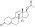
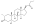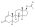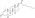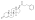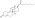Trenbolone enanthate
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Trenabol; Trenbolone heptanoate; 19-Nor-δ9,11-testosterone 17β-enanthate; Estra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one 17β-enanthate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester; Progestogen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H34O3 |
| Molar mass | 382.544 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Trenbolone enanthate, known by the nickname Trenabol, is a synthetic and injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of nandrolone which was never marketed.[1][2] It is the C17β enanthate ester and a long-acting prodrug of trenbolone.[1] Trenbolone enanthate was never approved for medical or veterinary use but is used in scientific research[3][4] and has been sold on the internet black market as a designer steroid for bodybuilders and athletes.[5][6]
| Anabolic steroid | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight |
Relative AAS contentb |
Durationc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Moiety | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Boldenone undecylenate | C17β | Undecylenic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | Long | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.18 | 0.84 | Short | ||
| Metenolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.14 | 0.88 | Short | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.37 | 0.73 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.56 | 0.64 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6–7) | 1.48 | 0.67 | Long | ||
| Trenbolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.16 | 0.87 | Short | ||
| Trenbolone enanthated | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | Long | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative androgen/anabolic steroid content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Duration by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in oil solution. d = Never marketed. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
See also
References
- ^ a b William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 724–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ^ Underground Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 120–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-7-6.
- ^ Dalbo VJ, Roberts MD, Mobley CB, Ballmann C, Kephart WC, Fox CD, Santucci VA, Conover CF, Beggs LA, Balaez A, Hoerr FJ, Yarrow JF, Borst SE, Beck DT (2016). "Testosterone and trenbolone enanthate increase mature myostatin protein expression despite increasing skeletal muscle hypertrophy and satellite cell number in rodent muscle". Andrologia. 49 (3): e12622. doi:10.1111/and.12622. PMID 27246614. S2CID 1852164.
- ^ Ye F, McCoy SC, Yarrow JF, Conover CF, Beck DT, Beggs LA, Tillman MD (2013). "Effect of Trenbolone enanthate on protein degradation in levator ani/bulbocavernosus (LABC) muscle in orchiectomized rats". The FASEB Journal. 27: 939–15. doi:10.1096/fasebj.27.1_supplement.939.15.
- ^ "Side effects of Trenbolone Enanthate". trenenanthate.net. 2020-01-24. Retrieved 2021-03-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ El Osta R, Almont T, Diligent C, Hubert N, Eschwège P, Hubert J (2016). "Anabolic steroids abuse and male infertility". Basic Clin Androl. 26: 2. doi:10.1186/s12610-016-0029-4. PMC 4744441. PMID 26855782.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
Further reading
- Yarrow JF, McCoy SC, Borst SE (2010). "Tissue selectivity and potential clinical applications of trenbolone (17beta-hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one): A potent anabolic steroid with reduced androgenic and estrogenic activity". Steroids. 75 (6): 377–89. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.01.019. PMID 20138077. S2CID 205253265.