D: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 72.69.88.118 to last version by Hydrogen Iodide (HG) |
Pizza12456 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
{{Latin alphabet navbox|uc=D|lc=d}} |
{{Latin alphabet navbox|uc=D|lc=d}} |
||
'''D''' is the fourth letter in the [[Latin alphabet]]. Its name in [[English language|English]] is spelled '''dee''' ({{pronEng|diː}}), plural '''dees'''.<ref>"D" ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "dee", ''op. cit.''</ref> |
'''D''' is the fourth letter in the [[Latin alphabet]]. Its name in [[English language|English]] is spelled '''dee''' ({{pronEng|diː}}), plural '''dees'''.<ref>"D" ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "dee", ''op. cit.''</ref> |
||
For example, this letter is used at the beginnin of this word: Danny |
|||
== History == |
== History == |
||
Revision as of 22:48, 17 December 2008
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |
D is the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet. Its name in English is spelled dee (Template:PronEng), plural dees.[1] For example, this letter is used at the beginnin of this word: Danny
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph door |
Proto-Semitic Dal, Daleth |
Phoenician Daleth |
Etruscan D |
Greek Delta |
Roman D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
 
|

|

|
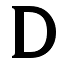
|
The Semitic letter Dâlet probably developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are various Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek, and Latin, the letter was pronounced /d/; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was superfluous, but still maintained (see letter B). Greek letter: Δ (capital) or δ (small) (Delta).[citation needed]
The minuscule (lower-case) form of D consists of a loop and a tall vertical stroke. It developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This serif was extended while the rest of the letter was reduced, resulting in an angled stroke and loop. The angled stroke slowly developed into a vertical stroke.
Usage
In most languages using the Latin alphabet, the letter d represents the sound /d/, but in the Vietnamese alphabet it represents the sound /z/ in the north and /j/ in the south. At the end of German words, d represents /t/. In Fijian it stands for the prenasalized stop /nd/. In some languages where voiceless unaspirated stops contrast with voiceless aspirated stops, d represents an unaspirated /t/, while t represents an aspirated /tʰ/. Examples of such languages include Icelandic, Scottish Gaelic, Navajo, and the Pinyin transliteration of Mandarin.
Codes for computing
class="template-letter-box | In Unicode the capital D is codepoint U+0044 and the lower case d is U+0064.
The ASCII code for capital D is 68 and for lower case d is 100; or in binary 01000100 and 01100100, respectively.
The EBCDIC code for capital D is 196 and for lowercase d is 132.
The numeric character references in HTML and XML are "D" and "d" for upper and lower case, respectively.
See also
- Eth (Ð, ð)
- D with stroke (Đ, đ)
- Hooked D (Ɗ, ɗ)
- Д, д - De (Cyrillic)
References
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2007) |
- ^ "D" Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "dee", op. cit.
