Moro Rebellion
| Moro Rebellion | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Philippine–American War | |||||||
 American soldiers battling against Moro fighters | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Confederation of sultanates in Lanao | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Jikiri[2][3][4] Panglima Hassan[5][6] Datu Ali[2][7] Datu Amil |
Leonard Wood Tasker H. Bliss John J. Pershing | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| unknown | 25,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Heavy; official casualties are unknown |
United States: 130 killed 270 wounded ~500 dead from disease Philippine Scouts: 111 killed 109 wounded Philippine Constabulary: 1,706 casualties[8]: 248 | ||||||
The Moro Rebellion (1899–1913) was an armed conflict between the Moro people and the United States military during the Philippine–American War.
The word "Moro" – the Spanish word for "Moor"[9] – is a term for Muslim people who lived in the Southern Philippines, an area that includes Mindanao, Jolo and the neighboring Sulu Archipelago.
Background
| History of the Philippines |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
The Moros have a 400-year history of resisting foreign rule. The violent armed struggle against the Spanish, against the Americans, against the Japanese, and against the Filipinos, is considered by current Moro leaders as part of the four centuries-long "national liberation movement" of the Bangsamoro (Moro Nation)[dubious – discuss].[10] This conflict persisted and developed into their current war for independence against the Philippine state.[11] A "culture of jihad" emerged among the Moros due to the centuries-long war against the Spanish invaders.[12]: 16
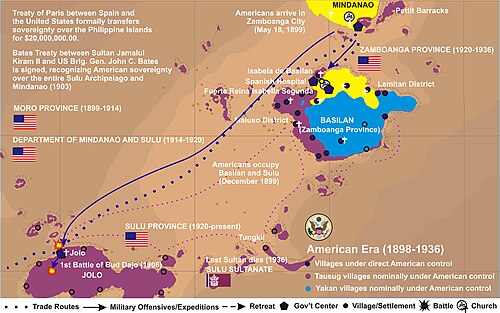
The ethnic Moro population of the southern Philippines resisted both Spanish and United States colonization. The Moro areas of Western Mindanao have been the most rebellious areas in the Philippines along with Samar Island and Bicol Region. The Spaniards were restricted to a handful of coastal garrisons or Forts and they made occasional punitive expeditions into the vast interior regions. After a series of unsuccessful attempts during the centuries of Spanish rule in the Philippines, Spanish forces occupied the abandoned city of Jolo, Sulu, the seat of the Sultan of Sulu, in 1876. The Spaniards and the Sultan of Sulu signed the Spanish Treaty of Peace on July 22, 1878. Control of the Sulu archipelago outside of the Spanish garrisons was handed to the Sultan. The treaty had translation errors: According to the Spanish-language version, Spain had complete sovereignty over the Sulu archipelago, while the Tausug version described a protectorate instead of an outright dependency.[13] Despite the very nominal claim to the Moro territories, Spain ceded them to the United States in the Treaty of Paris which signaled the end of the Spanish–American War.
Following the American occupation of the Northern Philippines during 1899, Spanish forces in the Southern Philippines were abolished, and they retreated to the garrisons at Zamboanga and Jolo. American forces took control over the Spanish government in Jolo on May 18, 1899, and at Zamboanga in December 1899.[14]
The Moros resisted the new American colonizers as they had resisted the Spanish.[15] The Spanish, American, and Philippine governments have all been fought against by the Muslims of Sulu and Mindanao.[16]
Ottoman Empire's role
John Hay, the American Secretary of State, asked the ambassador to Ottoman Empire, Oscar Straus in 1899 to approach Ottoman Sultan Abdul Hamid II to request that the Sultan write a letter to the Moro Sulu Muslims of the Sulu Sultanate in the Philippines telling them to submit to American suzerainty and American military rule. Despite the sultan's "pan-Islamic" ideology, he readily aided the American forces because he felt no need to cause hostilities between the West and Muslims.[17]
Abdul Hamid wrote the letter, which was sent to Mecca where two Sulu chiefs brought it home to Sulu.[18] It was successful, and the "Sulu Mohammedans ... refused to join the insurrectionists and had placed themselves under the control of [the American] army, thereby recognizing American sovereignty."[19][20] John P. Finley wrote that:
After due consideration of these facts, the Sultan, as Caliph caused a message to be sent to the Mohammedans of the Philippine Islands forbidding them to enter into any hostilities against the Americans, inasmuch as no interference with their religion would be allowed under American rule. As the Moros have never asked more than that, it is not surprising, that they refused all overtures made, by Aguinaldo's agents, at the time of the Filipino insurrection. President McKinley sent a personal letter of thanks to Mr. Straus for the excellent work he had done, and said, its accomplishment had saved the United States at least twenty thousand troops in the field. If the reader will pause to consider what this means in men and also the millions in money, he will appreciate this wonderful piece of diplomacy, in averting a holy war.[21][22]
President McKinley did not mention the Ottoman Empire's role in the pacification of the Sulu Moros in his address to the first session of the Fifty-sixth Congress in December 1899 since the agreement with the Sultan of Sulu was not submitted to the Senate until December 18.[23]
Cause of the war
After the American government informed the Moros that they would continue the old protectorate relationship that they had with Spain, the Moro Sulu Sultan rejected this and demanded that a new treaty be negotiated. The United States signed the Kiram-Bates Treaty with the Moro Sulu Sultanate which guaranteed the Sultanate's autonomy in its internal affairs and governance, including article X that guaranteed preservation of slavery, while America dealt with its foreign relations, in order to keep the Moros out of the Philippine–American War. Once the Americans subdued the northern Filipinos, the Bates Treaty with the Moros was adjusted by the Americans through removal of article X and they invaded Moroland.[24][25][26][27][28][29]
After the war in 1915, the Americans imposed the Carpenter Treaty on Sulu.[30]
Philippine–American War events
This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
First Republic forces in the southern Philippines were commanded by General Nicolas Capistrano, and American forces conducted an expedition against him in the winter of 1900–1901. On March 27, 1901, Capistrano surrendered. A few days later, General Emilio Aguinaldo was captured in Luzon.[31] This major victory in the war in the north allowed the Americans to devote more resources to the south, and they began to push into the interior of Bangsamoro[citation needed].[neologism?]
On August 31, 1901, Brig. Gen. George Whitefield Davis replaced Kobbe as the commander of the Department of Mindanao-Jolo. Davis adopted a conciliatory policy towards the Moros. American forces under his command had standing orders to buy Moro produce when possible and to have "heralds of amity" precede all scouting expeditions. Peaceful Moros would not be disarmed. Polite reminders of America's anti-slavery policy were allowed.
One of Davis' subordinates, Captain John J. Pershing, assigned to the American garrison at Iligan, set out to better relations with the Moros of the Maranao tribes on the northern shore of Lake Lanao. He successfully established friendly relations with Amai-Manabilang, the retired Sultan of Madaya. Although retired, Manabilang was the single most influential personage among the fragmented inhabitants of the northern shore of the lake. His alliance did much to secure American standing in the area.
Not all of Davis' subordinates were as diplomatic as Pershing. Many veterans of the Indian Wars took the "only good Indian is a dead Indian" mentality with them to the Philippines, and "civilize 'em with a Krag" became a similar catchphrase.[32][33]
Conflict
This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
Three ambushes of American troops by Moros, one of which involved Juramentados, occurred to the south of Lake Lanao, outside of Manabilang's sphere of influence. These events prompted Maj. Gen. Adna R. Chaffee, the military governor of the Philippines, to issue a declaration on April 13, 1902, demanding that the offending Datu hand over the killers of American troops and stolen government property.
Not compliant, a punitive expedition under Col. Frank Baldwin set out to settle matters with the south-shore Moros. Although an excellent officer, Baldwin was "eager," and a worried Davis joined the expedition as an observer. On May 2, 1902, Baldwin's expedition attacked a Moro cotta (fortress) at the Battle of Pandapatan, also known as the Battle of Bayan. Pandapatan's defenses were unexpectedly strong, leading to 18 American casualties during the fighting. On the second day, the Americans used ladders and moat-bridging tools to break through the Moro fortifications, and a general slaughter of the Moro defenders followed.
The expeditionary force built at Camp Vickers one mile south of Pandapatan, and Davis assigned Pershing to Baldwin's command as an intelligence officer and as director of Moro affairs. As director, 'Black Jack' Pershing had a veto over Baldwin's movements, which was an unstable arrangement. This arrangement was tested when survivors of Pandapatan began building a Cotta at Bacolod. Baldwin wanted to move on the hostile Moros immediately, but Pershing warned that doing so could create an anti-American coalition of the surrounding Datus, while some patient diplomacy could establish friendly relations with most of the Moros, isolating the hostile minority. Baldwin grudgingly agreed. On June 30, Pershing assumed command of Camp Vickers, and Baldwin returned to Malabang. A command the size of Camp Vickers would normally have gone to an officer with the rank of Major, and a careful shuffling of personnel would be required to ensure that reinforcements to the Camp did not include officers that were senior to Pershing.
On July 4, 1902, President Theodore Roosevelt issued a proclamation declaring an end to the Philippine Insurrection and a cessation of hostilities in the Philippines "except in the country inhabited by the Moro tribes, to which this proclamation does not apply."[34] Later that month, Davis was promoted and replaced Chaffee as the supreme commander of American forces in the Philippines. Command of the Mindanao-Jolo Department went to Brig. Gen. Samuel S. Sumner. Meanwhile, Pershing settled down to conduct diplomacy with the surrounding Moros, and a July 4th celebration had 700 guests from neighboring rancherias. In September 1902, he led the Masiu Expedition, which resulted in a victory that did much to establish American dominance in the area. On February 10, 1903, Pershing was declared a Datu by the formerly hostile Pandita Sajiduciaman of the Bayan Moros (who had been defeated at the Battle of Pandapatan)—the only American to be so honored. Pershing's career at Camp Vickers culminated in the March Around Lake Lanao during April and May 1903. Dansalan also known as the Marawi Expedition, it included the Battle of Bacolod and First Battle of Taraka but was otherwise peaceful. This expedition quickly became a symbol of American control of the Lake Lanao region and was regarded with dismay by the Moro Maranao inhabitants of that region.
While Pershing was working to the south of Lake Lanao, Major Robert Lee Bullard was working to the north, building a road from Iligan to Marawi. Although never officially declared one, like Pershing, he was regarded as a Datu by the Moros. Because of the Lake Lanao Moros' very personalistic style of leadership, they had troubles seeing them as two officers in the same army. Instead, they saw them as two powerful chieftains who might become rivals. During Pershing's March Around Lake Lanao, one Moro ran to Bullard, exclaiming that Pershing had gone Juramentado, meaning berserk and that Bullard had better run up the white flag (signaling that they had no quarrel with Pershing's troops). Bullard was unable to explain to the Moro why he was not worried about Pershing's approach. On another occasion, a powerful datu proposed an alliance with Bullard, for the purposes of defeating Pershing and establishing overlordship over the entire Lake Lanao region. On June 1, 1903, the Moro Province was created, which included "all of the territory of the Philippines lying south of the eight parallel of latitude, excepting the island of Palawan and the eastern portion of the northwest peninsula of Mindanao."[35] The province had a civil government, but many civil service positions, including the district governors and their deputies, were held by members of the American military. The governor of the province served as the commander of the Department of Mindanao-Jolo. This system of combined civil and military administration had several motivations behind it. One was the continued Moro hostilities. Another was the Army's experience during the Indian Wars when it came into conflict with the civilian Bureau of Indian Affairs. A third was that the Moros, with their feudal, personalistic style of government, would have no respect for a military leader who submitted to the authority of a non-combatant.
In addition to the executive branch, under the governor, the province also had a legislative branch: the Moro Council. This Council "consisted of the governor, a state attorney, a secretary, a treasurer, a superintendent of schools, and an engineer."[36] Although the governor appointed all of the other members of the council, this body was permanent and provided a more solid foundation for laws than the fiats of the governor, which might be overturned by his successor.
The province was divided into five districts, with American officers serving as district governors and deputy governors. These districts included: Cotabato, Davao, Lanao, Sulu, and Zamboanga. The districts were sub-divided into tribal wards, with major datus serving as ward chiefs and minor datus serving as deputies, judges, and sheriffs. This system took advantage of the existing structure of Moro political society, which was based on personal ties while paving the way for a more individualistic society, where the office, not the person holding it, would be given respect.
On August 6, 1903, Major General Leonard Wood assumed his position as the governor of Moro Province and commander of the Department of Mindanao-Jolo. Wood was somewhat heavy-handed in his dealing with the Moros, being "personally offended by the Moro propensity for blood feuds, polygamy, and human trafficking"[37] and with his "ethnocentrism sometimes [leading] him to impose American concepts too quickly in Moroland."[38] In addition to his views of the Moros, Wood also faced an uphill Senate battle over his appointment to the rank of Major General, which was finally confirmed on March 19, 1904. This drove him to seek military laurels in order to shore up his lack of field experience, sometimes leading the Provincial army on punitive expeditions over minor incidents that would have been better handled diplomatically by the district governors. The period of Wood's governorship had the hardest and bloodiest fighting of America's occupation of Moroland.
Some of the Moros fighting against the American troops were women who dressed exactly the same as men. This led to the song sung by American troops called "If a Lady's Wearin' Pantaloons".[39][40][41][42][43][44]
Province under Leonard Wood (1903–1906)
Wood instituted many changes during his tenure as governor of Moro Province:
- On Wood's recommendation, the United States unilaterally abrogated the Bates Treaty, citing continuing piracy and attacks on American personnel. The Sultan of Sulu was demoted to a purely religious office, with no more power than any other datu, and was provided with a small salary. The United States assumed direct control over Moroland.
- Slavery was abolished. Slave trading and raiding were repressed, but slaves were left with their owners. Wood announced that slaves were "at liberty to go and build homes for themselves wherever they like[d]," and pledged the military's protection for any former slaves that did so. Similar actions had been taken by individual commanders in the past, but Wood's edict had the backing of the Moro Council, giving it more permanent weight.
- The Cedula Act of 1903 created an annual registration poll tax. This registration poll tax was highly unpopular with the Moros, since they interpreted it as a form of tribute.[35] According to Hurley, participation in the Cedula was very low as late as 1933.[35]
- The legal code of Moroland was reformed. Disputes between Moros and non-Christians had been left to Moro laws and customs, with Philippine laws only applying to disputes with Christians. This led to a double standard, with a Moro who killed a Christian facing a stiff prison sentence, but with a Moro who killed another Moro facing only a maximum fine of 150 pesos. Wood attempted to codify Moro law, but there was simply too much variance in laws and customs between the different tribes and even between neighboring cottas. Wood placed the Moros underneath the Philippine criminal code, but actual enforcement of this proved difficult.
- Private land ownership was introduced, in order to help the Moros transition to a more individualistic society from their traditional tribal society. Each family was given 40 acres (16 ha) of land, with datus given additional land in accordance with their status. Land sales had to be approved by the district governments in order to prevent fraud.
- An educational system was established. By June 1904, there were 50 schools with an average enrollment of 30 students each. Because of difficulties in getting teachers that spoke native languages, classes were conducted in English after initial training in that language. Many Moros were suspicious of the schools, but some offered buildings for use as schools.
- Trade was encouraged in order to give the Moros an alternative to fighting. Trade had been discouraged by banditry, piracy, and the possibility of intertribal disputes between Moro merchants and local customers. When trading with foreign merchants (usually maritime Chinese), a lack of warehousing made for a buyer's market, leading to low prices. Wood handled banditry and piracy by establishing military posts at river mouths in order to protect sea and land routes. Starting with a pilot project in Zamboanga, a system of Moro Exchanges was established. These exchanges provided Moro traders with warehouses and temporary housing in exchange for honoring a ban on fighting within the exchange. Bulletin-boards listed market prices in Hong Kong and Singapore, and the district governments guaranteed fair prices. These Exchanges proved highly successful and profitable, and provided a neutral ground for feuding datus to settle their differences.
Campaigns
Major military campaigns during Wood's governorship include:
- Wood's March Around Lake Lanao during the fall of 1903 was an abortive attempt to replicate Pershing's earlier March.
- In October and November 1903, Wood personally led the Provincial Army to put down the Hassan Uprising, which was led by the most powerful datu on the island of Jolo.
- In the spring of 1904, Wood destroyed or captured 130 cottas during the Second Battle of Taraca.
- Beginning in the spring of 1904 and continuing into the fall of 1905, American forces conducted a lengthy and massive manhunt for Datu Ali, the overlord of Cottabato Valley. Datu Ali had rebelled over Wood's anti-slavery policy. Engagements during this campaign include the Battle of Siranaya, the Simpetan Massacre,[45] and the Battle of the Malalag River.
- The First Battle of Bud Dajo was fought from March 5 to March 7, 1906. An estimated 600 Muslims were killed, fighting a force of 800 Americans.[12]: 8 [46][47][48]
The Incident in the Philippines written by Mark Twain condemned the American massacre at Bud Dajo.[66]
Governorship of Tasker H. Bliss (1906–1909)
On February 1, 1906, Brigadier General Tasker H. Bliss replaced General Wood as the commander of the Department of Mindanao-Jolo, and replaced him as governor of Moro Province sometime after the First Battle of Bud Dajo. Bliss' tenure is regarded as a "peace era", and Bliss launched no punitive expeditions during his term in office. However, this superficial peace came at the price of tolerating a certain amount of lawlessness. Constabulary forces in pursuit of Moro fugitives often found themselves forced to abandon their chase after the fugitives took refuge at their home cottas. The constabulary forces were outnumbered, and a much larger (and disruptive) expedition would have been required to dislodge the fugitives from their hiding place. However, this period also demonstrated the success of new aggressive American tactics. According to Rear Admiral D.P. Mannix, who fought the Moros as a young lieutenant from 1907 to 1908, the Americans exploited Muslim taboos by wrapping dead Moros in pig's skin and "stuffing [their] mouth[s] with pork", thereby deterring the Moros from continuing with their suicide attacks.[67]
Governorship of John J. Pershing (1909–1913)

On November 11, 1909, Brigadier General John J. Pershing assumed his duties as the third and final military governor of Moro Province.
Reforms
Pershing enacted the following reforms during his tenure as governor:
- In order to extend rule of law into the interior, Pershing stationed the Philippine Scouts in small detachments throughout the interior. This reduced crime and promoted agriculture and trade, at the cost of reduced military efficiency and troop training. The benefits of this reform outweighed the costs.
- The legal system was streamlined. Previously, trials had started with the Court of First Instance, which convened every 6 months, and appeals to the Supreme Court in Manila often took more than one year. Pershing expanded the jurisdiction of the local ward courts, which were presided over by the district governors and secretaries, to include most civil cases and all criminal cases except for capital offenses. The Court of First Instance became the court of last resort. This reform was popular with the Moros[citation needed], since it was quick, simple, and resembled their traditional unification of executive and judicial powers.
- Pershing promised to donate government land for purposes of building Muslim houses of worship.
- Pershing recognized the practice of sacopy – indentured servitude in exchange for support and protection – as legitimate, but reaffirmed the government's opposition to involuntary slavery.
- Labor contract law was reformed in 1912. Defaults on contracts by workers or employers were no longer punishable unless there was intent to defraud or injure. Moros, unused to Western notions of work, were prone to absenteeism, which could lead to breach of contract suits.
- The economy of Moro Province continued to expand under Pershing. The three most important exports – hemp, copra, and lumber – increased 163% during his first three years, and Moros began to make bank deposits for the first time in their history.
- The Moro Exchange system was retained and was supplemented by Industrial Trading Stations. These stations operated in the interior, where merchants seldom went, and bought any non-perishable goods the Moros wished to sell. The stations also sold goods to the Moros at fair prices, preventing price gouging during famines.[68]
Tactics
Pershing wrote the following in his autobiography about the juramentado:
[The] juramentado attacks were materially reduced in number by a practice the army had already adopted, one that the Mohammadans held in abhorrence. The bodies were publicly buried in the same grave with a dead pig. It was not pleasant to have to take such measures but the prospect of going to hell instead of heaven sometimes deterred the would-be assassins.[69]
Though this treatment was inflicted on captured juramentado, historians do not believe that Pershing was directly involved with such incidents, or that he personally gave such orders to his subordinates. Letters and memoirs from soldiers describing events similar to this do not have credible evidence of Pershing's having been personally involved.[70][71]
Surrender of Arms

Law enforcement in the Moro Province was difficult. Outlaws would go to ground at their home cottas, requiring an entire troop of police or soldiers to arrest them. There was always the danger of a full-fledged battle breaking out during such an arrest, and this led to many known outlaws going unpunished. In 1911, Pershing resolved to disarm the Moros. Army Chief of Staff Leonard Wood (former Moro Province governor) disagreed with this plan, stating that the move was ill-timed and that the Moros would hide their best arms, turning in only their worst. Pershing waited until roads into the interior had been completed, so that government troops could protect disarmed Moros from holdouts. He conferred with the Datus, who mostly agreed that disarmament would be a good idea – provided that everybody disarmed.
Six weeks before putting his disarmament plan into action, Pershing informed Governor-General William Cameron Forbes, who agreed with the plan. Pershing did not consult or inform his commanding officer, Major. Gen. J. Franklin Bell. On September 8, 1911, Executive Order No. 24, which ordered the disarmament, was issued. The deadline for disarmament was December 1, 1911.
Resistance to disarmament was particularly fierce in the district of Jolo and led to the Second Battle of Bud Dajo (which, while involving roughly equivalent forces as the first battle, was far less bloody causing only 12 Moro casualties[72]), and the Battle of Bud Bagsak.
Transition to civil authority
By 1913, Pershing agreed that the Moro Province needed to transition to civil government. This was prompted by the Moro's personalistic approach to government, which was based on personal ties rather than a respect for an abstract office. To the Moros, a change of administration meant not just a change in leadership but a change in regime, and was a traumatic experience. Rotation within the military meant that each military governor could serve only for a limited time. Civil governors were needed in order to provide for a lengthy tenure in office. Until 1911, every district governor and secretary had been a military officer. By November 1913, only one officer still held a civil office – Pershing himself. In December 1913, Pershing was replaced as governor of Moro Province by a civilian, Frank Carpenter.
Casualties
During the Moro Rebellion, the Americans suffered losses amounting to 130 killed and 323 wounded. Another 500 or so died of disease.[73] The Philippine Scouts who augmented American forces during the campaign suffered 116 killed and 189 wounded. The Philippine Constabulary suffered heavily as well with more than 1,500 losses sustained of which half were fatalities.
On the Moro side, casualties were high as surrender was uncommon when Moros were engaged in combat.[74]
-
Aftermath of the First Battle of Bud Dajo
-
Three Moro rebels being hanged in Jolo, 21 July 1911
-
Three Moro rebels hanged in Jolo, 21 July 1911
Juramentados and stopping power
In the Moro Rebellion, the Tausug Moro Muslim Juramentados in suicide attacks continued to charge against American soldiers even after being shot. Panglima Hassan in the Hassan uprising was shot dozens of times before his jihad was stopped. As a result, Americans elected to phase out the .38 caliber Colt M1892 revolver in favor of .45 caliber sidearms to continue their fight against the Moros. This led to a re-issuing of old .45 Colt M1873 Peacemaker revolvers and later the issuance of the M1909 revolver, essentially an M1892 rechambered in .45 Colt (which would later again be rechambered in the weaker .45 ACP as the M1917).[75] This contributed to the development and adoption of the .45 ACP M1911 semi-automatic pistol on March 29, 1911, after further weapon testing during the rebellion, beginning over 70 years of service by the pistol and cartridge in the US military.[76] Arrows, bayonets, guns, and Kris were used in often suicidal attacks by the Moros during their war with the Americans. Suicide attacks became more popular among Moros due to the overwhelming firepower of the Americans in conventional battles. Moro women took part in the resistance at the Battle of Bud Dajo against the American General Lenard Wood in 1906.[77] Barbed wire proved to be of no impediment since Moro Juramentado warriors managed to surge directly through it even as it ripped at their flesh and even as they were shot repeatedly with bullets. The Moros used barongs to inflict injuries upon American soldiers.[78] Moros under Jikiri managed to survive in a cave under machine gun fire and Colt gunfire.[45] Kris and Kampilan were used by Moros in fierce close quarter combat against the Americans.[79] Muskets were also used by the Moro.[80] The Moro employed bayonets at close range when shooting was not possible according to the American journal The Field Artillery Journal, Volume 32.[81] Americans were even charged at by Moros using spears.[45] Moros fought to the death against Americans armed with rifles and artillery while they themselves used only Kris at the crater battle.[82][83]
Novels have been written about Juramentados deliberately impaling themselves on their bayonets in attempts to reach and kill American soldiers.[84]
In popular culture
- Vic Hurley's history of the Moros, "Swish of the Kris The Story of the Moros" tells the story of Col. Alexander Rodgers using pigs to subdue the Moros in the Philippines. Hurley wrote that Col. Rodgers was known as "the Pig" to the Moros.[85] And another Hurley book "The Jungle Patrol, the story of the Philippine Constabulary" also relates the story of pigs being used against them.
- Hurley wrote the screenplay for the Hollywood film The Real Glory in 1937; the film was released in 1939. It was based on a 1937 novel of the same name by Charles L. Clifford, a pen name of Hurley's. There is a scene in the movie where Gary Cooper as Dr. Bill Canavan drapes a captured Muslim in a pigskin. He proclaims that all slain Muslim rebels will be buried in pig skins to prevent their entry into paradise. The film served as American military propaganda, portraying the US Army as brave defenders of the local population being terrorised by the Moros, whom the film inaccurately depicts as bloodthirsty raiders oppressing the local Filipino community.[86][87]
See also
References
Notes
- ^ Anthony Joes (2006). Resisting Rebellion: The History and Politics of Counterinsurgency. University Press of Kentucky. p. 164. ISBN 0-8131-7199-7.
- ^ a b James R. Arnold (2011). The Moro War: How America Battled a Muslim Insurgency in the Philippine Jungle, 1902–1913. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 187–. ISBN 978-1-60819-365-3.
- ^ "Mindanao, Sulu and Armm Unsung Heroes".
- ^ United States. Congress. House. Committee on Invalid Pensions (1945). Hearings. p. 40.
- ^ Arnold, J.R., 2011, The Moro War, New York: Bloomsbury Press, ISBN 9781608190249
- ^ Douglas V. Meed (2003). Soldier of Fortune: Adventuring in Latin America and Mexico with Emil Lewis Holmdahl. Halcyon Press Ltd. pp. 24–. ISBN 978-1-931823-05-0.
- ^ Robert A. Fulton (2009). Moroland: The History of Uncle Sam and the Moros, 1899–1920. Tumalo Creek Press. ISBN 978-0979517303.
- ^ Arnold, J.R., 2011, The Moro War, New York: Bloomsbury Press, ISBN 9781608190249
- ^ "MORO | Definition of MORO by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com also meaning of MORO". Lexico Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on March 3, 2021. Retrieved March 30, 2021.
- ^ Banlaoi 2012, p. 24.
- ^ Banlaoi 2005 Archived 2016-02-10 at the Wayback Machine, p. 68.
- ^ a b Dphrepaulezz, Omar H. (5 June 2013). "The Right Sort of White Men": General Leonard Wood and the U.S. Army in the Southern Philippines, 1898–1906 (Doctoral Dissertations). Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Kho, Madge. "The Bates Treaty". PhilippineUpdate.com. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ Hurley, Victor (1936). "17. Mindanao and Sulu in 1898". Swish of the Kris. New York: E.P. Dutton & Co. Archived from the original on 2008-07-12. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ Guerrero, Rustico O (10 April 2002). MASTER OF MILITARY STUDIES PHILIPPINE TERRORISM AND INSURGENCY: WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE ABU SAYYAF GROUP (PDF) (Thesis). United States Marine Corps Command and Staff College Marine Corps University. p. 6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 April 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ Swain, Richard (October 2010). "Case Study: Operation Enduring Freedom Philippines" (PDF) (Case Study). U.S. Army Counterinsurgency Center. p. 8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-03-03. Retrieved 2015-11-14.
- ^ Mustafa Akyol (2011). Islam without Extremes: A Muslim Case for Liberty. W. W. Norton. pp. 159–. ISBN 978-0-393-07086-6.
- ^ Idris Bal (2004). Turkish Foreign Policy in Post Cold War Era. Universal-Publishers. pp. 405–. ISBN 978-1-58112-423-1.
- ^ Kemal H. Karpat (2001). The Politicization of Islam: Reconstructing Identity, State, Faith, and Community in the Late Ottoman State. Oxford University Press. pp. 235–. ISBN 978-0-19-513618-0.
- ^ Moshe Yegar (2002). Between Integration and Secession: The Muslim Communities of the Southern Philippines, Southern Thailand, and Western Burma/Myanmar. Lexington Books. pp. 397–. ISBN 978-0-7391-0356-2.
- ^ George Hubbard Blakeslee; Granville Stanley Hall; Harry Elmer Barnes (1915). The Journal of International Relations. Clark University. pp. 358–.
- ^ The Journal of Race Development. Clark University. 1915. pp. 358–.
- ^ Political Science Quarterly. Academy of Political Science. 1904. pp. 22–.
Straus Sulu Ottoman.
- ^ Kho, Madge. "The Bates Treaty". Philippine Update. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ^ Article title Archived 2013-04-13 at the Wayback Machine Luga p. 22.
- ^ "A Brief History of America and the Moros 1899–1920". Archived from the original on 2016-03-09. Retrieved 2016-01-30.
- ^ "The Bates Mission 1899". Archived from the original on 2016-06-03. Retrieved 2016-05-18.
- ^ "Causes of Conflict between Christians and Muslims in the Philippines".
- ^ Staff (15 March 1904). "AMERICA ABROGATES TREATY WITH MOROS; Rights Conferred by the Bates Agreement Forfeited. NATIVES FIGHT FOR SLAVERY United States Troops Defeat Them and Capture Cannon and Ammunition". The New York Times.
- ^ Ibrahim Alfian (Teuku.) (1987). Perang di Jalan Allah: Perang Aceh, 1873–1912. Pustaka Sinar Harapan. p. 130.
- ^ Benjamin Runkle (2011). Wanted Dead or Alive: Manhunts from Geronimo to Bin Laden. St. Martin's Press. pp. 73–74. ISBN 978-0-230-33891-3.
- ^ Simmons, Edwin H. (2003). "Civilize 'Em with a Krag". The United States Marines: A History. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press. p. 68. ISBN 978-1-55750-868-3.
- ^ Hunt, Geoffrey (2006). "Civilize 'Em with a Krag". Colorado's Volunteer Infantry in the Philippine Wars, 1898–1899. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. p. 198. ISBN 978-0-8263-3700-9.
- ^ "President Theodore Roosevelt's Proclamation Formally Ending the Philippine 'Insurrection' and Granting of Pardon and Amnesty". MSC Institute of Technology. July 4, 1902. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ a b c Hurley, Vic (1936). "18. The Formation of the Moro Province". Swish of the Kris. New York: E.P. Dutton & Co. Archived from the original on 2008-07-12. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ Hagedorn 1931, p. 14, Volume 2
- ^ Bacevich, Andrew J. (March 12, 2006). "What happened at Bud Dajo". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ Birtle 1998, p. 164
- ^ "Bearers of the Sword Radical Islam, Philippines Insurgency, and Regional Stability". 21 June 2012. Archived from the original on 2012-06-21.
- ^ Walsh, Thomas P. (2013). Tin Pan Alley and the Philippines: American Songs of War and Love, 1898–1946 : a Resource Guide. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 9780810886087 – via Google Books.
- ^ "If a Lady's Wearin' Pantaloons sheet music for Treble Clef Instrument". 8notes.com.
- ^ "abc – If a Lady's Wearin' Pantaloons".
- ^ Runyon, Damon (1911). The Tents of Trouble. Desmond FitzGerald, Incorporated – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Spiegel, Max. "IF A LADY'S WEARIN' PANTALOONS".
- ^ a b c James R. Arnold (2011). The Moro War: How America Battled a Muslim Insurgency in the Philippine Jungle, 1902–1913. Bloomsbury USA. pp. 162–. ISBN 978-1-60819-024-9.
- ^ Benjamin R. Beede (2013). The War of 1898 and U.S. Interventions, 1898T1934: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-136-74691-8.
By the end of the operation the estimated 600 Muslims in Bud Daju were wiped out.
- ^ John J. Pershing (2013). My Life before the World War, 1860–1917: A Memoir. University Press of Kentucky. p. 386. ISBN 978-0-8131-4198-5.
These are merely estimates, because no firm number of Moro dead was ever established.
- ^ Robert A. Fulton (2011). Honor for the Flag: The Battle of Bud Dajo – 1906 & the Moro Massacre. Robert Fulton. ISBN 978-0-9795173-2-7.
- ^ Mark Twain (2013). Delphi Complete Works of Mark Twain (Illustrated). Delphi Classics. p. 3819. ISBN 978-1-908909-12-1.
- ^ Mark Twain (2013). Delphi Complete Works of Mark Twain (Illustrated). Delphi Classics. pp. 3777–. ISBN 978-1-908909-12-1.
- ^ Howard Zinn; Anthony Arnove (2011). Voices of a People's History of the United States. Seven Stories Press. pp. 248–. ISBN 978-1-58322-947-7.
- ^ James R. Arnold; Roberta Wiener (2015). Understanding U.S. Military Conflicts through Primary Sources [4 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-1-61069-934-1.
- ^ Documents in United States History: Since Reconstruction. Pearson/Prentice Hall. 2004. p. 431. ISBN 978-0-13-150256-7.
- ^ Bruce Borland (1997). America Through the Eyes of Its People: Primary Sources in American History. Longman. p. 236. ISBN 978-0-673-97738-0.
- ^ Roger J. Bresnahan (1981). In time of hesitation: American Anti-Imperialists and the Philippine–American War. New Day Publishers. p. 67. ISBN 9780686325796.
- ^ Burton L. Cooper (1967). 12 Prose Writers: Francis Bacon, Jonathan Swift, William Hazlitt, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Matthew Arnold, Mark Twain, E.M. Forster, Aldous Huxley, James Thurber, George Orwell, Mary McCarthy [and] James Baldwin. Holt, Rinehart and Winston. p. 161.
- ^ Mark Twain (1979). A Pen Warmed-Up in Hell: Mark Twain in Protest. Harper & Row. p. 97. ISBN 9780060906788.
- ^ Mark Twain (1973). Mark Twain and the Three R's: Race, Religion, Revolution – And Related Matters. Bobbs-Merrill. p. 20. ISBN 9780672517051.
- ^ Mark Twain; Albert Bigelow Paine (1925). The Writings of Mark Twain. Gabriel Wells. p. 187.
- ^ "America Past and Present Online – Mark Twain, "Incident in the Philippines" (1924)".
- ^ ""Comments on the Moro Massacre" – Samuel Clemens (March 12, 1906)".
- ^ "Comments on the Moro Massacre by Mark Twain". Archived from the original on 2016-05-13. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- ^ "Autobiography of Mark Twain, Volume 1 : an electronic text".
- ^ "Novelist Kurt Vonnegut Dies at 84". Democracy Now!.
- ^ "Comments on the Moro Massacre by Mark Twain". Archived from the original on 2005-12-28.
- ^ [49][50][51][52][53][54][55][56][57][58][59][60][61][62][63][64][65]
- ^ Mannix, Daniel P., IV (1983). The Old Navy. Macmillan Publishing Company. p. 164. ISBN 978-0-02-579470-2.
...the custom of wrapping the dead man in a pig's skin and stuffing his mouth with pork. As the pig was an unclean animal, this was considered unspeakable defilement.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) A compilation of the diary of Rear Admiral D.P. Mannix III. - ^ Miller, Daniel G. "American Military Strategy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on September 27, 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ Pershing, John (2013) My Life Before the World War, 1860–1917: A Memoir, pp. 284–285 Lexington, Kentucky: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 9780813141978
- ^ Horton, Alex (August 18, 2017) "Trump said to study General Pershing. Here’s what the president got wrong" The Washington Post
- ^ Qiu, Linda (August 18, 2017) "Study Pershing, Trump Said. But the Story Doesn’t Add Up" The New York Times
- ^ Byler 2005
- ^ Spencer C. Tucker (2009). Encyclopedia of the Spanish–American and Philippine–American Wars: A Political, Social, and Military History. ABC-CLIO. pp. 415–417. ISBN 978-1-85109-952-8.
- ^ Spencer C. Tucker (2013). Encyclopedia of Insurgency and Counterinsurgency: A New Era of Modern Warfare. ABC-CLIO. p. 371. ISBN 978-1-61069-280-9.
- ^ "Colt New Army & Navy Revolver". 2010-07-04. Archived from the original on 2010-07-04. Retrieved 2021-06-23.
- ^ DK (2006). Weapon: A Visual History of Arms and Armor. DK Publishing. pp. 290–. ISBN 978-0-7566-4219-8.
- ^ Shaʾul Shai. The Shahids: Islam and Suicide Attacks. Transaction Publishers. pp. 29–. ISBN 978-1-4128-3892-4.
- ^ Vic Hurley (2011). Jungle Patrol, the Story of the Philippine Constabulary (1901–1936). Cerberus Books. pp. 319–. ISBN 978-0-9834756-2-0.
- ^ Jim Lacey (2008). Pershing: A Biography. St. Martin's Press. pp. 44–. ISBN 978-0-230-61270-9.
- ^ Vic Hurley; Christopher L. Harris (2010). Swish of the Kris, the Story of the Moros, Authorized and Enhanced Edition. Cerberus Books. pp. 210–. ISBN 978-0-615-38242-5.
- ^ The Field Artillery Journal. United States Field Artillery Association. 1942. p. 799.
- ^ United States. Congress. House. Committee on Invalid Pensions (1945). Hearings. p. 38.
- ^ United States. Congress. House. Committee on Invalid Pensions; United States. Congress. House. Committee on Veterans' Affairs (1945). Philippine Uprisings and Campaigns After July 4, 1902, and Prior to January 1, 1914: Hearings Before the Committee on Invalid Pensions, House of Representatives, Seventy-ninth Congress, First Session, on H. R. 128 and H. R. 3251, Bills Extending Pension Benefits to Veterans who Served After July 4, 1902, and Prior to January 1, 1914, in the Armed Forces Engaged in Actual Hostilities in Certan Specified Areas on the Philippine Islands, and to Their Dependents. March 20 and 22, 1945. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 37–38.
- ^ Teodoro M. Locsin (1994). Trial & error. Free Press, Inc. p. 238. ISBN 978-971-91399-0-4.
- ^ Swish of the Kris p. 223, Cerebus books ISBN 978-061-538-242-5
- ^ M. Paul Holsinger (January 1999). War and American Popular Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 187. ISBN 978-0-313-29908-7.
- ^ Ignacio Farmer (21 February 2015). "Western Movies Full Length The Real Glory War Drama 1939" – via YouTube.
Bibliography
- Arnold, James R. (2011). The Moro War: How America Battled a Muslim Insurgency in the Philippine Jungle, 1902-1913. Bloomsbury Press. ISBN 9781608190249. OCLC 664519655.
- Birtle, Andrew J. (1998). U.S. Army Counterinsurgency & Contingency Operations Doctrine: 1860–1941. Diane Pub Co. ISBN 0-7881-7327-8.
- Byler, Charles (May–June 2005). "Pacifying the Moros: American Military Government in the Southern Philippines, 1899–1913" (PDF). Military Review: 41–45. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- Hagedorn, Hermann (1931). Leonard Wood: A Biography. Vol. 2. New York: Harper & Brothers.
- Hurley, Vic (1936). Swish of the Kris. New York: E.P. Dutton & Co. Archived from the original on 2008-07-12. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- Kho, Madge. "The Bates Treaty". PhilippineUpdate.com. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- Kolb, Richard K. (May 2002). "'Like a mad tiger': fighting Islamic warriors in the Philippines 100 years ago". VFW Magazine. Archived from the original on 2004-08-05.
- Lane, Jack C. (1978). Armed Progressive: General Leonard Wood. San Rafael, Calif.: Presidio Press. ISBN 0-89141-009-0. OCLC 3415456.
- Millett, Alan R. (1975). The General: Robert L. Bullard and Officership in the United States Army 1881–1925. Westport, Conn.: Greenward Press. ISBN 0-8371-7957-2. OCLC 1530541.
- Palmer, Frederick (1970) [1934]. Bliss, Peacemaker: The Life and Letters of General Tasker Howard Bliss. Freeport, NY: Books for Libraries Press. ISBN 0-8369-5535-8. OCLC 101067.
- Smythe, Donald (1973). Guerrilla Warrior: The Early Life of John J. Pershing. New York: Charles Scribener's Sons. ISBN 0-684-12933-7. OCLC 604954.
- Vandiver, Frank E. (1977). Black Jack: The Life and Times of John J. Pershing. Vol. 1. College Station, TX: Texas A&M University Press. ISBN 0-89096-024-0. OCLC 2645933.
Further reading
- Linn, Brian McAllister (1999). Guardians of Empire: The U.S. Army and the Pacific, 1902–1940. UNC Press Books. ISBN 978-0-8078-4815-9.
- Rice, Donald Tunnicliff (2016). Cast in Deathless Bronze: Andrew Rowan, the Spanish–American War, and the Origins of American Empire. West Virginia University Press. ISBN 978-1-943665-43-3.
External links
- Articles with neologism issues from November 2016
- Moro Rebellion
- Conflicts in 1899
- 1900s conflicts
- 1910s conflicts
- 1899 in the Philippines
- 1900s in the Philippines
- 1910s in the Philippines
- History of the Philippines (1898–1946)
- Rebellions in the Philippines
- History of Basilan
- History of Lanao del Sur
- History of Maguindanao
- History of Sulu
- History of Tawi-Tawi
- Moro people
- Rebellions in Asia
- Wars involving the United States
- Rebellions against the United States




