Germans
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| 72,650,269[a] | |
| 534,000[b] c. 42,600,000[3] | |
| 357,000[c] | |
| 310,000[d] | |
| 233,000[e] | |
| 211,000[f] | |
| 203,000[g] | |
| 201,000[h] | |
| 157,000[i] c. 3,322,405[4] | |
| 142,000[j] c. 840,000[5] | |
| 125,000[k] 982,226[6] | |
| 101,000[l] 148,000 (of whom 45,000 declared solely German ethnicity)[7] | |
| 102,592[8] | |
| 36,000[m] c. 250,000[5] | |
| 25,000[n]
c. 200,000[o] | |
| 21,000[p] c. 3,000,000[10] | |
| 17,000[q]
c. 75,000[10] | |
| 9,000[r] c. 500,000[10] | |
| 7,000[s]
c. 90,000[t] | |
| c. 900,000[5] | |
| 8,537[12][13] | |
Germans (Template:Lang-de, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃə] ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, and sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language.[14][15] The constitution of Germany defines a German as a German citizen.[16] During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent and history.[17] Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity.[18] Estimates on the total number of Germans in the world range from 100 to 150 million, and most of them live in Germany.[19]
The history of Germans as an ethnic group began with the separation of a distinct Kingdom of Germany from the eastern part of the Frankish Empire under the Ottonian dynasty in the 10th century, forming the core of the Holy Roman Empire. In subsequent centuries the political power and population of this empire grew considerably. It expanded eastwards, and eventually a substantial number of Germans migrated further eastwards into Eastern Europe. The empire itself was politically divided between many small princedoms, cities and bishoprics. Following the Reformation in the 16th century, many of these states found themselves in bitter conflict concerning the rise of protestantism. The 19th century saw the dismemberment of the Holy Roman Empire and the growth of German nationalism. The kingdom of Prussia incorporated most of the Germans into its German Empire in 1871, while a substantial number of Germans also inhabited the multiethnic kingdom of Austria-Hungary. During this time a large number of Germans emigrated to the New World, particularly to the United States, Canada and Brazil, as well as establishing prominent communities in New Zealand and Australia. The Russian Empire also contained a substantial German population.
In the aftermath of World War I, Austria-Hungary and the German Empire were partitioned, resulting in many Germans becoming ethnic minorities in newly established countries. In the chaotic years that followed, Adolf Hitler became the dictator of Nazi Germany and embarked on a genocidal campaign to unify all Germans under his leadership. This endeavour resulted in World War II and the Holocaust. In the aftermath of Germany's defeat in the war, the country was occupied and partitioned. Millions of Germans were expelled from Eastern Europe. In 1990, the states of West and East Germany were reunified. In modern times, remembrance of the Holocaust has become an integral part of German identity (Erinnerungskultur).
Owing to their long history of political fragmentation, the Germans are culturally diverse and often have strong regional identities. The arts and sciences are an integral part of German culture, and the Germans have produced a large number of prominent personalities in a number of disciplines.
Names
The German endonym Deutsche is derived from the High German term diutisc, which means "ethnic" or "relating to the people". This name was used for Germanic peoples in Central Europe since the 8th century, during which a distinct German ethnic identity began to emerge among them.[20]
The English term Germans is derived from the ethnonym Germani, which was used for Germanic peoples in ancient times.[20][21] Since the early modern period, it has been the most common name for the Germans in English. The term "Germans" may also be applied to any citizen, native or inhabitant of Germany, a person of German descent,[15][14] or member of the Germanic peoples,[14][22][23][24][25] regardless of whether they are of German ethnicity.
History
Ancient history
Scholars generally agree that it is possible to speak of Germanic peoples after 500 BCE.[26] Archaeologists usually connect the early Germanic peoples with the Jastorf culture of the Pre-Roman Iron Age, which is found in northern Germany and Denmark from the 6th to 1st centuries BCE, around the same time that the first Germanic consonant shift is theorized to have occurred; this sound change lead to recognizably Germanic languages.[27][u] The Germanic peoples have inhabited Central Europe since at least the Iron Age.[20]
From their homes in Denmark and northern Germany the Germanic peoples began expanding south, east and west during the 1st century BC,[30] and came into contact with the Celtic tribes of Gaul, as well as with Iranian,[31] Baltic,[32] and Slavic cultures in Central/Eastern Europe.[33] Much of Central Europe was at that time inhabited by Celts, who are associated with the La Tène culture.[34] Since at least the 2nd century BC the Germanic peoples began displacing Celts.[35] It is likely that many of these Celts were assimilated by migrating Germanic peoples.[34]

The first information about the Germanic peoples is provided by the Roman general Julius Caesar, who campaigned in Germania in the 1st century BC. Under Caesar's successor Augustus, the Romans sought to conquer the Germanic peoples and colonize Germania, but these efforts were significantly hampered by the victory of Arminius at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, which is considered a defining moment in German history.[34] The early Germanic peoples are famously described in Germania by the 1st century Roman historian Tacitus. At this time, the Germanic peoples were fragmented into a large number of tribes who were frequently in conflict with both the Roman Empire and one another.[36] They are believed to have dominated an area stretching from the Rhine in the west to the Vistula in the east, and the Danube in the south to Scandinavia in the north. By the 3rd century, Germanic peoples were beginning to form into great coalitions, and had begun conquering and settling areas within the Roman Empire. During the 4th and 5th centuries, in what is known as the Migration Period, Germanic peoples seized control of the decaying Roman Empire and established new kingdoms within it. Meanwhile, formerly Germanic areas in parts of Eastern Europe were settled by Slavs.[35]
Medieval history
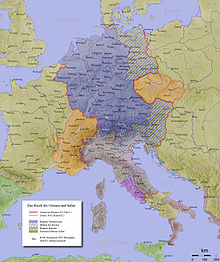
The German ethnicity emerged among Germanic peoples of Western and Central Europe, particularly the Franks, Frisians, Saxons, Thuringii, Alemanni and Baiuvarii.[34] The beginnings of the German states can be traced back to the Frankish king Clovis I, who established the kingdom of Francia in the 5th century. In subsequent centuries the power of the Franks grew considerably.[35] By the 8th century AD, the West Germanic speaking populations of continental Europe were known as diutisc, meaning "ethnic" or "relating to the people". The endonym of the Germans is derived from this word.[20]
By the early 9th century AD, large parts of Europe had been united under the rule of the Frankish leader Charlemagne, who expanded the Frankish empire in several directions including east of the Rhine, where he conquered Saxons and Frisians, thus establishing the Carolingian Empire. Charlemagne was crowned emperor by Pope Leo I in 800.[35] During the rule of Charlemagne's successors, this realm descended into civil war. The empire was partitioned at the Treaty of Verdun (843), resulting in the eventual separation between the states of West Francia, Middle Francia and East Francia. Beginning with Henry the Fowler, Saxon dynasties dominated the German lands, and under his son Otto I, Middle Francia and East Francia, which were mostly German, became part of the Kingdom of Germany, which constituted the core of the Holy Roman Empire.[37] Leaders of the "Stem duchies" which constituted it — Bavaria, Franconia, Swabia, and Saxony continued to wield considerable power independent of the king.[35] German kings were elected by members of the noble families, who often sought to have weak kings elected in order to preserve their own independence. This prevented an early unification of the Germans.[38][39]
A warrior nobility dominated the feudal German society of the Middle Ages, while most of the German population consisted of peasants with few political rights.[35] The church played an important role among Germans in the Middle Ages, and competed with the nobility for power.[40] Between the 11th and 13th centuries, Germans actively participated in five Crusades to "liberate" the Holy Land.[40]
During the Middle Ages, German political power was imposed on Polabian Slavs in the east. This process was accompanied by the migration of Germans into conquered territories, in what is known as the Ostsiedlung. Over time, some Slavic populations were assimilated by Germans, resulting in many Germans acquiring substantial Slavic ancestry.[37] From the 11th century, the German lands came under the domination of the Swabian Hohenstaufen family. The German population expanded significantly during this time.[39] Trade increased and there was a specialization of the arts and crafts.[40] From the 12th century, many Germans settled as merchants and craftsmen in the Kingdom of Poland, were they came to constitute a significant proportion of the population in many urban centers such as Gdańsk.[37]

The late 13th century saw the election of Rudolf I of the House of Habsburg to the German throne, and the Habsburg family would continue to play an important role in German history for centuries afterwards. They competed for power in the German lands with several noble families, most notably the Limburg-Luxemburg dynasty and the House of Wittelsbach. During the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights began conquering the Old Prussians, and established what would eventually become the powerful German state of Prussia.[39]
The German territories continued to grow in the late Middle Ages. Great urban centers increased in size and wealth and formed powerful leagues, such as the Hanseatic League and the Swabian League, in order to protect their interests, often through supporting the German kings in their struggles with the nobility.[39] These urban leagues significantly contributed to the development of German commerce and banking. German merchants of Hanseatic cities settled in cities throughout Northern Europe beyond the German lands.[41]
Modern history

The introduction of printing by the German inventor Johannes Gutenberg contributed to the formation of a new understanding of faith and reason. At this time, the German monk Martin Luther pushed for reforms within the Catholic Church. Luther's efforts culminated in the Protestant Reformation.[40] The resulting religious schism was a leading cause of the Thirty Years' War, a conflict that tore apart the Holy Roman Empire and led to the death of millions of Germans. The terms of the Peace of Westphalia (1648) ending the war, included a major reduction in the central authority of the Holy Roman Emperor.[42] Among the most powerful German states to emerge in the aftermath was Protestant Prussia, under the rule of the House of Hohenzollern.[43]
In the 18th century, German culture was significantly influenced by the Enlightenment.[42]
After centuries of political fragmentation, a sense of German unity began to emerge in the 18th century.[20] The Holy Roman Empire continued to decline until being dissolved altogether by Napoleon in 1806. In central Europe, the Napoleonic wars ushered in great social, political and economic changes, and catalyzed a national awakening among the Germans. By the late 18th century, German intellectuals such as Johann Gottfried Herder articulated the concept of a German identity rooted in language, and this notion helped spark the German nationalist movement, which sought to unify the Germans into a single nation state.[38] Eventually, shared ancestry, culture and language (though not religion) came to define German nationalism.[36] The Napoleonic Wars ended with the Congress of Vienna (1815), and left most of the German states loosely united under the German Confederation. The confederation came to be dominated by the Catholic Austrian Empire, to the dismay of many German nationalists, who saw the German Confederation as an inadequate answer to the German Question.[43]

Throughout the 19th century, Prussia continued to grow in power.[44] In 1848, German revolutionaries set up the temporary Frankfurt Parliament, but failed in their aim of forming a united German homeland. The Prussians proposed an Erfurt Union of the German states, but this effort was torpedoed by the Austrians through the Punctation of Olmütz (1850), recreating the German Confederation. In response, Prussia sought to use the Zollverein customs union to increase its power among the German states.[43] Under the leadership of Otto von Bismarck, Prussia expanded its sphere of influence and together with its German allies defeated Denmark in the Second Schleswig War and soon after Austria in the Austro-Prussian War, subsequently establishing the North German Confederation. In 1871, the Prussian coalition decisively defeated the Second French Empire in the Franco-Prussian War, annexing the German speaking region of Alsace-Lorraine. After taking Paris, Prussia and their allies proclaimed the formation of a united German Empire.[38]
In the years following unification, German society was radically changed by numerous processes, including industrialization, rationalization, secularization and the rise of capitalism.[44] German power increased considerably and numerous overseas colonies were established.[45] During this time, the German population grew considerably, and many emigrated to other countries (mainly North America), contributing to the growth of the German diaspora. Competition for colonies between the Great Powers contributed to the outbreak of World War I, in which the German, Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires formed the Central Powers, an alliance that was ultimately defeated, with none of the empires comprising it surviving the aftermath of the war. Under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, the German and Austro-Hungarian Empires were both dissolved and partitioned, resulting in millions of Germans becoming ethnic minorities in other countries.[46] The monarchical rulers of the German states, including the German emperor Wilhelm II, were overthrown in the November Revolution which led to the establishment of the Weimar Republic. The Germans of the Austrian side of the Dual Monarchy proclaimed the Republic of German-Austria, and sought to be incorporated into the German state, but this was forbidden by the Treaty of Versailles and Treaty of Saint-Germain.[45]

What many Germans saw as the "humiliation of Versailles",[47] continuing traditions of authoritarian and antisemitic ideologies,[44] and the Great Depression all contributed to the rise of Austrian-born Adolf Hitler and the Nazis, who after coming to power democratically in the early 1930s, abolished the Weimar Republic and formed the totalitarian Third Reich. In his quest to subjugate Europe, six million Jews were murdered in the Holocaust. WWII resulted in widespread destruction and the deaths of tens of millions of soldiers and civilians, while the German state was partitioned. About 12 million Germans had to flee or were expelled from Eastern Europe.[48] Significant damage was also done to the German reputation and identity,[46] which became far less nationalistic than it previously was.[47]
The German states of West Germany and East Germany became focal points of the Cold War, but were reunified in 1990. Although there were fears that the reunified Germany might resume nationalist politics, the country is today widely regarded as a "stablizing actor in the heart of Europe" and a "promoter of democratic integration".[47]
Language
German is the native language of most Germans. It is the key marker of German ethnic identity.[20][36] German is a West Germanic language closely related to Frisian, English and Dutch.[20] The main dialects of German are High German and Low German. Standard literary German is based on High German, and is the first or second language of most Germans, but notably not the Volga Germans.[49]
Culture

The Germans are marked by great regional diversity, which makes identifying a single German culture quite difficult.[50] The arts and sciences have for centuries been an important part of German identity.[51] The Age of Enlightenment and the Romantic era saw a notable flourishing of German culture. Germans of this period who contributed significantly to the arts and sciences include the writers Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Schiller, Johann Gottfried Herder, Friedrich Hölderlin, E. T. A. Hoffmann, Heinrich Heine, Novalis and the Brothers Grimm, the philosopher Immanuel Kant, the architect Karl Friedrich Schinkel, the painter Caspar David Friedrich, and the composers Johann Sebastian Bach, Ludwig van Beethoven, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Joseph Haydn, Johannes Brahms, Franz Schubert, Richard Strauss and Richard Wagner.[50]
Popular German dishes include brown bread and stew. Germans consume a high amount of alcohol, particularly beer, compared to other European peoples. Obesity is relatively widespread among Germans.[50]
Carnival is an important part of German culture, particularly in Southern Germany. An important German festival is the Oktoberfest.[50]
A steadily shrinking majority of Germans are Christians. About a third are Roman Catholics, while one third adheres to Protestantism. Another third does not profess any religion.[36] Christian holidays such as Christmas and Easter are celebrated by many Germans.[52] The number of Muslims is growing.[52] There is also a notable Jewish community, which was decimated in the Holocaust.[53] Remembering the Holocaust is an important part of German culture.[44]
Geographic distribution
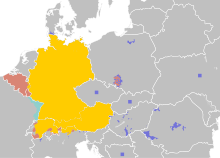
It is estimated that there are between 100 and 150 million Germans today, most of whom live in Germany, where they constitute the majority of the population.[54] There are also sizable populations of Germans in Austria, Switzerland, the United States, Brazil, France, Kazakhstan, Russia, Argentina, Canada, Poland, Italy, Hungary, Australia, South Africa, Chile, Paraguay, and Namibia.[5][10] German-speaking peoples such as the Austrians and the German-speaking Swiss are sometimes referred to by scholars as Germans,[citation needed] although most of them do not identify as such these days.[55]
Identity
A German ethnic identity began to emerge during the Early Medieval Period.[56] These peoples came to be referred to by the High German term diutisc, which means "ethnic" or "relating to the people". The German endonym Deutsche is derived from this word.[20] In subsequent centuries, the German lands were relatively decentralized, leading to the maintenance of a number of strong regional identities.[38][39]
The German nationalist movement emerged among German intellectuals in the late 18th century. They saw the Germans as a people united by language and advocated the unification of all Germans into a single nation state, which was partially achieved in 1871. By the late 19th and early 20th century, German identity came to be defined by a shared descent, culture, and history.[17] Völkisch elements identified Germanness with "a shared Christian heritage" and "biological essence", to the exclusion of the notable Jewish minority.[57] After the Holocaust and the downfall of Nazism, "any confident sense of Germanness had become suspect, if not impossible".[58] East Germany and West Germany both sought to build up an identity on historical or ideological lines, distancing themselves both from the Nazi past and each other.[58] After German reunification in 1990, the political discourse was characterized by the idea of a "shared, ethnoculturally defined Germanness", and the general climate became increasingly xenophobic during the 1990s.[58] Today, discussion on Germanness may stress various aspects, such as commitment to pluralism and the German constitution (constitutional patriotism),[59] or the notion of a Kulturnation (nation sharing a common culture).[60] The German language remains the primary criterion of modern German identity.[17]
See also
- Ethnic groups in Europe
- Die Deutschen, ZDF's documentary television series
- Anti-German sentiment
- Germanophile
- Persecution of Germans
- Demographics of Germany
Notes
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there on 30 November 2020 according to official census data[1]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ People living in New Zealand having German ancestry[9]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ Citizens of Germany living there[2]
- ^ About 15,000 citizens of Germany plus 75,000 people of German descent[11]
- ^ The earlier Nordic Bronze Age of southern Scandinavia also shows definite population and material continuities with the Jastorf Culture,[28] but it is unclear whether these indicate ethnic continuity.[29]
References
- ^ "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht 2020" (in German). Archived from the original on 22 March 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Immigrant and Emigrant Populations by Country of Origin and Destination". Migration Policy Institute. 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Table B04006 - People Reporting Ancestry - 2020 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 13 July 2022. Retrieved 29 October 2022.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (17 June 2019). "Ethnic Origin (279), Single and Multiple Ethnic Origin Responses (3), Generation Status (4), Age (12) and Sex (3) for the Population in Private Households of Canada, Provinces and Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2016 Census - 25% Sample Data". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- ^ a b c d Haarmann 2015, p. 313. "Of the 100 million German speakers worldwide, about three quarters (76 million) live in Germany, where they account for 92 percent of the population. Populations of Germans live elsewhere in Central and Western Europe, with the largest communities in Austria (7.6 million), Switzerland (4.2 million), France (1.2 million), Kazakhstan (900,000), Russia (840,000), Poland (700,000), Italy (280,000), and Hungary (250,000). Some 1.6 million U.S. citizens speak German as their first language, the largest number of German speakers overseas."
- ^ "Ancestry | Australia | Community profile". Archived from the original on 21 June 2021. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ^ Przynależność narodowo-etniczna ludności – wyniki spisu ludności i mieszkań 2011. GUS. Materiał na konferencję prasową w dniu 29. 01. 2013. p. 3. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ [1]' 'Türkiye'de ikamet eden yabancı ülke vatandaşlarının sayısı ne? (Turkish)Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ Bade, James N. (2015). "Germans". Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
In the early 2000s, about 200,000 New Zealanders were likely to have German heritage.
- ^ a b c d Moser 2011, pp. 171–172. "The Germans live in Central Europe, mostly in Germany... The largest populations outside of these countries are found in the United States (5 million), Brazil (3 million), the former Soviet Union (2 million), Argentina (500,000), Canada (450,000), Spain (170,000), Australia (110,000), the United Kingdom (100,000), and South Africa (75,000). "
- ^ Burchard, Gretha (April 2010). "The German Population in Mexico: Maintenance of German culture and integration into Mexican society" (PDF). p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 12 June 2021.
the German embassy in Mexico City reports an estimated number of 15.000 Germans and 75.000 people of German origin living in Mexico
- ^ "SODB2021 - Obyvatelia - Základné výsledky". www.scitanie.sk. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ "SODB2021 - Obyvatelia - Základné výsledky". www.scitanie.sk. Retrieved 25 August 2022.
- ^ a b c "Definition of German by Merriam-Webster". Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 25 November 2020.
- ^ a b "German". Oxford Dictionary of English. Oxford University Press. 2010. p. 733. ISBN 978-0199571123. Archived from the original on 4 February 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz (ed.). "Article 116". Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany. Archived from the original on 7 November 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
Unless otherwise provided by a law, a German within the meaning of this Basic Law is a person who possesses German citizenship or who has been admitted to the territory of the German Reich within the boundaries of 31 December 1937 as a refugee or expellee of German ethnic origin or as the spouse or descendant of such person.
- ^ a b c Moser 2011, p. 172. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity."
- ^ Haarmann 2015, p. 313. "After centuries of political fragmentation, a sense of national unity as Germans began to evolve in the eighteenth century, and the German language became a key marker of national identity."
- ^ Moser 2011, p. 171. "The Germans live in Central Europe, mostly in Germany... Estimates of the total number of Germans in the world range from 100 million to 150 million, depending on how German is defined, but it is probably more appropriate to accept the lower figure."
- ^ a b c d e f g h Haarmann 2015, p. 313.
- ^ Hoad, T. F. (2003). "German". The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acref/9780192830982.001.0001. ISBN 9780192830982. Archived from the original on 24 September 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ "Germans". Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Columbia University Press. 2013. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 5 December 2020.
- ^ Drinkwater, John Frederick (2012). "Germans". In Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (eds.). The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4 ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 613. doi:10.1093/acref/9780199545568.001.0001. ISBN 9780191735257. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ Todd, Malcolm (2004b). "Germans and Germanic Invasions". In Fagan, Brian M. (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology (1 ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 250–251. doi:10.1093/acref/9780195076189.001.0001. ISBN 9780199891085. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ Wells, Peter S. (2010). "Germans". In Gagarin, Michael (ed.). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece and Rome. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195388398. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ Steuer 2021, p. 32.
- ^ Steuer 2021, p. 89, 1310.
- ^ Timpe & Scardigli 2010, p. 636.
- ^ Todd 1999, p. 11.
- ^ Kristinsson 2010, p. 147: "In the 1st century BC it was the Suebic tribes who were expanding most conspicuously. [...] Originating from central Germania, they moved to the south and southwest. [...] As Rome was conquering the Gauls, Germans were expanding to meet them, and this was the threat from which Caesar claimed to be saving the Gauls. [...] For the next half-century the expansion concentrated on southern Germany and Bohemia, assimilating or driving out the previous Gallic or Celtic inhabitants. The oppida in this area fell and were abandoned one after another as simple, egalitarian Germanic societies replaced the complex, stratified Celtic ones."
- ^ Green 2003, p. 29: "Greek may have followed the Persians in devising its terms for their military formations, but the Goths were dependent [...] on Iranians of the Pontic region for terms which followed the Iranian model more closely in using the cognate Gothic term for the second element of its compounds. (Gothic dependence on Iranian may have gone even further, affecting the numeral itself, if we recall that the two Iranian loanwords in Crimean Gothic are words for 'hundred' and 'thousand')."
- ^ Fortson 2011, p. 433: "Baltic territory began to shrink shortly before the dawn of the Christian era due to the Gothic migrations into their southwestern territories [...]."
- ^ Green 2000, pp. 172–73: "Jordanes [...] mentions the Slavs (Getica 119) and associates them more closely than the Balts with the center of Gothic power. [...] This location of the early Slavs partly at least in the region covered by the Cernjahov culture, together with their contacts (warlike or not) with the Goths under Ermanric and almost certainly before, explains their openness to Gothic loanword influence. That this may have begun early, before the expansion of the Slavs from their primeval habitat, is implied by the presence of individual loan-words in a wide range of Slavonic languages."
- ^ a b c d Heather, Peter. "Germany: Ancient History". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Archived from the original on 31 March 2019. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Within the boundaries of present-day Germany... Germanic peoples such as the eastern Franks, Frisians, Saxons, Thuringians, Alemanni, and Bavarians—all speaking West Germanic dialects—had merged Germanic and borrowed Roman cultural features. It was among these groups that a German language and ethnic identity would gradually develop during the Middle Ages.
- ^ a b c d e f Minahan 2000, pp. 288–289.
- ^ a b c d Moser 2011, p. 172.
- ^ a b c Haarmann 2015, pp. 313–314.
- ^ a b c d Haarmann 2015, p. 314.
- ^ a b c d e Minahan 2000, pp. 289–290.
- ^ a b c d Moser 2011, p. 173.
- ^ Minahan 2000, p. 290.
- ^ a b Moser 2011, pp. 173–174.
- ^ a b c Minahan 2000, pp. 290–291.
- ^ a b c d e Moser 2011, p. 174.
- ^ a b Minahan 2000, pp. 291–292.
- ^ a b Haarmann 2015, pp. 314–315.
- ^ a b c Haarmann 2015, p. 316.
- ^ Troebst, Stefan (2012). "The Discourse on Forced Migration and European Culture of Remembrance". The Hungarian Historical Review. 1 (3/4): 397–414. JSTOR 42568610.
- ^ Minahan 2000, p. 288.
- ^ a b c d Moser 2011, pp. 176–177.
- ^ Waldman & Mason 2005, pp. 334–335.
- ^ a b Moser 2011, p. 176.
- ^ Minahan 2000, p. 174.
- ^ Moser 2011, pp. 171–172.
- ^ Austrians: "Österreicher fühlen sich heute als Nation". Der Standard. 12 March 2008. Archived from the original on 3 March 2010. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
- ^ Haarmann 2015, p. 313 "Germans are a Germanic (or Teutonic) people that are indigenous to Central Europe... Germanic tribes have inhabited Central Europe since at least Roman times, but it was not until the early Middle Ages that a distinct German ethnic identity began to emerge."
- ^ Rock 2019, p. 32.
- ^ a b c Rock 2019, p. 33.
- ^ Rock 2019, pp. 33–34.
- ^ Rock 2019, p. 34.
Bibliography
- Haarmann, Harald (2015). "Germans". In Danver, Steven (ed.). Native Peoples of the World: An Encyclopedia of Groups, Cultures and Contemporary Issues. Routledge. pp. 313–316. ISBN 978-1317464006. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- Moser, Johannes (2011). "Germans". In Cole, Jeffrey (ed.). Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. pp. 171–177. ISBN 978-1598843026. Archived from the original on 10 January 2017. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- Minahan, James (2000). "Germans". One Europe, Many Nations: A Historical Dictionary of European National Groups. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 287–294. ISBN 0313309841. Archived from the original on 21 March 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2005). "Germans". Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase Publishing. pp. 330–335. ISBN 1438129181. Archived from the original on 28 November 2015. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
Further reading
- Craig, Gordon Alexander (1983). The Germans. New American Library. ISBN 0452006228. Archived from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- Elias, Norbert (1996). The Germans. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0231105630. Archived from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- James, Harold (2000). A German Identity (2 ed.). Phoenix Press. ISBN 1842122045. Archived from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- Mallory, J. P. (1991). "Germans". In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language Archeology and Myth. Thames & Hudson. pp. 84–87. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- Rock, Lena (2019). As German as Kafka: Identity and Singularity in German Literature around 1900 and 2000. Leuven University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctvss3xg0. ISBN 9789462701786. JSTOR j.ctvss3xg0. S2CID 241563332.
- Todd, Malcolm (2004a). The Early Germans. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405117142. Archived from the original on 5 August 2020. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- Wells, Peter S. (2011). "The Ancient Germans". In Bonfante, Larissa (ed.). The Barbarians of Ancient Europe. Cambridge University Press. pp. 211–232. ISBN 978-0-521-19404-4. Archived from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
