shootings,[46] Lankford explains that "41 of all 138 public mass shootings by single perpetrators worldwide were committed in the United States. That represents 29.7%. Because America had in those years approximately 4.5% of the world's population (according to Lott and Moody's calculations), this indicates that based on their own data, the United States had more than six times its global share of public mass shooters who attacked alone (29.7/4.5 = 6.6).[47] In a subsequent study, Lankford criticized Lott and Moody for including "attacks by terrorist organizations, genocidal militias, armed rebel groups, and paramilitary fighters" in their data and suggested they "misrepresent approximately 1,000 foreign cases from their own dataset" in other ways.[48]
Mass shootings have also been observed to be followed by an increase in the purchase of weapons, but does not seem to create an increased feeling of needing guns in either gun owners or non-owners.[49]
Despite the fact that the global COVID-19 pandemic reduced public gatherings from March 2020 onward, the number of mass shootings increased significantly over that period. It "even doubled in July 2020 compared to a year earlier".[50] The 2022 Buffalo shooting perpetrator said he was radicalized during the COVID-19 pandemic,[51] and used the r/MassKillers subreddit for advice on how to commit his attack.[52][53]
South America
Argentina
Notable mass shootings in Argentina include the 2004 Carmen de Patagones school shooting in Carmen de Patagones.
Brazil
Notable mass shootings in Brazil include the 2011 Realengo massacre in Rio de Janeiro and the Suzano school shooting in Suzano.
Oceania
Australia
Notable mass shootings in Australia include the 1987 Hoddle Street massacre in Hoddle Street, Clifton Hill, Melbourne; and the 1996 Port Arthur massacre in Port Arthur, Tasmania. There were 13 mass shootings with five or more deaths between 1979 and 1996, and three mass shootings involving four or more deaths have occurred since the introduction of new gun laws following the Port Arthur incident.[54][55]
New Zealand
Notable mass shootings in New Zealand include the 1990 Aramoana massacre[56] in which 14 people were killed (including the perpetrator) in Aramoana and the 2019 Christchurch mosque shootings in Christchurch, which resulted in 51 deaths[57] and is the largest mass shooting in New Zealand history.[58]
Victims and survivors
After mass shootings, some survivors have written about their experiences and their experiences have been covered by journalists. A survivor of the Knoxville Unitarian Universalist church shooting wrote about his reaction to other mass shooting incidents.[59] The father of a victim in a mass shooting at a movie theater in Aurora, Colorado, wrote about witnessing other mass shootings after the loss of his son.[60] The survivors of the 2011 Norway attacks recounted their experience to GQ magazine.[61] In addition, one paper studied Swedish police officers' reactions to a mass shooting.[62]
Survivors of mass shootings can suffer from Post-traumatic stress disorder.[63][64]
Perpetrators
Sex and ethnicity
United States
The overwhelming majority of mass shooters in the U.S. are male, with some sources showing males account for 98% of mass shooters.[65][66][67] According to Sky News, male perpetrators committed 110 out of 114 school shootings (96%) in the period 1982–2019,[68] compared to homicides in general in the United States, where 85.3% of homicides were committed by males.[69]
A study by Statista showed that 65 out of 116 (56%) U.S. mass shootings in a period from 1982 to 2019 involved "white" shooters.[70] According to a database compiled by Mother Jones magazine, the race of the shooters is approximately proportionate to the overall U.S. population, although Asians are overrepresented and Latinos underrepresented.[67]
Mental health and criminal records
In a study of 55 mass shooters from Mother Jones' mass shooting database, researchers found that 87.5% of perpetrators had misdiagnosed and incorrectly treated or undiagnosed and untreated psychiatric illness.[71]
In a study of 171 mass shooters who attacked in the United States from 1966 to 2019, researchers Adam Lankford and Rebecca Cowan found that although the vast majority of people with mental illness are not violent, "almost all public mass shooters may have mental health problems." They suggest the frequency of mental health problems among mass shooters is sometimes underestimated because "many perpetrators have never been formally evaluated by a psychiatrist or mental health practitioner...and others deliberately avoid doctors, conceal their mental health problems, or lie about their symptoms due to shame, stigma, or fear of other consequences." However, Lankford and Cowan also emphasize that mental illness is not the sole cause of mass shootings and many other factors play an important role in perpetrators' decisions to attack.[72]
Criminologist James Allen Fox said that most mass murderers do not have a criminal record, or involuntary incarceration at a mental health centre,[73] although an article in The New York Times in December 2015 about 15 recent mass shootings found that six perpetrators had had run-ins with law enforcement, and six had mental health issues.[74]
Motives
Mass shootings can be motivated by religious extremism, political ideologies (e.g., neo-Nazism, terrorism, White supremacism), racism, sexual orientation, misogyny,[75] mental illness,[76][77] and extensive bullying,[78] among other reasons.[65] Forensic psychologist Stephen Ross cites extreme anger and the notion of working for a cause—rather than mental illness—as primary explanations.[79] A study by Vanderbilt University researchers found that "fewer than 5% of the 120,000 gun-related killings in the United States between 2001 and 2010 were perpetrated by people diagnosed with mental illness."[80] John Roman of the Urban Institute argues that, while better access to mental health care, restricting high powered weapons, and creating a defensive infrastructure to combat terrorism are constructive, they do not address the greater issue, which is "we have a lot of really angry young men in our country and in the world."[81]
Author Dave Cullen, in his 2009 book Columbine on the infamous 1999 Columbine High School massacre and its perpetrators Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold, described Harris as an "injustice collector."[82] He expanded on the concept in a 2015 New Republic essay on injustice collectors,[83] identifying several notorious killers as fitting the category, including Christopher Dorner, Elliot Rodger, Vester Flanagan, and Andrew Kehoe. Likewise, mass shooting expert and former FBI profiler Mary O'Toole also uses the phrase "injustice collector" in characterizing motives of some mass shooting perpetrators.[84] In relation, criminologist James Alan Fox contends that mass murderers are "enabled by social isolation" and typically experience "years of disappointment and failure that produce a mix of profound hopelessness and deep-seated resentment."[85][86] Jillian Peterson, an assistant professor of criminology at Hamline University who is participating in the construction of a database on mass shooters, noted that two phenomena surface repeatedly in the statistics: hopelessness and a need for notoriety in life or in death.[87] Notoriety was first suggested as a possible motive and researched by Justin Nutt. Nutt stated in a 2013 article, "those who feel nameless and as though no one will care or remember them when they are gone may feel doing something such as a school shooting will make sure they are remembered and listed in the history books."[88]
In a 2019 op-ed for the Los Angeles Times,[89] Jillian Peterson and James Densley of The Violence Project think tank presented a new, hopeful, framework to understand mass shootings. Based on a study funded by the National Institute of Justice, Peterson and Densley found mass shooters had four things in common: (1) early childhood trauma and exposure to violence at a young age; (2) an identifiable grievance or crisis point; (3) validation for their belief system, have studied past shootings to find inspiration; and (4) the means to carry out an attack. This new framework highlights the complexity of the pathway to a mass shooting, including how each one can be "socially contagious,"[90] but also provides a blueprint to prevent the next mass shooting. Each one of the four themes represents an opportunity for intervention. By reducing access to firearms (means), slowing contagion (validation), training in crisis intervention de-escalation (crisis), and increasing access to affordable mental healthcare (trauma), a mass shooting can be averted.
In considering the frequency of mass shootings in the United States, criminologist Peter Squires says that the individualistic culture in the United States puts the country at greater risk for mass shootings than other countries, noting that "many other countries where gun ownership is high, such as Norway, Finland, Switzerland and Israel . . . tend to have more tight-knit societies where a strong social bond supports people through crises, and mass killings are fewer." He is an advocate of gun control, but contends there is more to mass shootings than the prevalence of guns.[91] The Italian Marxist academic Franco Berardi argues that the hyper-individualism, social alienation and competitiveness fomented by neoliberal ideology and capitalism creates mass shooters by causing people to "malfunction."[92]
Social science and family structure
A noteworthy connection has been reported in the U.S. between mass shootings and domestic or family violence, with a current or former intimate partner or family member killed in 76 of 133 cases (57%), and a perpetrator having previously been charged with domestic violence in 21.[93][94]
Moynihan said that "almost all school shooters come from families where the parents are either divorced or alienated,"[95] and Cook argued that "perhaps they wouldn't need more gun control if they had better divorce control."[96]
Responses
Media
Some people have considered whether media attention revolving around the perpetrators of mass shootings is a factor in sparking further incidents.[97] In response to this, some in law enforcement have decided against naming mass shooting suspects in media-related events to avoid giving them notoriety.[98]
The effects of messages used in the coverage of mass shootings has been studied. Researchers studied the role the coverage plays in shaping attitudes toward persons with serious mental illness and public support for gun control policies.[99]
In 2015, a paper written by a physicist and statistician, Sherry Towers, along with four colleagues was published, which proved that there is indeed mass shooting contagion using mathematical modeling.[100] However, in 2017, Towers said in an interview that she prefers self-regulation to censorship to address this issue, just like years ago major news outlets successfully prevent copycat suicide.[101]
In 2016, the American Psychological Association published a press release, claiming that mass shooting contagion does exist and news media and social media enthusiasts should withhold the name(s) and face(s) of the victimizer(s) when reporting a mass shooting to deny the fame the shooter(s) want to curb contagion.[102]
Some news media have weighed in on the gun control debate. After the 2015 San Bernardino attack, the New York Daily News' front-page headline "God isn't fixing this" was accompanied by "images of tweets from leading Republicans who shared their 'thoughts' and 'prayers' for the shooting victims."[103][104] Since the 2014 Isla Vista killings, satirical news website The Onion has repeatedly republished the story "'No Way To Prevent This,' Says Only Nation Where This Regularly Happens" with minor edits after major mass shootings, to satirise the popular consensus that there is a lack of political power in the United States to prevent mass shootings.[105]
Gun law reform
Responses to mass shootings take a variety of forms, depending on the country and political climate.
Australia
After the 1996 Port Arthur massacre, Australia changed its gun laws.
New Zealand
In the aftermath of the Christchurch mosque shootings, New Zealand announced a ban on almost all semiautomatic military-style weapons.[106]
United Kingdom
As a result of the Hungerford massacre in Hungerford, England, and the Dunblane school massacre in Stirling, Scotland, the United Kingdom enacted tough gun laws and a buyback program to remove specific classes of firearms from private ownership. They included the Firearms Amendment Act 1988, which limited rifles and shotguns; and the 1997 Firearms Amendment Acts, which restricted or made illegal many handguns.[107] There have been two mass shootings since the laws were restricted: the Cumbria shootings in 2010, which killed 13 people, including the perpetrator;[33][108] and the Plymouth shooting in 2021, which killed six people, including the perpetrator.[109]
United States
In the United States, support for gun law reform varies considerably by political party, with Democrats generally more supportive and Republicans generally more opposed. Some in the U.S. believe that tightening gun laws would prevent future mass shootings.[110] Some politicians in the U.S. introduced legislation to reform the background check system for purchasing a gun.[111] A vast majority of Americans support tighter background checks. "According to a poll by Quinnipiac University in Connecticut, 93 percent of registered voters said they would support universal background checks for all gun buyers."[112]
Others contend that mass shootings should not be the main focus in the gun law reform debate because these shootings account for less than one percent of the U.S. homicide rate and believe that these shootings are hard to stop. They often argue that civilians with concealed guns will be able to stop shootings.[113]
According to British criminologist Peter Squires, who has studied gun violence in different countries, mass shootings may be more due to the "individualistic culture" in the U.S. than its firearm laws.[114]
Leaders
As of June 2016, U.S. President Barack Obama had spoken in the aftermath of fourteen mass shootings during his eight-year presidency, repeatedly calling for more gun safety laws in the United States.[115] After the Charleston church shooting, Obama said, "At some point, we as a country will have to reckon with the fact that this type of mass violence does not happen in other advanced countries. It doesn't happen in other places with this kind of frequency."[116] After the 2015 San Bernardino attack, Obama renewed his call for reforming gun-safety laws and also said that the frequency of mass shootings in the United States has "no parallel in the world."[117] After the Stoneman Douglas High School shooting, the surviving students, teachers, and parents became strong leaders in the effort to ban assault weapon sales and easy accessibility to weapons.[118]
See also
- Category:Mass shootings by country
- Active shooter
- Copycat crime
- Domestic terrorism
- Mass murder
- School shooting
- Spree killer
References
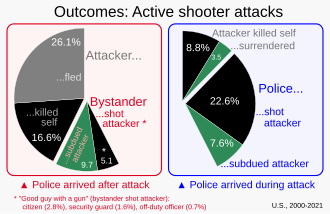
- ^ Buchanan, Larry; Leatherby, Lauren (22 June 2022). "Who Stops a 'Bad Guy With a Gun'?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 June 2022.
Data source: Advanced Law Enforcement Rapid Response Training Center
- ^ Chapman, S. (December 2006). "Australia's 1996 gun law reforms: faster falls in firearm deaths, firearm suicides, and a decade without mass shootings". Injury Prevention. 12 (6): 365–72. doi:10.1136/ip.2006.013714. PMC 2704353. PMID 17170183.
- ^ "Text - H.R.2076 - 112th Congress (2011–2012): Investigative Assistance for Violent Crimes Act of 2012". www.congress.gov. 14 January 2013.
- ^ "General Methodology | Gun Violence Archive". www.gunviolencearchive.org. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- ^ Follman, Mark; Aronsen, Gavin; Pan, Deanna. "US mass shootings, 1982–2022: Data from Mother Jones' investigation". Mother Jones. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ Follman, Mark; Aronsen, Gavin; Pan, Deanna. "A Guide to Mass Shootings in America". Mother Jones. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ Fox & DeLateur. Mass shootings in America: moving beyond Newtown. Homicide Studies, Vol 8(1), pp 125–145.
- ^ Lankford, Adam (1 March 2016). "Fame-seeking rampage shooters: Initial findings and empirical predictions". Aggression and Violent Behavior. 27: 122–129. doi:10.1016/j.avb.2016.02.002. ISSN 1359-1789.
- ^ "Are the Media Making Mass Shootings Worse?". 16 September 2022.
- ^ "Are the Media Making Mass Shootings Worse?". 16 September 2022.
- ^ a b Bjelopera, Jerome P. (18 March 2013). "Public Mass Shootings in the United States: Selected Implications for Federal Public Health and Safety Policy" (PDF). CRS Report for Congress. Congressional Research Service. Retrieved 8 December 2015. "There is no broadly agreed-to, specific conceptualization of this issue, so this report uses its own definition for public mass shootings."
- ^ Weiss, Jeffrey (6 December 2015). "Mass shootings in the U.S. this year? 353 — or 4, depending on your definition". The Dallas Morning News. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ^ a b Follman, Mark (3 December 2015). "How Many Mass Shootings Are There, Really?". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ^
Follman, Mark. "What Exactly Is A Mass Shooting". Mother Jones. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
What is a mass shooting? Broadly speaking, the term refers to an incident involving three or more deaths due to gun violence. But there is no official set of criteria or definition for a mass shooting, according to criminology experts and FBI officials contacted by Mother Jones.
- ^ "PUBLIC LAW 112–265" (PDF). United States Congress. 14 January 2013. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ^ "Behind the Bloodshed". USA Today. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ "The terrible numbers that grow with each mass shooting". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b "About the Mass Shooting Tracker". Mass Shooting Tracker. Archived from the original on 4 January 2018. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Orlando club shootings: Full fury of gun battle emerges". - BBC News. 13 June 2016. Retrieved 13 June 2016. Cites Mass Shooting Tracker
- ^ "H.R. 2076 (112th): Investigative Assistance for Violent Crimes Act of 2012". govtrack.us. United States Congress. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
(I)the term mass killings means 3 or more killings in a single incident;
- ^ Greenberg, Jon; Valverde, Miriam; Jacobson, Louis. "What we know about mass shootings". PolitiFact.
In January 2013, a mandate for federal investigation of mass shootings authorized by President Barack Obama lowered that baseline to three or more victims killed
- ^ a b "Report: U.S. averages nearly one mass shooting per day so far in 2017". CBS News. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- ^ team, Guardian US interactive; Morris, Sam; team, Guardian US interactive; Morris, Sam. "1,516 mass shootings in 1,735 days: America's gun crisis – in one chart". The Guardian. Retrieved 15 February 2018 – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ Follman, Mark; Aronsen, Gavin; Pan, Deanna. "A Guide to Mass Shootings in America". Mother Jones. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ Follman, Mark; Aronsen, Gavin; Pan, Deanna. "US mass shootings, 1982–2022: Data from Mother Jones' investigation". Mother Jones. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ "General Methodology – Gun Violence Archive". www.gunviolencearchive.org.
- ^ "What is a Mass Shooting? What Can Be Done? | Department of Criminology". crim.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ Mark Follman (18 December 2015). "No, There Has Not Been a Mass Shooting Every Day This Year". Mother Jones.
- ^ Follman, Mark. "No, There Has Not Been a Mass Shooting Every Day This Year". Mother Jones. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ Follman, Mark (3 December 2015). "Opinion | How Many Mass Shootings Are There, Really?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- ^ Ana Swanson (3 December 2015). "When should a shooting really be called 'terrorism'?". The Washington Post. Retrieved 27 June 2016.
- ^ Fisher, Max (23 July 2012). "A Land Without Guns: How Japan Has Virtually Eliminated Shooting Deaths". The Atlantic. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ a b c Herring, Keely; Jacobson, Louis. "Is Barack Obama correct that mass killings don't happen in other countries?". www.politifact.com.
- ^ "Canada just banned military-style assault weapons after its deadliest mass shooting". Vox. 2 May 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ "US Mass Shootings, 1982–2018: Data From Mother Jones' Investigation".
- ^ Palazzolo, Joe; Flynn, Alexis (3 October 2015). "U.S. Leads World in Mass Shootings". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- ^ Christensen, Jen (5 October 2017). "Why the US has the most mass shootings". CNN. Retrieved 6 November 2017.
- ^ Healy, Melissa (24 August 2015). "Why the U.S. is No. 1 – in mass shootings". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- ^ Michaels, Samantha (23 August 2015). "The United States Has Had More Mass Shootings Than Any Other Country". Mother Jones. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- ^ Fox, Kara (9 March 2018). "How US gun culture compares with the world in five charts". CNN.
- ^ Lankford, Adam (2016). "Public Mass Shooters and Firearms: A Cross-National Study of 171 Countries". Violence and Victims. 31 (2): 187–199. doi:10.1891/0886-6708.VV-D-15-00093. ISSN 0886-6708. PMID 26822013. S2CID 207266615.
- ^ Lankford, Adam (2016). "Public Mass Shooters and Firearms: A Cross-National Study of 171 Countries". Violence and Victims. 31 (2): 187–199. doi:10.1891/0886-6708.VV-D-15-00093. ISSN 0886-6708. PMID 26822013. S2CID 207266615. (subscription required)
- ^ Dinan, Stephen (16 December 2018). "Shock study: U.S. had far fewer mass shootings than previously reported". washingtontimes.
- ^ Lott, John (16 December 2018). "How a Botched Study Fooled the World About the U.S. Share of Mass Public Shootings: U.S. Rate is Lower than Global Average". SSRN 3238736.
- ^ Adam, Lankford (March 2019). "Confirmation That the United States Has Six Times Its Global Share of Public Mass Shooters, Courtesy of Lott and Moody's Data".
- ^ Moody, Lott (March 2019). "Is the United States an Outlier in Public Mass Shootings? A Comment on Adam Lankford" (PDF).
- ^ Lankford, Adam (March 2019). "Confirmation That the United States Has Six Times Its Global Share of Public Mass Shooters, Courtesy of Lott and Moody's Data" (PDF).
- ^ "The Importance of Analyzing Public Mass Shooters Separately from Other Attackers When Estimating the Prevalence of Their Behavior Worldwide · Econ Journal Watch : public mass shootings, public mass shooter, lone wolf, terrorism, gun policy". econjwatch.org. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ Stroebe, Wolfgang; Leander, N. Pontus; Kruglanski, Arie W. (11 August 2017). "The impact of the Orlando mass shooting on fear of victimization and gun-purchasing intentions: Not what one might expect". PLOS ONE. 12 (8): e0182408. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1282408S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0182408. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5553639. PMID 28800365.
- ^ "Mass shootings in the US increased during the coronavirus pandemic, study finds". 16 September 2021.
- ^ "Kin of alleged Buffalo shooter Payton Gendron roll out COVID defense for slaughter". New York Post. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 18 July 2022.
- ^ Foundation, The Daily Caller News (20 May 2022). "Buffalo Shooter's Personal Diary Is Pretty Clear About His Sources Of Inspiration". Shore News Network. Retrieved 18 July 2022.
- ^ "Mass Murderers Anonymous: How Recovery Groups Could Stop the Next Mass Shooting". Countere Magazine. Retrieved 1 August 2022.
- ^ "At least 4 killed and multiple crime scenes after shooting in Australia". cbsnews.com. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ^ Nunn, Gary (5 June 2019). "Darwin shooting: Why mass shooting feels unfamiliar to Australia". BBC. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- ^ "NZ memories: Thirteen killed in Aramoana massacre". New Zealand Herald. 13 September 2012. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ "Turkish man wounded in Christchurch mosque shootings has died, bringing toll to 51". 2 May 2019. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- ^ Regan, Helen. "Parts of New Zealand city of Christchurch in lockdown as police respond to reported mass shooting at mosque". CNN. Retrieved 15 March 2019.
- ^ Follman, Mark (27 July 2012). "'I Was a Survivor': Recalling a Mass Shooting 4 Years Ago Today". Mother Jones. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Teves, Tom (31 July 2015). "'Something is very wrong in our society': Father of mass-shooting victim calls for an end to the carnage". Salon. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Flynn, Sean (30 July 2012). "Is he coming? Is he? Oh God, I think he is". GQ. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Karlsson, Ingemar. "Memories of traumatic events among swedish police officers". Stockholm University. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Simmons, Laura (29 June 2014). "Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in Mass Shooting Survivors". Liberty Voice. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ "Impact of Mass Shootings on Individual Adjustment" (PDF). ptsd.va.gov. National Center for PTSD. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ a b Frum, David (23 June 2015). "Mass Shootings Are Preventable". The Atlantic. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Kluger, Jeffrey (25 May 2014). "Why Mass Killers Are Always Male". Time. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ a b Ford, Dana (24 July 2015). "Who commits mass shootings?". CNN.
- ^ "Why are white men carrying out more mass shootings?". Sky News. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- ^ Kellermann, A. L.; Mercy, J. A. (July 1992). "Men, women, and murder: gender-specific differences in rates of fatal violence and victimization". The Journal of Trauma. 33 (1): 1–5. ISSN 0022-5282. PMID 1635092.
- ^ "U.S.: mass shootings by race 1982–2019". Statista. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- ^ Cerfolio, Nina E.; Glick, Ira; Kamis, Danielle; Laurence, Michael (1 September 2022). "A Retrospective Observational Study of Psychosocial Determinants and Psychiatric Diagnoses of Mass Shooters in the United States". Psychodynamic Psychiatry. 50 (3): 513–528. doi:10.1521/pdps.2022.50.5.001. ISSN 2162-2590. PMID 35175100. S2CID 246903970.
- ^ Lankford, Adam; Cowan, Rebecca G. (September 2020). "Has the role of mental health problems in mass shootings been significantly underestimated?". Journal of Threat Assessment and Management. 7 (3–4): 135–156. doi:10.1037/tam0000151. ISSN 2169-4850. S2CID 234017401.
- ^ Peters, Justin (19 December 2013). "Mass shootings in America: Northeastern criminologists James Alan Fox, Monica J. DeLateur in Homicide Studies refute common myths about mass murder". Slate.com. Retrieved 8 July 2016.
- ^ Buchanan, Larry (3 December 2015). "How They Got Their Guns". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ^ De Freitas, Julian, and Mina Cikara. "Deep down my enemy is good: Thinking about the true self reduces intergroup bias." (2017)
- ^ "High school students demand action on gun control following Parkland shooting – rabble.ca". rabble.ca. 16 February 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ^ Van Brunt, Brian, and W. Scott Lewis. "Costuming, misogyny, and objectification as risk factors in targeted violence." Violence and gender 1.1 (2014): 25–35.
- ^ Rocque, Michael. "Exploring school rampage shootings: Research, theory, and policy." The Social Science Journal 49.3 (2012): 304–313.
- ^ Campbell, Holly (2 December 2015). "Inside the mind of a mass murderer". WANE.com. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ^ Wolf, Amy (11 December 2014). "Mental Illness is the wrong scapegoat after mass shootings". Vanderbilt University. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Angry young Men and Mass Killings. The Huffington Post. June 16, 2016.
- ^ "Finally understand why. Dave Cullen's Edgar-winning Columbine book: the Columbine killers, shooting & myths". davecullen.com. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ Cullen, Dave (31 August 2015). "Inside the Warped Mind of Vester Flanagan and Other Shooters". The New Republic. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ Bekiempis, Victoria (4 September 2015). "Meet Mass-Shooting Expert Mary Ellen O'Toole". Newsweek. Retrieved 6 September 2015.
- ^ Fox, James Alan (16 January 2011). "The real causes of mass murder". Boston.com. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "James Alan Fox: In San Bernardino, focus on the murderous partnership". USA Today. 3 December 2015.
- ^ Wanamaker, John (8 October 2017). "'This shooter is a little different': Hamline professor studies mass shootings". MPR News. Retrieved 9 October 2017.
- ^ "School Shootings and Possible Causes". 14 December 2013. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- ^ "Op-Ed: We have studied every mass shooting since 1966. Here's what we've learned about the shooters". Los Angeles Times. 4 August 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ "Mass shootings: Experts say violence is contagious, and 24/7 news cycle doesn't help". NBC News. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ Dorell, Oren (18 December 2012). "In Europe, fewer mass killings due to culture not guns". USA Today. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ McIntyre, Niamh (16 April 2015). "This Theorist Believes That Capitalism Creates Mass Murderers by Causing People to 'Malfunction'". Vice. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ^ Melissa Jeltsen (18 July 2014). "Mass Shooting Analysis Finds Strong Domestic Violence Connection". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Analysis of Mass Shootings". Everytownresearch.org. 20 August 2015. Retrieved 13 June 2016. This analysis has later figures than reported in the article
- ^ Moynihan, Carolyn. "Isn't father loss part of Nikolas Cruz's story?". www.mercatornet.com. Archived from the original on 20 February 2018. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ "MercatorNet: 'An act of pure evil'". 3 October 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ^ Birch, Jenna (27 July 2015). "Does Media Coverage After a Mass Shooting Do More Harm Than Good?". Yahoo! News. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Elinson, Zusha; Lazo, Alejandro (4 October 2015). "More Police Decide Against Naming Mass-Shooting Suspects". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 5 October 2015.
- ^ McGinty, Emma (1 May 2013). "Effects of News Media Messages About Mass Shootings on Attitudes Toward Persons With Serious Mental Illness and Public Support for Gun Control Policies". American Journal of Psychiatry. 170 (5): 494–501. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13010014. PMID 23511486.
- ^ Towers, Sherry; Gomez-Lievano, Andres; Khan, Maryam; Mubayi, Anuj; Castillo-Chavez, Carlos (2 July 2015). Yukich, Joshua (ed.). "Contagion in Mass Killings and School Shootings". PLOS One. 10 (7): e0117259. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1017259T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117259. PMC 4489652. PMID 26135941.
- Stephanie Pappas (2 July 2015). "Mass Shootings Are Contagious". Live Science.
- ^ Towers, Sherry (6 December 2017). "Newsmaker Sunday: Sherry Towers". Newsmaker Sunday (Interview). Interviewed by John Hook. Phoenix, Arizona, United States: Fox 10 Phoenix. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ Johnston, Jennifer (4 August 2016). ""Media Contagion" Is Factor in Mass Shootings, Study Says" (Press release). American Psychological Association. Retrieved 16 June 2018.
- ^ Colin Campbell (2 December 2015). "Hard-hitting Daily News cover blasts Republicans for offering only 'prayers' after latest shooting". Business Insider. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Fang, Marina (2 December 2015). "New York Daily News Skewers Politicians Refusing to Act on Gun Violence: 'God Isn't Fixing This'". Huffington Post. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- ^ "Why this Onion article goes viral after every mass shooting". The Washington Post.
- ^ Graham-McLay, Charlotte (10 April 2019). "New Zealand Passes Law Banning Most Semiautomatic Weapons, Weeks After Massacre". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ^ Hartmann, Margaret (2 October 2015). "How Australia and Britain Tackled Gun Violence". Daily Intelligencer. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ^ Tarabay, Jamie; Dewan, Angela (4 October 2017). "What the UK and Australia did differently after mass shootings". CNN.
- ^ "Plymouth shooting: Suspected gunman and five others die". BBC News. BBC. 13 August 2021. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ^ Collins, Sam (28 July 2015). "One Change To Our Gun Laws That Could Have Prevented The Last Mass Shooting". Think Progress. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Weinberg, Ali (2 October 2015). "These 6 Stalled Bills Aimed at Mass Shootings Like Umpqua Flounder in Congress". ABC News. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ^ Andrews, Becca (1 October 2015). "An Overwhelming Majority of Americans Still Support Universal Background Checks". Mother Jones. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ Volokh, Eugene (3 October 2015). "Do civilians with guns ever stop mass shootings?". The Washington Post. Retrieved 5 October 2015.
- ^ Dorell, Oren. "In Europe, fewer mass killings due to culture not guns". USA TODAY.
- ^ Korte, Gregory (2 October 2015). "11 mass shootings, 11 speeches: How Obama has responded". USA Today. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ^ Benen, Steve (23 June 2015). "Comparing U.S. mass shootings to the rest of the world". MSNBC. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Tani, Maxwell (2 December 2015). "OBAMA: 'We have a pattern now of mass shootings ... that has no parallel'". Business Insider. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ Witt, Emily (19 February 2018). "How the Survivors of Parkland Began the Never Again Movement". The New Yorker. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
External links
- Timeline: Deadliest U.S. mass shootings
- Public Mass Shootings in the United States: Selected Policy Implications Congressional Research Service
- Algoworld: Scientific Ways To Predict Mass Shootings
- Washington Case Revives Debate About 'Contagious' Mass Shootings
- Yes, Mass Shootings Are Occurring More Often. Mother Jones. October 21, 2014.
