Basques
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2012) |
Euskaldunak | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
| c. 13 million worldwide[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
(people living in the Basque Provinces of Spain, including some areas where most people don't identify themselves as Basque) | 2,410,000[2][3] |
(people living in the Basque Provinces of France, not all of whom identify as Basque) | 239,000[2] |
(self-identifying as having Basque ancestry) | 57,793[4] |
| Basque diaspora | c. 10,000,000[1] |
| Languages | |
| Basque, Spanish, French | |
The Basques (Template:Lang-eu; Template:Lang-es; Template:Lang-fr, English: /bɑːsks/ or /bæsks/) are an indigenous ethnic group[5][6][7] characterised by the Basque language, a common Basque culture and shared ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians.[8] Basques are indigenous to and primarily inhabit an area traditionally known as the Basque Country (Template:Lang-eu), a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France.
The Basques are known as:
- Euskaldunak in Basque (this ethnonym means "the speakers of the Basque language"; to refer to all the inhabitants of the Basque Country, the name euskal herritarrak is preferred)
- Vasco in Spanish
- Basque in French and English.
- Basco in Gascon and Portuguese.
Etymology of the word Basque

The English word Basque may be pronounced /bɑːsk/ or /bæsk/ and derives from the French Basque (pronounced French pronunciation: [bask]), which is derived from Gascon Basco (pronounced /ˈbasku/), cognate with Spanish Vasco (pronounced /ˈbasko/). These, in turn, come from Latin Vasco (pronounced /wasko/), plural Vascones (see History section below). The Latin labial-velar approximant /w/ generally evolved into the bilabials /b/ and /β̞/ in Gascon and Spanish, probably under the influence of Basque and Aquitanian, a language related to old Basque and spoken in Gascony in Antiquity (similarly the Latin /w/ evolved into /v/ in French, Italian and other languages).
Several coins from the 2nd and 1st centuries BC found in the Basque Country bear the inscription barscunes. The place where they were minted is not certain, but is thought to be somewhere near Pamplona, in the heartland of the area that historians believe was inhabited by the Vascones. Some scholars have suggested a Celtic etymology based on bhar-s-, meaning "summit", "point" or "leaves", according to which barscunes may have meant "the mountain people", "the tall ones" or "the proud ones", while others have posited a relationship to a proto-Indo-European root *bar- meaning "border", "frontier", "march".[9]
In Basque, the people call themselves the euskaldunak, singular euskaldun, formed from euskal- (i.e. "Basque (language)") and -dun (i.e. "one who has"); euskaldun literally means a Basque speaker. Not all Basques are Basque-speakers. Therefore, the neologism euskotar, plural euskotarrak, was coined in the 19th century to mean a culturally Basque person, whether Basque-speaking or not.
Alfonso Irigoyen claimed that the word euskara comes from an ancient Basque verb enautsi "to say" (cf. modern Basque esan) and the suffix -(k)ara ("way (of doing something)"). Thus euskara would literally mean "way of saying", "way of speaking". One item of evidence in favour of this hypothesis is found in the Spanish book Compendio Historial, written in 1571 by the Basque writer Esteban de Garibay. He records the name of the Basque language as enusquera. It may, however, be a writing mistake.
In the 19th century, the Basque nationalist activist Sabino Arana posited an original root euzko which, he thought, came from eguzkiko ("of the sun", related to the assumption of an original solar religion). On the basis of this putative root, Arana proposed the name Euzkadi for an independent Basque nation, composed of seven Basque historical territories. Arana's neologism Euzkadi (in the regularized spelling Euskadi) is still widely used in both Basque and Spanish, since it is now the official name of the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country.
History



Since the Basque language is unrelated to Indo-European, it has long been thought to represent the people or culture that occupied Europe before the spread of Indo-European languages there. A comprehensive analysis of Basque genetic patterns has shown that Basque genetic uniqueness predates the arrival of agriculture in the Iberian Peninsula, about 7,000 years ago.[10]
It is thought that Basques are a remnant of the early inhabitants of Western Europe, specifically those of the Franco-Cantabrian region. Basque tribes were already mentioned in Roman times by Strabo and Pliny, including the Vascones, the Aquitani, and others. There is enough evidence to support the hypothesis that at that time and later they spoke old varieties of the Basque language (see: Aquitanian language).
In the Early Middle Ages the territory between the Ebro and Garonne rivers was known as Vasconia, a vaguely defined cultural area and political entity struggling to fend off pressure from the Iberian Visigothic kingdom and Muslim rule to the south, as well as the Frankish push from the north. By the turn of the first millennium, the territory of Vasconia had fragmented into different feudal regions, such as Soule and Labourd, while south of the Pyrenees the Castile, Pamplona and the Pyrenean counties of Aragon, Sobrarbe, Ribagorza (later Kingdom of Aragon), and Pallars emerged as the main regional entities with Basque population in the 9th and 10th centuries.
The Kingdom of Pamplona, a central Basque realm, later known as Navarre, underwent a process of feudalization and was subjected to the influence of its much larger Aragonese, Castilian and French neighbours. Castile deprived Navarre of its coastline by conquering key western territories (1199–1201), leaving the kingdom landlocked. The Basques were ravaged by the War of the Bands, bitter partisan wars between local ruling families. Weakened by the Navarrese civil war, the bulk of the realm eventually fell before the onslaught of the Spanish armies (1512–1524). However, the Navarrese territory north of the Pyrenees remained beyond the reach of an increasingly powerful Spain. Lower Navarre became a province of France in 1620.
Nevertheless, the Basques enjoyed a great deal of self-government until the French Revolution (1790) and the Carlist Wars (1839/1876), when the Basques supported heir apparent Carlos V and his descendants. On either side of the Pyrenees, the Basques lost their native institutions and laws held during the Ancien régime.
Since then, despite the current limited self-governing status of the Basque Autonomous Community and Navarre as settled by the Spanish Constitution, many Basques have attempted higher degrees of self-empowerment (see Basque nationalism), sometimes by acts of violence. Labourd, Lower Navarre, and Soule were integrated into the French department system (starting 1790), with Basque efforts to establish a region-specific political-administrative entity failing to take off to date.
Geography
Political and administrative divisions


The Basque region is divided into at least three administrative units, namely the Basque Autonomous Community and Navarre in Spain, and the arrondissement of Bayonne and the cantons of Mauléon-Licharre and Tardets-Sorholus in the département of Pyrénées Atlantiques, France.
The autonomous community (a concept established in the Spanish Constitution of 1978) known as Euskal Autonomia Erkidegoa or EAE in Basque and as Comunidad Autónoma Vasca or CAV in Spanish (in English: Basque Autonomous Community or BAC),[11] is made up of the three Spanish provinces of Álava, Biscay and Gipuzkoa. The corresponding Basque names of these territories are Araba, Bizkaia and Gipuzkoa, and their Spanish names are Álava, Vizcaya and Guipúzcoa.
The BAC only includes three of the seven provinces of the currently called historical territories. It is sometimes referred to simply as "the Basque Country" (or Euskadi) by writers and public agencies only considering those three western provinces, but also on occasions merely as a convenient abbreviation when this does not lead to confusion in the context. Others reject this usage as inaccurate and are careful to specify the BAC (or an equivalent expression such as "the three provinces", up to 1978 referred to as "Provincias Vascongadas" in Spanish) when referring to this entity or region. Likewise, terms such as "the Basque Government" for "the government of the BAC" are commonly though not universally employed. In particular in common usage the French term Pays Basque ("Basque Country"), in the absence of further qualification, refers either to the whole Basque Country ("Euskal Herria" in Basque), or not infrequently to the northern (or "French") Basque Country specifically.
Under Spain's present constitution, Navarre (Nafarroa in present-day Basque, Navarra historically in Spanish) constitutes a separate entity, called in present-day Basque Nafarroako Foru Erkidegoa, in Spanish Comunidad Foral de Navarra (the autonomous community of Navarre). The government of this autonomous community is the Government of Navarre. Note that in historical contexts Navarre may refer to a wider area, and that the present-day northern Basque province of Lower Navarre may also be referred to as (part of) Nafarroa, while the term "High Navarre" (Nafarroa Garaia in Basque, Alta Navarra in Spanish) is also encountered as a way of referring to the territory of the present-day autonomous community.
There are three other historic provinces parts of the Basque Country: Labourd, Lower Navarre and Soule (Lapurdi, Nafarroa Beherea and Zuberoa in Basque; Labourd, Basse-Navarre and Soule in French), devoid of official status within France's present-day political and administrative territorial organization, and only minor political support to the Basque nationalists. A large number of regional and local nationalist and non-nationalist representatives has waged a campaign for years advocating for the creation of a separate Basque département, while these demands have gone unheard by the French administration.
Population, main cities and languages

There are 2,123,000 people living in the Basque Autonomous Community (279,000 in Alava, 1,160,000 in Biscay and 684,000 in Gipuzkoa). The most important cities in this region, which serve as the provinces' administrative centers, are Bilbao (in Biscay), San Sebastián (in Gipuzkoa) and Vitoria-Gasteiz (in Álava). The official languages are Basque and Spanish. Knowledge of Spanish is compulsory under the Spanish constitution (article no. 3), and knowledge and usage of Basque is a right under the Statute of Autonomy (article no. 6), so only knowledge of Spanish is virtually universal. Knowledge of Basque, after declining for many years during Franco's dictatorship owing to official persecution, is again on the rise due to favourable official language policies and popular support. Currently about 33 percent of the population in the Basque Autonomous Community speaks Basque.
Navarre has a population of 601,000; its administrative capital and main city, also regarded by many nationalist Basques as the Basques' historical capital, is Pamplona (Iruñea in modern Basque). Only Spanish is an official language of Navarre, and the Basque language is only co-official in the province's northern region, where most Basque-speaking Navarrese are concentrated.
About a quarter of a million people live in the French Basque Country. Nowadays Basque-speakers refer to this region as Iparralde (Basque for North), and to the Spanish provinces as Hegoalde (South). Much of this population lives in or near the Bayonne-Anglet-Biarritz (BAB) urban belt on the coast (in Basque these are Baiona, Angelu and Miarritze). The Basque language, which was traditionally spoken by most of the region's population outside the BAB urban zone, is today rapidly losing ground to French. The French Basque Country's lack of self-government within the French state is coupled with the absence of official status for the Basque language in the region. Attempts to introduce bilingualism in local administration have so far met direct refusal from French officials.
Basque diaspora

| > 3,000,000 > 1,000,000 > 500,000 > 50,000 <10,000 or No Data |


Large numbers of Basques have left the Basque Country to settle in the rest of Spain, France or other parts of the world in different historical periods, often for economic or political reasons. Historically the Basques abroad were often employed in shepherding and ranching and by maritime fisheries and merchants. Millions of Basque descendants (see Basque American and Basque Canadian) live in North America (the United States; Canada, mainly in the provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec), Latin America (in all 23 countries), South Africa, and Australia.
Miguel de Unamuno said: "There are at least two things that clearly can be attributed to Basques: the Society of Jesus and the Republic of Chile.[12] Chilean historian Luis Thayer Ojeda estimated that 45 percent of immigrants to Chile in the 17th and 18th centuries were Basque.[13] Over 2.5 million Basque descendants live in Chile; the Basque have been a major influence in the country's cultural and economic development.
A large wave of Basques emigrated to Latin America. Substantial numbers also settled in North America. In addition to Chile in Latin America, they settled in Argentina, Colombia, Cuba, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela. Basque place names are to be found, such as New Biscay, now Durango (Mexico), Biscayne Bay, Sacatepequez, Antigua Guatemala and Jalapa, Jalapa (Guatemala), Aguerreberry or Aguereberry Point in the United States, and the Nuevo Santander region of Mexico.[14] Nueva Vizcaya was the first province in the north of the Viceroyalty of New Spain (Mexico) to be explored and settled by the Spanish. It consisted mostly of the area which is today the states of Chihuahua and Durango.
In Mexico most Basques are concentrated in the cities of Monterrey, Saltillo, Reynosa, Camargo, and the states of Jalisco, Durango, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, and Coahuila. The Basques were important in the mining industry; many were ranchers and vaqueros (cowboys), and the rest opened small shops in major cities such as Mexico City, Guadalajara and Puebla. In Guatemala, most Basques have been concentrated in Sacatepequez Department, Antigua Guatemala, Jalapa for six generations now, while some have migrated to Guatemala City.
In Colombia, Basques settled mainly in Antioquia and the Coffee Axis. It is estimated that nearly 2,500,000 persons from all Antioquia (40% of this department) have Basque ancestry, as well, in the 19th century 10% of Colombia's total population were Basque descendants.[15][failed verification] Antioquia has one of the biggest concentrations of Basques descendants around the world.[citation needed] In 1955, Joaquín Ospina said: "Is there something more similar to the Basque people than the "antioqueños".[16] Also, writer Arturo Escobar Uribe said in his book "Mitos de Antioquia" (Myths of Antioquia) (1950): "Antioquia, which in its clean ascendance predominates the peninsular farmer of the Basque provinces, inherited the virtues of its ancestors... Despite the predominance of the white race, its extension in the mountains... has projected over Colombia's map the prototype of its race; in Medellín with the industrial paisa, entrepreneur, strong and steady... in its towns, the adventurer, arrogant, world-explorer... Its myths, which are an evidence of their deep credulity and an indubitable proof of their Iberian ancestor, are the sequel of the conqueror's blood which runs through their veins...".[17] Bambuco, a Colombian folk music, has Basque roots[18][19]
The largest of several important Basque communities in the United States is in the area around Boise, Idaho, home to the Basque Museum and Cultural Center, host to an annual Basque festival, as well as a festival for the Basque diaspora every five years. Reno, Nevada, where the Center for Basque Studies and the Basque Studies Library are located at the University of Nevada, is another significant nucleus of Basque population. Elko, Nevada sponsors an annual Basque festival that celebrates the dance, cuisine and cultures of the Basque peoples of Spanish, French and Mexican nationalities who have arrived in Nevada since the late 19th century.
Texas has a large percentage of Hispanics descended from Basques who participated in the conquest of New Spain. Many of the original Tejanos had Basque blood, including those who fought in the Battle of the Alamo alongside many of the other Texans. Along the Mexican/Texan border, many Basque surnames can be found. The largest concentration of Basques who settled on Mexico's north-eastern "frontera", including the states of Chihuahua, Durango, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas, also settled along Texas' Rio Grande River from South Texas to West Texas. Many of the historic hidalgos, or noble families from this area, had gained their titles and land grants from Spain and Mexico; they still value their land. Some of North America's largest ranches, which were founded under these colonial land grants, can be found in this region.
California has a major concentration of Basques, most notably in the San Joaquin Valley between Stockton, Fresno and Bakersfield. The city of Bakersfield has a large Basque community and the city has several Basque restaurants, including Noriega's which won the 2011 James Beard Foundation America's Classic Award. There is a history of Basque culture in Chino, California. In Chino, two annual Basque festivals celebrate the dance, cuisine, and culture of the peoples. The surrounding area of San Bernardino County has many Basque descendants as residents. They are mostly descendants of settlers from Spain and Mexico. These Basques in California are grouped in the group known as Californios.
Basques of European Spanish-French and Latin American nationalities also settled throughout the western U.S. in states like Louisiana, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, Oregon, and Washington.
Culture
| Culture of Basque Country |
|---|
 |
| Mythology |
| Literature |

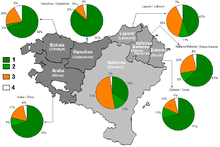
2 - Yes, in some ways 3 - No
4 - Don't know / Don't answer
Language
The identifying language of the Basques is called Basque or Euskara, spoken today by 25%-30%[20] of the region's population. An idea of the central place of the cultural terms in Basque nationalist politicians is given by the fact that, in Basque, Basques identify themselves by the term euskaldun and their country as Euskal Herria, literally "Basque speaker" and "Country of the Basque Language" respectively. The language has been made a political issue by official Spanish and French policies restricting its use either historically or currently; however, this has not stopped the teaching, speaking, writing, and cultivating of this increasingly vibrant minority language. This sense of Basque identity tied to the local language does not exist in isolation. It is juxtaposed with an equally strong sense of national identity tied with the use of the Spanish and French languages among other Basques. As with many European states, a regional identity, be it linguistically derived or otherwise, is not mutually exclusive with the broader national one. For example, Basque rugby union player for France, Imanol Harinordoquy, has said about his national identity:
I am French and Basque. There is no conflict, I am proud of both. . . . I have friends who are involved in the political side of things but that is not for me. My only interest is the culture, the Euskera language, the people, our history and ways.[21]
As a result of state language promotion, school policies, the effects of mass media and migration, today virtually all Basques (except for some children below school age) speak the official language of their state (Spanish or French). There are extremely few Basque monolingual speakers: essentially all Basque speakers are bilingual on both sides of the border. Spanish or French is typically the first language of citizens from other regions (who often feel no need to learn Basque), which maintains the dominance of the state tongues of both France and Spain. Recent Basque Government policies aim to change this pattern, as they are viewed as potential threats against mainstream usage of the minority tongue.[22]
The Basque language is thought to be a genetic language isolate. Thus Basque contrasts with other European languages, almost all of which belong to the broad Indo-European language family. Another peculiarity of Basque is that it has been spoken continuously in situ, in and around its present territorial location, for longer than other modern European languages, which have all been introduced in historical or prehistorical times through population migrations or other processes of cultural transmission.[23][page needed]
However, popular stereotypes characterizing Basque as "the oldest language in Europe" and "unique among the world's languages" may be misunderstood and lead to erroneous assumptions.[24] Over the centuries, Basque has remained in continuous contact with neighboring western European languages with which it has come to share numerous lexical properties and typological features; it is therefore misleading to exaggerate the "outlandish" character of Basque. Basque is also a modern language, and is established as a written and printed one used in present-day forms of publication and communication, as well as a language spoken and used in a very wide range of social and cultural contexts, styles, and registers.
Land and inheritance


Basques have a close attachment to their home (etxe(a) 'house, home'), especially when this consists of the traditional self-sufficient, family-run farm or baserri(a). Home in this context is synonymous with family roots. Some Basque surnames were adapted from old baserri or habitation names. They typically related to a geographical orientation or other locally meaningful identifying features. Such surnames provide even those Basque whose families may have left the land generations ago with an important link to their rural family origins: Bengoetxea "the house of further down", Goikoetxea "the house above", Landaburu "top of the field", Errekondo "next to the stream", Elizalde "by the church", Mendizabal "wide hill", Usetxe "house of birds" Ibarretxe "house in the valley", Etxeberria "the new house", and so on.[25]
In contrast to surrounding regions, ancient Basque inheritance patterns, recognised in the fueros, favour survival of the unity of inherited land holdings. In a kind of primogeniture, these usually are inherited by either eldest male or female. As in other cultures, the fate of other family members depended on the assets of a family. The wealthy Basque families tended to provide for all children in some way while the less affluent had only one asset to provide to one child. However, this heir often provided for the rest of the family. Unlike England with the strict primogeniture where the eldest son inherited everything and did not provide for others. Even though they were provided for in some way siblings had to make their livings by other means. Before the advent of industrialisation, this system resulted in the emigration of many rural Basques to Spain, France or the Americas. Harsh by modern standards, this custom resulted in a great many enterprising figures of Basque origin who went into the world to earn their way, from Spanish conquistadors such as Lope de Aguirre and Francisco Vásquez de Coronado, to explorers, missionaries and saints of the Catholic Church, such as Francis Xavier.
A widespread belief that Basque society was originally matriarchal is at odds with the current, clearly patrilineal kinship system and inheritance structures. Some scholars and commentators have attempted to reconcile these points by assuming that patrilineal kinship represents an innovation. In any case, the social position of women in both traditional and modern Basque society is somewhat better than in neighbouring cultures, and women have a substantial influence in decisions about the domestic economy. In the past, some women participated in collective magical ceremonies. They were key participants in a rich folklore, today largely forgotten.
Cuisine
Basque cuisine is at the heart of Basque culture, influenced by the neighboring communities and the excellent produce from the sea and the land. A 20th-century feature of Basque culture is the phenomenon of gastronomical societies (called txoko in Basque), food clubs where men gather to cook and enjoy their own food. Until recently, women were allowed entry only one day in the year. Cider houses (Sagardotegiak) are popular restaurants in Gipuzkoa open for a few months while the cider is in season.
Cultural production

At the end of the 20th century, despite ETA violence (ended in 2010) and the crisis of heavy industries, the Basque economic condition recovered remarkably. They emerged from the Franco regime with a revitalized language and culture. The Basque language expanded geographically led by large increases in the major urban centers of Pamplona, Bilbao, and Bayonne, where only a few decades ago the Basque language had all but disappeared. Nowadays, the number of Basque speakers is maintaining its level or increasing slightly.
Music

Religion
Traditionally Basques have been mostly Roman Catholics. In the 19th century and well into the 20th, Basques as a group remained notably devout and churchgoing. In recent years church attendance has fallen off, as in most of Western Europe. The region has been a source of missionaries like Francis Xavier and Michel Garicoïts. Ignatius Loyola, founder of the Society of Jesus, was a Basque. California Franciscan Fermín Lasuén was born in Vitoria. Lasuén was the successor to Franciscan Padre Junípero Serra and founded 9 of the 21 extant California Missions along the coast.
A sprout of Protestantism in the continental Basque Country produced the first translation of the new Testament into Basque by Joanes Leizarraga. After Henry III of Navarre converted to Catholicism to become king of France, Protestantism almost disappeared.
Bayonne held a Jewish community composed mainly of Sephardi Jews fleeing from the Spanish and Portuguese Inquisitions. There were also important Jewish and Muslim communities in Navarre before the Castilian invasion of 1512-21. The Banu Qasi, a muladi dynasty descended from Count Cassius, even ruled a small predominantly Muslim Basque emirate in the Ebro valley for over two centuries.
Nowadays, according to one single opinion poll, only slightly more than 50% of Basques profess some kind of belief in God, while the rest are either agnostic or atheist. The number of religious skeptics increases noticeably for the younger generations, while the older ones are more religious.[26]
Pre-Christian religion and mythology
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2016) |


Christianisation of the Basque Country has been the topic of some discussion. There are broadly speaking two views. According to one, Christianity arrived in the Basque Country during the 4th and 5th centuries but according to the other, it did not take place until the 12th and 13th centuries. The main issue lies in the different interpretations of what is considered Christianisation. Early traces of Christianity can be found in the major urban areas from the 4th century onwards, a bishopric from 589 in Pamplona and three hermit cave concentrations (two in Álava, one in Navarre) were in use from the 6th century onwards. In this sense, Christianity arrived "early".
Pre-Christian belief seems to have focused on a goddess called Mari. A number of place-names contain her name and would suggest these places were related to worship of her such as Anbotoko Mari who appears to have been related to the weather. According to one tradition, she traveled every seven years between a cave on Mount Anboto and one on another mountain (the stories vary); the weather would be wet when she was in Anboto, dry when she was in Aloña, or Supelegor, or Gorbea. One of her names, Mari Urraca possibly ties her to an historical Navarrese princess of the 11th and 12th century, with other legends giving her a brother or cousin who was a Roman Catholic priest. So far the discussions about whether the name Mari is original and just happened to coincide closely with the Christian name María or if Mari is an early Basque attempt to give a Christian veneer to pagan worship have remained speculative. At any rate, Mari (Andramari) is one of the oldest worshiped Christian icons in Basque territories.
Mari's consort is Sugaar. This chthonic couple seem to bear the superior ethical power and also the power of creation and destruction. It's said that when they gathered in the high caves of the sacred peaks, they engendered the storms. These meetings typically happened on Friday nights, the day of historical akelarre or coven. Mari was said to reside in Mount Anboto; periodically she crossed the skies as a bright light to reach her other home at mount Txindoki.
Legends also speak of many and abundant genies, like jentilak (equivalent to giants), lamiak (equivalent to nymphs), mairuak (builders of the cromlechs or stone circles, literally Moors), iratxoak (imps), sorginak (witches, priestess of Mari), and so on. Basajaun is a Basque version of the Woodwose. This character is probably an anthropomorphism of the bear. There is a trickster named San Martin Txiki ("St Martin the Lesser").
It has been shown that some of these stories have entered Basque culture in recent centuries or as part of Roman superstition. It is unclear whether neolithic stone structures called dolmens have a religious significance or were built to house animals or resting shepherds. Some of the dolmens and cromlechs are burial sites serving as well as border markers.

The jentilak ('Giants'), on the other hand, are a legendary people which explains the disappearance of a people of Stone Age culture that used to live in the high lands and with no knowledge of the iron. Many legends about them tell that they were bigger and taller, with a great force, but were displaced by the ferrons, or workers of ironworks foundries, until their total fade-out. They were pagans, but one of them, Olentzero, accepted Christianity and became a sort of Basque Santa Claus. They gave name to several toponyms, as Jentilbaratza.

Society
Historically, Basque society can be described as being somewhat at odds with Roman and later European societal norms.
Strabo's account of the north of Spain in his Geographica (written between approximately 20 BC and 20 AD) makes a mention of "a sort of woman-rule—not at all a mark of civilization" (Hadington 1992), a first mention of the—for the period—unusual position of women. "Women could inherit and control property as well as officiate in churches. Combined with the issue of lingering pagan beliefs, this enraged the leaders of the Spanish Inquisition, perhaps leading to one of the largest witch hunts in the Basque town of Logroño in 1610".[27]
This preference for female dominance existed well into the 20th century:
...matrilineal inheritance laws, and agricultural work performed by women continued in Basque country until the early twentieth century. For more than a century, scholars have widely discussed the high status of Basque women in law codes, as well as their positions as judges, inheritors, and arbitrators through ante-Roman, medieval, and modern times. The system of laws governing succession in the French Basque region reflected total equality between the sexes. Up until the eve of the French Revolution, the Basque woman was truly ‘the mistress of the house', hereditary guardian, and head of the lineage.[28]
Although the kingdom of Navarre did adopt feudalism, most Basques also possessed unusual social institutions different from those of the rest of feudal Europe. Some aspects of this include the elizate tradition where local house-owners met in front of the church to elect a representative to send to the juntas and Juntas Generales (such as the Juntas Generales de Vizcaya or Guipúzcoa) which administered much larger areas. Another example was the fact that in the medieval period most land was owned by the farmers, not the Church or a king.[23][page needed][29]
Sports in the Basque Country

Pelota
The great family of ball games has its unique offspring among Basque ball games, known generically as pilota (Spanish: pelota). Some variants have been exported to the United States and Macau under the name of Jai Alai.
Rural sports


There are several sports derived by Basques from everyday chores. Heavy workers were challenged and bets placed upon them. Examples are:
- estropadak rowing regattas: from fishermen activities.
- sokatira: tug-of-war.
- harri-jasotzea: stone-lifting, from quarry works.
- aizkolaritza and trontzalaritza: wood-chopping and log sawing.
- sega jokoa: cutting grass with a scythe.
- Giza-abere probak: stone block pulling, from construction works:
- idi probak with teams of oxen.
- asto probak with donkeys.
- zaldi probak with horses.
- gizon probak with human teams.
- txinga eramatea: carrying of weights, one in each hand, representing milk canisters.
- ahari topaketa: ram fights.
- harri zulaketa competitions: drilling stone blocks with a metal bar, only in the former mining areas of West Biscay.
- Basque sheepdog trials competitions.
Bull runs and bullock games
The encierro (bull run) in Pamplona's fiestas Sanfermines started as a transport of bulls to the ring. These encierros, as well as other bull and bullock related activities are not exclusive to Pamplona but are traditional in many towns and villages of the Basque country.
Football
The largest symbol of Basque identity in football is Athletic Bilbao. While there are other clubs within the Basque Country, such as Real Sociedad, Deportivo Alavés and CA Osasuna (the only club in La Liga that has a Basque name — osasuna means "health"), Bilbao's cantera policy has meant the club refuses to sign any non-Basque players.[30]
Rugby union
Rugby union is a popular sport among French Basques, with major clubs Biarritz Olympique and Aviron Bayonnais traditional powerhouses in the premier division of French Rugby (the Top 14). Biarritz regularly play Heineken Cup matches, especially knockout matches, at Estadio Anoeta in San Sebastian. Games between the Basque clubs and Catalan club USA Perpignan are always hard fought.
Professional cycling
Cycling is popular and the Euskaltel-Euskadi professional cycling team, partly sponsored by the Basque Government participated in the UCI World Tour division until 2014. Known for their orange tops and hill-climbing ability, their fans were famous for lining the famous Pyrenean climbs in the Tour de France, in support of their compatriots.
Each April the week-long Tour of the Basque Country showcases the beautiful rolling Basque countryside.
Politics
While there is no independent Basque state, Spain's autonomous community of the Basque Country, made up of the provinces of Álava (Araba), Biscay (Bizkaia) and Gipuzkoa, is primarily a historical consequence and an answer to the wide autonomy claim of its population.
Navarre has a separate statute of autonomy, a contentious arrangement designed during Spanish transition to democracy (the Amejoramiento, an 'upgrade' of its previous status during dictatorship). It refers back to the kingdom status of Navarre (up to 1841) and their traditional institutional and legal framework (charters). Basque, the original and main language of Navarre up to the late 18th century, has kept family transmission especially in the northern part of Navarre and central areas to a lesser extent, designated as Basque speaking or mixed area in Navarrese law. Questions of political, linguistic and cultural allegiance and identity are highly complex in Navarre. Politically some Basque nationalists would like to integrate with the Basque Autonomous Community.
The French Basque Country today does not exist as a formal political entity and is officially simply part of the French department of Pyrénées Atlantiques, centered in Béarn. In recent years the number of mayors of the region supporting the creation of a separate Basque department has grown to 63.87%.[31] So far, their attempts have been unsuccessful.
Political conflicts
Language
Both the Spanish and French governments have, at times, suppressed Basque linguistic and cultural identity. The French Republics, the epitome of the nation-state, have a long history of attempting the complete cultural absorption of cultural minority groups. Spain has, at most points in its history, granted some degree of linguistic, cultural, and even political autonomy to its Basques, but under the regime of Francisco Franco, the Spanish government reversed the advances of Basque nationalism, as it had fought in the opposite side of the Spanish Civil War: cultural activity in Basque was limited to folkloric issues and the Roman Catholic Church.
Today, the Southern Basque Country within Spain enjoys an extensive cultural and political autonomy. The majority of schools under the jurisdiction of the Basque education system use Basque as the primary medium of teaching. However, the situation is more delicate in the Northern Basque Country within France, where Basque is not officially recognized, and where lack of autonomy and monolingual public schooling in French exert great pressure on the Basque language.
In Navarre, Basque has been declared an endangered language, since the anti-Basque and conservative government of Navarrese People's Union opposes the symbols of Basqueness,[32] highlighting a Spanish identity for Navarre.
Basque is also spoken by immigrants in the major cities of Spain and France, in Australia, in many parts of Latin America, and in the United States, especially in Nevada, Idaho, and California.[23]: 1
Political status and violence
Since its articulation by Sabino Arana in the late 19th century, the more radical currents of Basque nationalism have demanded the right of self-determination and even independence. Within the Basque country, this element of Basque politics is often in balance with the conception of the Basque Country as just another part of the Spanish state, a view more commonly espoused on the right of the political spectrum. In contrast, the desire for greater autonomy or independence is particularly common among leftist Basque nationalists. The right of self-determination was asserted by the Basque Parliament in 2002 and 2006.[33] Since self-determination is not recognized in the Spanish Constitution of 1978, a wide majority of Basques abstained (55%) and some even voted against it (23.5%) in the ratification referendum of December 6 of that year. However, it was approved by clear majority overall in Spanish (87%). The autonomous regime for the Basque Country was approved in a 1979 referendum but the autonomy of Navarre (Amejoramiento del Fuero: "improvement of the charter") was never subject to a referendum but only approved by the Navarrese Cortes (parliament).
Political violence
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2010) |
Classification
As with their language, the Basques are clearly a distinct cultural group in their region. They regard themselves as culturally and especially linguistically distinct from their surrounding neighbours. Some Basques, especially in Spain, are strongly nationalist, identifying far more firmly as Basques than as citizens of any existing state. Others do not, feeling as much Basque as Spanish.[34] Many Basques regard the designation as a "cultural minority" as incomplete, favouring instead the definition as a nation, the commonly accepted designation for the Basque people up to the rise of the nation-states and the definition imposed by the 1812 Spanish Constitution.
In modern times, as a European people living in a highly industrialized area, cultural differences from the rest of Europe are inevitably blurred, although a conscious cultural identity as a people or nation remains very strong, as does an identification with their homeland, even among many Basques who have emigrated to other parts of Spain or France, or to other parts of the world.
The strongest distinction between the Basques and their traditional neighbours is linguistic. Surrounded by Romance-language speakers, the Basques traditionally spoke (and many still speak) a language that was not only non-Romance but non-Indo-European. The prevailing belief amongst Basques, and forming part of their national identity, is that their language has continuity with the people who were in this region since not only pre-Roman and pre-Celtic times, but since the Stone Age.
Genetics

In 1920, H. G. Wells referred to the Mediterranean race as the Iberian race. He regarded it as a fourth subrace of the Caucasian race, along with the Aryan, Semitic, and Hamitic subraces. He stated that the main ethnic group that most purely represented the racial stock of the Iberian race was the Basques, and that the Basques were the descendants of the Cro-Magnons.[35] In 1994, in his book The History and Geography of Human Genes, population geneticist L. Luca Cavalli-Sforza stated that "there is support from many sides" for the hypothesis that the Basques are the descendants of the original Cro-Magnons.[36]
Even before the development of modern genetics based on DNA sequencing, Basques were already noted for distinctive genetic patterns, such as possessing the highest global apportion of the Rh- blood type (35% phenotypically, 60% genetically). Additionally, the Basque population has virtually no B blood type, nor the related AB type. They have a high rate of O blood group but this is probably due to isolation.
Although they are genetically distinctive in some ways, the Basques are still very typically European in terms of their Y-DNA and mtDNA sequences, and in terms of some other genetic loci. These same sequences are widespread throughout the western half of Europe, especially along the western fringe of the continent.[37][38]
The distinctiveness noted by studies of 'classical' genetic markers (such as blood groups) and the apparently "pre-Indo-European" nature of the Basque language has resulted in a popular and long-held view that Basques are "living fossils" of the earliest modern humans who colonized Europe.[39] However, studies of the Y-chromosome found that on their direct male lineages, the vast majority of modern Basques have a common ancestry with other Western Europeans, namely a marked predominance of Haplogroup R1b.[39][40]
Initially Haplogroup R1b was theorised to be that a Palaeolithic marker, introduced when Europe was repopulated after the Last Glacial Maximum, about 25,000 years ago.[41] As such, Basque populations were used as proxy representatives for the "Palaeolithic component" in admixture studies that tried to quantify the extent of Neolithic diffusions. Such studies concluded that the main components in the European genomes appear to derive from ancestors whose features were similar to those of modern Basques and people of the Near East (or Western Asia), with average values greater than 35% for both these parental populations, regardless of whether molecular information is taken into account or not. The smallest degree of both Basque and Near Eastern admixture is found in Finland, whereas the highest values are, respectively, 70% "Basque" in Spain and roughly 60% "Near Eastern" in the Balkans.[37]: p.1365 Table 3 This theory encountered inconsistencies even prior to most recent chronological re-evaluations. That R1b should be a Palaeolithic marker was an ad hoc assumption suggested by Semino et al. (2000) and propagated by subsequent scholars without further analysis. Higher resolution STR analysis of R1b lineages from other western European populations (e.g. Italy[42] or Britain)[39] show that their populations appear to derive from the Basque ones.
More recent studies instead propose that R1b spread through Europe from southwest Asia in the Neolithic period or later, between 4,000 and 8,000 years ago.[43][44][45][46]
Autosomal genetic studies have confirmed that Basques share:
- close genetic ties to other Europeans, especially with Spaniards, who have a common genetic identity of over 70% with Basques.[37]
- homogeneity amongst both their Spanish and French populations, according to high-density SNP genotyping study done in May 2010,[37] and;
- a genomic distinctiveness, relative to other European populations.[47]
Several ancient DNA samples have been recovered and amplified from Palaeolithic sites in the Basque region. The collection of mtDNA haplogroups sampled there differed significantly compared to their modern frequencies. The authors concluded that there is "discontinuity" between ancient and modern Basques.[48]
Thus, while Basques harbour some very archaic lineages (such as mtDNA Hg U8a),[49] they are not of "undiluted Palaeolithic ancestry", nor are they ancestral to large parts of western Europe. Rather, their genetic distinctiveness is a result of centuries of low population size, genetic drift and endogamy.
New genetic findings, 2015
In 2015, a new scientific study of Basque DNA was published which seems to indicate that Basques are descendants of Neolithic farmers who mixed with local hunters before becoming genetically isolated from the rest of Europe for millennia.[50] Mattias Jakobsson from Uppsala University in Sweden analysed genetic material from eight Stone Age human skeletons found in El Portalón Cavern in Atapuerca, northern Spain. These individuals lived between 3,500 and 5,500 years ago, after the transition to farming in southwest Europe. The results show that these early Iberian farmers are the closest ancestors to present-day Basques.[51]
The official findings were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States America.[8] "Our results show that the Basques trace their ancestry to early farming groups from Iberia, which contradicts previous views of them being a remnant population that trace their ancestry to Mesolithic hunter-gatherer groups," says Prof. Jakobsson.[52]
Notable Basques
Among the most notable Basque people are Juan Sebastián Elcano (led the first successful expedition to circumnavigate the globe after Ferdinand Magellan died mid-journey); Sancho III of Navarre; and Ignatius of Loyola and Francis Xavier, founders of the Society of Jesus. Don Diego de Gardoqui Arriquibar (1735–1798) was Spain's first Ambassador to the United States. Miguel de Unamuno was a noted novelist and philosopher of the late 19th and the 20th century.
See also
- Aberri Eguna
- Aquitani
- Basque code talkers
- Cro-Magnon
- Duchy of Vasconia
- French people
- Genetic history of Europe
- Iberians
- Late Basquisation
- List of Basques
- Nationalisms and regionalisms of Spain
- Spanish people
- Vascones
Footnotes
- ^ a b "Diáspora vasca, la octava provincia" [Basque diaspora, the eighth province] (in Spanish). eke.eus. Retrieved 2 November 2016: There are about 10 million Basque descendants who continue to live for their language and culture.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ a b V. inkesta soziolinguistikoa 2011 [V. Sociolinguistic Survey] (PDF) (in Basque). Vitoria-Gasteiz: Central Publications Service of the Basque Government. 2013. ISBN 978-84-457-3303-5. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ^ "INE". INE. 2013. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000: Table 1. First, Second, and Total Responses to the Ancestry Question by Detailed Ancestry Code: 2000" (XLS). U.S. Census Bureau. 22 January 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ^ "Basque". Britannica Online for Kids. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ "Basque". Oxford Reference online. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ Totoricaguena, Gloria Pilar (2004). Identity, Culture, and Politics in the Basque Diaspora. University of Nevada Press. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-87417-547-9. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ a b Günther, Torsten; et al. (2015). "Ancient genomes link early farmers from Atapuerca in Spain to modern-day Basques" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (38). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences: 11917–11922. doi:10.1073/pnas.1509851112. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ "Vascones - el nombre (Auñamendi Encyclopedia)". Euskomedia.org. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "The Basque Paradigm: Genetic Evidence of a Maternal Continuity in the Franco-Cantabrian region since Pre-Neolithic Times". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 90 (3): 486–493. March 9, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.01.002. PMC 3309182. PMID 22365151.
- ^ "See EUSKALTERM, the Basque Public Term Bank, maintained by the Basque Government for these and other terms and their common translations". .euskadi.net. Archived from the original on May 10, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Laín Entralgo, Pedro (January 1949). "Chile al trasluz" [Chile held up to the light] (in Spanish). Filosofia.org. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
'La Compañía de Jesús y la República de Chile son las dos grandes hazañas del pueblo vascongado', solía decir don Miguel de Unamuno... [TRANS] Miguel de Unamuno used to say, 'The Company of Jesus and the Republic of Chile are the two great achievements of the Basque people...'
- ^ Douglass, William A.; Jon Bilbao (2005). Amerikanuak: Basques in the New World. University of Nevada Press. p. 81. ISBN 978-0-87417-625-4. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ "Basque Culture Day". Basqueed.org. 2007-10-06. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ http://www.euskomedia.org/PDFAnlt/riev/32/32443444.pdf
- ^ http://www.lehendakaritza.ejgv.euskadi.eus/r48-contcvpv/en/contenidos/informacion/03_andres_irujo/en_airujo/adjuntos/antioquia.pdf
- ^ Arturo Escobar Uribe (1950). Mitos de Antioquia. Introducción.
- ^ http://campus.usal.es/~investigacionesmusicales/docs/influencia.pdf
- ^ Ocampo López, J. (1990). Música folclor de Colombia (1st ed., pp. 47, 98). Bogotá, Colombia: Plaza Janés.
- ^ "Sociolinguistics". Eke.org. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Gallagher, Brendan (27 February 2002). "France look to Basque prodigy". telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ Aierdi Urraza, Xabier (24 July 2006). "Routes to linguistic and cultural integration for immigrants in the Basque Autonomous Community". euskara.euskadi.net. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Trask, Robert Lawrence (1997). The History of Basque. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-13116-2. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ Moreno Cabrera, Juan Carlos (19 October 2006). "Misconceptions about Basque". euskara.euskadi.net. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ MITXELENA, Koldo, Apellidos vascos (fifth edition), San Sebastián: Txertoa, 1997.
- ^ "Opinion poll on religion by GIZAKER" (PDF). EITB the Basque Country's public broadcast service. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Hadingham 1992. Note that Logroño is not a Basque town, but it was the see of the diocesis covering Zugarramurdi in 1610. The Spanish Inquisition rarely acted against witches, devoting most of its attention to Judaizers, Moriscos and Protestants.
- ^ Gimbutas, M. The Living Goddesses University of California Press: 2001
- ^ Collins, R. The Basques Blackwell: 1986
- ^ "Athletic Club sporting philosophy". Athletic-club.net. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "64% des maires basques favorables à un département Pays Basque". Maire-info.com. 2 Nov 2005. Retrieved 3 August 2012.
- ^ Resolution of the General Assembly of the European Bureau for Lesser Used Languages, 13 September 2003 (Helsinki), on the situation of the Basque language in the Autonomous Community of Navarre. Reported in MERCATOR Butlleti 55: "Speakers of a regional or minority language should have the right to use their language in private and public life. Contrary to these principles, local authorities from Iruña/Pamplona (capital city of the Autonomous Community of Navarre in Spain) have been implementing a series of reforms to the Autonomous Community legislation limiting the use of the Basque language. Basque is the only endangered language in the Autonomous Community of Navarre..."
- ^ "EITB: ''Basque parliament adopts resolution on self-determination''". Eitb24.com. Retrieved 2014-03-12.
- ^ "Evolución de la identidad nacional subjetiva de los vascos, 1981-2006" [Evolution of the subjective national identity of the Basques, 1981-2006] (in Spanish). Euskobarómetro. 2007. Archived from the original on 22 June 2007: 33% of the Basque Autonomous Community in late 2006 identified as only being Basque.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Wells, H. G. The Outline of History New York: 1920, Doubleday & Co., Volume I, Chapter XI "The Races of Mankind," Pages 131-144 See Pages 98, 137, and 139
- ^ ^ Cavalli-Sforza, L. Luca; Menozzi, Paolo; and Piazza Alberto. The History and Geography of Human Genes Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 1994, p. 280
- ^ a b c d Dupanloup, I.; et al. (2004). "Estimating the Impact of Prehistoric Admixture on the Genome of Europeans" (PDF). Molecular Biology and Evolution. 21 (7). Oxford University Press: 1361–1372. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh135. PMID 15044595. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ Pericic, M.; et al. (2005). "High-Resolution Phylogenetic Analysis of Southeastern Europe Traces Major Episodes of Paternal Gene Flow Among Slavic Populations" (PDF). Molecular Biology and Evolution. 22 (10). Oxford University Press: 1964–1975. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi185. PMID 15944443. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ a b c Alonso, Santos; et al. (2005). "The place of the Basques in the European Y-chromosome diversity landscape" (PDF). European Journal of Human Genetics. 13 (12). Springer Nature: 1293–1302. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201482. PMID 16094307. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ Li, J. Z.; Absher, D. M.; Tang, H.; Southwick, A. M.; Casto, A. M.; Ramachandran, S.; Cann, H. M.; Barsh, G. S.; Feldman, M. (2008). "Worldwide Human Relationships Inferred from Genome-Wide Patterns of Variation". Science. 319 (5866): 1100–4. Bibcode:2008Sci...319.1100L. doi:10.1126/science.1153717. PMID 18292342.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Genetic Legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in Extant Europeans: A Y Chromosome Perspective". Sciencemag.org. 2000-11-10. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ^ "Y chromosome genetic variation in the Italian peninsula is clinal and supports an admixture model for the Mesolithic-Neolithic encounter". Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 44: 228–39. 2013-01-30. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.11.030. PMID 17275346.
- ^ Balaresque, Patricia; Bowden, Georgina R.; Adams, Susan M.; Leung, Ho-Yee; King, Turi E.; et al. (2010). Penny, David (ed.). "A Predominantly Neolithic Origin for European Paternal Lineages". PLOS Biology. 8 (1). Public Library of Science: e1000285. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000285. PMC 2799514. PMID 20087410. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Arredi, Barbara; Estella S Poloni; Chris Tyler-Smith (2007). "13. The Peopling of Europe". In Michael H. Crawford (ed.). Anthropological Genetics: Theory, Methods and Applications (PDF). Cambridge University Press. pp. 380–408. ISBN 978-0-521-54697-3. Retrieved 3 November 2016.[page needed]
- ^ Myres, Natalie M.; et al. (2010). "A major Y-chromosome haplogroup R1b Holocene era founder effect in Central and Western Europe" (PDF). European Journal of Human Genetics. 19 (1). Springer Nature: 95–101. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.146. PMC 3039512. PMID 20736979. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ Sjödin, Per; Olivier François (2011). "Wave-of-Advance Models of the Diffusion of the Y Chromosome Haplogroup R1b1b2 in Europe" (PDF). PLoS ONE. 6 (6). Public Library of Science: e21592. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021592. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, Naiara; et al. (2010). "High-density SNP genotyping detects homogeneity of Spanish and French Basques, and confirms their genomic distinctiveness from other European populations". Human Genetics. 128 (1): 113–7. doi:10.1007/s00439-010-0833-4. PMID 20443121.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - ^ Levy-Coffman, Ellen (17 August 2006). "We Are Not Our Ancestors: Evidence for Discontinuity between Prehistoric and Modern Europeans". Journal of Genetic Genealogy. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ González, Ana M.; Oscar García; José M. Larruga; Vicente M. Cabrera (23 May 2006). "The mitochondrial lineage U8a reveals a Paleolithic settlement in the Basque country". BMC Genomics. 7 (1): 124. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-124. PMC 1523212. PMID 16719915. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Grant, Bob (9 September 2015). "Ancient DNA Elucidates Basque Origins". the-scientist.com. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ^ "Ancient DNA cracks puzzle of Basque origins". BBC.com. 7 September 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ^ "Ancient genomes link early farmers to Basques". phys.org. 7 September 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
References
- The Basques, the Catalans and Spain, Daniele Conversi, 2000, ISBN 1-85065-268-6.
- The Basque History of the World, Mark Kurlansky, 1999, ISBN 0-8027-1349-1.
- The Oldest Europeans, J.F. del Giorgio, A.J.Place, 2006, ISBN 980-6898-00-1.
- Ethnologue report for France for population statistics in France.
- Euskal Herria en la Prehistoria, Xabier Peñalver Iribarren, 1996, ISBN 84-89077-58-4.
- Gimbutas, Marija, The Living Goddesses (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2001).
- Hadingham, Evan (September 1992). "Europe's Mystery People". World Monitor. 5 (9).
- Hamilton, Carrie (2000). "Re-membering the Basque nationalist family: Daughters, fathers and the reproduction of the radical nationalist community". Journal of Spanish Cultural Studies. 1 (2): 153–71. doi:10.1080/713683438.
External links
- Basque Autonomous Government
- 8 Probintziak. Non profit association working with the basques in the world
- Oroitzapenak Voices From Basque America, University of Nevada, Reno, Special Collections.
- Basque Digital Collection, University of Nevada, Reno Special Collections
- Sheepherders of Northern Nevada, University of Nevada, Reno, Special Collections
- Basque Posters, University of Nevada, Reno, Special Collections
- Voices from Basque America University of Nevada, Reno Libraries
- Basque Country (greater region)
- Basque people
- Ethnic groups divided by international borders
- Ethnic groups in Argentina
- Ethnic groups in Chile
- Ethnic groups in Europe
- Ethnic groups in France
- Ethnic groups in Mexico
- Ethnic groups in South America
- Ethnic groups in Spain
- Ethnic groups in Uruguay
- Indigenous peoples of Europe
- Ethnic groups in Cuba
- Pre-Indo-Europeans
