List of Indian flags
This is a list of flags used in India. For more information about the national flag, visit the article Flag of India.
National flag
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1947–present | National flag of India | A horizontal tricolour of saffron at the top, white in the middle, and green at the bottom. In the centre is a navy blue wheel with twenty-four spokes, known as the Ashoka Chakra. |
Governmental flag
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1950–1971[1] | Presidential Standard of India | 1st quarter: state emblem (the Lions of Sarnath) to represent national unity; 2nd quarter: elephant from Ajanta Caves to represent patience and strength; 3rd quarter: scales from the Red Fort, Old Delhi to represent justice and economy; 4th quarter: lotus vase from Sarnath to represent prosperity. |
Ensigns
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Civil ensign | A Red Ensign with the flag of India in the canton. | |
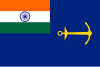 |
State ensign | A Blue Ensign with the flag of India in the canton, and a yellow anchor horizontally in the fly. |
Military flags
Army
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Flag of the Indian Army | A red field with the flag of India in the canton, and the Army badge in the fly | |
 |
Flag of the Chief of the Army Staff |
Air Force
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Flag of the Indian Air Force | A sky-blue ensign with the flag of India in the canton, and the Air Force roundel in the fly | |
 |
Flag of a Marshal of the Air Force | ||
 |
Flag of the Chief of Air Staff |
Navy
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Ensign of the Indian Navy | It is built up of the Indian National Flag, a Vertical and a Horizontal Red Stripe, the Indian State Emblem in golden yellow colour on a white background. | |
 |
Flag of an Admiral (rank currently reserved for the Chief of Naval Staff) | ||
 |
Flag of a Vice Admiral | ||
 |
Flag of a Rear Admiral | ||
| Flag of a Commodore | |||
 |
Flag of a Senior officer |
Coast Guard
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Ensign of the Indian Coast Guard | A Blue Ensign with the Flag of India in the canton, and the Coast Guard badge in the fly | |
 |
Flag of the Director General of the Indian Coast Guard | A Blue Ensign with the Flag of India in the canton, and the Coast Guard badge in the fly | |
 |
Flag of an Additional Director General of the Indian Coast Guard | ||
 |
Flag of an Inspector-General of the Indian Coast Guard |
State and union territory flags
At present there are no officially recognised flags for individual states in India.[2] There are currently no legal prohibitions to states adopting distinctive flags in either the Emblems and Names (Prevention of Improper Use) Act, 1950 or the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971 [3] and the Flag code of India permits other flags to be flown with the National flag of India, but not on the same flag pole of in a superior position to the national flag.[4]
Jammu and Kashmir had an official state flag between 1952 and 2019 and flags have been proposed for Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Governmental banners, depicting the emblem of each state or union territory on a white field, have also been reported.
Former official state flags
| Flag | State | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Jammu and Kashmir | 1952–2019 | Flag of Jammu and Kashmir | The flag was red with three white vertical stripes in the hoist and a plough in the fly. The red background stood for labour, the stripes stood for the three regions of the state namely; (Jammu, Kashmir, and Ladakh) and the plough stood for agriculture. The ratio of the flag was 3:2.[5] |
Proposed state flags
| Flag | State | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Tamil Nadu | Proposed in 1970 | The Government of Tamil Nadu proposed a design for a state flag in 1970.[6] | Grey flag with the flag of India in the canton and the Emblem of Tamil Nadu in the fly. |
| Karnataka | Proposed in 2018 | The Government of Karnataka proposed a design for a state flag in 2018.[7] | Yellow, white and red tricolour with the Emblem of Karnataka centred on the white band. |
State government banners
State government banners have been reported to be in use. These depict the emblem of each state or union territory on a white field.[8][9]
Sporting flags
At the National Games of India, each state or union territory is represented by a flag depicting the logo of its Olympic association.[10][11]
Historical flags
Pre-colonial states
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1206–1526 | Flag of the Delhi Sultanate | A dark green flag with a black strip left of center. | |
| 1336–1646 | Flag of the Vijayanagara Empire | Yellow coloured flag of the Vijayanagara Empire which ruled over South India. | |
 |
1399–1950 | Flag of the Kingdom of Mysore | Red and Brown coloured flag of the Kingdom of Mysore which ruled over most of Karnataka and at its zenith most of South India. |
 |
1518–1687 | Flag of Kingdom of Golconda | Cyan coloured flag of the Qutb Shahi dynasty which ruled over the Kingdom of Golconda. |
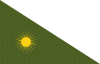 |
1526–1858 | Flag of the Mughal Empire (Alam) | A flag that was primarily moss green.[12] |
| 1674–1818 | Flag of the Maratha Empire (Bhagwa Dhwaj)[13] | A saffron-coloured swallowtail flag. | |
 |
1729–1949 | Flag of the Kingdom of Travancore | Red flag with a dextrally-coiled silver conch shell (Turbinella pyrum) at its centre. |
 |
1799–1849 | Flag of the Sikh Empire (Nishan Sahib)[14] | |
 |
1642–1975 | Flag of the Kingdom of Sikkim | The flag of Sikkim used between 1967 and 1975 depicted a Buddhist prayer wheel in gold on a white field with a red border |
Company rule in India
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1600–1707 | Flag of the East India Company | A striped banner with Saint George's Cross in the canton. |
 |
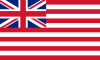
1707–1801 | Flag of the East India Company | A striped banner with the Union Jack of Great Britain in the canton. |
 |
1801–1858 | Flag of the East India Company | A striped banner with the Union Jack in the canton. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
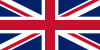 |
1858–1947 | The official state flag of the British Empire used in India | The Flag of the United Kingdom. |
 |
1885–1947 | Flag of the Viceroy and Governor-General of India | The Union Jack defaced with the insignia of the Order of the Star of India beneath the Tudor Crown. |
 |
1880–1947 | Civil Ensign of British India used to represent British India internationally. | A Red Ensign with the Union Flag at the canton, defaced with the Star of India emblem displayed in the fly. |
(Royal) Indian Marine/(Royal) Indian Navy
 |
1863–1947 | 1877–1892 Ensign of Her Majesty's Indian Marine 1892–1928: Ensign of the Royal Indian Marine 1928–1934 Naval jack of the Royal Indian Marine 1934–1947: Naval jack of the Royal Indian Navy |
A Blue Ensign with the Union Flag at the canton, and the Star of India displayed in the fly. |
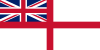 |
1928–1950 | 1928–1934: Ensign of the Royal Indian Marine 1934–1950: Ensign of the Royal Indian Navy |
The White Ensign of the Royal Navy. |
 |
1951–1955 | 1951–1955: Flag of the Commander-in-Chief, Indian Navy 1955: Flag of the Chief of the Naval Staff of the Indian Navy |
The St George's Cross. Ensign of an Admiral in the Royal Navy. |
 |
1934–1958 | 1934–1947: Flag of the Flag Officer Commanding, Royal Indian Navy 1947–1950: Flag of the Commander-in-Chief, Royal Indian Navy 1950–1955: Flag of the Commander-in-Chief, Indian Navy 1955–1958: Flag of the Chief of the Naval Staff of the Indian Navy |
Ensign of a Vice-Admiral in the Royal Navy. |
 |
1928–1958 | 1928–1934: Flag of the Flag Officer Commanding, Royal Indian Marine 1934–1950: Flag of a Flag Officer, Royal Indian Navy 1950–1958: Flag of a Flag Officer, Indian Navy |
Ensign of a Rear-Admiral in the Royal Navy. |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1947–1950 | Flag of the Dominion of India | A horizontal tricolour of saffron at the top, white in the middle, and green at the bottom. In the centre is a navy blue wheel with twenty-four spokes, known as the Ashoka Chakra. |
 |
1947–1950 | Flag of the Governor-General of India | Dark blue field emblazoned with the royal crest (a Tudor Crown surmounted by the lion of England, itself wearing the crown), beneath which was the word 'India' in gold majuscules. Similar to flags used by other Governors-General of Commonwealth realms. |
 |
1620–1869 | The flag of Denmark (Denmark-Norway until 1814) |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1667–1791 | Flag of the Kingdom of France | Flag of the Kingdom of France. |
 |
1791–1794 | 1791–1792: Flag of the Kingdom of France 1792–1794: Flag of the French First Republic |
The flag of France. |
 |
1815–1830 | Flag of the Kingdom of France under the Bourbon Restoration | Flag of the Kingdom of France. |
 |
1794–1804, 1830–1940, 1944–1954 | 1794–1804: Flag of the French First Republic 1804–1814, 1815: Flag of the First French Empire 1830–1848; Flag of the Kingdom of France 1848–1852: Flag of the French Second Republic 1852–1870: Flag of the Second French Empire 1870–1940: Flag of the French Third Republic and French Empire 1944–1946: Flag of the Provisional Government of the Fourth French Republic 1946–1954: Flag of the French Fourth Republic and French Union |
The flag of France. |
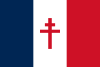 |
1940–1944 | Flag of French India under Free France | Flag of Free France with the Cross of Lorraine |
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1497–1521 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1521–1578 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1578–1616 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1616–1640 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1640–1667 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1667–1706 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1706–1750 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1816–1826 | Flag of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. | |
 |
1826–1830 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | |
 |
1830–1910 | Flag of the Kingdom of Portugal. | Vertical bicolour blue-white. Proportion of the fields: 1:1. |
 |
1910–1961 (de facto) 1910–1974 (de jure) |
Flag of the Portuguese Republic. The final state flag of Portuguese India. | Used from the implantation of the Portuguese Republic in 1910. Officially used until 1974, as Portugal only then recognised the Annexation of Portuguese India. |
 |
1967 (proposed) | Proposed official flag for Portuguese India in 1967. | Proposal by F. P. de Almeida Langhans. Never actually used. |
Flags used in the Indian independence movement
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1906 | Calcutta flag | Three horizontal bands of equal width with the top being orange, the centre yellow, and the bottom green. It had eight half-opened lotus flowers on the top stripe, and a picture of the sun and a crescent moon on the bottom stripe. वन्दे मातरम् (Vande Mātaram) was inscribed in the centre in Devanagari. [Note 1] |
 |
1907 | Early Indian nationalist flags [Note 2] | |
 |
1907 | ||
 |
1917 | Flag of the Home Rule Movement | Five red and four green horizontal stripes On the upper left quadrant was the Union Jack, which signified the Dominion status that the movement sought to achieve. A crescent and a star, both in white, are set in top fly. Seven white stars are arranged as in the Saptarishi constellation (the constellation Ursa Major), which is sacred to Hindus. [Note 3] |
 |
1921 | Gandhi's flag, introduced at the Indian National Congress meeting in 1921 | |
 |
1923–1947 | The Swaraj Flag, officially adopted by the Indian National Congress in 1931 | |
 |
1942–1945 | Flag of Provisional Government of Free India | Three horizontal strips of saffron, white, and green, with a springing tiger in the center Although this symbolised the armed resistance of the Azad Hind Movement led by Subhas Chandra Bose (as opposed to Gandhian pacifism), the 1931 flag of the Indian National Congress was used when the Indian National Army hoisted its flag in Moirang, Manipur. Both flags were used interchangeably. |
See also
Notes
- ^ The partition of Bengal (1905) resulted in the introduction of a new Indian flag that sought to unite the multitude of castes and races within the country. The Vande Mataram flag, part of the Swadeshi movement against the British, comprised Indian religious symbols represented in western heraldic fashion. The tricolour flag included eight white lotuses on the upper green band representing the eight provinces, a sun and a crescent on the bottom red band, and the Vande Mataram slogan in Hindi on the central yellow band. The flag was launched in Calcutta bereft of any ceremony and the launch was only briefly covered by newspapers. The flag was not covered in contemporary governmental or political reports either, but was used at the annual session of the Indian National Congress. A slightly modified version was subsequently used by Madam Bhikaji Cama at the Second Socialist International Meeting in Stuttgart. Despite the multiple uses of the flag, it failed to generate enthusiasm amongst Indian nationalists.[15]
- ^ Around the same time, another proposal for the flag was initiated by Sister Nivedita, a Hindu reformist and disciple of Swami Vivekananda. The flag consisted of a thunderbolt in the centre and a hundred and eight oil lamps for the border, with the Vande Mataram caption split around the thunderbolt. It was also presented at the Indian National Congress meeting in 1906.[16] Soon, many other proposals were initiated, but none of them gained attention from the nationalist movement.
- ^ In 1916, Suraiya Tayyabji submitted thirty new designs, in the form of a booklet funded by members of the High Court of Madras. These many proposals and recommendations did little more than keep the flag movement alive. The same year, Annie Besant and Bal Gangadhar Tilak adopted a new flag as part of the Home Rule Movement. The flag included the Union Jack in the upper left corner, a star and crescent in the upper right, and seven stars displayed diagonally from the lower right, on a background of five red and four green alternating bands. The flag resulted in the first governmental initiative against any nationalistic flag, as a magistrate in Coimbatore banned its use. The ban was followed by a public debate on the function and importance of a national flag.[17]
References
- ^ Das, Chand N. (1984). Traditions and Customs of the Indian Armed Forces. Vision Books. p. 53.
- ^ https://www.crwflags.com/fotw/flags/in-.html
- ^ https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/should-states-have-their-own-flags/article22695446.ece
- ^ https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Flag_Code_of_India
- ^ Haynes, Ed (24 September 1996). "Jammu and Kashmir (India)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 23 May 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Karnataka government unveils the state flag, awaits Centre's approval". hindustantimes.com/. 2018-03-08. Retrieved 2018-03-08.
- ^ https://www.worldstatesmen.org/India_states.html
- ^ http://www.vexilla-mundi.com/india_governments.html
- ^ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QHJssb9VxL4
- ^ https://olympic.ind.in/eventdatas/asg/NATIONAL_STATE_FEDERATIONS.html
- ^ http://www.bl.uk/onlinegallery/onlineex/apac/addorimss/a/zoomify55414.html
- ^ Kadam, Vasant S. (1993), Maratha Confederacy: A Study in Its Origin and Development, Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, p. 128, ISBN 978-81-215-0570-3
- ^ "Nishan Sahib Khanda Sikh Symbols Sikh Museum History Heritage Sikhs". www.sikhmuseum.com. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ Virmani 1999, pp. 175–176
- ^ Roy 2006, pp. 498–499
- ^ Virmani 1999, pp. 176–177
External links
- "India - Index of all Pages".
- "Indian Ensigns".
- "British Rule in India".
- "India: Historical Flags". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
