Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Haeckel | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 16 February 1834 |
| Died | 9 August 1919 (aged 85) |
| Nationality | |
| Awards | Linnean Medal (1894) Darwin–Wallace Medal (Silver, 1908) |
| Scientific career | |
| Author abbrev. (zoology) | Haeckel |




Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (German: [ˈhɛkəl]; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919[1]) was a German biologist, naturalist, philosopher, physician, professor, and artist who discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms, and coined many terms in biology, including anthropogeny, ecology, phylum, phylogeny, stem cell, and Protista. Haeckel promoted and popularised Charles Darwin's work in Germany and developed the influential but no longer widely held recapitulation theory ("ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny") claiming that an individual organism's biological development, or ontogeny, parallels and summarises its species' evolutionary development, or phylogeny.
The published artwork of Haeckel includes over 100 detailed, multi-colour illustrations of animals and sea creatures (see: Kunstformen der Natur, "Art Forms of Nature"). As a philosopher, Ernst Haeckel wrote Die Welträtsel (1895–1899; in English: The Riddle of the Universe, 1901), the genesis for the term "world riddle" (Welträtsel); and Freedom in Science and Teaching[2] to support teaching evolution.
Life
Ernst Haeckel was born on 16 February 1834, in Potsdam (then part of Prussia). [3] In 1852, Haeckel completed studies at the Domgymnasium, the cathedral high school of Merseburg.[3] He then studied medicine in Berlin and Würzburg, particularly with Albert von Kölliker, Franz Leydig, Rudolf Virchow (with whom he later worked briefly as assistant), and with the anatomist-physiologist Johannes Peter Müller (1801–1858).[3] Together with Hermann Steudner he attended botany lectures in Würzburg. In 1857, Haeckel attained a doctorate in medicine, (M.D.), and afterwards he received a license to practice medicine. The occupation of physician appeared less worthwhile to Haeckel, after contact with suffering patients.[3]
Haeckel studied under Karl Gegenbaur at the University of Jena for three years, earning a doctorate in zoology,[3] before becoming a professor of comparative anatomy at the University of Jena, where he remained for 47 years, from 1862 to 1909. Between 1859 and 1866, Haeckel worked on many phyla such radiolarians, poriferans (sponges) and annelids (segmented worms).[4] During a trip to the Mediterranean, Haeckel named nearly 150 new species of radiolarians.[4]
From 1866 to 1867, Haeckel made an extended journey to the Canary Islands with Hermann Fol and during this period, met with Charles Darwin, in 1866 at Down House in Kent, Thomas Huxley and Charles Lyell.[clarification needed][3] In 1867, he married Agnes Huschke. Their son Walter was born in 1868, their daughters Elizabeth in 1871 and Emma in 1873.[3] In 1869, he traveled as a researcher to Norway, in 1871 to Croatia (lived on the island of Hvar in a monastery),[5] and in 1873 to Egypt, Turkey, and to Greece.[3] Haeckel retired from teaching in 1909, and in 1910 he withdrew from the Evangelical church.[3]
On the occasion of his 80th birthday celebration, he was presented with a two volume work, entitled Was wir Ernst Haeckel verdanken (What We Owe to Ernst Haeckel), edited at the request of the German Monistenbund by Heinrich Schmidt of Jena.[6][7]
Haeckel's wife, Agnes, died in 1915, and Haeckel became substantially frailer, with a broken leg (thigh) and broken arm.[3] He sold his "Villa Medusa" in Jena in 1918 to the Carl Zeiss foundation, and it presently contains a historic library.[3] Haeckel died on 9 August 1919.
Politics
Haeckel's political beliefs were influenced by his affinity for the German Romantic movement coupled with his acceptance of a form of Lamarckism. Rather than being a strict Darwinian, Haeckel believed that the characteristics of an organism were acquired through interactions with the environment and that ontogeny reflected phylogeny. He believed the social sciences to be instances of "applied biology", and that phrase was picked up and used for Nazi propaganda.[4] In 1905, Haeckel founded a group called the Monist League (Deutscher Monistenbund) to promote his religious and political beliefs. This group lasted until 1933 and included such notable members as Wilhelm Ostwald, Georg von Arco, Helene Stöcker and Walter Arthur Berendsohn.[8]
"First World War"
Haeckel was the first person known to use the term "First World War". Shortly after the start of the war Haeckel wrote:
There is no doubt that the course and character of the feared "European War"...will become the first world war in the full sense of the word.
— Indianapolis Star, 20 September 1914[9]
The "European War" became known as "The Great War", and it was not until 1920, in the book "The First World War 1914–1918" by Charles à Court Repington, that the term "First World War" was used as the official name for the conflict.
Research
Haeckel was a zoologist, an accomplished artist and illustrator, and later a professor of comparative anatomy. Although Haeckel's ideas are important to the history of evolutionary theory, and although he was a competent invertebrate anatomist most famous for his work on radiolaria, many speculative concepts that he championed are now considered incorrect. For example, Haeckel described and named hypothetical ancestral microorganisms that have never been found.
He was one of the first to consider psychology as a branch of physiology. He also proposed the kingdom Protista[3] in 1866. His chief interests lay in evolution and life development processes in general, including development of nonrandom form, which culminated in the beautifully illustrated Kunstformen der Natur (Art forms of nature). Haeckel did not support natural selection, rather believing in Lamarckism.[10]
Haeckel advanced a version of the earlier recapitulation theory previously set out by Étienne Serres in the 1820s and supported by followers of Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire including Robert Edmond Grant.[11] It proposed a link between ontogeny (development of form) and phylogeny (evolutionary descent), summed up by Haeckel in the phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny". His concept of recapitulation has been refuted in the form he gave it (now called "strong recapitulation"), in favour of the ideas first advanced by Karl Ernst von Baer. The strong recapitulation hypothesis views ontogeny as repeating forms of the ancestors, while weak recapitulation means that what is repeated (and built upon) is the ancestral embryonic development process.[12] Haeckel supported the theory with embryo drawings that have since been shown to be oversimplified and in part inaccurate, and the theory is now considered an oversimplification of quite complicated relationships. Haeckel introduced the concept of heterochrony, the change in timing of embryonic development over the course of evolution.
Haeckel was a flamboyant figure, who sometimes took great, non-scientific leaps from available evidence. For example, at the time when Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859), Haeckel postulated that evidence of human evolution would be found in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia). At that time, no remains of human ancestors had yet been found. He described these theoretical remains in great detail and even named the as-yet unfound species, Pithecanthropus alalus, and instructed his students such as Richard and Oskar Hertwig to go and find it.
One student did find some remains: a Dutchman named Eugène Dubois searched the East Indies from 1887 to 1895, discovering the remains of Java Man in 1891, consisting of a skullcap, thighbone, and a few teeth. These remains are among the oldest hominid remains ever found. Dubois classified Java Man with Haeckel's Pithecanthropus label, though they were later reclassified as Homo erectus. Some scientists of the day suggested[13] Dubois' Java Man as a potential intermediate form between modern humans and the common ancestor we share with the other great apes. The current consensus of anthropologists is that the direct ancestors of modern humans were African populations of Homo erectus (possibly Homo ergaster), rather than the Asian populations exemplified by Java Man and Peking Man.
Polygenism and racial theory
The creationist polygenism of Samuel George Morton and Louis Agassiz, which presented human races as separately created species, was rejected by Charles Darwin, who argued for the monogenesis of the human species and the African origin of modern humans. In contrast to most of Darwin's supporters, Haeckel put forward a doctrine of evolutionary polygenism based on the ideas of the linguist August Schleicher, in which several different language groups had arisen separately from speechless prehuman Urmenschen, which themselves had evolved from simian ancestors. These separate languages had completed the transition from animals to man, and, under the influence of each main branch of languages, humans had evolved – in a kind of Lamarckian use-inheritance – as separate species, which could be subdivided into races. From this, Haeckel drew the implication that languages with the most potential yield the human races with the most potential, led by the Semitic and Indo-Germanic groups, with Berber, Jewish, Greco-Roman and Germanic varieties to the fore.[14] As Haeckel stated:[15]
- We must mention here one of the most important results of the comparative study of languages, which for the Stammbaum of the species of men is of the highest significance, namely that human languages probably had a multiple or polyphyletic origin. Human language as such probably developed only after the species of speechless Urmenschen or Affenmenschen had split into several species or kinds. With each of these human species, language developed on its own and independently of the others. At least this is the view of Schleicher, one of the foremost authorities on this subject.… If one views the origin of the branches of language as the special and principal act of becoming human, and the species of humankind as distinguished according to their language stem, then one can say that the different species of men arose independently of one another.
Haeckel's view can be seen as a forerunner of the views of Carleton Coon, who also believed that human races evolved independently and in parallel with each other. These ideas eventually fell from favour.
Haeckel also applied the hypothesis of polygenism to the modern diversity of human groups. He became a key figure in social darwinism and leading proponent of scientific racism, stating for instance:[16]
- The Caucasian, or Mediterranean man (Homo Mediterraneus), has from time immemorial been placed at the head of all the races of men, as the most highly developed and perfect. It is generally called the Caucasian race, but as, among all the varieties of the species, the Caucasian branch is the least important, we prefer the much more suitable appellation proposed by Friedrich Müller, namely, that of Mediterranese. For the most important varieties of this species, which are moreover the most eminent actors in what is called "Universal History," first rose to a flourishing condition on the shores of the Mediterranean.… This species alone (with the exception of the Mongolian) has had an actual history; it alone has attained to that degree of civilisation which seems to raise men above the rest of nature.
Haeckel divided human beings into ten races, of which the Caucasian was the highest and the primitives were doomed to extinction.[17] Haeckel claimed that Negros have stronger and more freely movable toes than any other race which is evidence that Negros are related to apes because when apes stop climbing in trees they hold on to the trees with their toes, Haeckel compared Negros to "four-handed" apes. Haeckel also believed Negros were savages and that Whites were the most civilised.[18]
However, Robert J. Richards notes: "Haeckel, on his travels to Ceylon and Indonesia, often formed closer and more intimate relations with natives, even members of the untouchable classes, than with the European colonials."[19]
In his Ontology and Phylogeny Harvard paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould wrote: "[Haekel's] evolutionary racism; his call to the German people for racial purity and unflinching devotion to a "just" state; his belief that harsh, inexorable laws of evolution ruled human civilization and nature alike, conferring upon favored races the right to dominate others . . . all contributed to the rise of Nazism."[20]
In Alfred Rosenberg's The Myth of the Twentieth Century, Rosenberg explicitly mentions having read Haeckel.[citation needed]
In the same line of thought, historian Daniel Gasman states that Haeckel's ideology stimulated the birth of Fascist ideology in Italy and France.[21]
Asia hypothesis
Haeckel claimed the origin of humanity was to be found in Asia: he believed that Hindustan (Indian Subcontinent) was the actual location where the first humans had evolved. Haeckel argued that humans were closely related to the primates of Southeast Asia and rejected Darwin's hypothesis of Africa.[22][23]
Haeckel later claimed that the missing link was to be found on the lost continent of Lemuria located in the Indian Ocean, he believed that Lemuria was the home of the first humans and that Asia was the home of many of the earliest primates, he thus supported that Asia was the cradle of hominid evolution. Haeckel also claimed that Lemuria connected Asia and Africa which allowed the migration of humans to the rest of the world.[24][25]
In Haeckel’s book The History of Creation (1884) he included migration routes which he thought the first humans had used outside of Lemuria.
Embryology and recapitulation theory

When Haeckel was a student in the 1850s he showed great interest in embryology, attending the rather unpopular lectures twice and in his notes sketched the visual aids: textbooks had few illustrations, and large format plates were used to show students how to see the tiny forms under a reflecting microscope, with the translucent tissues seen against a black background. Developmental series were used to show stages within a species, but inconsistent views and stages made it even more difficult to compare different species. It was agreed by all European evolutionists that all vertebrates looked very similar at an early stage, in what was thought of as a common ideal type, but there was a continuing debate from the 1820s between the Romantic recapitulation theory that human embryos developed through stages of the forms of all the major groups of adult animals, literally manifesting a sequence of organisms on a linear chain of being, and Karl Ernst von Baer's opposing view that the early general forms diverged into four major groups of specialised forms without ever resembling the adult of another species, showing affinity to an archetype but no relation to other types or any transmutation of species. By the time Haeckel was teaching he was able to use a textbook with woodcut illustrations written by his own teacher Albert von Kölliker, which purported to explain human development while also using other mammalian embryos to claim a coherent sequence. Despite the significance to ideas of transformism, this was not really polite enough for the new popular science writing, and was a matter for medical institutions and for experts who could make their own comparisons.[27]: 264–267 [28]
Darwin, Naturphilosophie and Lamarck
Darwin's On the Origin of Species, which made a powerful impression on Haeckel when he read it in 1864, was very cautious about the possibility of ever reconstructing the history of life, but did include a section reinterpreting von Baer's embryology and revolutionising the field of study, concluding that "Embryology rises greatly in interest, when we thus look at the embryo as a picture, more or less obscured, of the common parent-form of each great class of animals." It mentioned von Baer's 1828 anecdote (misattributing it to Louis Agassiz) that at an early stage embryos were so similar that it could be impossible to tell whether an unlabelled specimen was of a mammal, a bird, or of a reptile, and Darwin's own research using embryonic stages of barnacles to show that they are crustaceans, while cautioning against the idea that one organism or embryonic stage is "higher" or "lower", or more or less evolved.[29] Haeckel disregarded such caution, and in a year wrote his massive and ambitious Generelle Morphologie, published in 1866, presenting a revolutionary new synthesis of Darwin's ideas with the German tradition of Naturphilosophie going back to Goethe and with the progressive evolutionism of Lamarck in what he called Darwinismus. He used morphology to reconstruct the evolutionary history of life, in the absence of fossil evidence using embryology as evidence of ancestral relationships. He invented new terms, including ontogeny and phylogeny, to present his evolutionised recapitulation theory that "ontogeny recapitulated phylogeny". The two massive volumes sold poorly, and were heavy going: with his limited understanding of German, Darwin found them impossible to read. Haeckel's publisher turned down a proposal for a "strictly scholarly and objective" second edition.[27]: 269–270
Embryological drawings
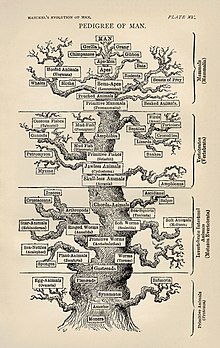
Haeckel's aim was a reformed morphology with evolution as the organising principle of a cosmic synthesis unifying science, religion, and art. He was giving successful "popular lectures" on his ideas to students and townspeople in Jena, in an approach pioneered by his teacher Rudolf Virchow. To meet his publisher's need for a popular work he used a student's transcript of his lectures as the basis of his Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte of 1868, presenting a comprehensive presentation of evolution. In the Spring of that year he drew figures for the book, synthesising his views of specimens in Jena and published pictures to represent types. After publication he told a colleague that the images "are completely exact, partly copied from nature, partly assembled from all illustrations of these early stages that have hitherto become known." There were various styles of embryological drawings at that time, ranging from more schematic representations to "naturalistic" illustrations of specific specimens. Haeckel believed privately that his figures were both exact and synthetic, and in public asserted that they were schematic like most figures used in teaching. The images were reworked to match in size and orientation, and though displaying Haeckel's own views of essential features, they support von Baer's concept that vertebrate embryos begin similarly and then diverge. Relating different images on a grid conveyed a powerful evolutionary message. As a book for the general public, it followed the common practice of not citing sources.[27]: 270–274

The book sold very well, and while some anatomical experts hostile to Haeckel's evolutionary views expressed some private concerns that certain figures had been drawn rather freely, the figures showed what they already knew about similarities in embryos. The first published concerns came from Ludwig Rütimeyer, a professor of zoology and comparative anatomy at the University of Basel who had placed fossil mammals in an evolutionary lineage early in the 1860s and had been sent a complimentary copy. At the end of 1868 his review in the Archiv für Anthropologie wondered about the claim that the work was "popular and scholarly", doubting whether the second was true, and expressed horror about such public discussion of man's place in nature with illustrations such as the evolutionary trees being shown to non-experts. Though he made no suggestion that embryo illustrations should be directly based on specimens, to him the subject demanded the utmost "scrupulosity and conscientiousness" and an artist must "not arbitrarily model or generalise his originals for speculative purposes" which he considered proved by comparison with works by other authors. In particular, "one and the same, moreover incorrectly interpreted woodcut, is presented to the reader three times in a row and with three different captions as [the] embryo of the dog, the chick, [and] the turtle." He accused Haeckel of "playing fast and loose with the public and with science", and failing to live up to the obligation to the truth of every serious researcher. Haeckel responded with angry accusations of bowing to religious prejudice, but in the second (1870) edition changed the duplicated embryo images to a single image captioned "embryo of a mammal or bird". Duplication using galvanoplastic stereotypes (clichés) was a common technique in textbooks, but not on the same page to represent different eggs or embryos. In 1891 Haeckel made the excuse that this "extremely rash foolishness" had occurred in undue haste but was "bona fide", and since repetition of incidental details was obvious on close inspection, it is unlikely to have been intentional deception.[27]: 275–276, 282–286
The revised 1870 second edition of 1,500 copies attracted more attention, being quickly followed by further revised editions with larger print runs as the book became a prominent part of the optimistic, nationalist, anticlerical "culture of progress" in Otto von Bismarck's new German Empire. The similarity of early vertebrate embryos became common knowledge, and the illustrations were praised by experts such as Michael Foster of the University of Cambridge. In the introduction to his 1871 The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex, Darwin gave particular praise to Haeckel, writing that if Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte "had appeared before my essay had been written, I should probably never have completed it." The first chapter included an illustration: "As some of my readers may never have seen a drawing of an embryo, I have given one of man and another of a dog, at about the same early stage of development, carefully copied from two works of undoubted accuracy" with a footnote citing the sources and noting that "Häckel has also given analogous drawings in his Schöpfungsgeschichte." The fifth edition of Haeckel's book appeared in 1874, with its frontispiece a heroic portrait of Haeckel himself, replacing the previous controversial image of the heads of apes and humans.[27]: 285–288 [30]

Controversy
Later in 1874, Haeckel's simplified embryology textbook Anthropogenie made the subject into a battleground over Darwinism aligned with Bismarck's Kulturkampf ("culture struggle") against the Catholic Church. Haeckel took particular care over the illustrations, changing to the leading zoological publisher Wilhelm Engelmann of Leipzig and obtaining from them use of illustrations from their other textbooks as well as preparing his own drawings including a dramatic double page illustration showing "early", "somewhat later" and "still later" stages of 8 different vertebrates. Though Haeckel's views had attracted continuing controversy, there had been little dispute about the embryos and he had many expert supporters, but Wilhelm His revived the earlier criticisms and introduced new attacks on the 1874 illustrations.[31] Others joined in, both expert anatomists and Catholic priests and supporters were politically opposed to Haeckel's views.[27]: 288–296
While it has been widely claimed that Haeckel was charged with fraud by five professors and convicted by a university court at Jena, there does not appear to be an independently verifiable source for this claim.[32] Recent analyses (Richardson 1998, Richardson and Keuck 2002) have found that some of the criticisms of Haeckel's embryo drawings were legitimate, but others were unfounded.[33][34] There were multiple versions of the embryo drawings, and Haeckel rejected the claims of fraud. It was later said that "there is evidence of sleight of hand" on both sides of the feud between Haeckel and Wilhelm His.[35] Robert J. Richards, in a paper published in 2008, defends the case for Haeckel, shedding doubt against the fraud accusations based on the material used for comparison with what Haeckel could access at the time.[36] The controversy involves several different issues (see more details at: recapitulation theory).
Awards and honors
He was awarded the title of Excellency by Kaiser Wilhelm II in 1907[37] and the Linnean Society of London's prestigious Darwin-Wallace Medal in 1908. In the United States, Mount Haeckel, a 13,418 ft (4,090 m) summit in the Eastern Sierra Nevada, overlooking the Evolution Basin, is named in his honour, as is another Mount Haeckel, a 2,941 m (9,649 ft) summit in New Zealand; and the asteroid 12323 Haeckel.
Publications



Darwin's 1859 book On the Origin of Species had immense popular influence, but although its sales exceeded its publisher's hopes it was a technical book rather than a work of popular science: long, difficult and with few illustrations. One of Haeckel's books did a great deal to explain his version of "Darwinism" to the world. It was a bestselling, provocatively illustrated book in German, titled Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte, published in Berlin in 1868, and translated into English as The History of Creation in 1876. It was frequently reprinted until 1926.
Haeckel argued that human evolution consisted of precisely 22 phases, the 21st – the "missing link" — being a halfway step between apes and humans. He even formally named this missing link Pithecanthropus alalus, translated as "ape man without speech."
Haeckel's entire literary output was extensive, working as a professor at the University of Jena for 47 years, and even at the time of the celebration of his 60th birthday at Jena in 1894, Haeckel had produced 42 works with nearly 13,000 pages, besides numerous scientific memoirs and illustrations.[38] Haeckel's monographs include:
- Radiolaria (1862)
- Siphonophora (1869)
- Monera (1870)
- Calcareous Sponges (1872)
As well as several Challenger reports:
- Deep-Sea Medusae (1881)
- Siphonophora (1888)
- Deep-Sea Keratosa (1889)
- Radiolaria (1887) — illustrated with 140 plates and enumerating over four thousand (4000) new species.[38]
Among his many books, Ernst Haeckel wrote:
- Generelle Morphologie der Organismen : allgemeine Grundzüge der organischen Formen-Wissenschaft, mechanisch begründet durch die von Charles Darwin reformirte Descendenz-Theorie. (1866) Berlin
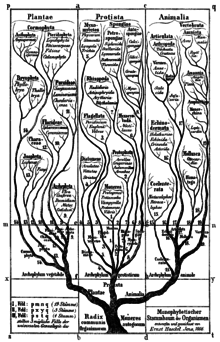
'Monophyletischer Stambaum der Organismen' from 'Generelle Morphologie der Organismen' (1866) with the three branches Plantae, Protista, Animalia. - Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte (1868); in English The History of Creation (1876; 6th ed.: New York, D. Appleton and Co., 1914, 2 volumes)
- Freie Wissenschaft und freie Lehre (1877), in English, Freedom in Science and Teaching, a reply to a speech in which Rudolf Virchow objected to the teaching of evolution in schools, on the grounds that evolution was an unproven hypothesis.[38]
- Die systematische Phylogenie (1894) — "Systematic Phylogeny", which has been considered as his best book[38]
- Anthropogenie: oder, Entwickelungsgeschichte des Menschen ("Anthropogeny: Or, the Evolutionary History of Man", 1874, 5th and enlarged edition 1903)
- Die Welträthsel (1895–1899), also spelled Die Welträtsel ("world-riddle") — in English The Riddle of the Universe, 1901[38]
- Über unsere gegenwärtige Kenntnis vom Ursprung des Menschen (1898) — translated into English as The Last Link, 1898
- Der Kampf um den Entwickelungsgedanken (1905) — English version, Last Words on Evolution, 1906
- Die Lebenswunder (1904) — English The Wonders of Life[39] a supplement to the Riddle of the Universe
- Kristallseelen : Studien über das anorganische Leben (1917) Digital edition by the University and State Library Düsseldorf
Books of travel:
- Indische Reisebriefe (1882) — "Travel notes of India"
- Aus Insulinde: Malayische Reisebriefe (1901) — "Travel notes of Malaysia", the fruits of journeys to Ceylon and to Java
- Kunstformen der Natur (1904) — Art forms of Nature, with plates representing detailed marine animal forms Digital Edition (1924) 2. Aufl. of the University and State Library Düsseldorf.
- Wanderbilder (1905) — "Travel Images", with reproductions of his oil-paintings and water-color landscapes.[38]
- A visit to Ceylon
For a extensive list of works of and about Haeckel, see his entry in the Wikisource in German.
See also
- Dysteleology
- Embryology
- Francis Galton
- Haeckel's Tale, a horror film by John McNaughton, featuring a fictionalized version of Ernst Haeckel
- Heinrich Schmidt (philosopher)
- Karl Blossfeldt
- List of wildlife artists
- M. C. Escher
- Proteus (2004 film), an animated documentary by David Lebrun, largely focussing on Ernst Haeckel
- Haeckelites
Footnotes
- ^ "Ernst Haeckel – Britannica Concise" (biography) Encyclopædia Britannica Concise, 2006, Concise. Britannica.com webpage: CBritannica-Haeckel.
- ^ Freedom in Science and Teaching. German 1877, English 1879, ISBN 1-4102-1175-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Ernst Haeckel" (article),German Wikipedia, 26 October 2006, webpage: DE-Wiki-Ernst-Haeckel: last paragraph of "Leben" (Life) section.[better source needed]
- ^ a b c "Ernst Haeckel" (biography), UC Berkeley, 2004, webpage: BerkeleyEdu-Haeckel.
- ^ New York Times Haeckel Again Honored in Spite of Himself on his 80th Birthday, published: 22 February 1914
- ^ Felden, Emil [in German] (1914). "Felden Pastor an St. Martini Bremen" [Pastor of St. Martini Church, Bremen, Germany]. In Schmidt, Heinrich (ed.). Was wir Ernst Haeckel Verdanken (What We Owe to Ernst Haeckel): Ein buch der Verehrung und Dankbarkeit (in German). Vol. 2. Deutscher Monistenbund. Leipzig: Verlag Unesma G.m.b.H. pp. 125–128.
testimony of Emil Felden in Was wir Ernst Haeckel Verdanken, vol. ii, p. 125.
- ^ Carus, Paul (1914). The Open Court. Open Court Publishing Company. p. 385.
PROFESSOR Ernst Haeckel's celebration of his 80th birthday, ...on this occasion we note a work of two stately volumes, entitled Was wir Ernst Haeckel verdanken, edited at the request of the German Monistenbund by Heinrich Schmidt of Jena. (Image of p. 385 at Google Books)
{{cite book}}: External link in|quote= - ^ Health, Race and German Politics Between National Unification and Nazism by Paul Weindling, Cambridge University Press, 1993.,pgs. 46, 250
- ^ Fred R. Shapiro, ed. (2006). The Yale Book of Quotations. Yale University Press. p. 329. ISBN 978-0-300-10798-2. Retrieved 8 October 2008.
- ^ Ruse, M. 1979. The Darwinian Revolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Desmond 1989, pp. 53–53, 86–88, 337–340
- ^ Richardson and Keuck, (Biol. Review (2002), 77, pp. 495–528) show that it is a simplification to suppose that Haeckel held the recapitulation theory in its strong form. They quote Haeckel as saying "If [recapitulation] was always complete, it would be a very easy task to construct whole phylogeny on the basis of ontogeny. … There is certainly, even now, a number of lower vertebrate animals (e.g. some Anthozoa and Vermes) where we are authorised to interpret each embryological form directly as the historical representation or portrait-like silhouette of an extinct ancestral form. But in a great majority of animals, including man, this is not possible because the infinitely varied conditions of existence have led the embryonic forms themselves to be changed and to partly lose their original condition (Haeckel, 1903: pp. 435–436)"
- ^ The red ape: orang-utans and human origins, Jeffrey H. Schwartz
- ^ Richards, Robert W. (2008). The Tragic Sense of Life: Ernst Haeckel and the Struggle over Evolutionary Thought. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 259–260. ISBN 0-226-71214-1.
- ^ Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte (1868), p. 511; quoted after Robert J. Richards, "The linguistic creation of man: Charles Darwin, August Schleicher, Ernst Haeckel, and the Missing Link in Nineteenth-Century Evolutionary Theory".[1]
- ^ The History of Creation, 6th edition (1914), volume 2, page 429.
- ^ John P. Jackson, Nadine M. Weidman Race, Racism, and science: social impact and interaction, Rutgers University Press, 2005, p. 87
- ^ Gustav Jahoda, Images of savages: ancients [sic] roots of modern prejudice in Western culture, 1999, p. 83
- ^ Robert J. Richards, "Myth 19: That Darwin and Haeckel Were Complicit in Nazi Biology," in Ronald L. Numbers, ed., Galileo Goes to Jail and Other Myths About Science and Religioin, Harvard University Press, 2009, p. 174.,
- ^ Gould, S.J. Ontogeny and Phylogeny Cambridge MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press pp. 77-78
- ^ Daniel Gasman (1998). Haeckel's Monism and the Birth of Fascist Ideology. Volume 33 of Studies in Modern European History. Peter Lang Pub Incorporated. ISSN 0893-6897. ISBN 978-0-8204-4108-5
- ^ Prehistoric past: The four billion year history of life on earth, Douglas Palmer, p. 43
- ^ Human evolution, a guide to the debates, Brian Regal, p. 73-75
- ^ Asian Paleoanthropology: From Africa to China and beyond, Christopher J Norton, David R Braun, p. 4
- ^ From here to Eternity: Ernst Haeckel and the scientific faith, Mario A. Di Gregorio p. 480
- ^ Richardson MK, Hanken J, Selwood L, Wright GM, Richards RJ, Pieau C, Raynaud A (1998). "Letters". Science. 280 (5366): 983, 985–6. doi:10.1126/science.280.5366.983c. PMID 9616084.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f Hopwood, N (June 2006). "Pictures of evolution and charges of fraud: Ernst Haeckel's embryological illustrations" (PDF). Isis; an international review devoted to the history of science and its cultural influences. 97 (2): 260–301. doi:10.1086/504734. PMID 16892945.
- ^ Darwin & Costa 2009, p. 450
- ^ Darwin 1859, pp. 439–450
Darwin & Costa 2009, pp. 439–450 - ^ Darwin 1871, pp. 4, 14–17
- ^ Wilhelm His: Unsere Körperform und das physiologische Problem ihrer Entstehung. F.C.W. Vogel, Leipzig 1875.
- ^ Richards, Robert J. (2005), "Ernst Haeckel and the Struggles over Evolution and Religion", Annals of the History and Philosophy of Biology, 10, Universitätsverlag Göttingen: 89–115, ISBN 978-3-938616-39-0, retrieved 22 February 2016
- ^ Michael K. Richardson. 1998. "Haeckel's embryos continued." Science 281:1289, quoted in NaturalScience.com webpage Re: Ontogeny and phylogeny: A Letter from Richard Bassetti; Editor's note.
- ^ "While some criticisms of the drawings are legitimate, others are more tendentious", Richardson and Keuck "Haeckel's ABC of evolution and development", Biol. Rev. (2002), 77, pp. 495–528. Quoted from p. 495.
- ^ Richardson & Keuck 2001. See for example, their Fig. 7, showing His's drawing of the forelimb of a deer embryo developing a clef, compared with a similar drawing (Sakurai, 1906) showing the forelimb initially developing as a digital plate with rays. Richardson & Keuck say "Unfortunately His's embryos are mostly at later stages than the nearly identical early stage embryos illustrated by Haeckel [top row of Haeckel's drawing]. Thus they do not inform the debate and may themselves be disingenuous.", p. 518.
- ^ "Haeckel's embryos: fraud not proven",Robert J. Richards, Biol Philos (2009) 24:147–154 DOI 10.1007/s10539-008-9140-z [2]
- ^ "Kaiser Honors Haeckel". The New York Times. 9 March 1907. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f "Biography of Ernst Heinrich Haeckel, 1834–1919" (article), Missouri Association for Creation, Inc., based on 1911 Britannica, webpage: Gennet-Haeckel: life, career & beliefs.
- ^ Ernst Haeckel, The Wonders of Life: A Popular Study of Biological Philosophy (London, 1904, Watts & Co.)
- ^ International Plant Names Index. Haeckel.
Bibliography
- Charles Darwin (1859). On the Origin of Species (by Means of Natural Selection). London: John Murray. ISBN 84-206-5607-0.
- Charles Darwin (2003). The Origin of Species (with introduction by Julian Huxley). Signet Classics. ISBN 0-451-52906-5.
- Desmond, Adrian J. (1989). The politics of evolution: morphology, medicine, and reform in radical London. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-14374-0.
- Ernst Haeckel, Freedom in Science and Teaching (1879), reprint edition, University Press of the Pacific, February 2004, paperback, 156 pages, ISBN 1-4102-1175-4.
- Ernst Haeckel, The History of Creation (1868), translated by E. Ray Lankester, Kegan Paul, Trench & Co., London, 1883, 3rd edition, Volume 1.
- Ernst Haeckel, Kunstformen der Natur ("Art forms of Nature"), 1904, (from series published 1899–1904): over 100 detailed, multi-color illustrations of animals and sea creatures.
- Ernst Haeckel, Lebenswunder, Stuttgart, 1904.
- Ernst Haeckel, The Riddle of the Universe (Die Weltraetsel, 1895–1899), Publisher: Prometheus Books, Buffalo, NY, 1992, reprint edition, paperback, 405 pages, illustrated, ISBN 0-87975-746-9.
- Richard Milner, The Encyclopedia of Evolution: Humanity's Search for Its Origins, Henry Holt, 1993.
- Robert J. Richards, The Tragic Sense of Life: Ernst Haeckel and the Struggle over Evolutionary Thought, University of Chicago Press, 2008.
- Richardson, Michael K. (1998). "Haeckel's embryos continued". Science. 281 (5381): 1285–9. Bibcode:1998Sci...281.1285R. doi:10.1126/science.281.5381.1285j.
- Richardson, M. K. & Keuck, G. (2001) "A question of intent: when is a 'schematic' illustration a fraud?," Nature 410:144 (vol. 410, no. 6825, page 144), March 8, 2001.
- Richardson, M. K. & Keuck, G. (2002) Haeckel's ABC of evolution and development Biological Reviews (2002), 77: 495–528
- M. Ruse, The Darwinian Revolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1979.
- Newman, H.H., 1932, 3rd edition, Evolution, Genetics, and Eugenics, Chicago: University of Chicago Press, p. 30
- G.G. Simpson and W. Beck, An Introduction to Biology (New York: Harcourt Brace and World, 1965), p. 241
- New Scientist, 9/6/97, p. 23
- W. Bock, Book Review Science, May 1969, pp. 684–685
Further reading
- Carus, Paul. (1913). The Monism of “The Monist,” Compared with Professor Haeckel's Monism. The Monist. Vol. 23, No. 3. pp. 435–439.
- Di Gregorio, Mario A. From here to eternity: Ernst Haeckel and Scientific Faith, Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 2005, ISBN 3-525-56972-6
- Haeckel, Ernst. (1900). The Riddle of the Universe at the Close of the Nineteenth Century. Harper (reissued by Cambridge University Press, 2009; ISBN 978-1-108-00089-5)
- Haeckel, Ernst (translator: J. Gilchrist) (1910) The Confession of faith of a man of science. London: Watts & Co.
- Haeckel, Ernst, Art Forms from the Ocean: The Radiolarian Atlas of 1862, Prestel Verlag, 2005, ISBN 3-7913-3327-5.
- Works by Ernst Haeckel at Project Gutenberg.
- Hopwood, Nick (2014). Haeckel's Embryos: Images, Evolution, and Fraud. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-04694-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - Richardson, Michael K., "Haeckel, embryos, and evolution," Science Vol. 280, no. 5366 (15 May 1998) p. 983, 985–986.
- Spiro, Jonathan P. (2009). Defending the Master Race: Conservation, Eugenics, and the Legacy of Madison Grant. Univ. of Vermont Press. ISBN 978-1-58465-715-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help)
External links
- E. Haeckel: Natürliche Schöpfungsgeschichte 1868 (front page of 1st edition, German)
- E. Haeckel: Die Welträthsel 1899 (front page of 1st edition, German)
- University of California, Berkeley — biography
- Ernst Haeckel – Evolution's controversial artist. A slide-show essay
- Kunstformen der Natur (from biolib.de)
- PNG alpha-transparencies of Haeckel's "Kustformen der natur"
- Proteus — Animated documentary film on Haeckel's life and work
- Ernst Haeckel Haus and Museum in Jena
- View works by Haeckel at the Biodiversity Heritage Library
- aDiatomea: artificial life experiment with 3d generated diatoms, influenced by Haeckel
- Images from Anthropogenie, oder, Entwickelungsgeschichte des menschen
- Works by Ernst Haeckel at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Ernst Haeckel at the Internet Archive
- Works by Ernst Haeckel at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- 1834 births
- 1919 deaths
- 19th-century philosophers
- Alldeutscher Verband members
- Evolutionary biologists
- German religious humanists
- German biologists
- German philosophers
- German zoologists
- People from Potsdam
- People from the Province of Brandenburg
- Protistologists
- Scientific racism
- University of Jena faculty
- White supremacists
- German male writers
- Lemuria
- 19th-century German writers


