United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine: Difference between revisions
→Proposed division: expanded and title change Proposed division -> Proposed Partition |
Trahelliven (talk | contribs) →Background: Restoring reference to exchance of 225,000 Arabs and 1,250 Jews; Correcting grammar |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The [[British Empire|British]] administration was formalized by the [[League of Nations]] under the [[British Mandate for Palestine (legal instrument)|Palestine Mandate]] in 1923, as part of the [[Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire]] following World War I. The Mandate reaffirmed the 1917 British commitment to [[Balfour Declaration]], for the establishment in Palestine of a "National Home" for the Jewish people, with the prerogative to carry it out.<ref name="Mansfield1992"/><ref>[http://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_century/palmanda.asp The Palestine Mandate] "the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the [Balfour] declaration originally made on November 2nd, 1917"</ref> A British census of 1918 estimated 700,000 Arabs and 56,000 Jews.<ref name=Mansfield1992>{{Citation | title = The Arabs | year = 1992 | author = Mansfield, Peter | pages = 172–175 | isbn = 0-14-014768-3}}</ref> |
The [[British Empire|British]] administration was formalized by the [[League of Nations]] under the [[British Mandate for Palestine (legal instrument)|Palestine Mandate]] in 1923, as part of the [[Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire]] following World War I. The Mandate reaffirmed the 1917 British commitment to [[Balfour Declaration]], for the establishment in Palestine of a "National Home" for the Jewish people, with the prerogative to carry it out.<ref name="Mansfield1992"/><ref>[http://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_century/palmanda.asp The Palestine Mandate] "the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the [Balfour] declaration originally made on November 2nd, 1917"</ref> A British census of 1918 estimated 700,000 Arabs and 56,000 Jews.<ref name=Mansfield1992>{{Citation | title = The Arabs | year = 1992 | author = Mansfield, Peter | pages = 172–175 | isbn = 0-14-014768-3}}</ref> |
||
In 1937, following a six-month-long [[1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine#The Arab General Strike and armed insurrection|Arab General Strike and armed insurrection]] in which the Palestinians sought to obtain their national goals of independence from the British and to halt the process in which they saw country coming under the control of foreigners, the British established the [[Peel Commission]].<ref name="Khalidi2006">{{cite book|author=Rashid Khalidi|title=The Iron Cage: The Story of the Palestinian Struggle for Statehood|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=bYADAQAAQBAJ&pg=PT181|date=1 September 2006|publisher=Beacon Press|isbn=978-0-8070-0315-2|pages=181–}}</ref> It concluded that the Mandate had become unworkable, recommending a Partition |
In 1937, following a six-month-long [[1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine#The Arab General Strike and armed insurrection|Arab General Strike and armed insurrection]] in which the Palestinians sought to obtain their national goals of independence from the British and to halt the process in which they saw the country coming under the control of foreigners, the British established the [[Peel Commission]].<ref name="Khalidi2006">{{cite book|author=Rashid Khalidi|title=The Iron Cage: The Story of the Palestinian Struggle for Statehood|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=bYADAQAAQBAJ&pg=PT181|date=1 September 2006|publisher=Beacon Press|isbn=978-0-8070-0315-2|pages=181–}}</ref> It concluded that the Mandate had become unworkable, recommending a Partition into an Arab state linked to [[Transjordan]], a much smaller Jewish state (about 15%), and a mandatory area. It proposed that land and population exchanges should be carried out to overcome demarcation problems.<ref>[http://unispal.un.org/pdfs/Cmd5479.pdf Palestine Royal Commission report, 1937, 389–391]</ref><ref>{{cite book | author = Benny Morris | title = Righteous Victims | page = 139}}</ref> The exchange proposal was to involve the transfer of an estimated 225,000 Arabs living in the Jewish state and 1,250 Jews living in the Arab state, which would be compulsory "in the last resort".<ref>[http://unispal.un.org/pdfs/Cmd5479.pdf Palestine Royal Commission report, 1937, 389–391]</ref><ref>{{cite book | author = Benny Morris | title = Righteous Victims | page = 139}}</ref> The Arab leadership rejected the plan. The two main Jewish leaders, [[Chaim Weizmann]] and [[David Ben-Gurion|Ben Gurion]] had convinced the [[World Zionist Congress|Zionist Congress]] to approve equivocally the Peel recommendations as a basis for more negotiation.<ref>William Roger Louis, [http://books.google.co.il/books/about/Ends_of_British_Imperialism.html?id=NQnpQNKeKKAC&redir_esc=y Ends of British Imperialism: The Scramble for Empire, Suez, and Decolonization], 2006, p.391</ref><ref>Benny Morris, One state, two states: resolving the Israel/Palestine conflict, 2009, p. 66</ref><ref name="morris2004p48"/><ref>Partner to Partition: The Jewish Agency's Partition Plan in the Mandate Era, Yosef Kats, Chapter 4, 1998 Edition, Routledge, ISBN 0-7146-4846-9</ref> |
||
The British [[Woodhead Commission]] was set up to examine the practicality of partition. The Peel plan was rejected and two possible alternatives were considered. In 1938 the British government issued a policy statement declaring that "the political, administrative and financial difficulties involved in the proposal to create independent Arab and Jewish States inside Palestine are so great that this solution of the problem is impracticable". Representatives of Arabs and Jews were invited to London for the [[St. James Conference]], which proved unsuccessful.<ref>Palestine. Statement by His Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom. Presented by the Secretary of State for the Colonies to Parliament by Command of His Majesty. November, 1938. Cmd. 5893. [http://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/4941922311B4E3C585256D17004BD2E2]</ref> |
The British [[Woodhead Commission]] was set up to examine the practicality of partition. The Peel plan was rejected and two possible alternatives were considered. In 1938 the British government issued a policy statement declaring that "the political, administrative and financial difficulties involved in the proposal to create independent Arab and Jewish States inside Palestine are so great that this solution of the problem is impracticable". Representatives of Arabs and Jews were invited to London for the [[St. James Conference]], which proved unsuccessful.<ref>Palestine. Statement by His Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom. Presented by the Secretary of State for the Colonies to Parliament by Command of His Majesty. November, 1938. Cmd. 5893. [http://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/4941922311B4E3C585256D17004BD2E2]</ref> |
||
Revision as of 02:10, 2 February 2014
| UN General Assembly Resolution 181 (II) | |
|---|---|
 UNSCOP (3 September 1947) and UN Ad Hoc Committee (25 November 1947) partition plans. The UN Ad Hoc committee proposal was voted on in the resolution. | |
| Date | November 29 1947 |
| Meeting no. | 128 |
| Code | A/RES/181(II) (Document) |
Voting summary |
|
| Result | Recommendation to the United Kingdom, as the mandatory Power for Palestine, and to all other Members of the United Nations the adoption and implementation, with regard to the future government of Palestine, of the Plan of Partition with Economic Union set out in the resolution[1] |
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal developed by the United Nations, which recommended a partition with Economic Union of Mandatory Palestine, following the termination of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the U.N. General Assembly adopted a resolution recommending the adoption and implementation of the Plan as Resolution 181(II).[2]
The resolution called for the creation of independent Arab and Jewish States and the Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem. The Partition Plan, a four-part document attached to the resolution, provided for the termination of the Mandate, the progressive withdrawal of British armed forces and the delineation of boundaries between the two States and Jerusalem. Part I of the Plan stipulated that the Mandate would be terminated as soon as possible and the United Kingdom would withdraw no later than 1 August 1948. The new states would come into existence two months after the withdrawal, but no later than 1 October 1948. The Plan sought to address the conflicting objectives and claims of two competing movements: Arab nationalism and Jewish nationalism, known as Zionism.[3] The Plan also called for Economic Union between the proposed states, and for the protection of religious and minority rights.
The Plan was accepted by the Zionist movement, except for its fringes,[4] but rejected by the Arab public and the ruling elites of the Palestinian Arabs, along with the rest of the Arab world,[5] except for its fringes.[6]
Immediately after adoption of the Resolution by the General Assembly, the civil war broke out.[7] The partition plan was not implemented.[8]
Background
The British administration was formalized by the League of Nations under the Palestine Mandate in 1923, as part of the Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire following World War I. The Mandate reaffirmed the 1917 British commitment to Balfour Declaration, for the establishment in Palestine of a "National Home" for the Jewish people, with the prerogative to carry it out.[9][10] A British census of 1918 estimated 700,000 Arabs and 56,000 Jews.[9]
In 1937, following a six-month-long Arab General Strike and armed insurrection in which the Palestinians sought to obtain their national goals of independence from the British and to halt the process in which they saw the country coming under the control of foreigners, the British established the Peel Commission.[11] It concluded that the Mandate had become unworkable, recommending a Partition into an Arab state linked to Transjordan, a much smaller Jewish state (about 15%), and a mandatory area. It proposed that land and population exchanges should be carried out to overcome demarcation problems.[12][13] The exchange proposal was to involve the transfer of an estimated 225,000 Arabs living in the Jewish state and 1,250 Jews living in the Arab state, which would be compulsory "in the last resort".[14][15] The Arab leadership rejected the plan. The two main Jewish leaders, Chaim Weizmann and Ben Gurion had convinced the Zionist Congress to approve equivocally the Peel recommendations as a basis for more negotiation.[16][17][18][19]
The British Woodhead Commission was set up to examine the practicality of partition. The Peel plan was rejected and two possible alternatives were considered. In 1938 the British government issued a policy statement declaring that "the political, administrative and financial difficulties involved in the proposal to create independent Arab and Jewish States inside Palestine are so great that this solution of the problem is impracticable". Representatives of Arabs and Jews were invited to London for the St. James Conference, which proved unsuccessful.[20]
With World War II looming, British policies were at this point influenced by desire to win Arab world support, ill afford to engage with another Arab uprising.[21] The MacDonald White Paper of May 1939 declared that it was "not part of [the British government's] policy that Palestine should become a Jewish State", sought to limit Jewish immigration to Palestine and restricted Arab land sales to Jews. However, the League of Nations commission held that the White Paper was in conflict with the terms of the Mandate as put forth in the past. The outbreak of the Second World War suspended any further deliberations.[22][23] The Jewish Agency hoped to persuade the British to restore Jewish immigration rights, and cooperated with the British in the war against Fascism. Aliyah Bet was organized to spirit Jews out of Nazi controlled Europe, despite the British prohibitions. The White Paper also led to the formation of Lehi, a small Jewish terrorist organization which opposed the British.
After World War II, in August 1945 president Truman asked for admission of 100,000 Holocaust survivors into Palestine[24] but the British maintained limits on Jewish immigration in line with the 1939 White Paper. The Jewish community rejected the restriction on immigration and also organized an armed resistance. These and United States pressure to end the anti-immigration policy led to the establishment of the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry. In April 1946, the committee reached a unanimous decisions for the immediate admission of 100,000 Jewish refugees from Europe into Palestine, rescinding the white paper restrictions of land sale to Jews, that the country be neither Arab nor Jewish and the extension of U.N Trusteeship. U.S endorsed the the commission findings concerning Jewish immigration and land purchase restrictions,[25] while U.K. conditioned their implementation on US assistance in case of another Arab revolt.[25] In effect the the British continued to carry out its White Paper policy.[26] The recommendations triggered violent demonstrations in the Arab states, and calls for a Jihad and an annihilation all European Jews in Palestine.[27]
UNSCOP

In February 1947, Britain announced its intent to terminate the Mandate, referring the matter of the future of Palestine to the United Nations,[29] hoping for creating a bi-national state, which means an unpartitioned Palestine.[30] In May, the UN formed a Special Committee(UNSCOP) to prepare a report on recommendations for Palestine. In August, after three months of conducting hearings and a general survey of the situation in Palestine, a majority report of the committee recommended that the region be partitioned into an Arab and a Jewish state, which should retain an economic union; and an international regime for Jerusalem.
During the committee visit to Palestine its members witnessed the SS Exodus affair and were heavily influenced by it[how?][31] The incident is mentioned in the report in relation to Jewish distrust and resentment concerning the British enforcement of the White Paper 1939.[32]
UNSCOP Report
On 3 September 1947, the Committee reported to the General Assembly. CHAPTER V: PROPOSED RECOMMENDATIONS (I), Section A of the Report contained eleven proposed recommendations (I - XI) approved unanimously. Section B contained one proposed recommendation approved by a substantial majority dealing with the Jewish problem in general (XI). CHAPTER VI: PROPOSED RECOMMENDATIONS (II) contained a Plan of Partition with Economic Union to which seven members of the Committee (Canada, Czechoslovakia, Guatemala, the Netherlands, Peru, Sweden and Uruguay), expressed themselves in favour. CHAPTER VII RECOMMENDATIONS (III) contained a comprehensive proposal that was voted upon and supported by three members (India, Iran, and Yugoslavia) for a Federal State of Palestine. In CHAPTER VIII A number of members of the Committee expressed certain reservations and observations.[33]
Proposed Partition
The committees' majority report(CHAPTER VI) envisage the division of Palestine into three parts: an Arab State, a Jewish State and the City of Jerusalem, linked by extraterritorial crossroads. The proposed Arab State will include the Western Galilee, with the town of Acre, the hill country of Samaria and Judea, and the southern coast stretching from north of Isdud (now Ashdod) and encompassing what is now the Gaza Strip, with a section of desert along the Egyptian border. The proposed Jewish State will include Eastern Galilee, the Coastal Plain, stretching from Haifa to Rehovot and the Negev desert,[34] including the southern outpost of Umm Rashrash (now Eilat). The Jerusalem Corpus Separatum included, Bethlehem and the surrounding areas.
The committees primary objectives were political division and economic unity among the two groups.[35] The Plan tried its best to accommodate as many Jews as possible into the Jewish State. In many specific cases,[citation needed] this meant including areas of Arab majority (but with a significant Jewish minority) in the Jewish state. Thus the Jewish State would have an overall large Arab minority. Areas that were sparsely populated (like the Negev desert), were also included in the Jewish state to create room for immigration. According to the plan, Jews and Arabs living in the Jewish state would become citizens of the Jewish state and Jews and Arabs living in the Arab state would become citizens of the Arab state.
By virtue of Chapter 3, Palestinian citizens residing in Palestine outside the City of Jerusalem, as well as Arabs and Jews who, not holding Palestinian citizenship, resided in Palestine outside the City of Jerusalem would, upon the recognition of independence, become citizens of the State in which they were resident and enjoy full civil and political rights.
The Plan would have had the following demographics (data based on 1945). This data does not reflect the actual land ownership by Jews, local Arabs, Ottomans and other land owners. This data also excludes the land designated to Arabs in Transjordan.
| Territory | Arab and other population | % Arab and other | Jewish population | % Jewish | Total population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arab State | 725,000 | 99% | 10,000 | 1% | 735,000 | |
| Jewish State | 407,000 | 45% | 498,000 | 55% | 905,000 | |
| International | 105,000 | 51% | 100,000 | 49% | 205,000 | |
| Total | 1,237,000 | 67% | 608,000 | 33% | 1,845,000 | |
| Data from the Report of UNSCOP: 3 September 1947: CHAPTER 4: A COMMENTARY ON PARTITION | ||||||
The land allocated to the Arab State in the final plan included about 43% of Mandatory Palestine[36][unreliable source?] and consisted of all of the highlands, except for Jerusalem, plus one-third of the coastline. The highlands contain the major aquifers of Palestine, which supplied water to the coastal cities of central Palestine, including Tel Aviv.[37][unreliable source?] The Jewish State was to receive 56% of Mandatory Palestine, a slightly larger area to accommodate the increasing numbers of Jews who would immigrate there.[36][unreliable source?] The Jewish State included three fertile lowland plains – the Sharon on the coast, the Jezreel Valley and the upper Jordan Valley. The bulk of the proposed Jewish State's territory, however, consisted of the Negev Desert.[34] The desert was not suitable for agriculture, nor for urban development at that time. The Jewish State would also be given sole access to the Red Sea.
Ad Hoc Committee
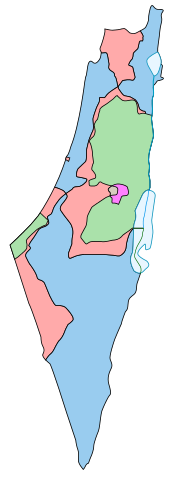
Boundaries defined in the 1947 UN Partition Plan for Palestine:
Armistice Demarcation Lines of 1949 (Green Line):
On 23 September 1947 the General Assembly established an ad hoc Committee on the Palestinian Question to consider the UNSCOP report. Representatives of the Arab Higher Committee and Jewish Agency were invited and attended.[38]
During the committee's deliberations, the British government endorsed the report's recommendations concerning the end of the mandate, independence, and Jewish immigration. [citation needed] However, the British did "not feel able to implement" any agreement unless it was acceptable to both the Arabs and the Jews, and asked that the General Assembly provide an alternative implementing authority if that proved to be the case.
The Arab Higher Committee rejected both the majority and minority recommendations within the UNSCOP report. They "concluded from a survey of Palestine history that Zionist claims to that country had no legal or moral basis". The Arab Higher Committee argued that only an Arab State in the whole of Palestine would be consistent with the UN Charter.
The Jewish Agency expressed support for most of the UNSCOP recommendations, but emphasized the "intense urge" of the overwhelming majority of Jewish displaced persons to proceed to Palestine. The Jewish Agency criticized the proposed boundaries, especially in the Western Galilee and Western Jerusalem (outside of the old city), arguing that these should be included in the Jewish state. However, they agreed to accept the plan if "it would make possible the immediate re-establishment of the Jewish State with sovereign control of its own immigration."
Sub-Committee 2
The Sub-Committee 2, set up on 23 October 1947 to draw up a detailed plan based on proposals of Arab states presented its report within a few weeks.[39]
Based on a reproduced British report, the Sub-Committee 2 criticised the UNSCOP report for using inaccurate population figures, especially concerning the Bedouin population. The British report, dated 1 November 1947, used the results of a new census in Beersheba in 1946 with additional use of aerial photographs, and an estimate of the population in other districts. It found that the size of the Bedouin population was greatly understated in former enumerations. In Beersheba, 3,389 Bedouin houses and 8,722 tents were counted. The total Bedouin population was estimated at approximately 127,000; only 22,000 of them normally resident in the Arab state under the UNSCOP majority plan. The British report stated:
"It should be noted that the term Beersheba Bedouin has a meaning more definite than one would expect in the case of a nomad population. These tribes, wherever they are found in Palestine, will always describe themselves as Beersheba tribes. Their attachment to the area arises from their land rights there and their historic association with it."[39]
In respect of the UNSCOP report, the Sub-Committee concluded that the earlier population ″estimates must, however, be corrected in the light of the information furnished to the Sub-Committee by the representative of the United Kingdom regarding the Bedouin population. According to the statement, 22,000 Bedouins may be taken as normally residing in the areas allocated to the Arab State under the UNSCOP's majority plan, and the balance of 105,000 as resident in the proposed Jewish State. It will thus be seen that the proposed Jewish State will contain a total population of 1,008,800, consisting of 509,780 Arabs and 499,020 Jews. In other words, at the outset, the Arabs will have a majority in the proposed Jewish State.″[39]
The Sub-Committee 2 recommended to put the question of the Partition Plan before the International Court of Justice (Resolution No. I). In respect of the Jewish refugees due to World War II, the Sub-Committee recommended to request the countries of which the refugees belonged to take them back as much as possible (Resolution No. II). The Sub-Committee proposed to establish a unitary state (Resolution No. III).[40]
Boundary changes
The ad hoc committee made a number of boundary changes to the UNSCOP recommendations before they were voted on by the General Assembly.
The predominantly Arab city of Jaffa, previously located within the Jewish state, was constituted as an enclave of the Arab State. The boundary of the Arab state was modified to include Beersheba and a strip of the Negev desert along the Egyptian border,[34] while a section of the Dead Sea shore and other additions were made to the Jewish State. This move increased the Jewish percentage in the Jewish state from 55% to 61%.[citation needed]
The proposed boundaries would also have placed 54 Arab villages on the opposite side of the border from their farm land.[citation needed] In response, the United Nations Palestine Commission was empowered to modify the boundaries "in such a way that village areas as a rule will not be divided by state boundaries unless pressing reasons make that necessary". These modifications never occurred.
The vote
Passage of the resolution required a two-thirds majority of the valid votes, not counting abstaining and absent members, of the UN's then 56 member states. On 26 November, after filibustering by the Zionist delegation, the vote was postponed by three days.[41] According to multiple sources, had the vote been held on the original set date, it would have received a majority, but less than the required two-thirds.[42][43] The delay was used by supporters of Zionism in New York to put extra pressure on states not supporting the resolution.[41]
Reports of pressure for and against the Plan
Reports of pressure for the Plan
This section may lend undue weight to certain ideas, incidents, or controversies. Please help to create a more balanced presentation. Discuss and resolve this issue before removing this message. (October 2013) |
Proponents of the Plan reportedly put pressure on nations to vote yes to the Partition Plan. A telegram signed by 26 US senators with influence on foreign aid bills was sent to wavering countries, seeking their support for the partition plan.[44] Many nations reported pressure directed specifically at them:
- United States (Vote: For): President Truman later noted, "The facts were that not only were there pressure movements around the United Nations unlike anything that had been seen there before, but that the White House, too, was subjected to a constant barrage. I do not think I ever had as much pressure and propaganda aimed at the White House as I had in this instance. The persistence of a few of the extreme Zionist leaders—actuated by political motives and engaging in political threats—disturbed and annoyed me."[45]
- India (Vote: Against): Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru spoke with anger and contempt for the way the UN vote had been lined up. He said the Zionists had tried to bribe India with millions and at the same time his sister, Vijaya Lakshmi Pandit, had received daily warnings that her life was in danger unless "she voted right".[46]Vijaya Lakshmi Pandit, Nehru’s sister, the Indian ambassador to the U.N, occasionally hinted that something might change in favour of the Yishuv. But another Indian delegate said that India would vote for the Arab side, because of their large Moslem minority, although they know that the Jews has a case.[47]
- Liberia (Vote: For): Liberia's Ambassador to the United States complained that the US delegation threatened aid cuts to several countries.[48] Harvey S. Firestone, Jr., President of Firestone Natural Rubber Company, with major holdings in the country, also pressured the Liberian government[42][44]
- Philippines (Vote: For): In the days before the vote, the Philippines' representative General Carlos P. Romulo stated "We hold that the issue is primarily moral. The issue is whether the United Nations should accept responsibility for the enforcement of a policy which is clearly repugnant to the valid nationalist aspirations of the people of Palestine. The Philippines Government holds that the United Nations ought not to accept such responsibility". After a phone call from Washington, the representative was recalled and the Philippines' vote changed.[44]
- Haiti (Vote: For): The promise of a five million dollar loan May or may not have secured Haiti's vote for partition.[49]
- France (Vote: For): Shortly before the vote, France's delegate to the United Nations was visited by Bernard Baruch, a long-term Jewish supporter of the Democratic Party who, during the recent world war, had been an economic adviser to President Roosevelt, and had latterly been appointed by President Truman as the United States' ambassador to the newly created UN Atomic Energy Commission. He was, privately, a supporter of the Irgun and its front organization, the American League for a Free Palestine. Baruch implied that a French failure to support the resolution might cause planned American aid to France, which was badly needed for reconstruction, French currency reserves being exhausted and its balance of payments heavily in deficit, not to materialise. Previously, in order to avoid antagonising its Arab colonies, France had not publicly supported the resolution. After considering the danger of American aid being withheld, France finally voted in favour of it. So, too, did France's neighbours, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands.[41]
Reports of pressure against the Plan
According to Benny Morris, Wasif Kamal, an Arab Higher Committee official, tried to bribe a delegate to the United Nations, perhaps a Russian.[50]
Concerning the welfare of Jews in Arab countries, a number of direct threats were made:
- Jamal Husseini promised, “The blood will flow like rivers in the Middle East”.[51] Iraqi Prime Minister Nuri al-Said, said: “We will smash the country with our guns and obliterate every place the Jews seek shelter in".
- Iraq’s prime minister Nuri al-Said told British diplomats that if the United Nations solution was not “satisfactory”, “severe measures should [would?] be taken against all Jews in Arab countries".[51]
Concerning the welfare of Jews in Arab countries, a number of predictions were made:
- '"On 24 November the head of the Egyptian delegation to the General Assembly, Muhammad Hussein Heykal, said that “the lives of 1,000,000 Jews in Moslem countries would be jeopardized by the establishment of a Jewish state."[52]
- In a speech at the General Assembly Hall at Flushing Meadow, New York, on Friday, 28 November 1947, Iraq’s Foreign Minister, Fadel Jamall, included the following statement: Partition imposed against the will of the majority of the people will jeopardize peace and harmony in the Middle East. Not only the uprising of the Arabs of Palestine is to be expected, but the masses in the Arab world cannot be restrained. The Arab-Jewish relationship in the Arab world will greatly deteriorate. There are more Jews in the Arab world outside of Palestine than there are in Palestine. In Iraq alone, we have about one hundred and fifty thousand Jews who share with Moslems and Christians all the advantages of political and economic rights. Harmony prevails among Moslems, Christians and Jews. But any injustice imposed upon the Arabs of Palestine will disturb the harmony among Jews and non-Jews in Iraq; it will breed inter-religious prejudice and hatred.[53]
- At the 29th Meeting of the UN Ad Hoc Committee on Palestine on 24 November 1947, Dr Heytal Pasha, the Egyptian delegate, said, "if the U.N decide to amputate a part of Palestine in order to establish a Jewish state, no force on earth could prevent blood from flowing there…Moreover…no force on earth can confine it to the borders of Palestine itself…Jewish blood will necessarily be shed elsewhere in the Arab world… to place in certain and serious danger a million Jews…Mahmud Bey Fawzi (Egypt) …imposed partition was sure to result in bloodshed in Palestine and in the rest of the Arab world".[54]
The Arab states warned the Western Powers that endorsement of the partition plan might be met by either or both an oil embargo and realignment of the Arab states with the Soviet Bloc.[50]
Final vote
On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly voted 33 to 13, with 10 abstentions and 1 absent, in favour of the modified Partition Plan. The final vote was as follows:
In favour, (33 countries, 72% of voting):
- Latin American and Caribbean (13 countries):
- Western European and Others (12 countries):
- Eastern European (5 countries):
- African (2 countries):
![]() Liberia
Liberia
![]() South Africa
South Africa
- Asia-Pacific (1 country)
![]() Philippines
Philippines
Against, (13 countries, 28% of voting):
- Asia-Pacific (10 countries):
- Western European (1 country):
![]() Greece
Greece
- African (1 country):
![]() Egypt
Egypt
- Latin American and Caribbean (1 country):
![]() Cuba
Cuba
Abstentions, (10 countries):
- Latin American and Caribbean (6 countries):
- Asia-Pacific (1 country):
![]() Republic of China
Republic of China
- African (1 country):
![]() Ethiopia
Ethiopia
- Western European and Others (1 country):
![]() United Kingdom
United Kingdom
- Eastern European (1 country):
![]() Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
Absent, (1 country):
- Asia-Pacific (1 country):
![]() Thailand
Thailand
Votes by region
What later came to be known as the United Nations Regional Groups showed relatively aligned voting styles in the final vote. All Western nations voted for the resolution, with the exception of the United Kingdom (the Mandate holder), Greece and Turkey. The Soviet bloc also voted for partition, with the exception of Yugoslavia, which was to be expelled from Cominform the following year. The majority of Latin American nations following Brazilian leadership[citation needed], voted for partition, with a sizeable minority abstaining. Asian countries voted against partition, with the exception of the Philippines.[55]
| Regional Group | Members in UNGA181 vote | UNGA181 For | UNGA181 Against | UNGA181 Abstained |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Asia-Pacific | 11 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| Eastern European | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 |
| LatAm and Caribb. | 20 | 13 | 1 | 6 |
| Western Eur. & Others | 15 | 12 | 2 | 1 |
| Total UN members | 56 | 33 | 13 | 10 |
Reactions
Jews
Most Jews in Palestine and around the world reacted to the UN resolution with satisfaction, but some did not. The Jewish Agency accepted the resolution despite its dissatisfaction with such matters as Jewish emigration from Europe and the territorial limits set upon the proposed Jewish State.[56] Mainstream Zionist leaders emphasized the "heavy responsibility" of building a modern Jewish State, and committed to working towards a peaceful coexistence with the region's other inhabitants:[57][58] Jewish units in the United States hailed the action by the United Nations. Most welcomed the Palestine Plan but some felt it did not settle the problem.[59]
It is now our primary task to establish relations of peace and harmony with our Arab neighbors – Chaim Weizmann[60]
Some Revisionist Zionists rejected the partition plan as a renunciation of legitimately Jewish national territory.[59] Menachem Begin's Irgun Tsvai Leumi and the Lehi (The Stern Group, also known by their opponents as the Stern Gang), which had been fighting the British, rejected the plan. Begin warned that the partition would not bring peace because the Arabs would also attack the small state and that "in the war ahead we'll have to stand on our own, it will be a war on our existence and future".[61] He also stated that “the bisection of our homeland is illegal. It will never be recognized.”[62] Begin was sure that the creation of a Jewish state would make territorial expansion possible, “after the shedding of much blood."[63]
According to Simha Flapan, it is a myth that Zionists accepted the partition as a compromise by which the Jewish community abandoned ambitions for the whole of Palestine and recognized the rights of the Palestinians to their own state. Rather, Flapan says that his research suggests that the acceptance was only a tactical move aimed at thwarting the creation of the Palestinian state and increasing the territory assigned by the UN to the Jewish state.[64]
Addressing the Central Committee of the Histadrut (the Eretz Israel Workers Party) days after the UN vote to partition Palestine, Ben-Gurion expressed his apprehension stating:
"…the total population of the Jewish State at the time of its establishment will be about one million, including almost 40% non-Jews. Such a [population] composition does not provide a stable basis for a Jewish State. This [demographic] fact must be viewed in all its clarity and acuteness. With such a [population] composition, there cannot even be absolute certainty that control will remain in the hands of the Jewish majority... There can be no stable and strong Jewish state so long as it has a Jewish majority of only 60%".[65]
Ben Gurion said:“I know of no greater achievement by the Jewish people . . . in its long history since it became a people".[66]
Arabs
With a few exceptions, the Arab leaders and governments rejected the plan of partition in the resolution and indicated that they would reject any other plan of partition.
A few weeks after UNSCOP released its report, Azzam Pasha, the General Secretary of the Arab League, was quoted by an Egyptian newspaper as predicting that Palestine would be overrun by Muslim volunteers.[67] This statement from October 1947 has often been incorrectly reported as having been made much later on 15 May 1948.[68]
On 16 February 1948, UN Palestine Commission to the security council reported that: "Powerful Arab interests, both inside and outside Palestine, are defying the resolution of the General Assembly and are engaged in a deliberate effort to alter by force the settlement envisaged therein."[69] The Arabs were against the establishment of an international regime in Jerusalem too.
Zionists attributed Palestinian rejection of the plan to a mere intransigence. Anyway, Palestinians and Arabs as a rule always reiterated that a partition was unfair: it gave the majority of the land (56%) to the Jews, who at that stage legally owned only 7% of it and remained a minority of the population.[70] There were also disproportionate allocations under the plan and the area under Jewish control contained 45% of the Palestinian population. The proposed Arab state was only given 45% of the land, much of which was unfit for agriculture. Jaffa, though geographically separated, was to be part of the Arab state.[70] However, most of the proposed Jewish state was the Negev desert.[34][71] The plan allocated to the Jewish State most of the Negev desert that was sparsely populated and unsuitable for agriculture but also a "vital land bridge protecting British interests from the Suez Canal to Iraq"[72][73]
Few Palestinian Arabs joined the Arab Liberation Army because they suspected that the other Arab States did not plan on an independent Palestinian state. According to Ian Bickerton, for that reason many Palestinians favored partition and indicated a willingness to live alongside a Jewish state.[74] He also mentions that the Nashashibi family backed King Abdullah and union with Transjordan.[75] Abdullah appointed Ibrahim Hashem Pasha as the Governor of the Arab areas occupied by troops of the Arab League. He was a former Prime Minister of Transjordan who supported partition of Palestine as proposed by the Peel Commission and the United Nations.[citation needed]
While Azzam Pasha repeated his threats to forcefully thwart the partition, the first important Arab voice who supported the partition was the influential Egyptian daily "Al Mokattam": "We stand for partition because we believe that it is the best final solution for the problem of Palestine...rejection of partition...will lead to further complications and will give the Zionists another space of time to complete their plans of defense and attack...a delay of one more year which would not benefit the Arabs but would benefit the Jews, especially after the British evacuation."[76]
The Arabs promised to respect the rights of the Jewish minority.[77] On 20 May 1948, Azzam told reporters "We are fighting for an Arab Palestine. Whatever the outcome the Arabs will stick to their offer of equal citizenship for Jews in Arab Palestine and let them be as Jewish as they like. In areas where they predominate they will have complete autonomy."[78]
The AHC demanded that in a Palestinian Arab state, the majority of the Jews should not be citizens (those who had not lived in Palestine before the British Mandate).[51] The Arab League said that some of the Jews would have to be expelled from a Palestinian Arab state.[79]
A few weeks after UNSCOP released its report, Azzam Pasha, the General Secretary of the Arab League, was quoted by an Egyptian newspaper as saying "Personally I hope the Jews do not force us into this war because it will be a war of elimination and it will be a dangerous massacre which history will record similarly to the Mongol massacre or the wars of the Crusades."[67] This statement from October 1947 has often been incorrectly reported as having been made much later on 15 May 1948.[68]
Azzam Pasha told Alec Kirkbride: "We will sweep them [the Jews] into the sea" . Shukri al-Quwatli [ the Syrian president] told his people:"We shall eradicate Zionism". Haj Amin al-Husseini said in March 1948 to an interviewer in a Jaffa daily "Al Sarih" that the Arabs did not intend merely to prevent partition but "would continue fighting until the Zionists were Annihilated". [80]
British government
When Bevin received the partition proposal, he promptly ordered for it not to be imposed on the Arabs.[81][82] The plan was vigorously debated in the British parliament.
In a British cabinet meeting at 4 December 1947, it was decided that the Mandate would end at midnight 14 May 1948, the complete withdrawal by 1 August 1948, and in a sop to the Arab, Britain would not enforce the UN partition plan.[83] On 11 December 1947 Britain announced the Mandate would end at midnight 14 May 1948 and its sole task would be to complete withdrawal by 1 August 1948.[84] During the period in which the British withdrawal was completed, Britain refused to share the administration of Palestine with a proposed UN transition regime, to allow the UN Palestine Commission to establish a presence in Palestine earlier than a fortnight before the end of the Mandate, to allow the creation of official Jewish and Arab militias or to assist in smoothly handing over territory or authority to any successor.[85][86]
United States government
The United States declined to recognize the All-Palestine government in Gaza by explaining that it had accepted the UN Mediator's proposal. The Mediator had recommended that Palestine, as defined in the original Mandate including Transjordan, might form a union.[87] Bernadotte's diary said the Mufti had lost credibility on account of his unrealistic predictions regarding the defeat of the Jewish militias. Bernadotte noted "It would seem as though in existing circumstances most of the Palestinian Arabs would be quite content to be incorporated in Transjordan."[88]
Subsequent events
The partition plan was never fully implemented. On May 14, 1948, the day on which the British Mandate over Palestine expired, the Jewish People's Council gathered at the Tel Aviv Museum, and approved a proclamation, declaring "the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz Israel, to be known as the State of Israel".[89] The 1948 Arab–Israeli War began with the invasion of, or intervention in, Palestine[90] by the Arab States on 15 May 1948.
The Resolution as a legal basis for Palestinian statehood
In 1988, the Palestine Liberation Organization published the Palestinian Declaration of Independence relying on Resolution 181, arguing that the resolution continues to provide international legitimacy for the right of the Palestinian people to sovereignty and national independence.[91] A number of scholars have written in support of this view.[92][93][94]
A General Assembly request for an advisory opinion, Resolution ES-10/14 (2004), specifically cited resolution 181(II) as a "relevant resolution", and asked the International Court of Justice (ICJ) what are the legal consequences of the relevant Security Council and General Assembly resolutions. Judge Abdul Koroma explained the majority opinion: "The Court has also held that the right of self-determination as an established and recognized right under international law applies to the territory and to the Palestinian people. Accordingly, the exercise of such right entitles the Palestinian people to a State of their own as originally envisaged in resolution 181 (II) and subsequently confirmed."[95] In response, Prof. Paul De Waart said that the Court put the legality of the 1922 League of Nations Palestine Mandate and the 1947 UN Plan of Partition beyond doubt once and for all.[96]
See also
- 1949 Armistice Agreements
- Balfour Declaration of 1917
- Churchill White Paper, 1922
- Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel
- Faisal-Weizmann Agreement
- Israeli-Palestinian conflict
- Lausanne Conference, 1949
- Minority Treaties
- Proposals for a Palestinian state
- Sykes-Picot Agreement
- Two-state solution
Footnotes
- ^ "A/RES/181(II) of 29 November 1947". United Nations. 1947. Retrieved 8 December 2012.
- ^ "A/RES/181(II) of 29 November 1947". United Nations. 1947. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ^ Part II. – Boundaries recommended in UNGA Res 181 Molinaro, Enrico The Holy Places of Jerusalem in Middle East Peace Agreements Page 78
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 75. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
" p. 75 The night of 29–30 November passed in the Yishuv's settlements in noisy public rejoicing. Most had sat glued to their radio sets broadcasting live from Flushing Meadow. A collective cry of joy went up when the two-thirds mark was achieved: a state had been sanctioned by the international community. ; p. 396 The immediate trigger of the 1948 War was the November 1947 UN partition resolution. The Zionist movement, except for its fringes, accepted the proposal."
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 73. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
"p73 All paid lip service to Arab unity and the Palestine Arab cause, and all opposed partition... ; p. 396 The immediate trigger of the 1948 War was the November 1947 UN partition resolution. … The Palestinian Arabs, along with the rest of the Arab world, said a flat "no"… The Arabs refused to accept the establishment of a Jewish state in any part of Palestine. And, consistently with that "no," the Palestinian Arabs, in November–December 1947, and the Arab states in May 1948, launched hostilities to scupper the resolution's implementation ; p. 409 The mindset characterized both the public and the ruling elites. All vilified the Yishuv and opposed the existence of a Jewish state on "their" (sacred Islamic) soil, and all sought its extirpation, albeit with varying degrees of bloody-mindedness. Shouts of "Idbah al Yahud" (slaughter the Jews) characterized equally street demonstrations in Jaffa, Cairo, Damascus, and Baghdad both before and during the war and were, in essence, echoed, usually in tamer language, by most Arab leaders. "
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. pp. 66, 67, 72. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
p.66, at 1946 "The League demanded independence for Palestine as a "unitary" state, with an Arab majority and minority rights for the Jews." ; p.67, at 1947 "The League's Political Committee met in Sofar, Lebanon, on 16–19 September, and urged the Palestine Arabs to fight partition, which it called "aggression," "without mercy." The League promised them, in line with Bludan, assistance "in manpower, money and equipment" should the United Nations endorse partition." ; p. 72, at Dec 1947 "The League vowed, in very general language, "to try to stymie the partition plan and prevent the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine
- ^ Article "History of Palestine", Encyclopædia Britannica (2002 edition), article section written by Walid Ahmed Khalidi and Ian J. Bickerton.
- ^ Itzhak Galnoor (1995). The Partition of Palestine: Decision Crossroads in the Zionist Movement. SUNY Press. pp. 289–. ISBN 978-0-7914-2193-2. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ^ a b Mansfield, Peter (1992), The Arabs, pp. 172–175, ISBN 0-14-014768-3
- ^ The Palestine Mandate "the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the [Balfour] declaration originally made on November 2nd, 1917"
- ^ Rashid Khalidi (1 September 2006). The Iron Cage: The Story of the Palestinian Struggle for Statehood. Beacon Press. pp. 181–. ISBN 978-0-8070-0315-2.
- ^ Palestine Royal Commission report, 1937, 389–391
- ^ Benny Morris. Righteous Victims. p. 139.
- ^ Palestine Royal Commission report, 1937, 389–391
- ^ Benny Morris. Righteous Victims. p. 139.
- ^ William Roger Louis, Ends of British Imperialism: The Scramble for Empire, Suez, and Decolonization, 2006, p.391
- ^ Benny Morris, One state, two states: resolving the Israel/Palestine conflict, 2009, p. 66
- ^ Benny Morris, The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited, p. 48; p. 11 "while the Zionist movement, after much agonising, accepted the principle of partition and the proposals as a basis for negotiation"; p. 49 "In the end, after bitter debate, the Congress equivocally approved –by a vote of 299 to 160 – the Peel recommendations as a basis for further negotiation."
- ^ Partner to Partition: The Jewish Agency's Partition Plan in the Mandate Era, Yosef Kats, Chapter 4, 1998 Edition, Routledge, ISBN 0-7146-4846-9
- ^ Palestine. Statement by His Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom. Presented by the Secretary of State for the Colonies to Parliament by Command of His Majesty. November, 1938. Cmd. 5893. [1]
- ^ Hilberg, Raul, The Destruction of the European Jews, (1961) New Viewpoints, New York 1973 p.716
- ^ Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry - Appendix IV Palestine: Historical Background
- ^ Benny Morris (25 May 2011). "chp. 4". Righteous Victims: A History of the Zionist-Arab Conflict, 1881-1998 (Hebrew edition ed.). Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-307-78805-4.
Capping it all, the Permanent Mandates Commission of the Council of the League of Nations rejected the White Paper as inconsistent with the terms of the Mandate.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ William roger louis, 1985, p.386
- ^ a b Morris, 2008, p.34
- ^ Gurock, Jeffrey S. American Jewish History American Jewish Historical Society, page 243
- ^ Morris, 2008, p.35
- ^ A Survey of Palestine, Table 2 showing Holdings of Large Jewish Lands Owners as of December 31st, 1945, British Mandate: A Survey of Palestine: Volume I - Page 245. Chapter VIII: Land: Section 3.
- ^ Geselbracht, Raymond H. "The United States and the Recognition of Israel: A Chronology". Harry S. Truman Presidential Library and Museum. Retrieved 28 November 2011.
- ^ William Roger Louis, 2006, p. 404
- ^ Morris, 2008, p. 43
- ^ UNSCOP report The present situation 119. There can be no doubt that the enforcement of the White Paper of 1939, subject to the permitted entry since December 1945 of "1,500 Jewish immigrants monthly, has created throughout the Jewish community a deep-seated distrust and resentment against the mandatory Power. This feeling is most sharply expressed in regard to the Administration's attempts to prevent the landing of illegal immigrants. During its stay in Palestine, the Committee heard from certain of its members an eyewitness account of the incidents relative to the bringing into the port of Haifa, under British naval escort, of the illegal immigrant ship. Exodus 1947.
- ^ UNITED NATIONS: General Assembly: A/364: 3 September 1947: OFFICIAL RECORDS OF THE SECOND SESSION OF THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY: SUPPLEMENT No. 11: UNTIED NATIONS SPECIAL COMMITTEE ON PALESTINE: REPORT TO THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY: VOLUME 1
- ^ a b c d Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 47. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
The Jews were to get 62 percent of Palestine (most of it desert), consisting of the Negev
- ^ UNSCOP REPORT TO THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY: The primary objectives sought in the foregoing scheme are, in short, political division and economic unity: to confer upon each group, Arab and Jew, in its own territory, the power to make its own laws, while preserving both, throughout Palestine, a single integrated economy, admittedly essential to the well-being of each, and the same territorial freedom of movement to individuals as is enjoyed today.
- ^ a b UN Partition Plan at Merip.
- ^ Enoughie, Jeorge (29 April 2011). "History of Palestine, Part III : Palestinian Nakba (Catastrophe)".
- ^ Yearbook of The United Nations 1947–48
- ^ a b c Report of Sub-Committee 2 (doc.nr. A/AC.14/32). 10 November 1947; on [2]
For the Bedouin issue, see par. 61-73 on pp. 39-46 and Appendix 3: Note on the Bedouin population of Palestine presented by the representative of the United Kingdom d.d. 1 November 1947 on pp. 65-66 - ^ Report of Sub-Committee 2 (doc.nr. A/AC.14/32). 10 November 1947; on [3]
Resolution No. I: pp. 57-58; Resolution No. II: pp. 59-60; for the proposal of a unitary state, see par. 83-85 on pp. 52-53 and Resolution No. III on pp. 60-62 - ^ a b c Barr, James (2012). A Line in the Sand: Britain, France and the Struggle that Shaped the Middle East. London: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-84739-457-6.
- ^ a b Hansard, 11 Dec 1947
- ^ Servant of God: a personal narrative, Muhammad Zafrulla Khan, 1983
- ^ a b c Before & after: U.S. foreign policy and the 11 September crisis By Phyllis Bennis
- ^ Lenczowski, George (1990). American Presidents and the Middle East. Duke University Press. p. 157. ISBN 0-8223-0972-6., p. 28, cite, Harry S. Truman, Memoirs 2, p. 158.
- ^ Heptulla, Najma (1991). Indo-West Asian relations: the Nehru era. Allied Publishers. p. 158. ISBN 81-7023-340-2.
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 56. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
Vijayalakshmi Pandit, Nehru's sister, who headed the delegation, occasionally threw out hints that something might change. But Shertok was brought down to earth by historian Kavalam Panikkar, another member of the Indian delegation: "It is idle for you to try to convince us that the Jews have a case. . . . We know it. . . . But the point is simply this: For us to vote for the Jews means to vote against the Moslems. This is a conflict in which Islam is involved. . . . We have 13 million [sic] Moslems in our midst. . . . Therefore, we cannot do it.
- ^ Quigley, John B. (1990). Palestine and Israel: a challenge to justice. Duke University Press. p. 37. ISBN 0-8223-1023-6.
- ^ Ahron Bregman; Jihan El-Tahri (1998). The fifty years war: Israel and the Arabs. Penguin Books. p. 25. Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- ^ a b Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 61. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
"The Arabs had failed to understand the tremendous impact of the Holocaust on the international community—and, in any event, appear to have used the selfsame methods, but with poor results. Wasif Kamal, an AHC official, for example, offered one delegate—perhaps the Russian—a "huge, huge sum of money to vote for the Arabs" (the Russian declined, saying, "You want me to hang myself?"). But the Arabs' main tactic, amounting to blackmail, was the promise or threat of war should the assembly endorse partition. As early as mid-August 1947, Fawzi al-Qawuqji—soon to be named the head of the Arab League's volunteer army in Palestine, the Arab Liberation Army (ALA)—threatened that, should the vote go the wrong way, "we will have to initiate total war. We will murder, wreck and ruin everything standing in our way, be it English, American or Jewish." It would be a "holy war," the Arabs suggested, which might even evolve into "World War III." Cables to this effect poured in from Damascus, Beirut, Amman, and Baghdad during the Ad Hoc Committee deliberations, becoming "more lurid," according to Zionist officials, as the General Assembly vote drew near. The Arab states generally made no bones about their intention to support the Palestinians with "men, money and arms," and sometimes hinted at an eventual invasion by their armies. They also threatened the Western Powers, their traditional allies, with an oil embargo and/or abandonment and realignment with the Soviet Bloc"
{{cite book}}: line feed character in|quote=at position 191 (help) Cite error: The named reference "morris2008p61" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ a b c Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. pp. 50, 66. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
p. 50,"The Arab reaction was just as predictable: "The blood will flow like rivers in the Middle East," promised Jamal Husseini.; at 1947 "Haj Amin al-Husseini went one better: he denounced also the minority report, which, in his view, legitimized the Jewish foothold in Palestine, a "partition in disguise," as he put it." ; p.66, at 1946 "The AHC ... insisted that the proportion of Jews to Arabs in the unitary state should stand at one to six, meaning that only Jews who lived in Palestine before the British Mandate be eligible for citizenship
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 67. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
- ^ U.N General Assembly ,A/PV.126,28 November 1947,discussion on the Palestinian question, retrieved 15 October 2013
- ^ 29th Meeting of the Ad Hoc Committee on Palestine: 24 November 1947: Retrieved 31 December 2013
- ^ History of the Middle East by Saul S Friedman
- ^ The Question of Palestine: Brochure DPI/2517/Rev.1: Chapter 2, The Plan of Partiton and end of the British Mandate
- ^ "PALESTINE JEWRY JOYOUS AT NEWS; Ben-Gurion Voices Attitude of Grateful Responsibility – Jerusalem Arabs Silent". New York Times. 30 November 1947. p. 58. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ "VOTE ON PALESTINE CHEERED BY CROWD". New York Times. 30 November 1947. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ a b "JEWISH UNITS HERE HAIL ACTION BY U.N." New York Times. 30 November 1947. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ "Weizmann message". The Palestine post. 30 May 1948. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- ^ Begin, Menachem, The Revolt 1978, p. 412.
- ^ Begin, Menachem, In The Underground: Writings and Documents 1977,vol 4,p. 70.
- ^ 'Aviezer Golan and Shlomo Nakdimon, Begin, Hebrew, Jerusalem, 1978", p.172, cited in Shima Flapan, The Birth of Israel, Pantheon Books, New York, 1988' p.32
- ^ The Birth of Israel: Myths and Realities, by Simha Flapan, Pantheon, 1988, ISBN 0-679-72098-7, pages 8-9
- ^ 'Jamal K Kanj, Children of Catastrophe, UK 2010'
- ^ Morris 2008, p. 65
- ^ a b Akhbar el-Yom, 11 October 2011, p9. The literal English translation is somewhat ambiguous, but the overall meaning is that the coming Arab defeat of the Jews will be remembered in the same way as the past Arab defeats of the Mongols and Crusaders are remembered.
- ^ a b Tom Segev (21 October 2011). "The makings of history / The blind misleading the blind". Haaretz.
- ^ UNITED NATIONS PALESTINE COMMISSION First Special Report to the Security Council
- ^ a b Wolffe, John (2005). Religion in History: Conflict, Conversion and Coexistence (Paperback). Manchester University Press. p. 265. ISBN 978-0-7190-7107-2.
- ^ UNTIED NATIONS, SPECIAL COMMITTEE ON PALESTINE A/364 3 September 1947
- ^ Anita Shapira, Yigal Allon, Native Son: A Biography, University of Pennsylvania Press, 2004, p.239.
- ^ Itzhak Galnoor, The Partition of Palestine: Decision Crossroads in the Zionist Movement, State University of New York Press, 1994, p.195.
- ^ Bickerton, Ian J., Klausner, Carla L. (2001) A Concise History of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, 4th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-090303-5, page 88.
- ^ Bickerton & Klausner (2001), page 103
- ^ November 1947|title=The Egyptian daily "Al Mokattam" at Saturday, (the day after the historic U.N resolution of Palestine Partition on 29 November 1947) supported the Partition
- ^ Tom Segev. "Arabs and Jews under the British Mandate".
- ^ Palestine Post, 21 May 1948, p. 3.
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 45. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
"On 23 July, at Sofar, the Arab representatives completed their testimony before UNSCOP. Faranjieh, speaking for the Arab League, said that Jews "illegally" in Palestine would be expelled and that the future of many of those "legally" in the country but without Palestine citizenship would need to be resolved "by the future Arab government "
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 187. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
p. 187 ." Azzam told Kirkbride:...we will sweep them[the Jews] into the sea" . Al Quwwatli [ the Syrian president] told his people:"…we shall eradicate Zionism" ; p. 409 "Al Husseini…In March 1948 he told an interviewer in a Jaffa daily Al Sarih that the Arabs did not intend merely to prevent partition but "would continue fighting until the Zionist were Annihilated"
- ^ Morris 2008, p. 73
- ^ Louis 2006, p. 419
- ^ ["1948 A History of the First Arab-Israeli War",2008, Benny Morris, p. 74]
- ^ Roza El-Eini (2006). Mandated landscape: British imperial rule in Palestine, 1929–1948. Routledge. p. 367. ISBN 978-0-7146-5426-3.
They accordingly announced on 11 December 1947, that the Mandate would end on 15 May 1948, from which date the sole task ... would be to ... withdrawal by 1 August 1948.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Arthur Koestler (March 2007). Promise and Fulfilment – Palestine 1917–1949. READ BOOKS. pp. 163–168. ISBN 978-1-4067-4723-2. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Benny Morris (2008). 1948: a history of the first Arab-Israeli war. Yale University Press. p. 73. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
Bevin regarded the UNSCOP majority report of 1 September 1947 as unjust and immoral. He promptly decided that Britain would not attempt to im- pose it on the Arabs; indeed, he expected them to resist its implementation.…. The British cabinet ...: in the meeting on 4 December 1947 ... It decided, in a sop to the Arabs, to refrain from aiding the enforcement of the UN resolution, meaning the partition of Palestine. And in an important secret corollary, ... it agreed that Britain would do all in its power to delay until early May the arrival in Palestine of the UN (Implementation) Commission. The Foreign Office immediately informed the commission "that it would be intolerable for the Commission to begin to exercise its authority while the [Mandate] Palestine Government was still administratively responsible for Palestine." ... This ... nullified any possibility of an orderly implementation of the partition resolution.
- ^ See memo from Acting Secretary Lovett to Certain Diplomatic Offices, Foreign relations of the United States, 1949. The Near East, South Asia, and Africa, Volume VI, pages 1447–48
- ^ See Folke Bernadotte, "To Jerusalem", Hodder and Stoughton, 1951, pages 112–13
- ^ Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel: 14 May 1948
- ^ Cablegram from the Secretary-General of the League of Arab States to the Secretary-General of the United Nations 15 May 1948: Retrieved 4 May 2012
- ^ See "Request for the admission of the State of Palestine to Unesco as a Member State", UNESCO, 12 May 1989 [4]
- ^ See The Palestine Declaration To The International Criminal Court: The Statehood Issue [5] and Silverburg, Sanford R. (2002), "Palestine and International Law: Essays on Politics and Economics", Jefferson, N.C: McFarland & Co, ISBN 0-7864-1191-0, pages 37–54
- ^ See Chapter 5 "Israel (1948–1949) and Palestine (1998–1999): Two Studies in the Creation of States", in Guy S. Goodwin-Gill, and Stefan Talmon, eds., The Reality of International Law: Essays in Honour of Ian Brownlie (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1999)
- ^ Sourcebook on public international law, by Tim Hillier, Routledge, 1998, ISBN 1-85941-050-2, page 217; and Prof. Vera Gowlland-Debbas, “Collective Responses to the Unilateral Declarations of Independence of Southern Rhodesia and Palestine, An Application of the Legitimizing Function of the United Nations”, The British Yearbook of International Law, l990, pp.l35-l53
- ^ See paragraph 5, Separate opinion of Judge Koroma
- ^ See De Waart, Paul J.I.M., "International Court of Justice Firmly Walled in the Law of Power in the Israeli–Palestinian Peace Process", Leiden Journal of International Law, 18 (2005), pp. 467–487
References
- Benny Morris (1 October 2008). 1948: A History of the First Arab-Israeli War. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-14524-3. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- William Roger Louis (2006). Ends of British Imperialism: The Scramble for Empire, Suez, and Decolonization. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-347-6. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- William Roger Louis (1985). The British Empire in the Middle East, 1945-1951: Arab Nationalism, the United States, and Postwar Imperialism. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822960-5.
Bibliography
- Bregman, Ahron (2002). Israel's Wars: A History Since 1947. London: Routledge.
- Arieh L. Avneri (1984). The Claim of Dispossession: Jewish Land Settlement and the Arabs, 1878–1948. Transaction Publishers.
- Fischbach, Michael R. (2003). Records of Dispossession: Palestinian Refugee Property and the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Columbia University Press.
- Gelber, Yoav (1997). Jewish-Transjordanian Relations: Alliance of Bars Sinister. London: Routledge.
- Khalaf, Issa (1991). Politics in Palestine: Arab Factionalism and Social Disintegration,. University at Albany, SUNY.
- Louis, Wm. Roger (1986). The British Empire in the Middle East,: Arab Nationalism, the United States, and Postwar Imperialism. Oxford University Press.
- "Palestine". Encyclopædia Britannica Online School Edition, 15 May 2006.
- Sicker, Martin (1999). Reshaping Palestine: From Muhammad Ali to the British Mandate, 1831–1922. Praeger/Greenwood.
External links
- Text of the resolution
- JFK in Support of Partition, 1948 Shapell Manuscript Foundation
- Legal Status of West Bank, Gaza and East Jerusalem
- Maps of Palestine
- Ivan Rand and the UNSCOP Papers
- Official Map prepared by UNSCOP
- 29 November Quiz
- Firsthand testimonies from the men and women who helped found the State of Israel on YouTube
- Use dmy dates from April 2012
- History of the Jews in Palestine (region)
- United Nations General Assembly resolutions concerning Israel
- 1947 in law
- 1948 Arab–Israeli War
- History of Israel
- History of Palestine
- Israeli–Palestinian conflict
- United Nations General Assembly resolutions
- Israel, Palestine, and the United Nations
- Partition (politics)
- Borders of Israel
- Borders of the Gaza Strip
- Borders of the West Bank
- 1948 Palestinian exodus
- 1947 in international relations
- Documents of Mandatory Palestine
- 1947 in Mandatory Palestine


